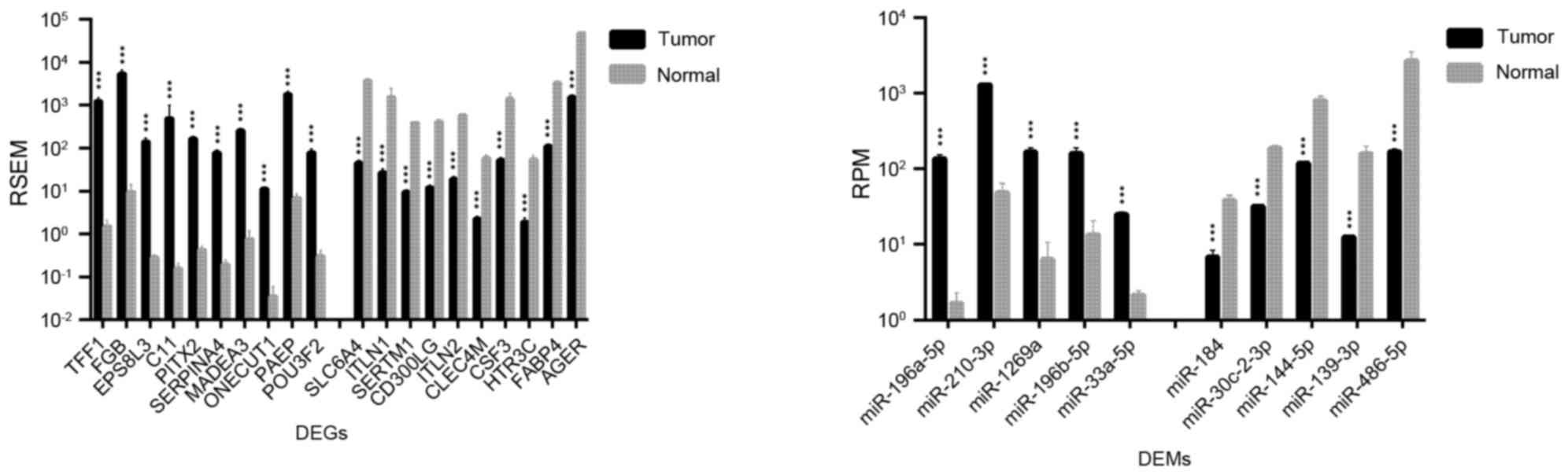
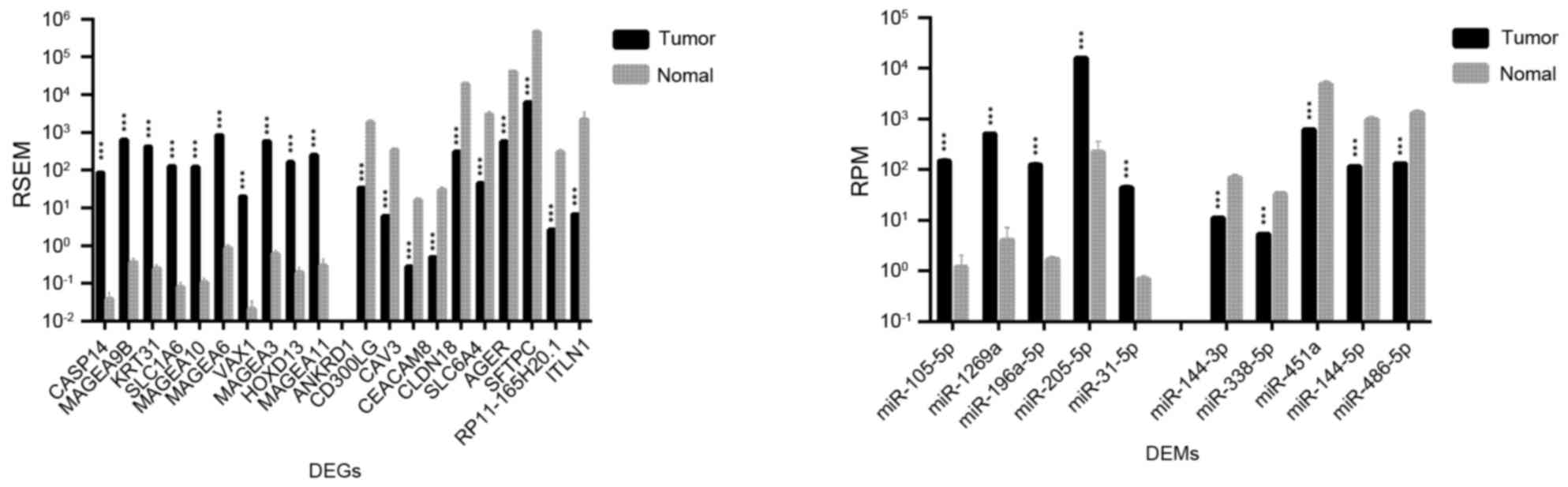
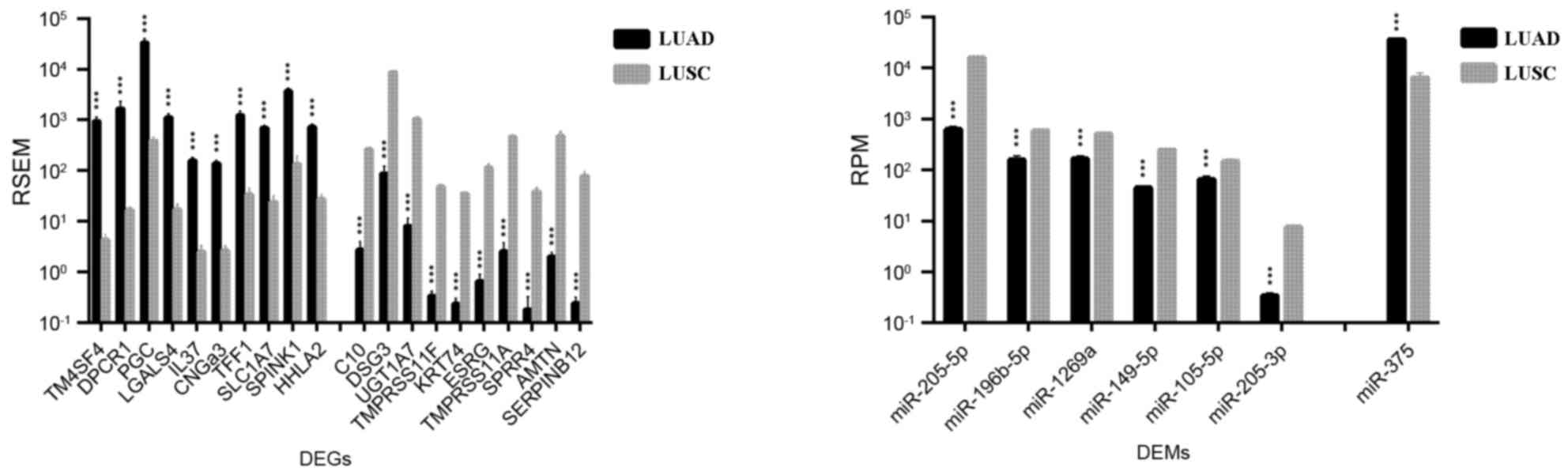
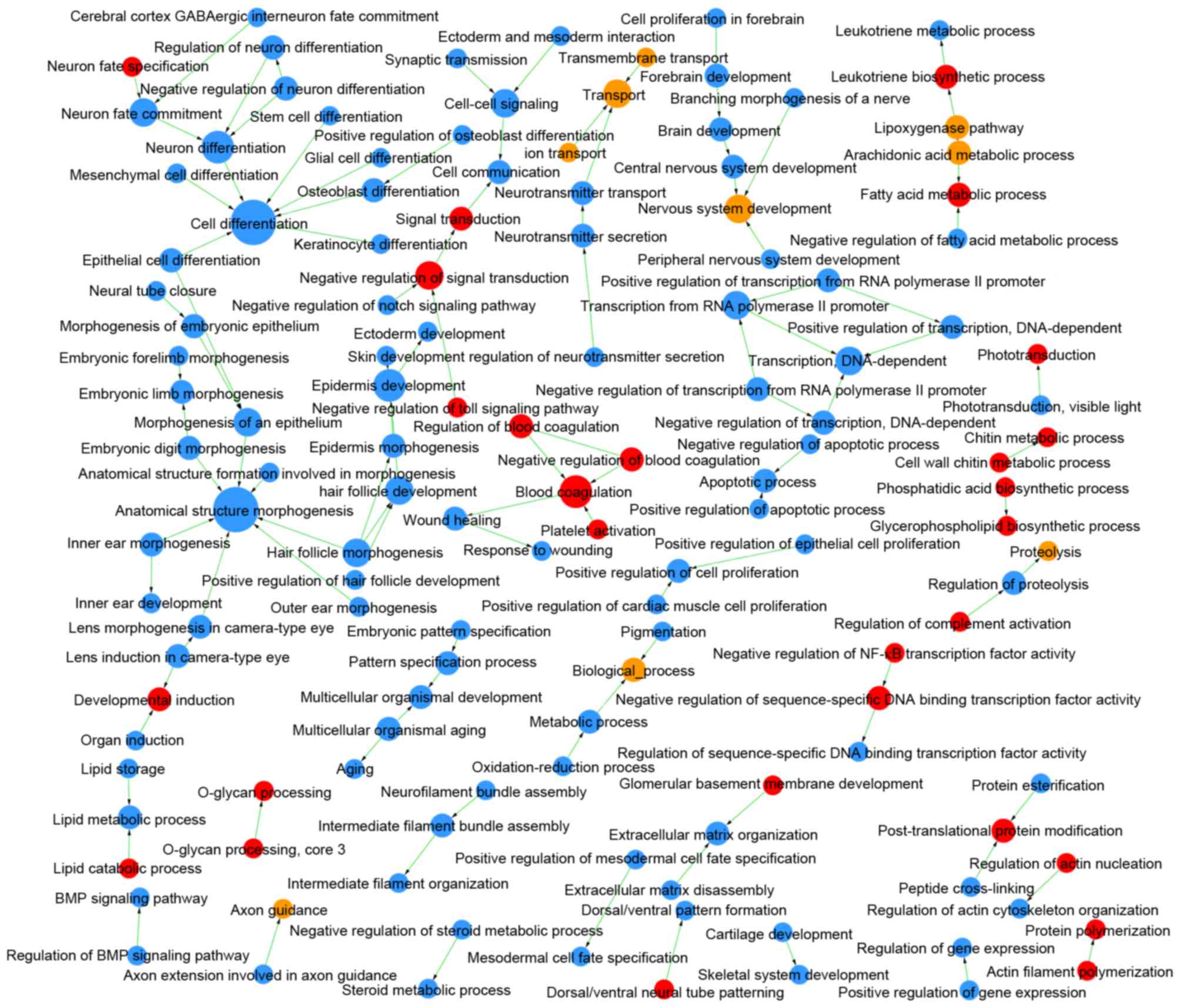
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Zeng H, Zhang S and He J:
Annual report on status of cancer in China, 2011. Chin J Cancer
Res. 27:2–12. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Allemani C, Weir HK, Carreira H, Harewood
R, Spika D, Wang XS, Bannon F, Ahn JV, Johnson CJ, Bonaventure A,
et al: Global surveillance of cancer survival 1995–2009: Analysis
of individual data for 25,676,887 patients from 279
population-based registries in 67 countries (CONCORD-2). Lancet.
