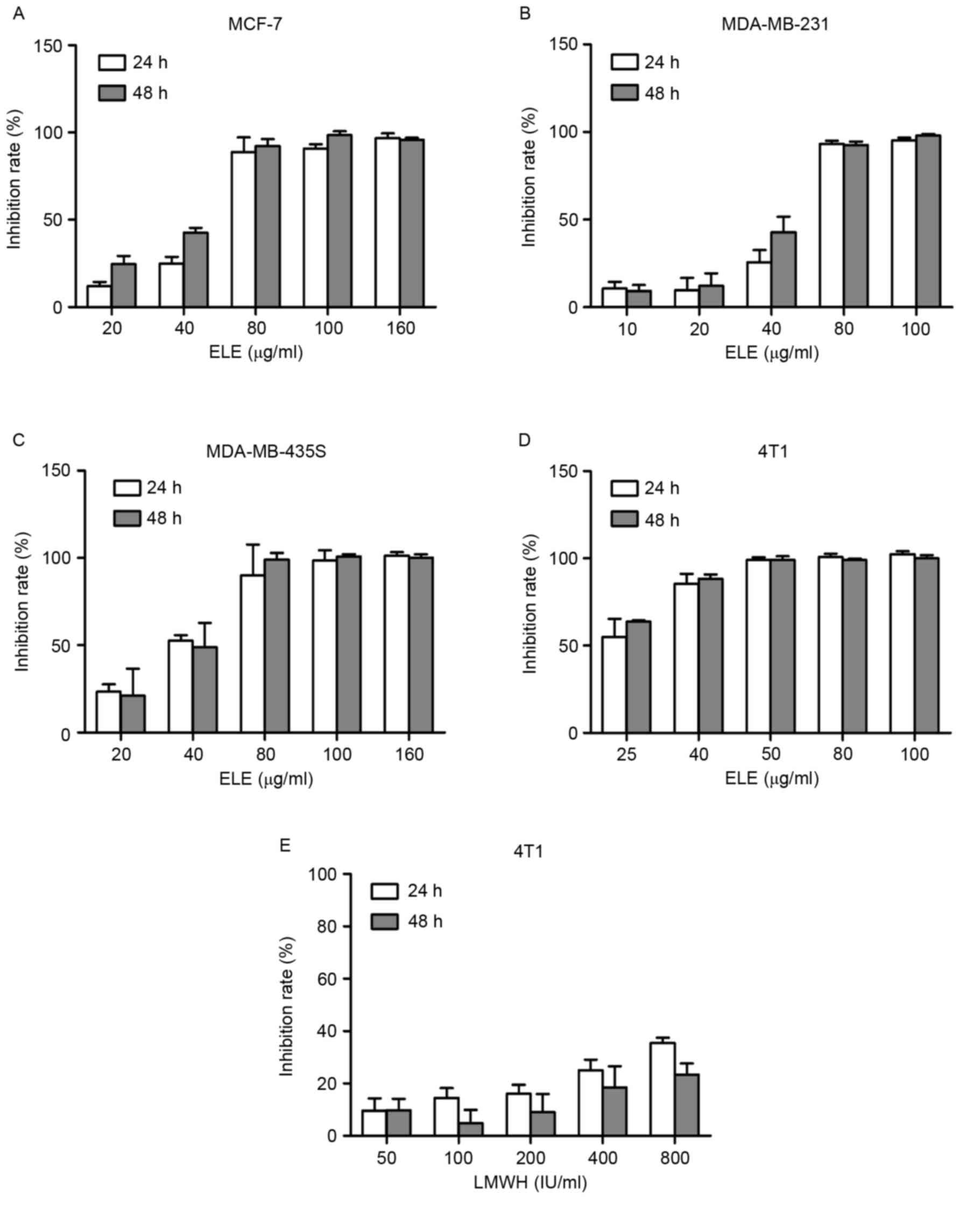
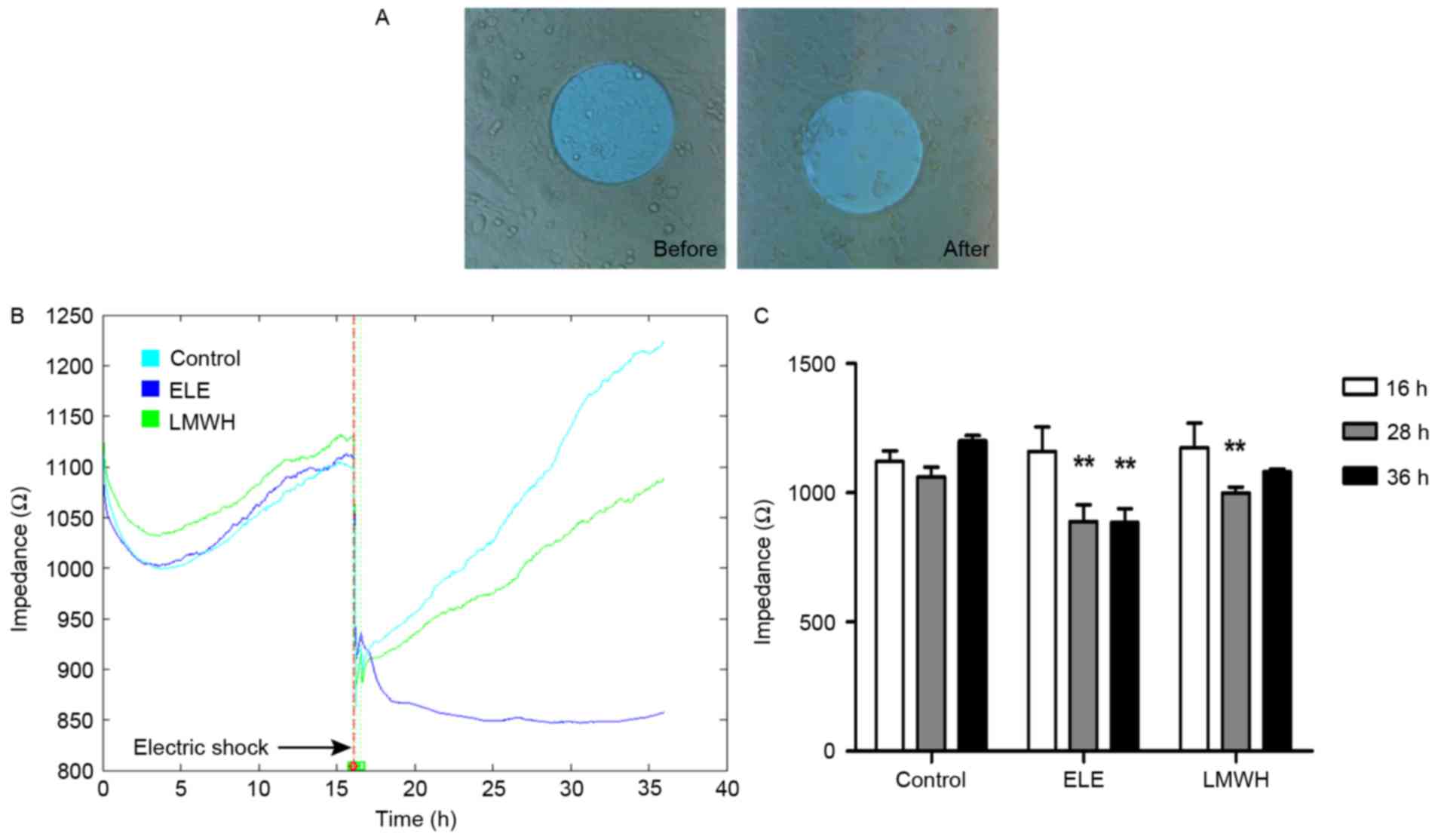
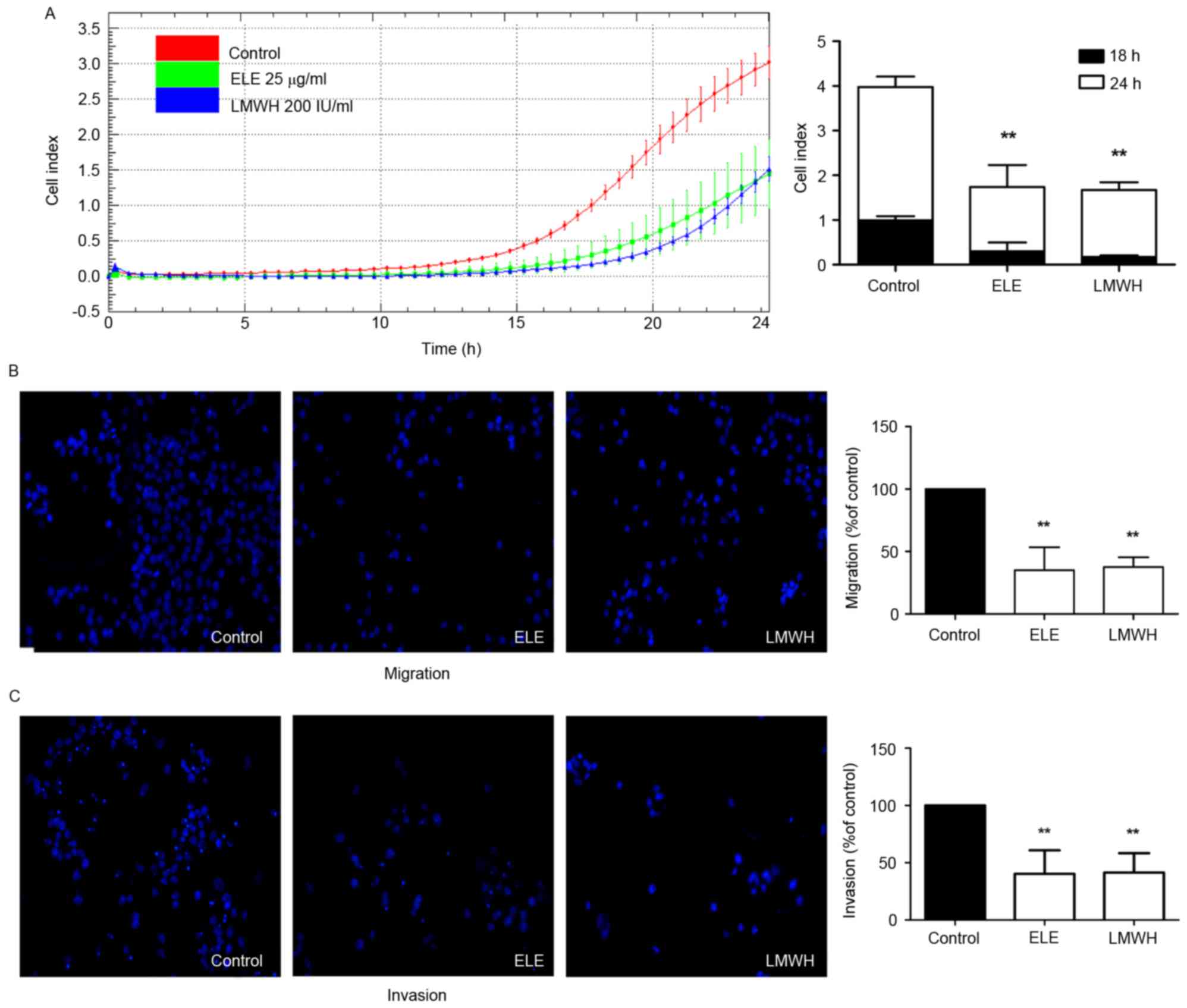
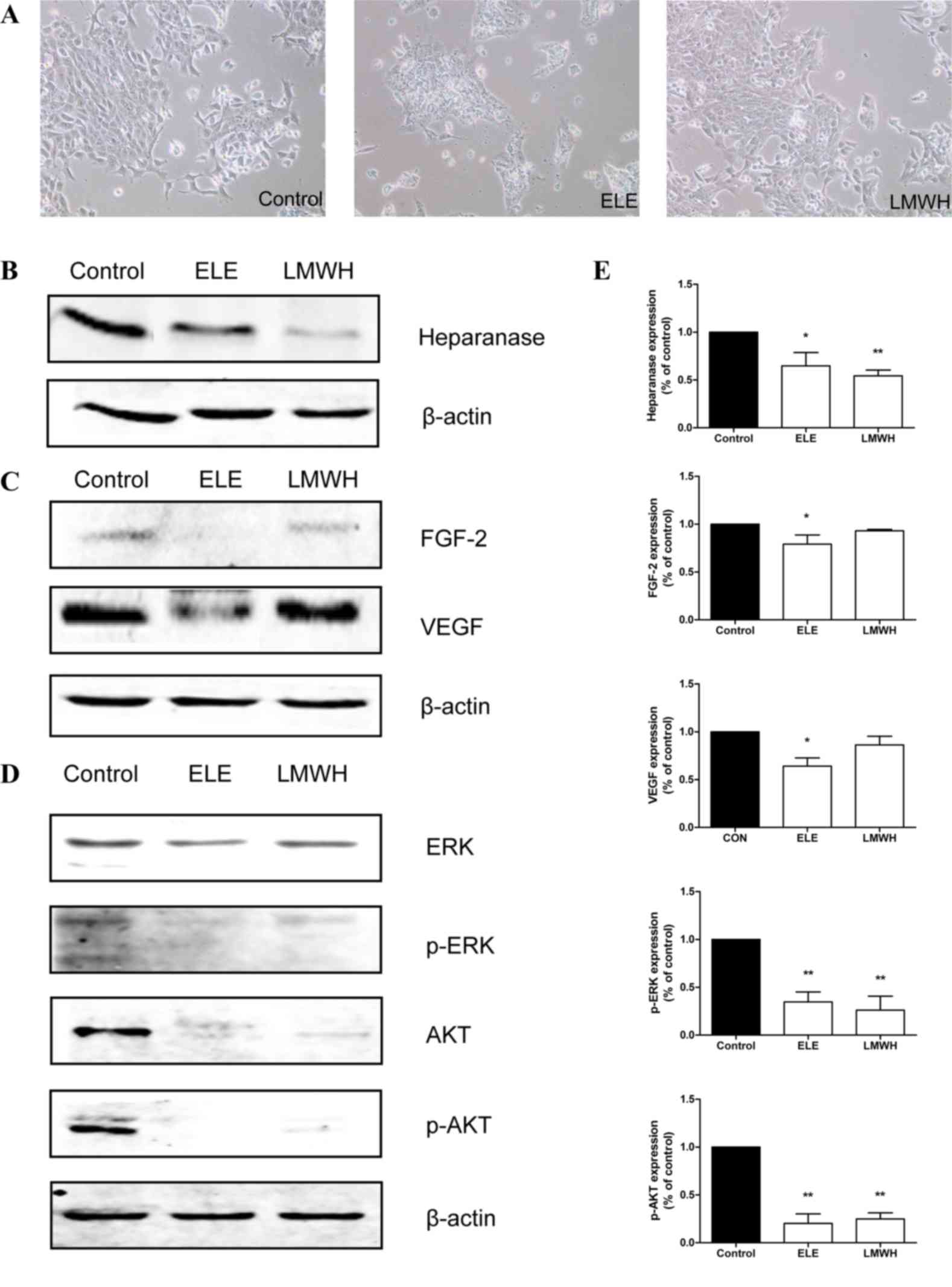
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Shi XJ, Au WW, Wu KS, Chen LX and Lin K:
Mortality characteristics and prediction of female breast cancer in
China from 1991 to 2011. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 15:2785–2791.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Guan X: Cancer metastases: Challenges and
opportunities. Acta Pharm Sin B. 5:402–418. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Brown GT and Murray GI: Current
mechanistic insights into the roles of matrix metalloproteinases in
tumour invasion and metastasis. J Pathol. 237:273–281. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Vlodavsky I, Friedmann Y, Elkin M, Aingorn
