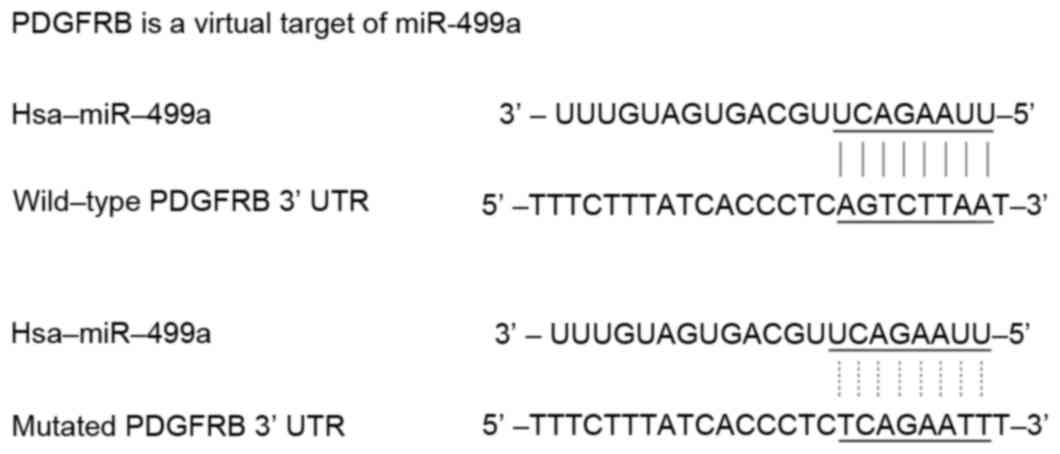
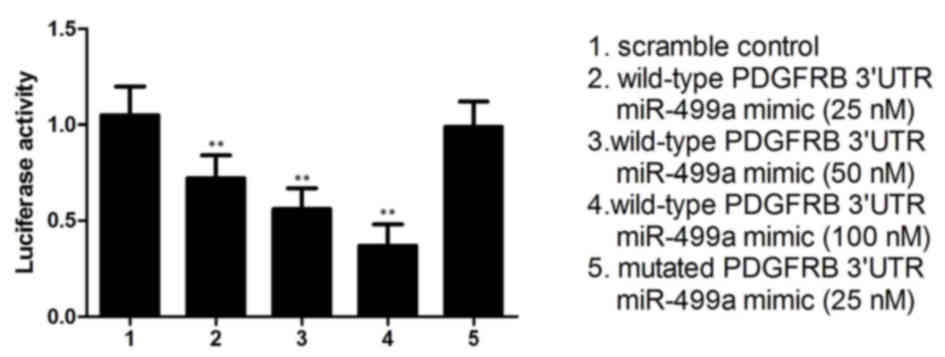
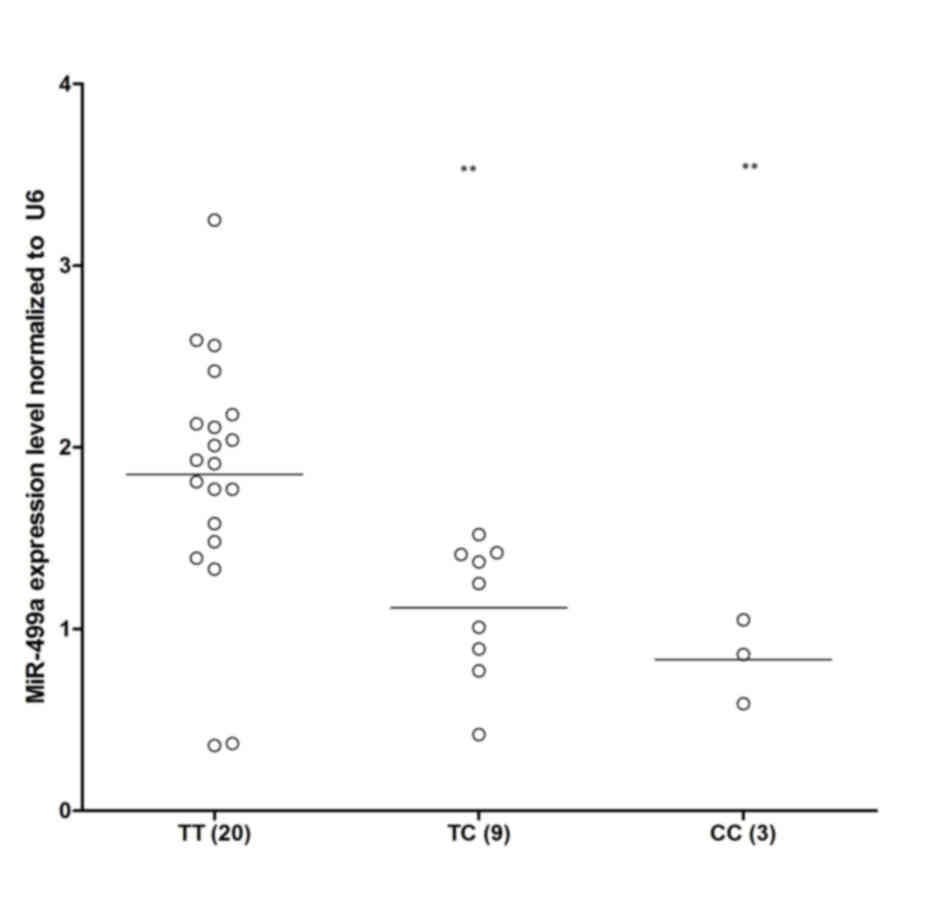
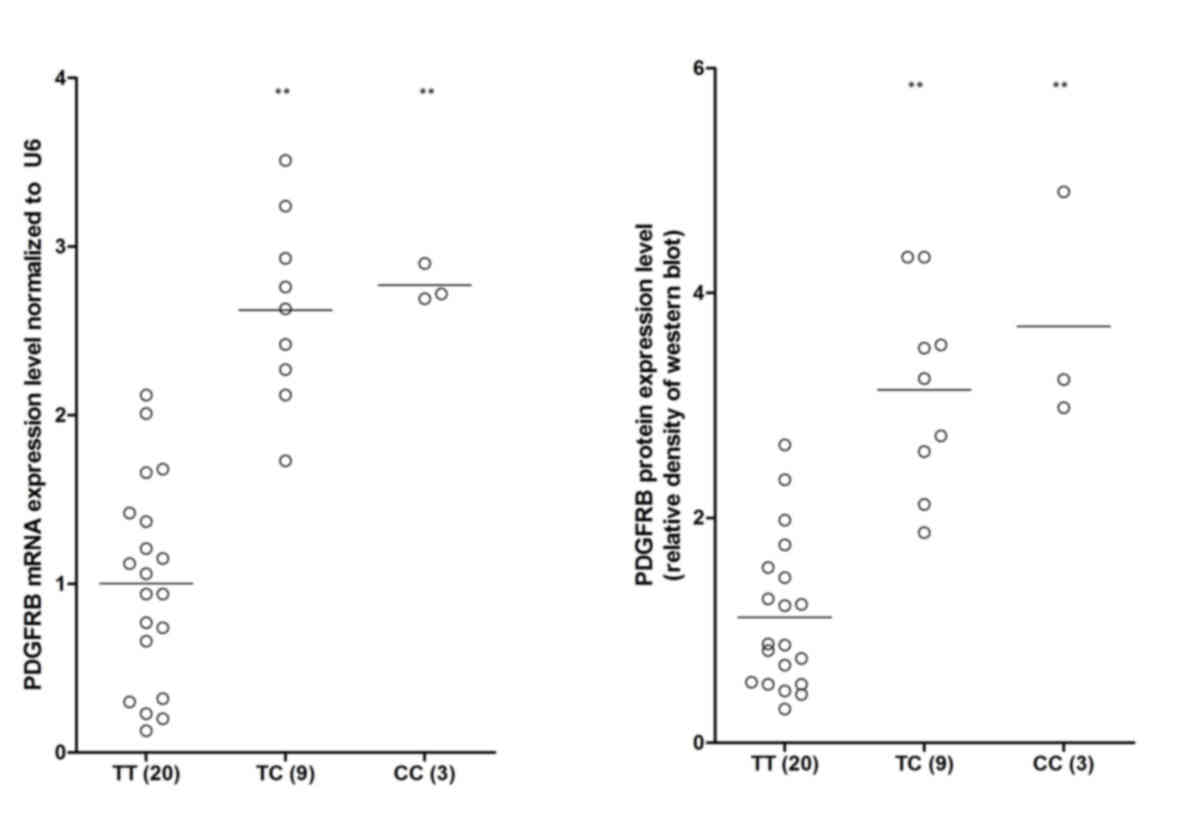