385:977–1010. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Herbst RS, Heymach JV and Lippman SM: Lung
cancer. N Engl J Med. 359:1367–1380. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Travis WD, Brambilla E, Noguchi M,
Nicholson AG, Geisinger KR, Yatabe Y, Beer DG, Powell CA, Riely GJ,
Van Schil PE, et al: International association for the study of
lung cancer/American thoracic society/European respiratory society
international multidisciplinary classification of lung
adenocarcinoma. J Thorac Oncol. 6:244–285. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Travis WD, Rekhtman N, Riley GJ, Geisinger
KR, Asamura H, Brambilla E, Garg K, Hirsch FR, Noguchi M, Powell
CA, et al: Pathologic diagnosis of advanced lung cancer based on
small biopsies and cytology: A paradigm shift. J Thorac Oncol.
5:411–414. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhan C, Yan L, Wang L, Sun Y, Wang X, Lin
Z, Zhang Y, Shi Y, Jiang W and Wang Q: Identification of
immunohistochemical markers for distinguishing lung adenocarcinoma
from squamous cell carcinoma. J Thorac Dis. 7:1398–1405.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network:
Comprehensive genomic characterization of squamous cell lung
cancers. Nature. 489:519–525. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rekhtman N, Paik PK, Arcila ME, Tafe LJ,
