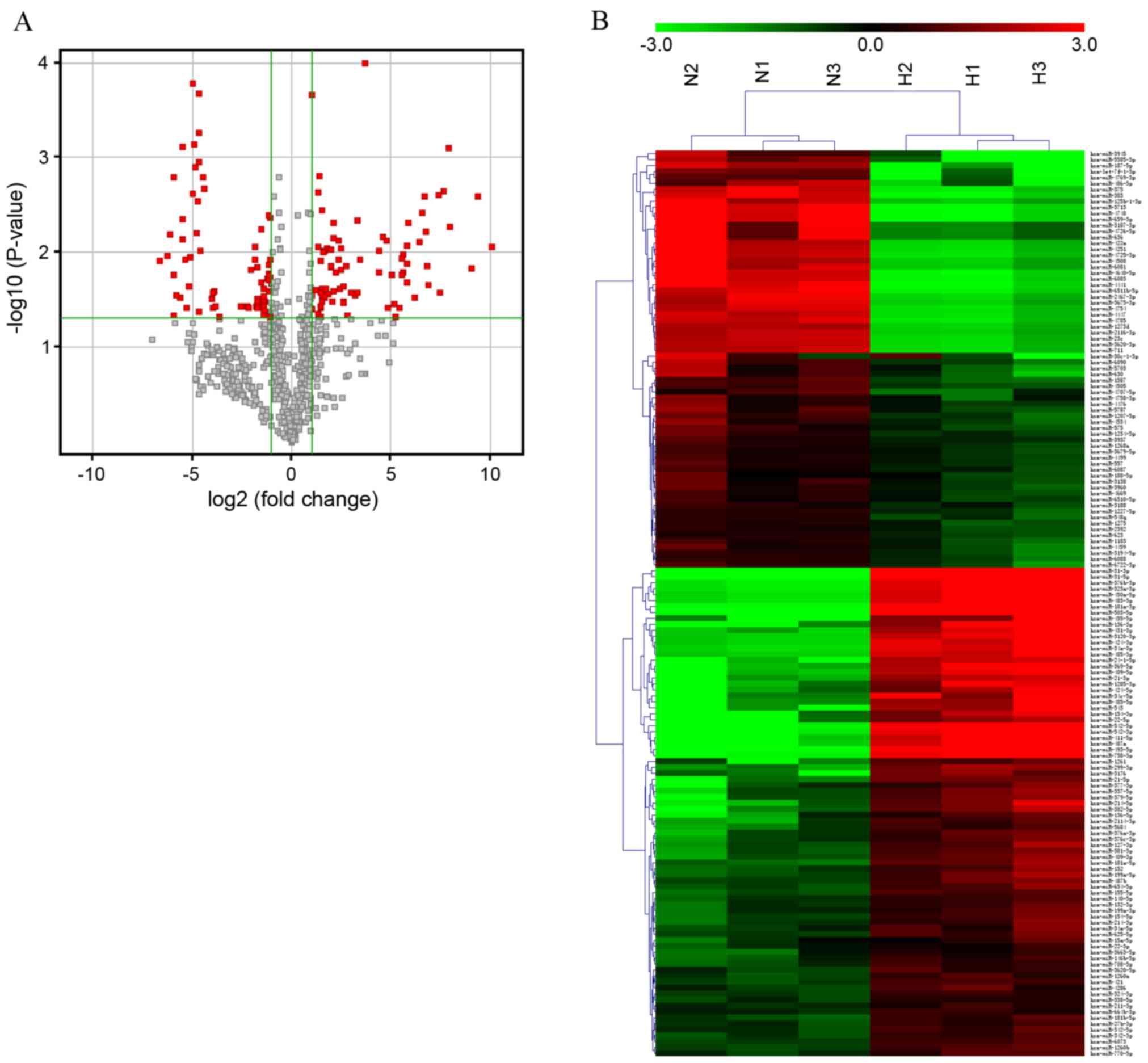
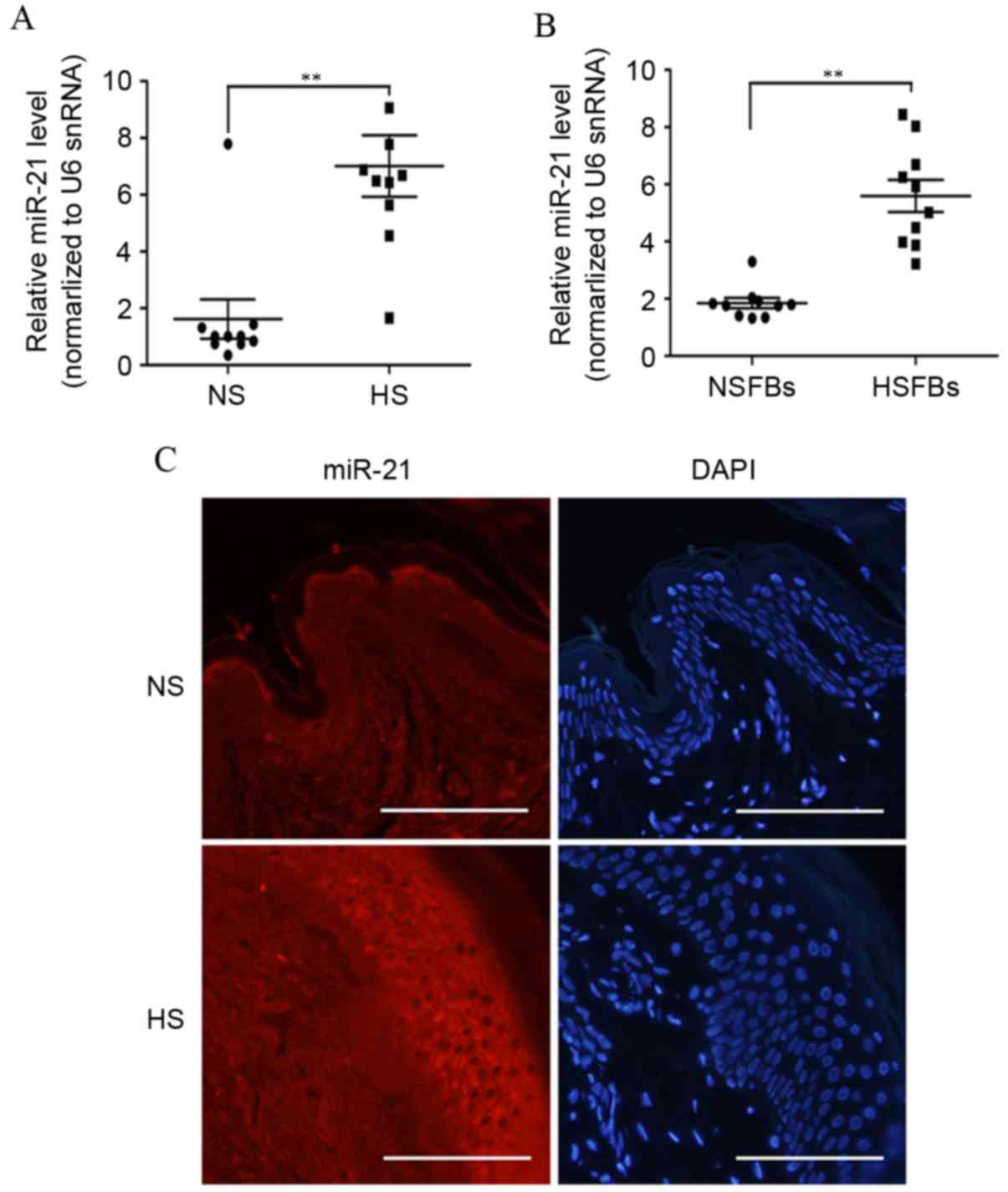
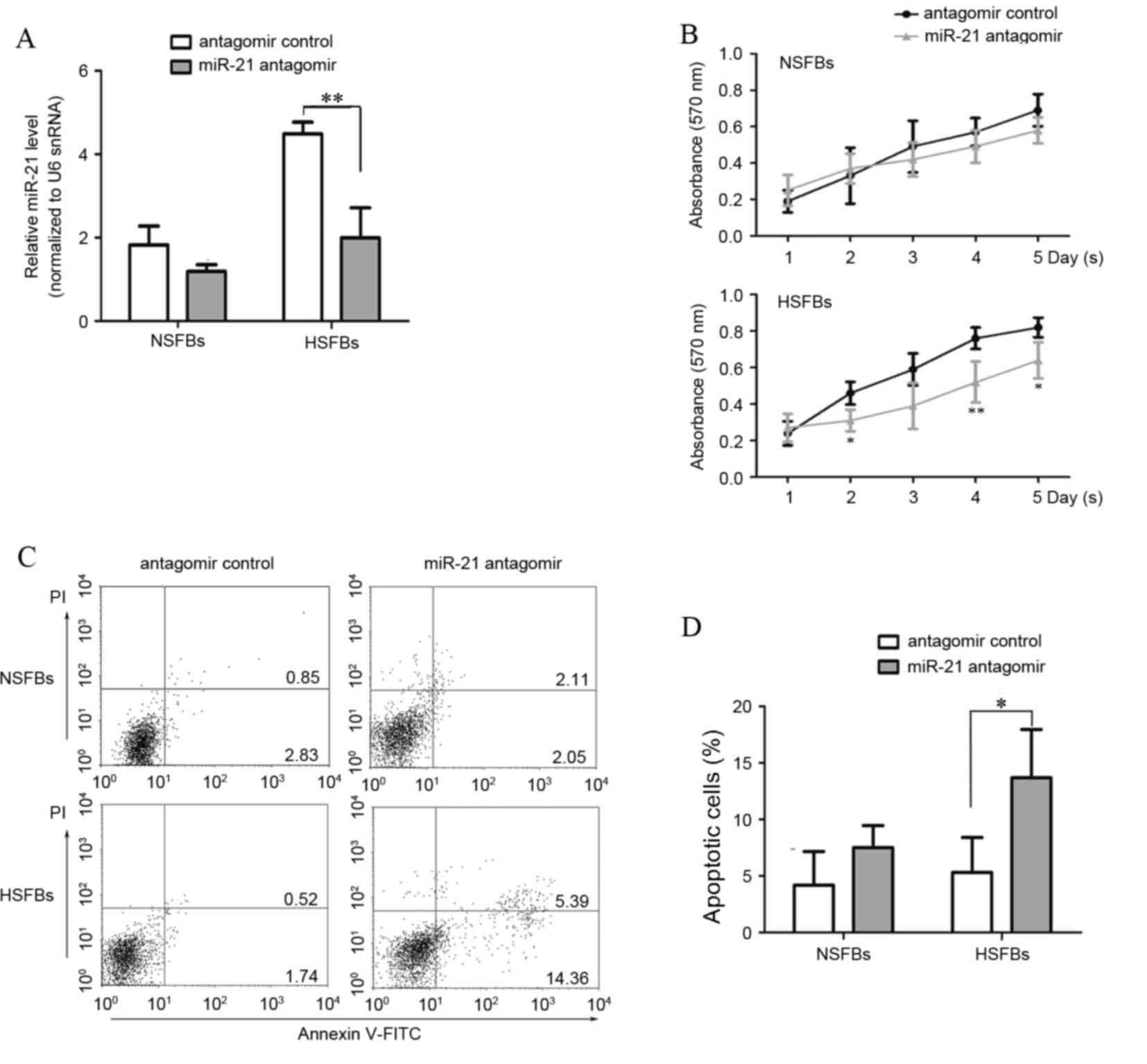
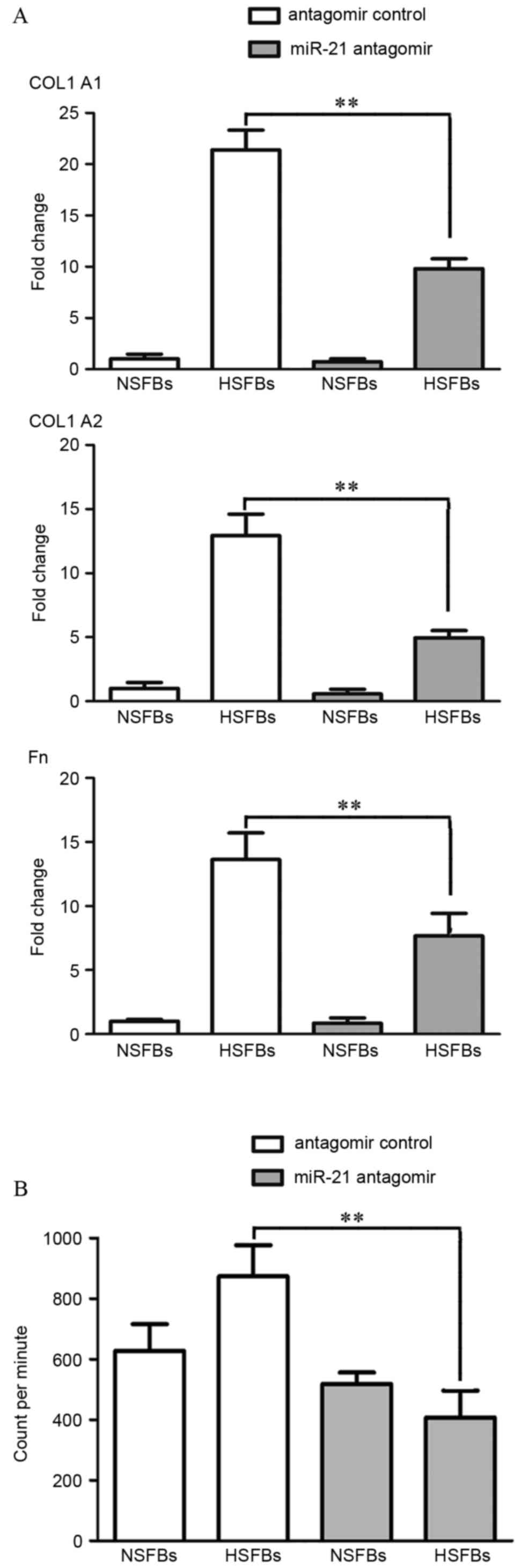
|
1
|
Wolfram D, Tzankov A, Pülzl P and
Piza-Katzer H: Hypertrophic scars and keloids-a review of their
pathophysiology, risk factors, and therapeutic management. Dermatol
Surg. 35:171–181. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Karagoz H, Bayram Y, Sever C, Sahin C,
Kulahci Y and Ulkur E: A review of the prevention and treatment of
hypertrophic scars: Part II experimental studies. Arch Clin Exp
Surg. 2:49–58. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Bentwich I, Avniel A, Karov Y, Aharonov R,
Gilad S, Barad O, Barzilai A, Einat P, Einav U, Meiri E, et al:
Identification of hundreds of conserved and nonconserved human
microRNAs. Nat Genet. 37:766–770. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Backes C and Keller A: Reanalysis of 3,707
