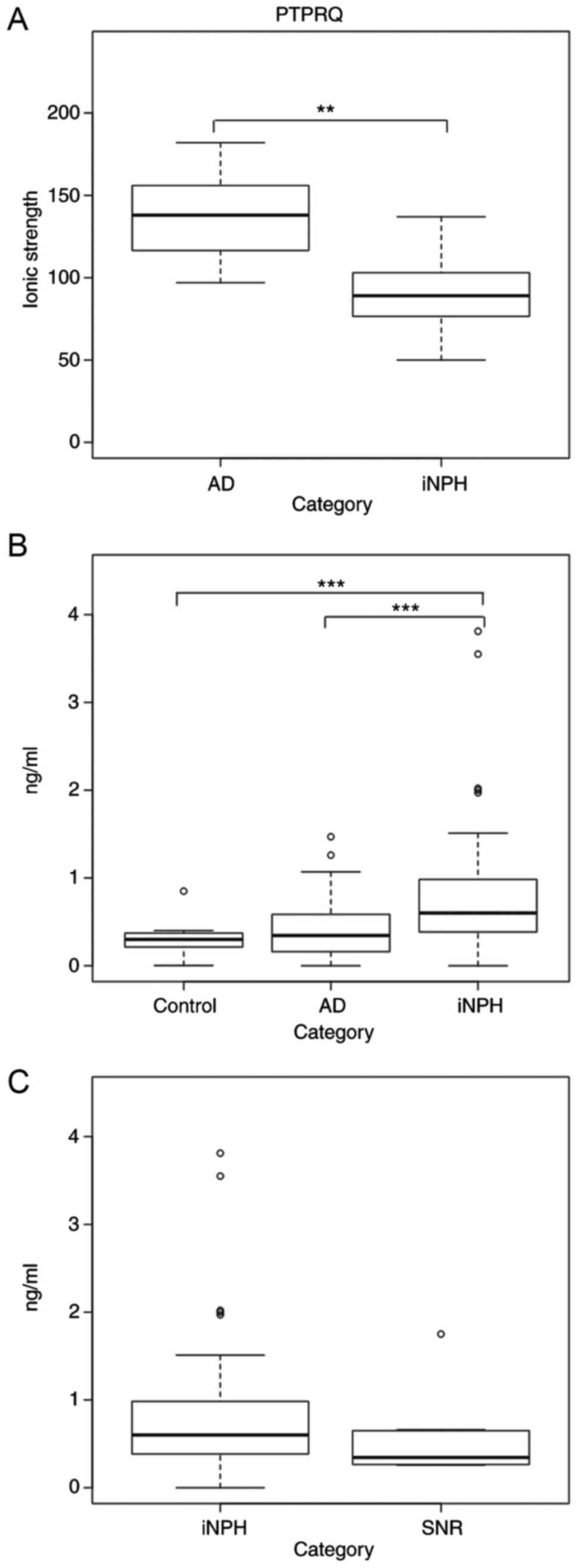
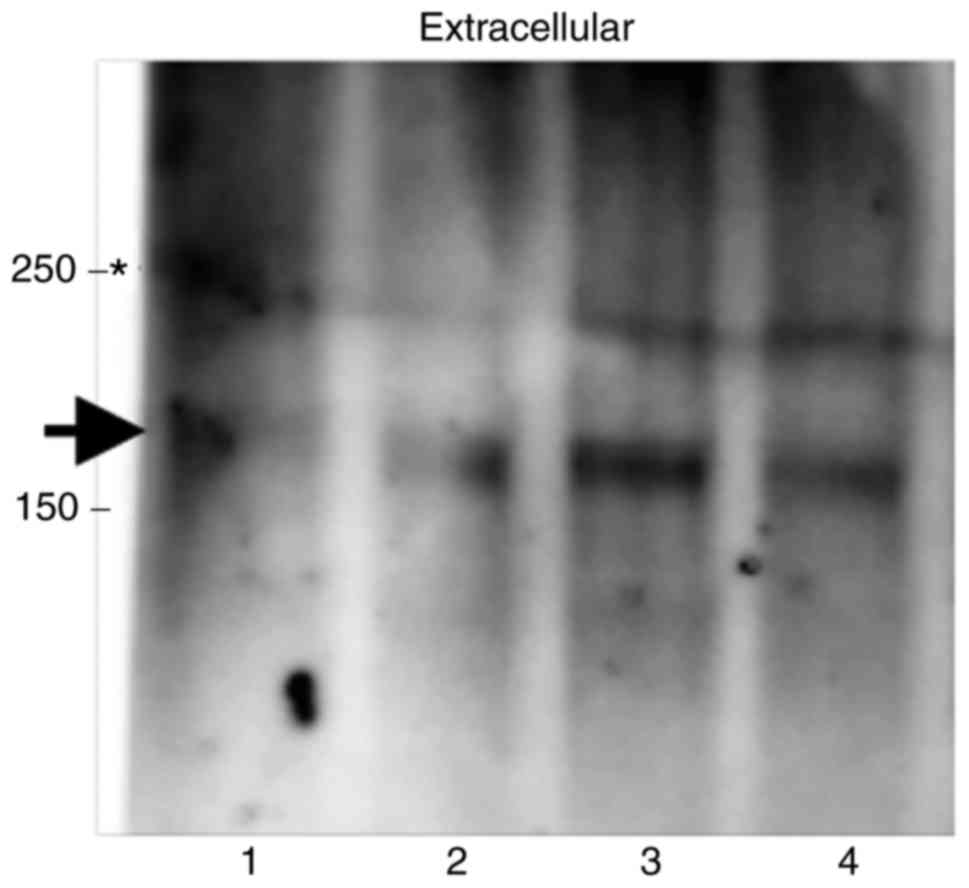
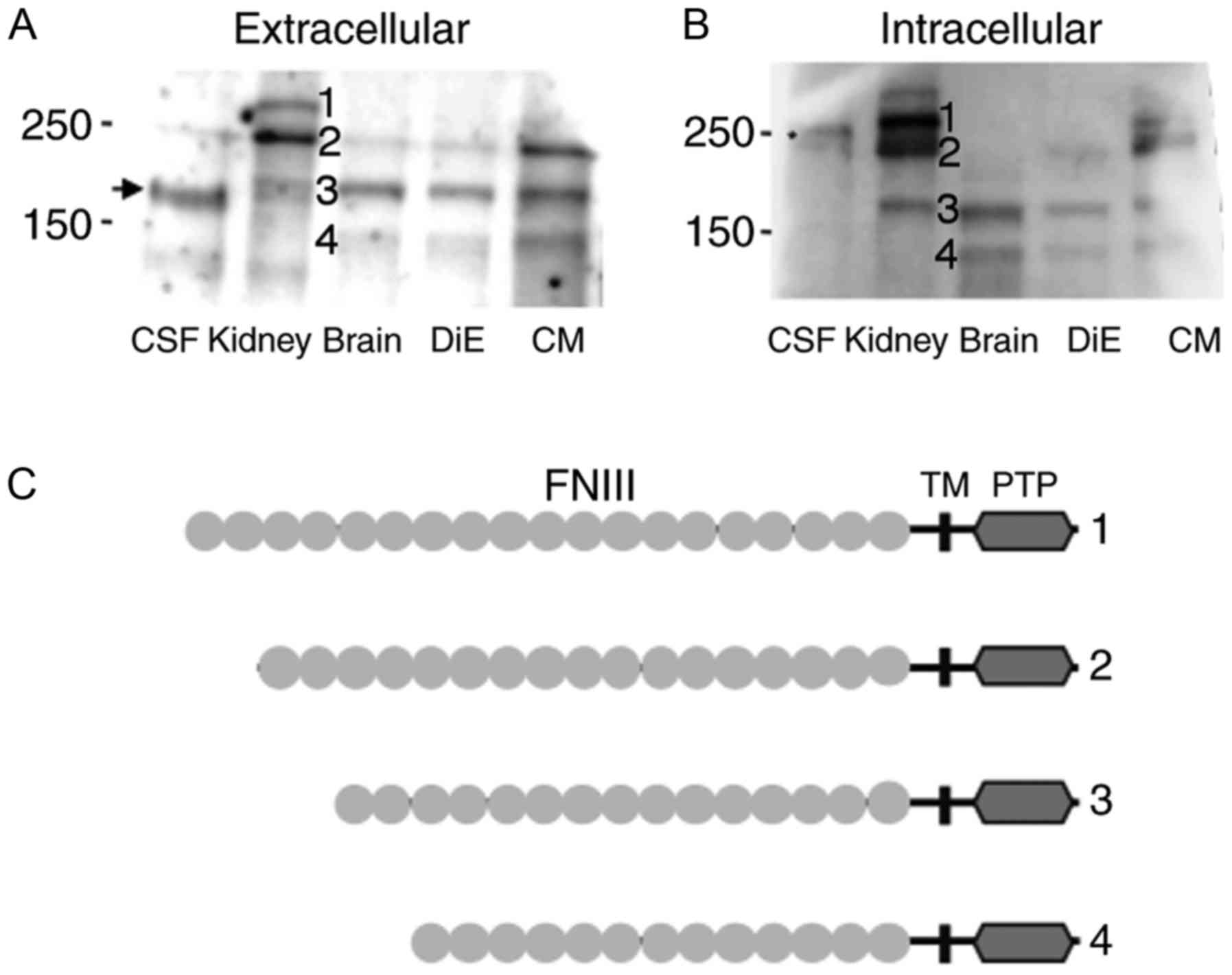
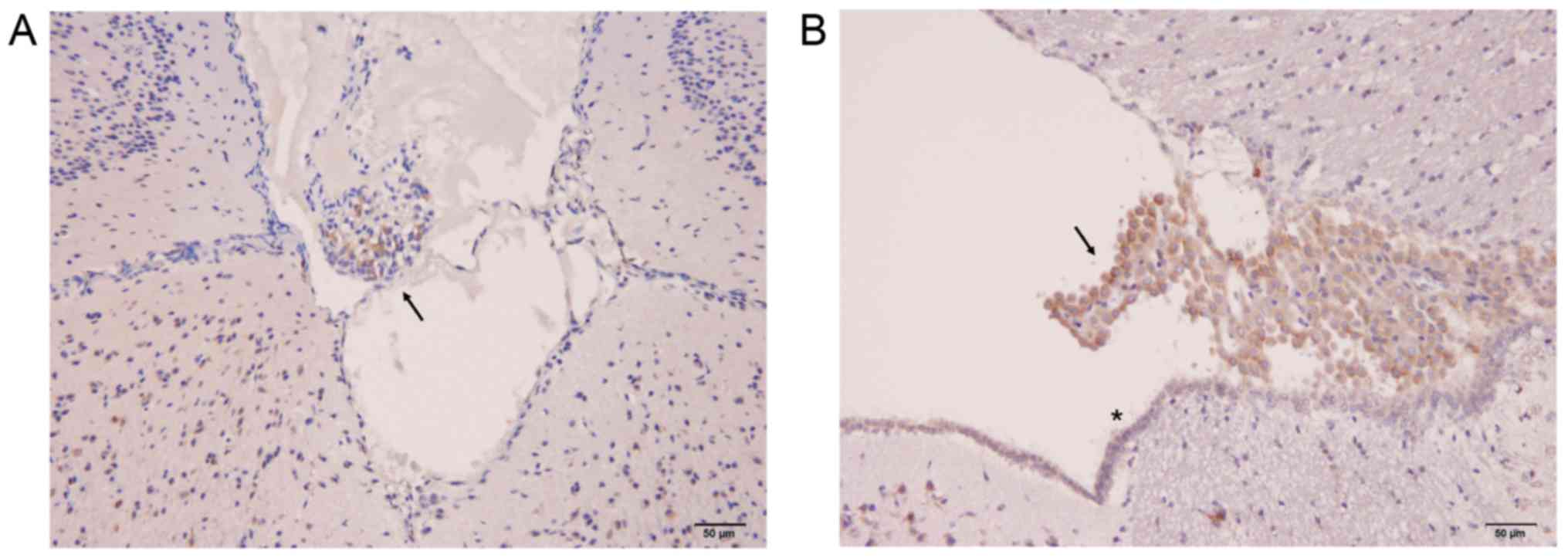
|
1
|
Adams RD, Fisher CM, Hakim S, Ojemann RG
and Sweet WH: Symptomatic occult hydrocephalus with normal
cerebrospinal-fluid pressure. New Engl J Med. 273:117–126. 1965.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bradley WG Jr, Bahl G and Alksne JF:
Idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus may be a ‘two hit’
disease: Benign external hydrocephalus in infancy followed by deep
white matter ischemia in late adulthood. J Magn Reson Imaging.