Oxnard GR, Moreira AL, Travis WD, Zakowski MF, Kris MG and Ladanyi
M: Clarifying the spectrum of driver oncogene mutations in
biomarker-verified squamous carcinoma of lung: Lack of EGFR/KRAS
and presence of PIK3CA/AKT1 mutations. Clin Cancer Res.
18:1167–1176. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhan C, Yan L, Wang L, Jiang W, Zhang Y,
Xi J, Jin Y, Chen L, Shi Y, Lin Z and Wang Q: Landscape of
expression profiles in esophageal carcinoma by the cancer genome
atlas data. Dis Esophagus. 29:920–928. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wright GW and Simon RM: A random variance
model for detection of differential gene expression in small
microarray experiments. Bioinformatics. 19:2448–2455. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein
D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT,
et al: Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. The Gene
Ontology Consortium. Nat Genet. 25:25–29. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
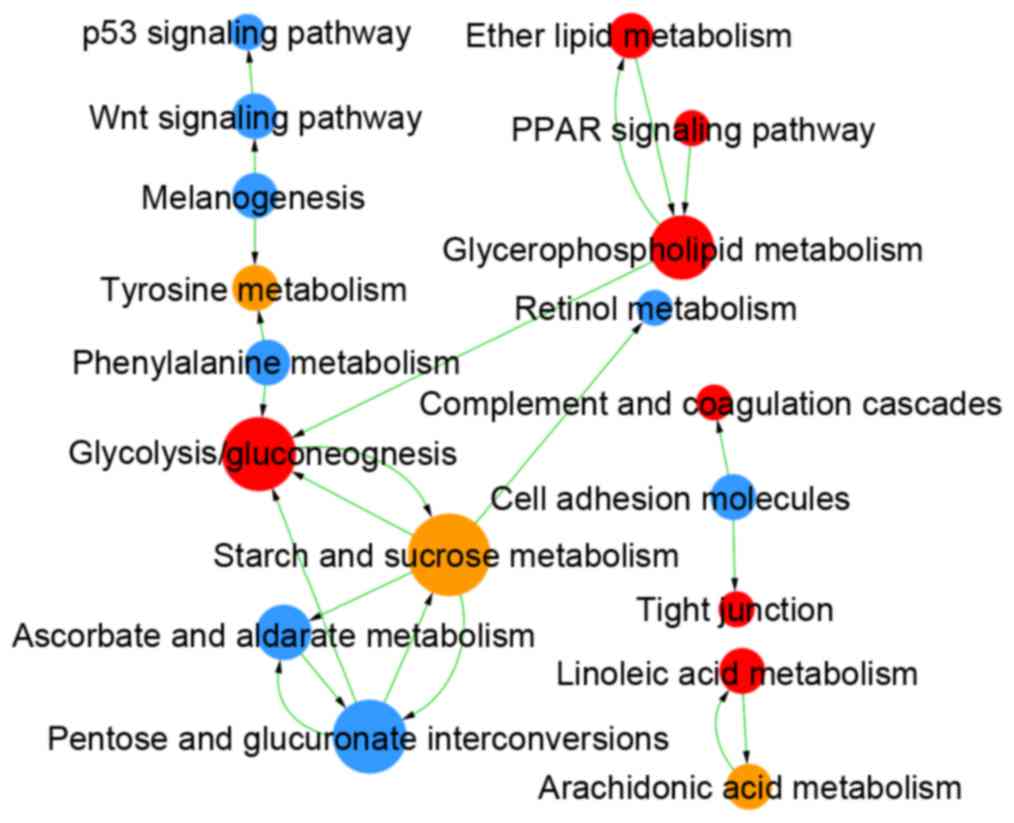
Kanehisa M, Goto S, Kawashima S, Okuno Y
and Hattori M: The KEGG resource for deciphering the genome.
Nucleic Acids Res. 32:D277–D280. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yan L, Zhan C, Wu J and Wang S: Expression
