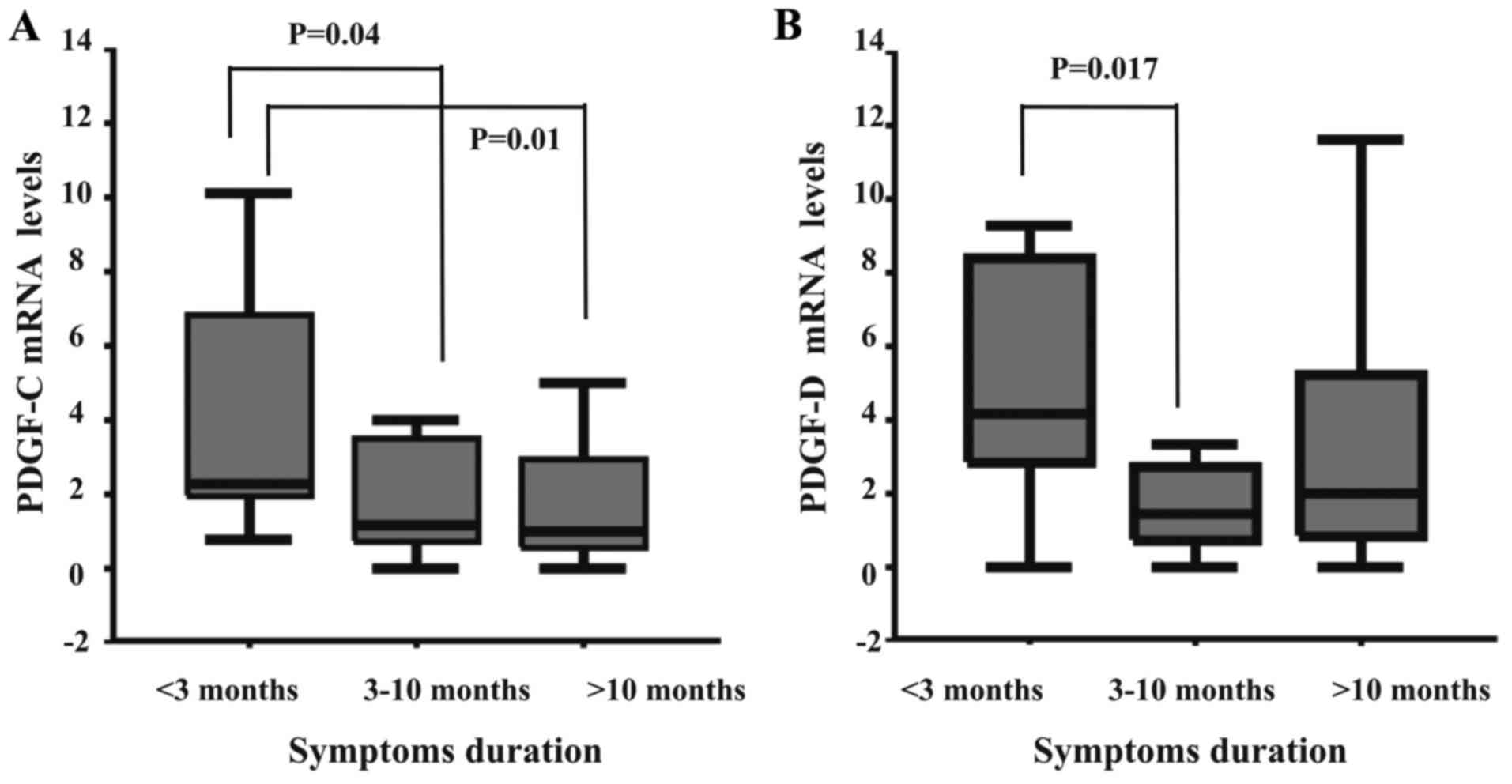
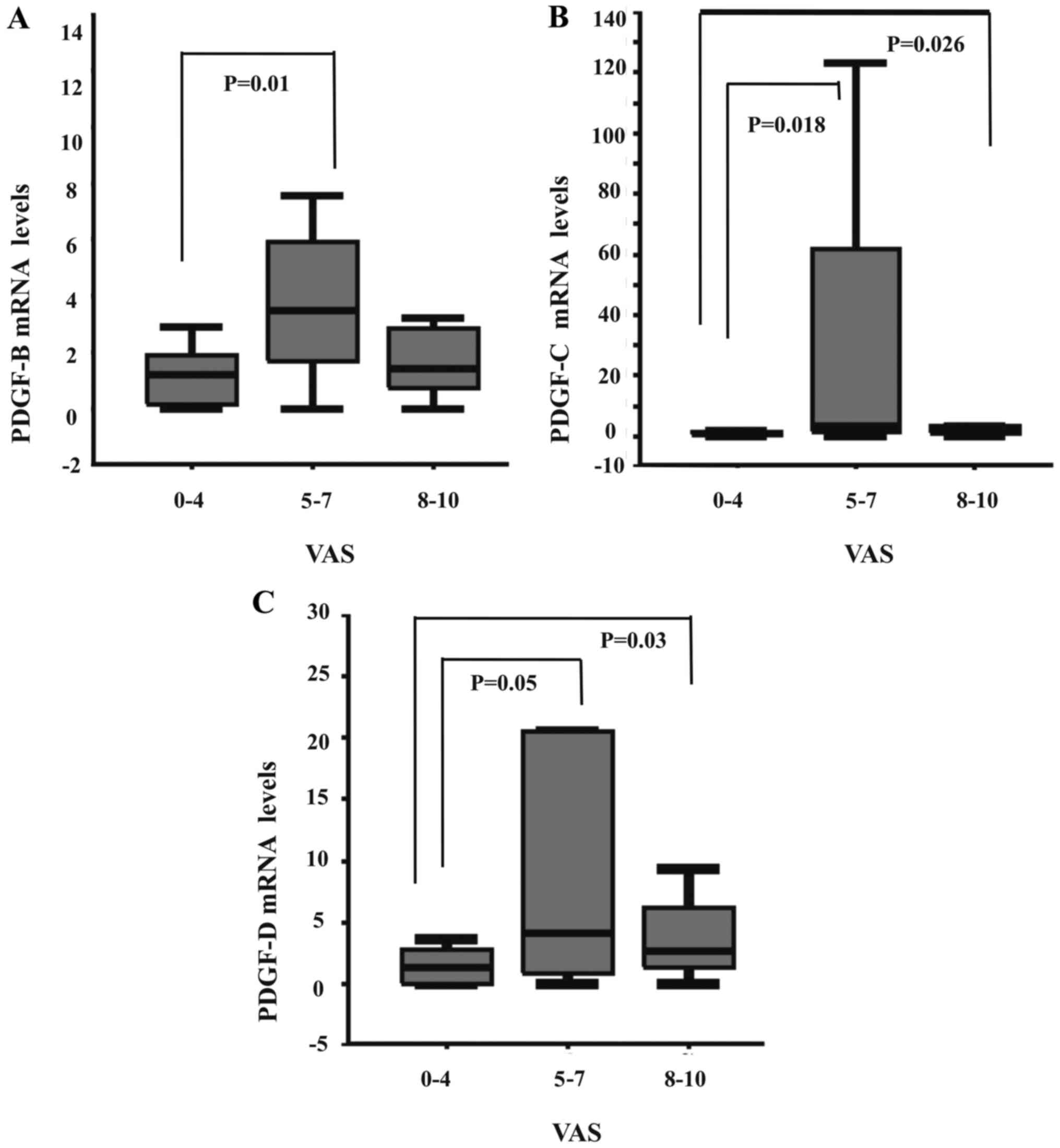
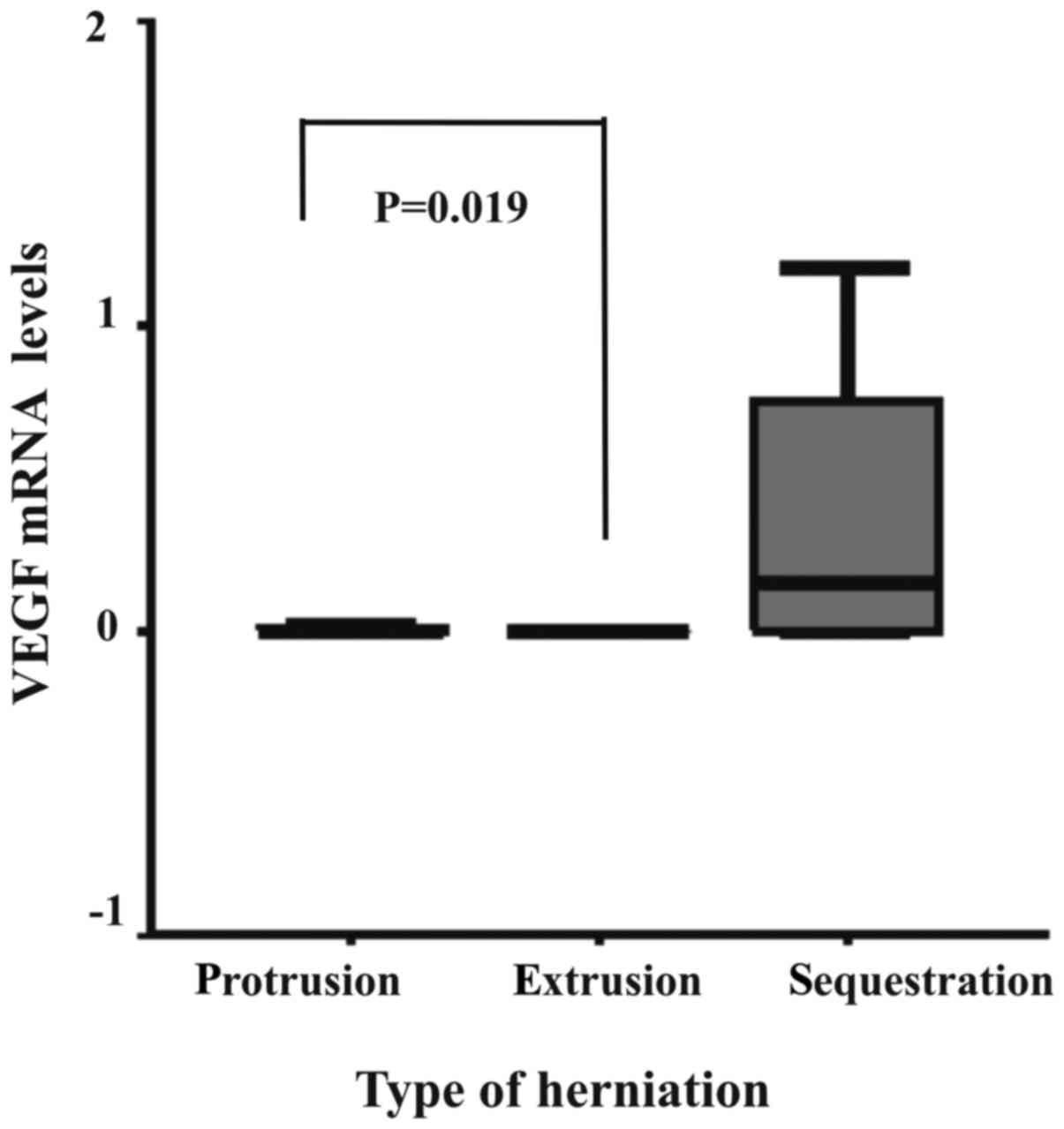
|
1
|
Taylor VM, Deyo RA, Cherkin DC and Kreuter
W: Low back pain hospitalization. Recent United States trends and
regional variations. Spine. 19:1207–1212; discussion 13. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Katz JN: Lumbar disc disorders and
low-back pain: Socioeconomic factors and consequences. J Bone Joint
Surg Am. 88:21–24. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Komori H, Shinomiya K, Nakai O, Yamaura I,
Takeda S and Furuya K: The natural history of herniated nucleus
pulposus with radiculopathy. Spine. 21:225–229. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Saal JA, Saal JS and Herzog RJ: The
natural history of lumbar intervertebral disc extrusions treated
nonoperatively. Spine. 15:683–686. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tsarouhas A, Soufla G, Katonis P, Pasku D,
Vakis A and Spandidos DA: Transcript levels of major MMPs and
ADAMTS-4 in relation to the clinicopathological profile of patients
with lumbar disc herniation. Eur Spine J. 20:781–790. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Masuda K, Oegema TR Jr and An HS: Growth
factors and treatment of intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine.