novel human microRNA candidates. Proc Natl AcadSci USA.
112:E2849–E2850. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Bouyssou JM, Manier S, Huynh D, Issa S,
Roccaro AM and Ghobrial IM: Regulation of microRNAs in cancer
metastasis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1845:255–265. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lei W, Li G, Zheng J, Shui X, Huang S and
Chen C: Roles of microRNA in vascular diseases in cardiac and
pulmonary systems. Pharmazie. 69:643–647. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Obernosterer G, Martinez J and Alenius M:
Locked nucleic acid-based in situ detection of microRNAs in
mouse tissue sections. Nat Protoc. 2:1508–1514. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tandara AA and Mustoe TA: The role of the
epidermis in the control of scarring: Evidence for mechanism of
action for silicone gel. J Plast ReconstrAesthet Surg.
61:1219–1225. 2008.
|
|
10
|
Guo L, Chen L, Bi S, Chai L, Wang Z, Cao
C, Tao L and Li S: PTEN inhibits proliferation and functions of
hypertrophic scar fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biochem. 361:161–168. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ou H, Li Y and Kang M: Activation of
miR-21 by STAT3 induces proliferation and suppresses apoptosis in
nasopharyngeal carcinoma by targeting PTEN gene. PLoS One.
9:e1099292014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Duffield JS, Grafals M and Portilla D:
MicroRNAs are potential therapeutic targets in fibrosing kidney
disease: Lessons from animal models. Drug Discov Today Dis Models.
10:e127–e135. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dong S, Ma W, Hao B, Hu F, Yan L, Yan X,
Wang Y, Chen Z and Wang Z: microRNA-21 promotes cardiac fibrosis
and development of heart failure with preserved left ventricular
ejection fraction by up-regulating Bcl-2. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
7:565–574. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gabriel V: Hypertrophic scar. Phys Med
Rehabil Clin N Am. 22:301–310. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li C, Bai Y, Liu H, Zuo X, Yao H, Xu Y and
Cao M: Comparative study of microRNA profiling in keloid fibroblast
and annotation of differential expressed microRNAs. Acta Biochim
Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 45:692–699. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhu H, Li Y, Qu S, Luo H, Zhou Y, Wang Y,
Zhao H, You Y, Xiao X and Zuo X: MicroRNA expression abnormalities
in limited cutaneous scleroderma and diffuse cutaneous scleroderma.
