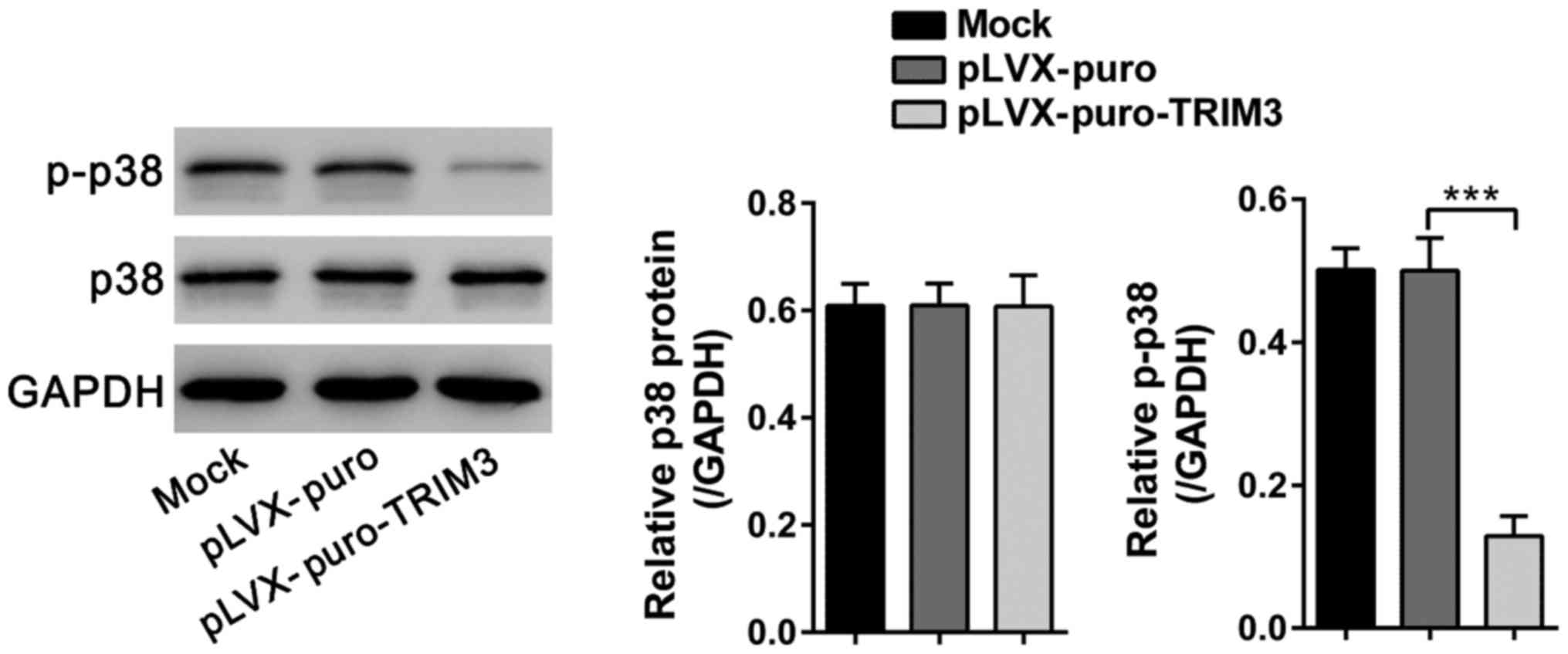
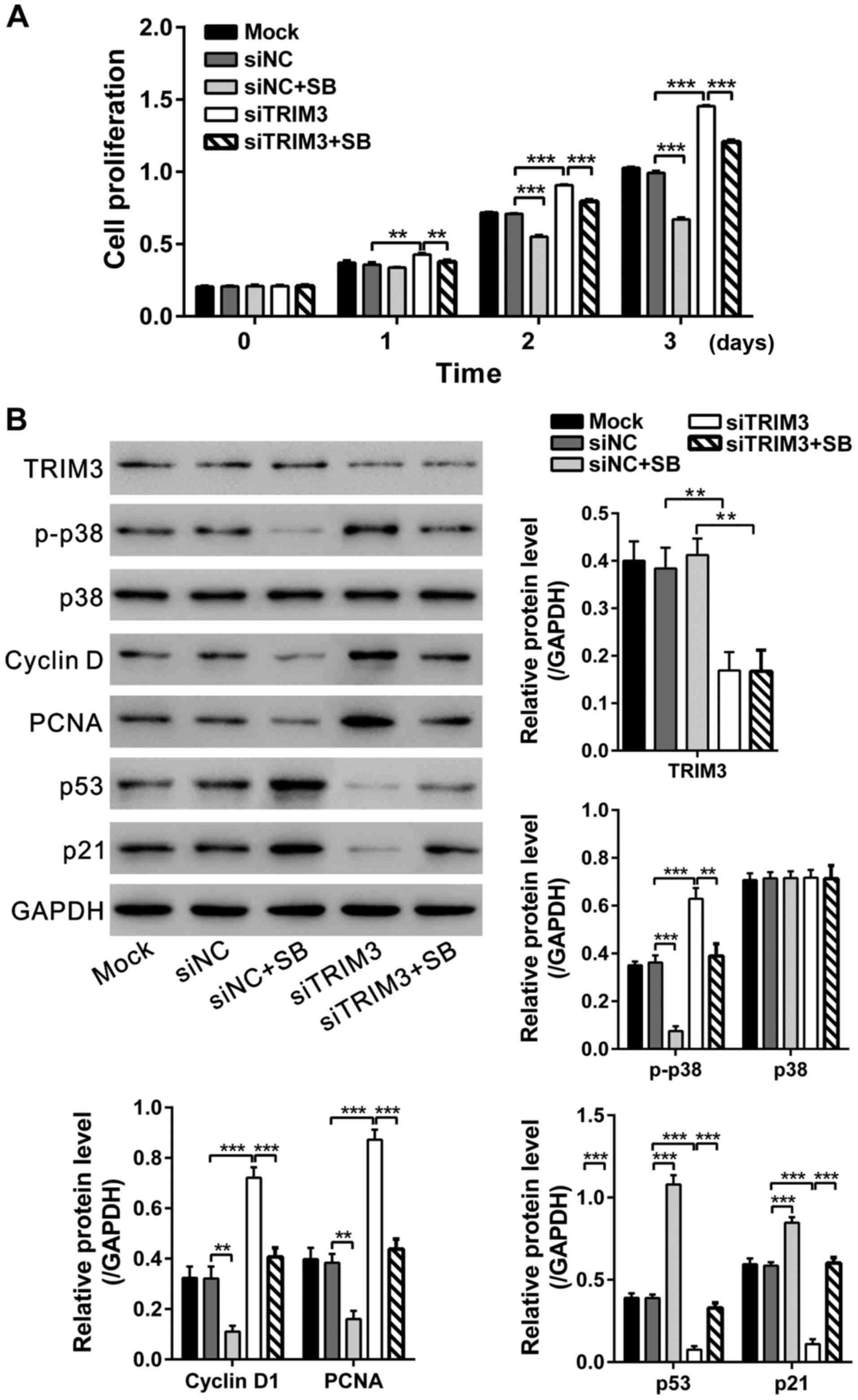
|
1
|
Majithia V and Geraci SA: Rheumatoid
arthritis: Diagnosis and management. Am J Med. 120:936–939. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ritchlin C, Dwyer E, Bucala R and
Winchester R: Sustained and distinctive patterns of gene activation
in synovial fibroblasts and whole synovial tissue obtained from
inflammatory synovitis. Scand J Immunol. 40:292–298. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bucala R, Ritchlin C, Winchester R and
Cerami A: Constitutive production of inflammatory and mitogenic
cytokines by rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts. J Exp Med.
173:569–574. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lafyatis R, Remmers EF, Roberts AB, Yocum
DE, Sporn MB and Wilder RL: Anchorage-independent growth of
synoviocytes from arthritic and normal joints. Stimulation by
exogenous platelet-derived growth factor and inhibition by
transforming growth factor-beta and retinoids. J Clin Invest.