profile analysis of head and neck squamous cell carcinomas using
data from the Cancer Genome Atlas. Mol Med Rep. 13:4259–4265.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Garcia DM, Baek D, Shin C, Bell GW,
Grimson A and Bartel DP: Weak seed-pairing stability and high
target-site abundance decrease the proficiency of lsy-6 and other
microRNAs. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 18:1139–1146. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Betel D, Koppal A, Agius P, Sander C and
Leslie C: Comprehensive modeling of microRNA targets predicts
functional non-conserved and non-canonical sites. Genome Biol.
11:R902010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
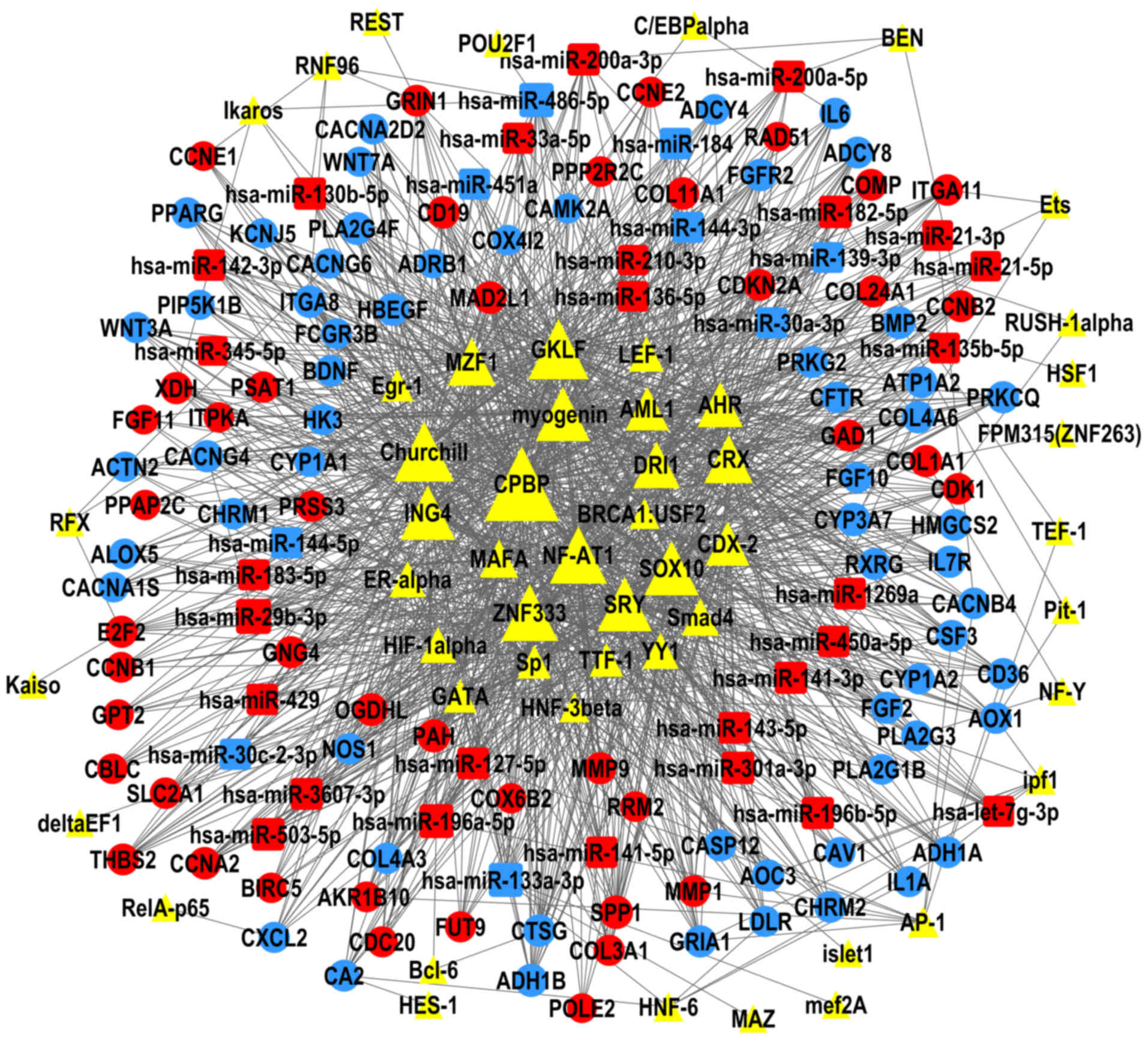
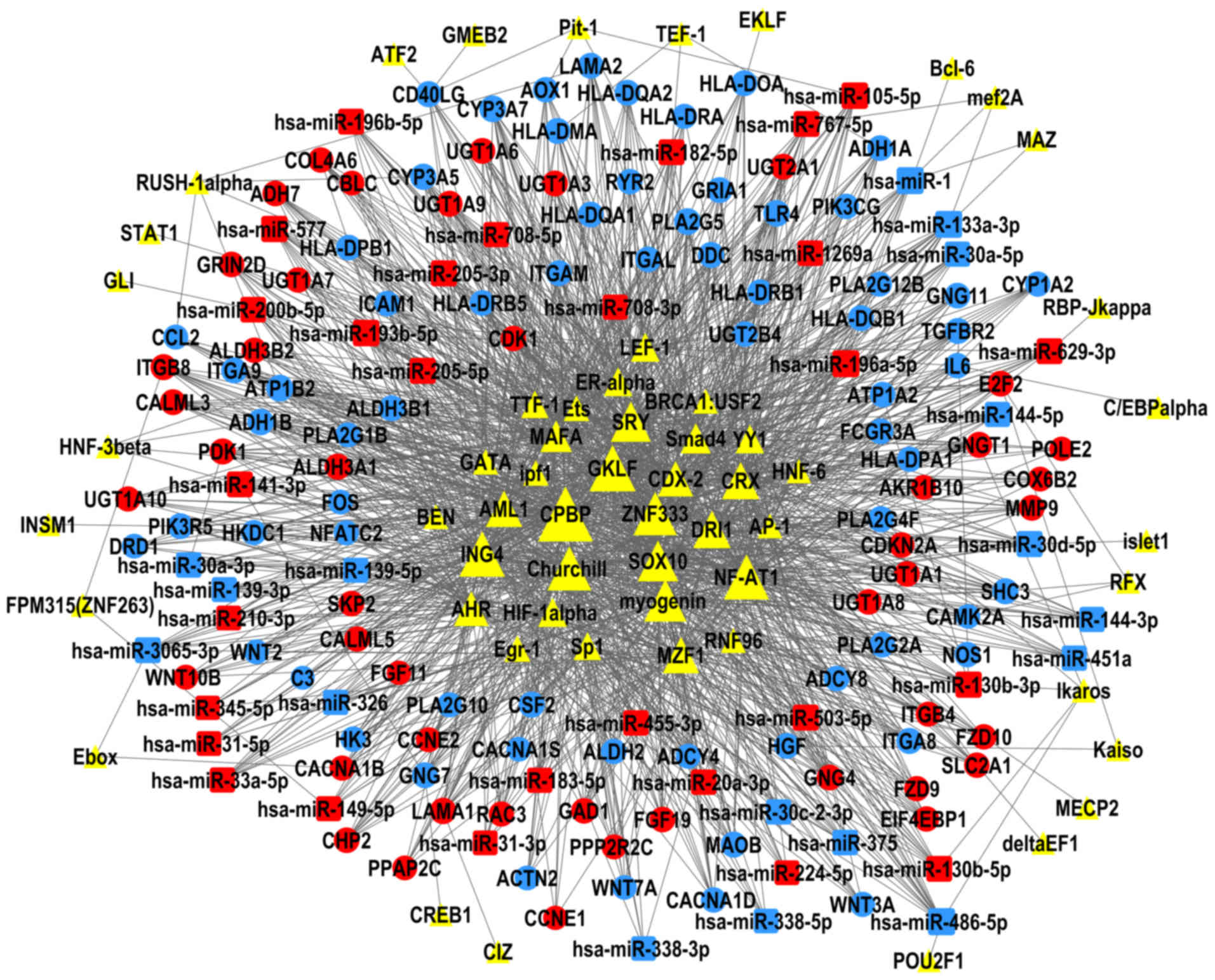
Kel AE, Gössling E, Reuter I, Cheremushkin
E, Kel-Margoulis OV and Wingender E: MATCH: A tool for searching
transcription factor binding sites in DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids
Res. 31:3576–3579. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Travis WD and Rekhtman N: Pathological
diagnosis and classification of lung cancer in small biopsies and
cytology: Strategic management of tissue for molecular testing.
Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 32:22–31. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Schwartz AM and Rezaei MK: Diagnostic
surgical pathology in lung cancer: Diagnosis and management of lung
cancer, 3rd ed: American college of chest physicians evidence-based
clinical practice guidelines. Chest. 143:(Suppl 5). e251S–e262S.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jiang M, Zhang P, Hu G, Xiao Z, Xu F,
Zhong T, Huang F, Kuang H and Zhang W: Relative expressions of
miR-205-5p, miR-205-3p, and miR-21 in tissues and serum of
non-small cell lung cancer patients. Mol Cell Biochem. 383:67–75.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yu L, Todd NW, Xing L, Xie Y, Zhang H, Liu
Z, Fang H, Zhang J, Katz RL and Jiang F: Early detection of lung
adenocarcinoma in sputum by a panel of microRNA markers. Int J
Cancer. 127:2870–2878. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mehner C, Miller E, Nassar A, Bamlet WR,
Radisky ES and Radisky DC: Tumor cell expression of MMP3 as a
prognostic factor for poor survival in pancreatic, pulmonary, and
mammary carcinoma. Genes Cancer. 6:480–489. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kessenbrock K, Plaks V and Werb Z: Matrix
metalloproteinases: Regulators of the tumor microenvironment. Cell.