H, Atzmon R, Ishai-Michaeli R, Bitan M, Pappo O, Peretz T, Michal
I, et al: Mammalian heparanase: Gene cloning, expression and
function in tumor progression and metastasis. Nat Med. 5:793–802.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Maxhimer JB, Quiros RM, Stewart R,
Dowlatshahi K, Gattuso P, Fan M, Prinz RA and Xu X: Heparanase-1
expression is associated with the metastatic potential of breast
cancer. Surgery. 132:326–333. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li JP: Heparin, heparan sulfate and
heparanase in cancer: Remedy for metastasis? Anticancer Agents Med
Chem. 8:64–76. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wu BW, Li DF, Ke ZF, Ma D, Li YJ, Gang D,
Zheng ZG, Zhang KJ and Zhang YH: Expression characteristics of
heparanase in colon carcinoma and its close relationship with
cyclooxygenase-2 and angiogenesis. Hepatogastroenterology.
57:1510–1514. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
dos Santos Fernandes TC, Gomes AM,
Paschoal ME, Stelling MP, Rumjanek VM, Ado Junior R, Valiante PM,
Madi K, de Souza Pereira HS, Pavão MS and Castelo-Branco MT:
Heparanase expression and localization in different types of human
lung cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1840:2599–2608. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Davidson B, Shafat I, Risberg B, Ilan N,
Trope' CG, Vlodavsky I and Reich R: Heparanase expression
correlates with poor survival in metastatic ovarian carcinoma.
Gynecol Oncol. 104:311–319. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang L, Sullivan PS, Goodman JC,
Gunaratne PH and Marchetti D: MicroRNA-1258 suppresses breast
cancer brain metastasis by targeting heparanase. Cancer Res.
71:645–654. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Vlodavsky I, Fuks Z, Ishai-Michaeli R,