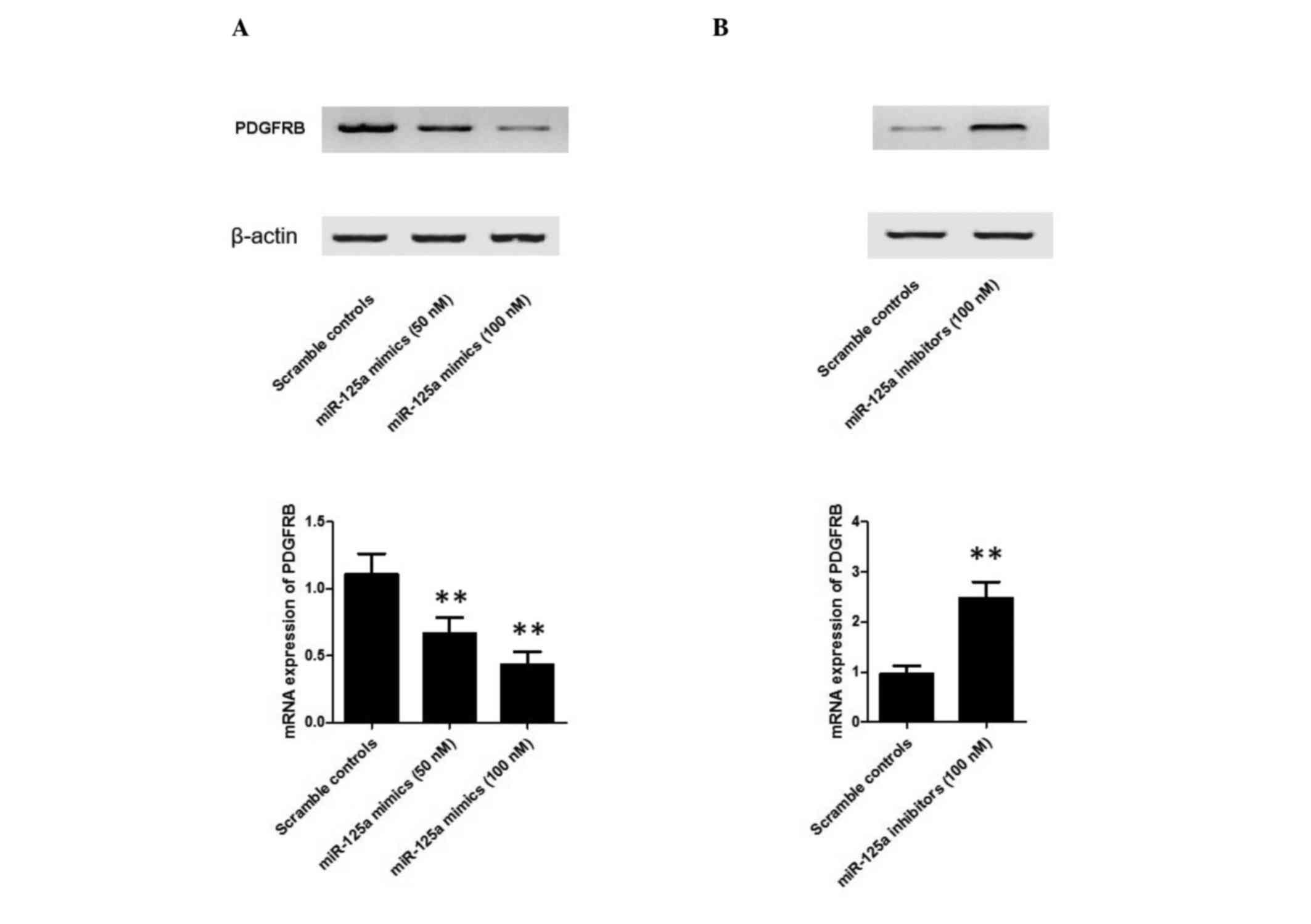
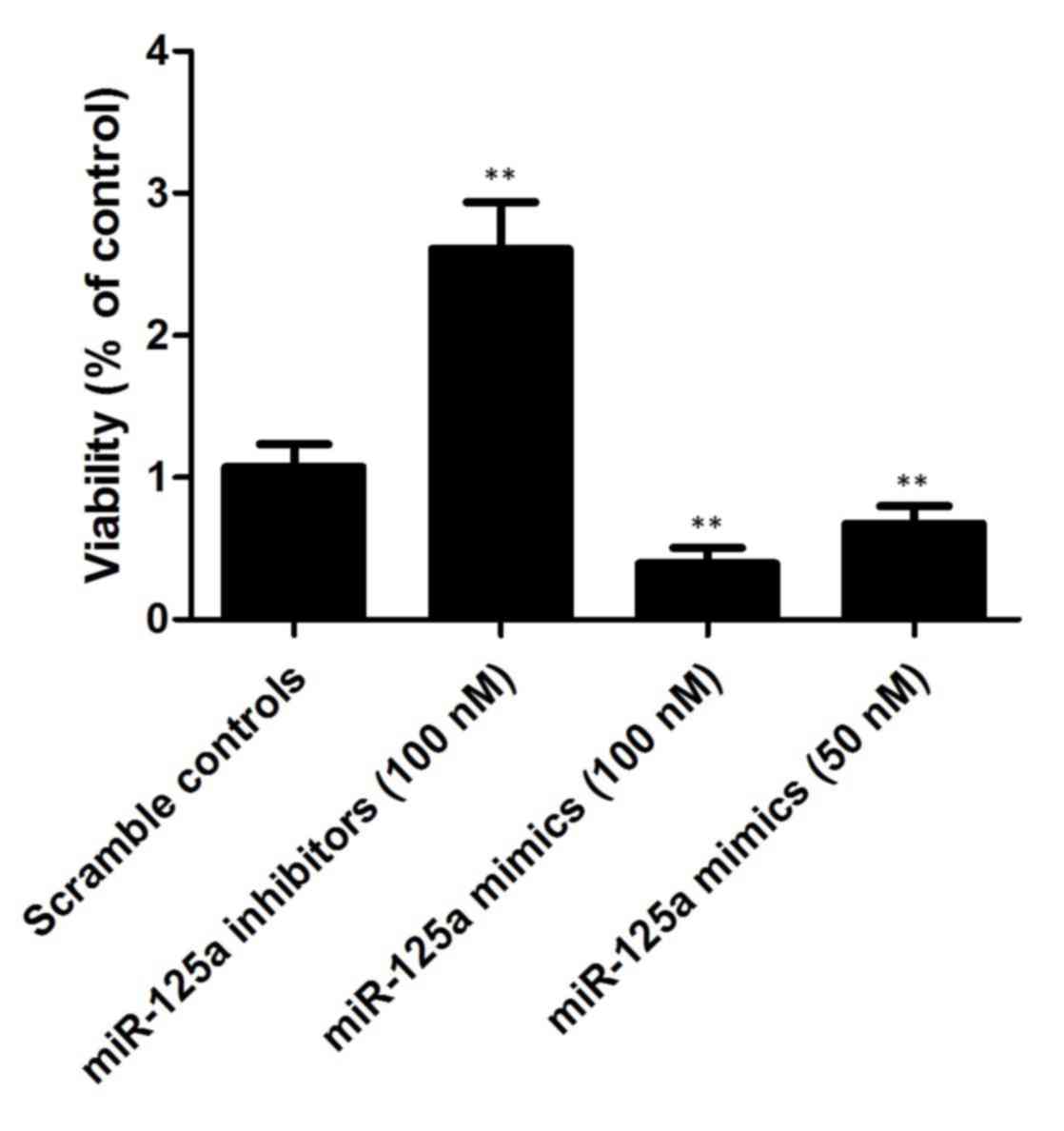
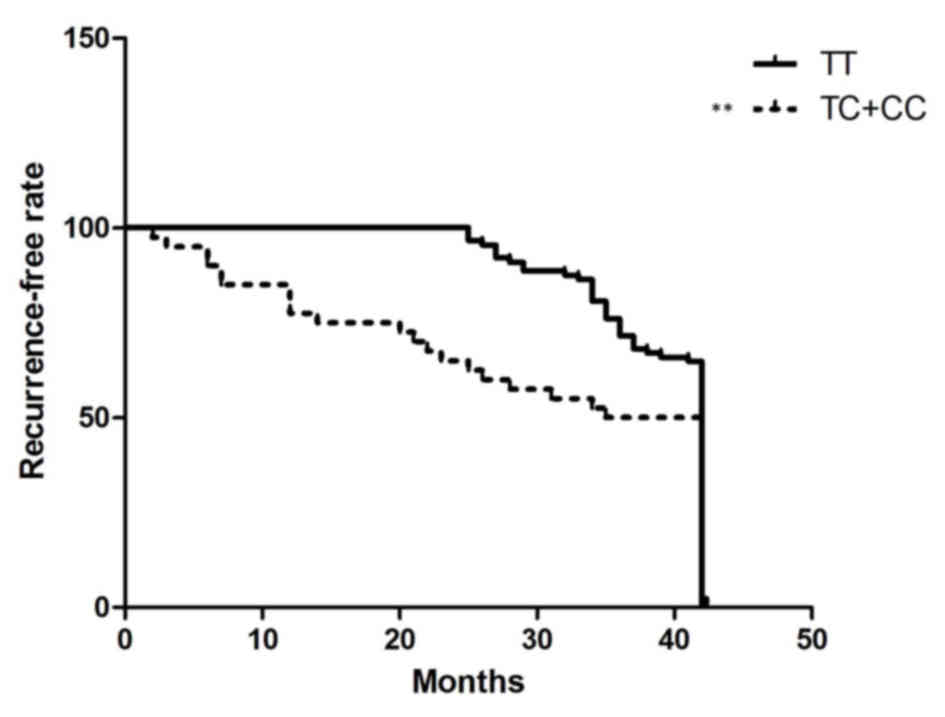
|
1
|
Correa P: International cancer
epidemiology meetings. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 1:245–247.
1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Nagano H, Ohyama S, Fukunaga T, Seto Y,
Fujisaki J, Yamaguchi T, Yamamoto N, Kato Y and Yamaguchi A:
Indications for gastrectomy after incomplete EMR for early gastric
cancer. Gastric Cancer. 8:149–154. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ono H, Kondo H, Gotoda T, Shirao K,
Yamaguchi H, Saito D, Hosokawa K, Shimoda T and Yoshida S:
Endoscopic mucosal resection for treatment of early gastric cancer.