J Clin Immunol. 32:514–522. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Peng Y, Liu YM, Li LC, Wang LL and Wu XL:
microRNA-503 inhibits gastric cancer cell growth and
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Oncol Lett. 7:1233–1238.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Huang Y, Qi Y, Du JQ and Zhang DF:
MicroRNA-34a regulates cardiac fibrosis after myocardial infarction
by targeting Smad4. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 18:1355–1365.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zarjou A, Yang S, Abraham E, Agarwal A and
Liu G: Identification of a microRNA signature in renal fibrosis:
Role of miR-21. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 301:F793–F801. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Simone BA, Ly D, Savage JE, Hewitt SM, Dan
TD, Ylaya K, Shankavaram U, Lim M, Jin L and Camphausen K: microRNA
alterations driving acute and late stages of radiation-induced
fibrosis in a murine skin model. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
90:44–52. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wu ZY, Lu L, Liang J, Guo XR, Zhang PH and
Luo SJ: Keloid microRNA expression analysis and the influence of
miR-199a-5p on the proliferation of keloid fibroblasts. Genet Mol
Res. 13:2727–2738. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Glowacki F, Savary G, Gnemmi V, Buob D,
Van der Hauwaert C, Lo-Guidice JM, Bouyé S, Hazzan M, Pottier N,
Perrais M, et al: Increased circulating miR-21 levels are
associated with kidney fibrosis. PLoS One. 8:e580142013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhu H, Luo H, Li Y, Zhou Y, Jiang Y, Chai
J, Xiao X, You Y and Zuo X: MicroRNA-21 in scleroderma fibrosis and
its function in TGF-β-regulated fibrosis-related genes expression.
J Clin Immunol. 33:1100–1109. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li P, Li J, Chen T, Wang H, Chu H, Chang
J, Zang W, Wang Y, Ma Y, Du Y, et al: Expression analysis of serum
microRNAs in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Int J Mol Med.
33:1554–1562. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
da Costa Martins PA and De Windt LJ:
miR-21: A miRaculous Socratic paradox. Cardiovasc Res. 87:397–400.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang T, Feng Y, Sun H, Zhang L, Hao L, Shi
C, Wang J, Li R, Ran X, Su Y and Zou Z: miR-21 regulates skin wound
healing by targeting multiple aspects of the healing process. Am J
Pathol. 181:1911–1920. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Buscaglia LE and Li Y: Apoptosis and the
target genes of microRNA-21. Chin J Cancer. 30:371–380. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Morris DE, Wu L, Zhao LL, Bolton L, Roth
SI, Ladin DA and Mustoe TA: Acute and chronic animal models for
excessive dermal scarring: Quantitative studies. Plast Reconstr
Surg. 100:674–681. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mattes J, Yang M and Foster PS: Regulation
of microRNA by antagomirs: A new class of pharmacological
antagonists for the specific regulation of gene function? Am J
Respir Cell Mol Biol. 36:8–12. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liu G, Friggeri A, Yang Y, Milosevic J,
Ding Q, Thannickal VJ, Kaminski N and Abraham E: miR-21 mediates
fibrogenic activation of pulmonary fibroblasts and lung fibrosis. J
Exp Med. 207:1589–1597. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hatley ME, Patrick DM, Garcia MR,
Richardson JA, Bassel-Duby R, van Rooij E and Olson EN: Modulation
of K-Ras-dependent lung tumorigenesis by MicroRNA-21. Cancer Cell.
18:282–293. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Parapuram SK, Shi-wen X, Elliott C, Welch
ID, Jones H, Baron M, Denton CP, Abraham DJ and Leask A: Loss of
PTEN expression by dermal fibroblasts causes skin fibrosis. J
Invest Dermatol. 131:1996–2003. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhu HY, Li C, Bai WD, Su LL, Liu JQ, Li Y,
Shi JH, Cai WX, Bai XZ, Jia YH, et al: MicroRNA-21 regulates hTERT
via PTEN in hypertrophic scar fibroblasts. PLoS One. 9:e971142014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|