Bashkin P, Levi E, Korner G, Bar-Shavit R and Klagsbrun M:
Extracellular matrix-resident basic fibroblast growth factor:
Implication for the control of angiogenesis. J Cell Biochem.
45:167–176. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Vlodavsky I, Goldshmidt O, Zcharia E,
Atzmon R, Rangini-Guatta Z, Elkin M, Peretz T and Friedmann Y:
Mammalian heparanase: Involvement in cancer metastasis,
angiogenesis and normal development. Semin Cancer Biol. 12:121–129.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gingis-Velitski S, Zetser A, Flugelman MY,
Vlodavsky I and Ilan N: Heparanase induces endothelial cell
migration via protein kinase B/Akt activation. J Biol Chem.
279:23536–23541. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lu JJ, Dang YY, Huang M, Xu WS, Chen XP
and Wang YT: Anti-cancer properties of terpenoids isolated from
Rhizoma Curcumae-a review. J Ethnopharmacol. 143:406–411.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang X, Li Y, Zhang Y, Song J, Wang Q,
Zheng L and Liu D: Beta-elemene blocks epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in human breast cancer cell line MCF-7 through
Smad3-mediated down-regulation of nuclear transcription factors.
PLoS One. 8:e587192013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yan B, Zhou Y, Feng S, Lv C, Xiu L, Zhang
Y, Shi J, Li Y, Wei P and Qin Z: β-Elemene-attenuated tumor
angiogenesis by targeting notch-1 in gastric cancer stem-like
cells. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013:2684682013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shi H, Liu L, Liu L, Geng J, Zhou Y and
Chen L: β-Elemene inhibits the metastasis of B16F10 melanoma cells
by downregulation of the expression of uPA, uPAR, MMP-2, and MMP-9.