141:52–67. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Radisky ES and Radisky DC: Matrix
metalloproteinase-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
breast cancer. J Mammary Gland Biol. 15:201–212. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Han S and Roman J: Peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor gamma: A novel target for cancer
therapeutics? Anticancer Drug. 18:237–244. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Tsubouchi Y, Sano H, Kawahito Y, Mukai S,
Yamada R, Kohno M, Inoue K, Hla T and Kondo M: Inhibition of human
lung cancer cell growth by the peroxisome proliferator-activated
receptor-gamma agonists through induction of apoptosis. Biochem
Bioph Res Commun. 270:400–405. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Harvey M, Vogel H, Morris D, Bradley A,
Bernstein A and Donehower LA: A mutant p53 transgene accelerates
tumour development in heterozygous but not nullizygous
p53-deficient mice. Nat Genet. 9:305–311. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kemp CJ, Donehower LA, Bradley A and
Balmain A: Reduction of p53 gene dosage does not increase
initiation or promotion but enhances malignant progression of
chemically induced skin tumors. Cell. 74:813–822. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jackson EL, Olive KP, Tuveson DA, Bronson
R, Crowley D, Brown M and Jacks T: The differential effects of
mutant p53 alleles on advanced murine lung cancer. Cancer Res.
65:10280–10288. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gibbons DL, Byers LA and Kurie JM:
Smoking, p53 mutation, and lung cancer. Mol Cancer Res. 12:3–13.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shinden Y, Iguchi T, Akiyoshi S, Ueo H,
Ueda M, Hirata H, Sakimura S, Uchi R, Takano Y, Eguchi H, et al:
miR-29b is an indicator of prognosis in breast cancer patients. Mol
Clin Oncol. 3:919–923. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ma J, Lin Y, Zhan M, Mann DL, Stass SA and
Jiang F: Differential miRNA expressions in peripheral blood
mononuclear cells for diagnosis of lung cancer. Lab Invest.
95:1197–1206. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Nohata N, Hanazawa T, Enokida H and Seki
N: microRNA-1/133a and microRNA-206/133b clusters: Dysregulation
and functional roles in human cancers. Oncotarget. 3:9–21.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Mataki H, Enokida H, Chiyomaru T, Mizuno
K, Matsushita R, Goto Y, Nishikawa R, Higashimoto I, Samukawa T,
Nakagawa M, et al: Downregulation of the microRNA-1/133a cluster
enhances cancer cell migration and invasion in lung-squamous cell
carcinoma via regulation of Coronin1C. J Hum Genet. 60:53–61. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Nasser MW, Datta J, Nuovo G, Kutay H,
Motiwala T, Majumder S, Wang B, Suster S, Jacob ST and Ghoshal K:
Down-regulation of micro-RNA-1 (miR-1) in lung cancer. Suppression
of tumorigenic property of lung cancer cells and their
sensitization to doxorubicin-induced apoptosis by miR-1. J Biol
Chem. 283:33394–33405. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Jonsdottir K, Janssen SR, Da Rosa FC,
Gudlaugsson E, Skaland I, Baak JP and Janssen EA: Validation of
expression patterns for nine miRNAs in 204 lymph-node negative
breast cancers. PLoS One. 7:e486922012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Shao X, Mei W, Weng W, Qin J, Zhou J, Liu
J and Cheng J: Mir-375 enhances ruthenium-derived compound Rawq01
induced cell death in human ovarian cancer. Int J Clin Exp Patho.
6:1095–1102. 2013.
|
|
38
|
Nishikawa E, Osada H, Okazaki Y, Arima C,
Tomida S, Tatematsu Y, Taguchi A, Shimada Y, Yanagisawa K, Yatabe
Y, et al: miR-375 is activated by ASH1 and inhibits YAP1 in a
lineage-dependent manner in lung cancer. Cancer Res. 71:6165–6173.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yu H, Jiang L, Sun C, Li Guo L, Lin M,
Huang J and Zhu L: Decreased circulating miR-375: A potential
biomarker for patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. Gene.
534:60–65. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|