Gut. 48:225–229. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Toyonaga T, Nishino E, Hirooka T, Ueda C
and Noda K: Intraoperative bleeding in endoscopic submucosal
dissection in the stomach and strategy for prevention and
treatment. Digestive Endoscopy. 18:(Suppl). S123–S127. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Imaeda H, Iwao Y, Ogata H, Ichikawa H,
Mori M, Hosoe N, Masaoka T, Nakashita M, Suzuki H, Inoue N, et al:
A new technique for endoscopic submucosal dissection for early
gastric cancer using an external grasping forceps. Endoscopy.
38:1007–1010. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gotoda T: Endoscopic resection of early
gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer. 10:1–11. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Huang JQ, Sridhar S, Chen Y and Hunt RH:
Meta-analysis of the relationship between Helicobacter
pylori seropositivity and gastric cancer. Gastroenterology.
114:1169–1179. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Parsonnet J, Friedman GD, Vandersteen DP,
Chang Y, Vogelman JH, Orentreich N and Sibley RK:
Helicobacter-pylori infection and the risk of
gastric-carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 325:1127–1131. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nomura A, Stemmermann GN, Chyou PH, Kato
I, Perezperez GI and Blaser MJ: Helicobacter-pylori
infection and gastric-carcinoma among Japanese-Americans in Hawaii.
N Engl J Med. 325:1132–1136. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ebert MS and Sharp PA: Roles for microRNAs
in conferring robustness to biological processes. Cell.
149:515–524. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pritchard CC, Cheng HH and Tewari M:
MicroRNA profiling: Approaches and considerations. Nat Rev Genet.
13:358–369. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yang JS and Lai EC: Alternative miRNA
biogenesis pathways and the interpretation of core miRNA pathway
mutants. Mol Cell. 43:892–903. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ryan BM, Robles AI and Harris CC: Genetic
variation in microRNA networks: The implications for cancer
research. Nat Rev Cancer. 10:398–402. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Hou YY, Lee JH, Chen HC, Yang CM, Huang
SJ, Liou HH, Chi CC, Tsai KW and Ger LP: The association between
miR-499a polymorphism and oral squamous cell carcinoma progression.
Oral Dis. 21:195–206. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Guo Y, Yin J, Zha L and Wang Z:
Clinicopathological significance of platelet-derived growth factor
B, platelet-derived growth factor receptor-β and E-cadherin
expression in gastric carcinoma. Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 17:150–155.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sachinidis A, Skach RA, Seul C, Ko Y,
Hescheler J, Ahn HY and Fingerle J: Inhibition of the PDGF
beta-receptor tyrosine phosphorylation and its downstream
intracellular signal transduction pathway in rat and human vascular
smooth muscle cells by different catechins. FASEB J. 16:893–895.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu J, Xie B, Chen S, Jiang F and Meng W:
Association study of two inflammation-related polymorphisms with
susceptibility to hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis. BMC
Med Genet. 15:922014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Amano Y, Ishihara S, Amano K, Hirakawa K,
Adachi K, Fukuda R, Watanabe M, Fukumoto S, Fujishiro H and Imaoka
T: An assessment of local curability of endoscopic surgery in early
gastric cancer without satisfaction of current therapeutic
indications. Endoscopy. 30:548–552. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sano T, Kobori O and Muto T: Lymph node
metastasis from early gastric cancer: Endoscopic resection of
tumour. Br J Surg. 79:241–244. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Haruma K, Sumii K, Inoue K, Teshima H and
Kajiyama G: Endoscopic therapy in patients with inoperable early
gastric cancer. Am J Gastroenterol. 85:522–526. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kato M: Endoscopic submucosal dissection
(ESD is being accepted as a new procedure of endoscopic treatment
of early gastric cancer. Intern Med. 44:85–86. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hirasaki S, Tanimizu M, Nasu J, Shinji T
and Koide N: Treatment of elderly patients with early gastric
cancer by endoscopic submucosal dissection using an insulated-tip
diathermic knife. Intern Med. 44:1033–1038. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Miyoshi E, Haruma K, Hiyama T, Tanaka S,
Yoshihara M, Shimamoto F and Chayama K: Microsatellite instability
is a genetic marker for the development of multiple gastric
cancers. Int J Cancer. 95:350–353. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hanaoka N, Uedo N, Shiotani A, Inoue T,
Takeuchi Y, Higashino K, Ishihara R, Iishi H, Haruma K and Tatsuta
M: Autofluorescence imaging for predicting development of
metachronous gastric cancer after Helicobacter pylori
eradication. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 25:1844–1849. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Shiotani A, Uedo N, Iishi H, Yoshiyuki Y,
Ishii M, Manabe N, Kamada T, Kusunoki H, Hata J and Haruma K:
Predictive factors for metachronous gastric cancer in high-risk
patients after successful Helicobacter pylori eradication.