Melanoma Res. 24:99–107. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Teoh ML, Fitzgerald MP, Oberley LW and
Domann FE: Overexpression of extracellular superoxide dismutase
attenuates heparanase expression and inhibits breast carcinoma cell
growth and invasion. Cancer Res. 69:6355–6363. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gong F, Jemth P, Galvis Escobar ML,
Vlodavsky I, Horner A, Lindahl U and Li JP: Processing of
macromolecular heparin by heparanase. J Biol Chem. 278:35152–35158.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Szulcek R, Bogaard HJ and van Nieuw
Amerongen GP: Electric cell-substrate impedance sensing for the
quantification of endothelial proliferation, barrier function, and
motility. J Vis Exp. 2014.doi: 10.3791/51300. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mandel K, Seidl D, Rades D, Lehnert H,
Gieseler F, Hass R and Ungefroren H: Characterization of
spontaneous and TGF-β-induced cell motility of primary human normal
and neoplastic mammary cells in vitro using novel real-time
technology. PLoS One. 8:e565912013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li QQ, Wang G, Huang F, Banda M and Reed
E: Antineoplastic effect of beta-elemene on prostate cancer cells
and other types of solid tumour cells. J Pharm Pharmacol.
62:1018–1027. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chen W, Lu Y, Wu J, Gao M, Wang A and Xu
B: Beta-elemene inhibits melanoma growth and metastasis via
suppressing vascular endothelial growth factor-mediated
angiogenesis. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 67:799–808. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ettelaie C, Fountain D, Collier ME, Beeby
E, Xiao YP and Maraveyas A: Low molecular weight heparin suppresses
tissue factor-mediated cancer cell invasion and migration in
vitro. Exp Ther Med. 2:363–367. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhong GX, Gong Y, Yu CJ, Wu SF, Ma QP,
Wang Y, Ren J, Zhang XC, Yang WH and Zhu W: Significantly
inhibitory effects of low molecular weight heparin (Fraxiparine) on
the motility of lung cancer cells and its related mechanism. Tumour
Biol. 36:4689–4697. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liu H, Chen X, Gao W and Jiang G: The
expression of heparanase and microRNA-1258 in human non-small cell
lung cancer. Tumour Biol. 33:1327–1334. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang X, Zhang Y and Li Y: β-elemene
decreases cell invasion by upregulating E-cadherin expression in
MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 30:745–750.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Joyce JA, Freeman C, Meyer-Morse N, Parish
CR and Hanahan D: A functional heparan sulfate mimetic implicates
both heparanase and heparan sulfate in tumor angiogenesis and
invasion in a mouse model of multistage cancer. Oncogene.
24:4037–4051. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhou H, Roy S, Cochran E, Zouaoui R, Chu
CL, Duffner J, Zhao G, Smith S, Galcheva-Gargova Z, Karlgren J, et
al: M402, a novel heparan sulfate mimetic, targets multiple
pathways implicated in tumor progression and metastasis. PLoS One.
6:e211062011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Winterhoff B, Freyer L, Hammond E, Giri S,
Mondal S, Roy D, Teoman A, Mullany SA, Hoffmann R, von Bismarck A,
et al: PG545 enhances anti-cancer activity of chemotherapy in
ovarian models and increases surrogate biomarkers such as VEGF in
preclinical and clinical plasma samples. Eur J Cancer. 51:879–892.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hammond E, Brandt R and Dredge K: PG545, a
heparan sulfate mimetic, reduces heparanase expression in vivo,
blocks spontaneous metastases and enhances overall survival in the
4T1 breast carcinoma model. PLoS One. 7:e521752012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ritchie JP, Ramani VC, Ren Y, Naggi A,
Torri G, Casu B, Penco S, Pisano C, Carminati P, Tortoreto M, et
al: SST0001, a chemically modified heparin, inhibits myeloma growth
and angiogenesis via disruption of the heparanase/syndecan-1 axis.
Clin Cancer Res. 17:1382–1393. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|