24:747–755. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cusimano MD, Rewilak D, Stuss DT,
Barrera-Martinez JC, Salehi F and Freedman M: Normal-pressure
hydrocephalus: Is there a genetic predisposition? Can J Neurol Sci.
38:274–281. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Takahashi Y, Kawanami T, Nagasawa H, Iseki
C, Hanyu H and Kato T: Familial normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH)
with an autosomal-dominant inheritance: A novel subgroup of NPH. J
Neurol Sci. 308:149–151. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Schraders M, Oostrik J, Huygen PL, Strom
TM, van Wijk E, Kunst HP, Hoefsloot LH, Cremers CW, Admiraal RJ and
Kremer H: Mutations in PTPRQ are a cause of autosomal-recessive
nonsyndromic hearing impairment DFNB84 and associated with
vestibular dysfunction. Am J Hum Genet. 86:604–610. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shahin H, Rahil M, Abu Rayan A, Avraham
KB, King MC, Kanaan M and Walsh T: Nonsense mutation of the
stereociliar membrane protein gene PTPRQ in human hearing loss
DFNB84. J Med Genet. 47:643–645. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Goodyear RJ, Jones SM, Sharifi L, Forge A
and Richardson GP: Hair-bundle defects and loss of function in the
vestibular end organs of mice lacking the receptor-like inositol
lipid phosphatase, PTPRQ. J Neurosci. 32:2762–2772. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nayak G, Goodyear RJ, Legan PK, Noda M and
Richardson GP: Evidence for multiple, developmentally regulated
isoforms of Ptprq on hair cells of the inner ear. Dev Neurobiol.
71:129–141. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dixon JF and Jones RO:
Hydrocephalus-associated hearing loss and resolution after
ventriculostomy. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 146:1037–1039. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sammons VJ, Jacobson E and Lawson J:
Resolution of hydrocephalus-associated sensorineural hearing loss
after insertion of ventriculoperitoneal shunt. J Neurosurg Pediatr.
4:394–396. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
van Veelen-Vincent ML, Delwel EJ, Teeuw R,
Kurt E, de Jong DA, Brocaar MP, Pauw BK, Avezaat CJ and van Zanten
BG: Analysis of hearing loss after shunt placement in patients with
normal-pressure hydrocephalus. J Neurosurg. 95:432–434. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mori E, Ishikawa M, Kato T, Kazui H,
Miyake H, Miyajima M, Nakajima M, Hashimoto M, Kuriyama N, Tokuda
T, et al: Guidelines for management of idiopathic normal pressure
hydrocephalus: Second edition. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 52:775–809.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kubo Y, Kazui H, Yoshida T, Kito Y, Kimura
N, Tokunaga H, Ogino A, Miyake H, Ishikawa M and Takeda M:
Validation of grading scale for evaluating symptoms of idiopathic
normal-pressure hydrocephalus. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord.