29:2757–2769. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Alvarez RH, Kantarjian HM and Cortes JE:
Biology of platelet-derived growth factor and its involvement in
disease. Mayo Clin Proc. 81:1241–1257. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tolonen J, Grönblad M, Virri J, Seitsalo
S, Rytömaa T and Karaharju E: Transforming growth factor beta
receptor induction in herniated intervertebral disc tissue: An
immunohistochemical study. Eur Spine J. 10:172–176. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tolonen J, Grönblad M, Virri J, Seitsalo
S, Rytömaa T and Karaharju EO: Platelet-derived growth factor and
vascular endothelial growth factor expression in disc herniation
tissue: And immunohistochemical study. Eur Spine J. 6:63–69. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Specchia N, Pagnotta A, Toesca A and Greco
F: Cytokines and growth factors in the protruded intervertebral
disc of the lumbar spine. Eur Spine J. 11:145–151. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tolonen J, Grönblad M, Virri J, Seitsalo
S, Rytömaa T and Karaharju E: Basic fibroblast growth factor
immunoreactivity in blood vessels and cells of disc herniations.
Spine. 20:271–276. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Konttinen YT, Kemppinen P, Li TF, Waris E,
Pihlajamäki H, Sorsa T, Takagi M, Santavirta S, Schultz GS and
Humphreys-Beher MG: Transforming and epidermal growth factors in
degenerated intervertebral discs. J Bone Joint Surg Br.
81:1058–1063. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Thompson JP, Oegema TR Jr and Bradford DS:
Stimulation of mature canine intervertebral disc by growth factors.
Spine. 16:253–260. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Masuda K: Biological repair of the
degenerated intervertebral disc by the injection of growth factors.
Eur Spine J (Suppl 17). 4:441–451. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Milette PC: Classification, diagnostic
imaging, and imaging characterization of a lumbar herniated disk.
Radiol Clin North Am. 38:1267–1292. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ahn SH, Cho YW, Ahn MW, Jang SH, Sohn YK
and Kim HS: mRNA expression of cytokines and chemokines in
herniated lumbar intervertebral discs. Spine. 27:911–917. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pepper MS, Ferrara N, Orci L and Montesano
R: Potent synergism between vascular endothelial growth factor and
basic fibroblast growth factor in the induction of angiogenesis in
vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 189:824–831. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Guo P, Hu B, Gu W, Xu L, Wang D, Huang HJ,
Cavenee WK and Cheng SY: Platelet-derived growth factor-B enhances
glioma angiogenesis by stimulating vascular endothelial growth
factor expression in tumor endothelia and by promoting pericyte
recruitment. Am J Pathol. 162:1083–1093. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Warren RS, Yuan H, Matli MR, Ferrara N and
Donner DB: Induction of vascular endothelial growth factor by
insulin-like growth factor 1 in colorectal carcinoma. J Biol Chem.