Digestion. 78:113–119. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Fukase K, Kato M, Kikuchi S, Inoue K,
Uemura N, Okamoto S, Terao S, Amagai K, Hayashi S and Asaka M:
Japan Gast Study Group: Effect of eradication of Helicobacter
pylori on incidence of metachronous gastric carcinoma after
endoscopic resection of early gastric cancer: An open-label,
randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 372:392–397. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Salzman DW and Weidhaas JB: SNPing cancer
in the bud: microRNA and microRNA-target site polymorphisms as
diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers in cancer. Pharmacol Ther.
137:55–63. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
MacDonald TJ, Brown KM, LaFleur B,
Peterson K, Lawlor C, Chen Y, Packer RJ, Cogen P and Stephan DA:
Expression profiling of medulloblastoma: PDGFRA and the RAS/MAPK
pathway as therapeutic targets for metastatic disease. Nat Genet.
29:143–152. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Mathey S, Graeser MK, Eulenburg Zu C,
Woelber L, Trillsch F, Jaenicke F, Müller V, Milde-Langosch K and
Mahner S: Platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta serum
concentrations during first-line therapy in ovarian cancer.
Oncology. 85:69–77. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kitadai Y, Sasaki T, Kuwai T, Nakamura T,
Bucana CD, Hamilton SR and Fidler IJ: Expression of activated
platelet-derived growth factor receptor in stromal cells of human
colon carcinomas is associated with metastatic potential. Int J
Cancer. 119:2567–2574. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mancuso MR, Davis R, Norberg SM, O'Brien
S, Sennino B, Nakahara T, Yao VJ, Inai T, Brooks P, Freimark B, et
al: Rapid vascular regrowth in tumors after reversal of VEGF
inhibition. J Clin Invest. 116:2610–2621. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Song S, Ewald AJ, Stallcup W, Werb Z and
Bergers G: PDGFRbeta+ perivascular progenitor cells in tumours
regulate pericyte differentiation and vascular survival. Nat Cell
Biol. 7:870–879. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Erben P, Horisberger K, Muessle B, Müller
MC, Treschl A, Ernst T, Kähler G, Ströbel P, Wenz F, Kienle P, et
al: mRNA expression of platelet-derived growth factor receptor-beta
and C-KIT: Correlation with pathologic response to cetuximab-based
chemoradiotherapy in patients with rectal cancer. Int J Radiat
Oncol Biol Phys. 72:1544–1550. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liotta LA and Kohn EC: The
microenvironment of the tumour-host interface. Nature. 411:375–379.
2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Radinsky R and Fidler IJ: Regulation of
tumor cell growth at organ-specific metastases. In Vivo. 6:325–331.
1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Gialeli C, Nikitovic D, Kletsas D,
Theocharis AD, Tzanakakis GN and Karamanos NK: PDGF/PDGFR signaling
and targeting in cancer growth and progression: Focus on tumor
microenvironment and cancer-associated fibroblasts. Curr Pharm Des.
20:2843–2848. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|