25:37–45. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dubois B, Feldman HH, Jacova C, Dekosky
ST, Barberger-Gateau P, Cummings J, Delacourte A, Galasko D,
Gauthier S, Jicha G, et al: Research criteria for the diagnosis of
Alzheimer's disease: Revising the NINCDS-ADRDA criteria. Lancet
Neurol. 6:734–746. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Matsubara J, Ono M, Negishi A, Ueno H,
Okusaka T, Furuse J, Furuta K, Sugiyama E, Saito Y, Kaniwa N, et
al: Identification of a predictive biomarker for hematologic
toxicities of gemcitabine. J Clin Oncol. 27:2261–2268. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ono M, Matsubara J, Honda K, Sakuma T,
Hashiguchi T, Nose H, Nakamori S, Okusaka T, Kosuge T, Sata N, et
al: Prolyl 4-hydroxylation of alpha-fibrinogen: A novel protein
modification revealed by plasma proteomics. J Biol Chem.
284:29041–29049. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Takakura M, Yokomizo A, Tanaka Y,
Kobayashi M, Jung G, Banno M, Sakuma T, Imada K, Oda Y, Kamita M,
et al: Carbonic anhydrase I as a new plasma biomarker for prostate
cancer. ISRN Oncol. 2012:7681902012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ono M, Shitashige M, Honda K, Isobe T,
Kuwabara H, Matsuzuki H, Hirohashi S and Yamada T: Label-free
quantitative proteomics using large peptide data sets generated by
nanoflow liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry. Mol Cell
Proteomics. 5:1338–1347. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mann M, Højrup P and Roepstorff P: Use of
mass spectrometric molecular weight information to identify
proteins in sequence databases. Biol Mass Spectrom. 22:338–345.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Seifert RA, Coats SA, Oganesian A, Wright
MB, Dishmon M, Booth CJ, Johnson RJ, Alpers CE and Bowen-Pope DF:
PTPRQ is a novel phosphatidylinositol phosphatase that can be
expressed as a cytoplasmic protein or as a subcellularly localized
receptor-like protein. Exp Cell Res. 287:374–386. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Futakawa S, Nara K, Miyajima M, Kuno A,
Ito H, Kaji H, Shirotani K, Honda T, Tohyama Y, Hoshi K, et al: A
unique N-glycan on human transferrin in CSF: A possible biomarker
for iNPH. Neurobiol Aging. 33:1807–1815. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
McComb JG: Recent research into the nature
of cerebrospinal fluid formation and absorption. J Neurosurg.
59:369–383. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Narita K and Takeda S: Cilia in the
choroid plexus: Their roles in hydrocephalus and beyond. Front Cell
Neurosci. 9:392015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Banizs B, Pike MM, Millican CL, Ferguson
WB, Komlosi P, Sheetz J, Bell PD, Schwiebert EM and Yoder BK:
Dysfunctional cilia lead to altered ependyma and choroid plexus
function, and result in the formation of hydrocephalus.
Development. 132:5329–5339. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Siyahhan B, Knobloch V, de Zélicourt D,
Asgari M, Daners M Schmid, Poulikakos D and Kurtcuoglu V: Flow
induced by ependymal cilia dominates near-wall cerebrospinal fluid
dynamics in the lateral ventricles. J R Soc Interface.
11:201311892014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ibañez-Tallon I, Pagenstecher A, Fliegauf
M, Olbrich H, Kispert A, Ketelsen UP, North A, Heintz N and Omran
H: Dysfunction of axonemal dynein heavy chain Mdnah5 inhibits
ependymal flow and reveals a novel mechanism for hydrocephalus
formation. Hum Mol Genet. 13:2133–2141. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lechtreck KF, Delmotte P, Robinson ML,
Sanderson MJ and Witman GB: Mutations in Hydin impair ciliary
motility in mice. J Cell Biol. 180:633–643. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lee L: Riding the wave of ependymal cilia:
Genetic susceptibility to hydrocephalus in primary ciliary
dyskinesia. J Neurosci Res. 91:1117–1132. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tissir F, Qu Y, Montcouquiol M, Zhou L,
Komatsu K, Shi D, Fujimori T, Labeau J, Tyteca D, Courtoy P, et al:
Lack of cadherins Celsr2 and Celsr3 impairs ependymal ciliogenesis,
leading to fatal hydrocephalus. Nat Neurosci. 13:700–707. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gordon AG: Endolymphatic hydrops and CSF
pressure. J Neurosurg. 60:1332–1334. 1984.PubMed/NCBI
|