271:29483–29488. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kato T, Haro H, Komori H and Shinomiya K:
Sequential dynamics of inflammatory cytokine, angiogenesis inducing
factor and matrix degrading enzymes during spontaneous resorption
of the herniated disc. J Orthop Res. 22:895–900. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Pratsinis H, Constantinou V, Pavlakis K,
Sapkas G and Kletsas D: Exogenous and autocrine growth factors
stimulate human intervertebral disc cell proliferation via the ERK
and Akt pathways. J Orthop Res. 30:958–964. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Smith RJ, Justen JM, Sam LM, Rohloff NA,
Ruppel PL, Brunden MN and Chin JE: Platelet-derived growth factor
potentiates cellular responses of articular chondrocytes to
interleukin-1. Arthritis Rheum. 34:697–706. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ferrara N and Davis-Smyth T: The biology
of vascular endothelial growth factor. Endocr Rev. 18:4–25. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Koike Y, Uzuki M, Kokubun S and Sawai T:
Angiogenesis and inflammatory cell infiltration in lumbar disc
herniation. Spine. 28:1928–1933. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ozaki S, Muro T, Ito S and Mizushima M:
Neovascularization of the outermost area of herniated lumbar
intervertebral discs. J Orthop Sci. 4:286–292. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Heldin CH and Westermark B: Mechanism of
action and in vivo role of platelet-derived growth factor. Physiol
Rev. 79:1283–1316. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Digiovanni CW, Baumhauer J, Lin SS,
Berberian WS, Flemister AS, Enna MJ, Evangelista P and Newman J:
Prospective, randomized, multi-center feasibility trial of
rhPDGF-BB versus autologous bone graft in a foot and ankle fusion
model. Foot Ankle Int. 32:344–354. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hee CK, Dines JS, Dines DM, Roden CM,
Wisner-Lynch LA, Turner AS, McGilvray KC, Lyons AS, Puttlitz CM and
Santoni BG: Augmentation of a rotator cuff suture repair using
rhPDGF-BB and a type I bovine collagen matrix in an ovine model. Am
J Sports Med. 39:1630–1639. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Uutela M, Wirzenius M, Paavonen K,
Rajantie I, He Y, Karpanen T, Lohela M, Wiig H, Salven P, Pajusola
K, et al: PDGF-D induces macrophage recruitment, increased
interstitial pressure, and blood vessel maturation during
angiogenesis. Blood. 104:3198–3204. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Rubin K, Tingström A, Hansson GK, Larsson
E, Rönnstrand L, Klareskog L, Claesson-Welsh L, Heldin CH,
Fellström B and Terracio L: Induction of B-type receptors for
platelet-derived growth factor in vascular inflammation: Possible
implications for development of vascular proliferative lesions.
Lancet. 1:1353–1356. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Weiler C, Lopez-Ramos M, Mayer HM, Korge
A, Siepe CJ, Wuertz K, Weiler V, Boos N and Nerlich AG:
Histological analysis of surgical lumbar intervertebral disc tissue
provides evidence for an association between disc degeneration and
increased body mass index. BMC Res Notes. 4:4972011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Pye SR, Reid DM, Adams JE, Silman AJ and
O'Neill TW: Influence of weight, body mass index and lifestyle
factors on radiographic features of lumbar disc degeneration. Ann
Rheum Dis. 66:426–427. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hangai M, Kaneoka K, Kuno S, Hinotsu S,
Sakane M, Mamizuka N, Sakai S and Ochiai N: Factors associated with
lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration in the elderly. Spine J.
8:732–740. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kern PA, Saghizadeh M, Ong JM, Bosch RJ,
Deem R and Simsolo RB: The expression of tumor necrosis factor in
human adipose tissue. Regulation by obesity, weight loss, and
relationship to lipoprotein lipase. J Clin Invest. 95:2111–2119.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|