83:1267–1276. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bartok B and Firestein GS: Fibroblast-like
synoviocytes: Key effector cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol
Rev. 233:233–255. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wicks I, Cooley H and Szer J: Autologous
hemopoietic stem cell transplantation: A possible cure for
rheumatoid arthritis? Arthritis Rheum. 40:1005–1011. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Firestein GS: Invasive fibroblast-like
synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Passive responders or
transformed aggressors? Arthritis Rheum. 39:1781–1790. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ozato K, Shin DM, Chang TH and Morse HC
3rd: TRIM family proteins and their emerging roles in innate
immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 8:849–860. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hatakeyama S: TRIM proteins and cancer.
Nat Rev Cancer. 11:792–804. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liu Y, Raheja R, Yeh N, Ciznadija D,
Pedraza AM, Ozawa T, Hukkelhoven E, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P,
Gauthier NP, et al: TRIM3, a tumor suppressor linked to regulation
of p21Waf1/Cip1. Oncogene. 33:308–315. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen G, Kong J, Tucker-Burden C, Anand M,
Rong Y, Rahman F, Moreno CS, Van Meir EG, Hadjipanayis CG and Brat
DJ: Human Brat ortholog TRIM3 is a tumor suppressor that regulates
asymmetric cell division in glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 74:4536–4548.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Boulay JL, Stiefel U, Taylor E, Dolder B,
Merlo A and Hirth F: Loss of heterozygosity of TRIM3 in malignant
gliomas. BMC Cancer. 9:712009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Piao MY, Cao HL, He NN, Xu MQ, Dong WX,
Wang WQ, Wang BM and Zhou B: Potential role of TRIM3 as a novel
tumour suppressor in colorectal cancer (CRC) development. Scand J
Gastroenterol. 51:572–582. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Raheja R, Liu Y, Hukkelhoven E, Yeh N and
Koff A: The ability of TRIM3 to induce growth arrest depends on
RING-dependent E3 ligase activity. Biochem J. 458:537–545. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cohen S and Emery P: The American College
of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism criteria for the
classification of rheumatoid arthritis: A game changer. Arthritis
Rheum. 62:2592–2594. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Saha SK, Roy S and Khuda-Bukhsh AR:
Ultra-highly diluted plant extracts of Hydrastis canadensis and
Marsdenia condurango induce epigenetic modifications and alter gene
expression profiles in HeLa cells in vitro. J Integr Med.
13:400–411. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Nishida K, Komiyama T, Miyazawa S, Shen
ZN, Furumatsu T, Doi H, Yoshida A, Yamana J, Yamamura M, Ninomiya
Y, et al: Histone deacetylase inhibitor suppression of
autoantibody-mediated arthritis in mice via regulation of p16INK4a
and p21WAF1/Cip1 expression. Arthritis Rheum. 50:3365–3376. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Robbins BA, de la Vega D, Ogata K, Tan EM
and Nakamura RM: Immunohistochemical detection of proliferating
cell nuclear antigen in solid human malignancies. Arch Pathol Lab
Med. 111:841–845. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fu M, Wang C, Li Z, Sakamaki T and Pestell
RG: Minireview: Cyclin D1: Normal and abnormal functions.
Endocrinology. 145:5439–5447. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Montenarh M: Functional implications of
the growth-suppressor oncoprotein p53 (Review). Int J Oncol.
1:37–45. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Pargellis C and Regan J: Inhibitors of p38
mitogen-activated protein kinase for the treatment of rheumatoid
arthritis (Review). Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 4:566–571.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
McInnes IB and Schett G: Cytokines in the
pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Immunol. 7:429–442.
2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Nishimoto N, Hashimoto J, Miyasaka N,
Yamamoto K, Kawai S, Takeuchi T, Murata N, van der Heijde D and
Kishimoto T: Study of active controlled monotherapy used for
rheumatoid arthritis, an IL-6 inhibitor (SAMURAI): Evidence of
clinical and radiographic benefit from an × ray reader-blinded
randomised controlled trial of tocilizumab. Ann Rheum Dis.
66:1162–1167. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Maini RN and Taylor PC: Anti-cytokine
therapy for rheumatoid arthritis. Annu Rev Med. 51:207–229. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sanchez-Prieto R, Rojas JM, Taya Y and
Gutkind JS: A role for the p38 mitogen-acitvated protein kinase
pathway in the transcriptional activation of p53 on genotoxic
stress by chemotherapeutic agents. Cancer Res. 60:2464–2472.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|