|
1
|
Scheckenbach KE, Crespin S, Kwak BR and
Chanson M: Connexin channel-dependent signaling pathways in
inflammation. J Vascular Res. 48:91–103. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Berardi DE and Tarbell JM: Stretch and
shear interactions affect intercellular junction protein expression
and turnover in endothelial cells. Cell Mol Bioeng. 2:320–331.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Morel S, Burnier L and Kwak BR: Connexins
participate in the initiation and progression of atherosclerosis.
Semin Immunopathol. 31:49–61. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhou T, He Q, Tong Y, Zhan R, Xu F, Fan D,
Guo X, Han H, Qin S and Chui D: Phospholipid transfer protein
(PLTP) deficiency impaired blood-brain barrier integrity by
increasing cerebrovascular oxidative stress. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 445:352–356. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wong CW, Burger F, Pelli G, Mach F and
Kwak BR: Dual benefit of reduced Cx43 on atherosclerosis in LDL
receptor-deficient mice. Cell Commun Adhes. 10:395–400. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wei JM, Wang X, Gong H, Shi YJ and Zou Y:
Ginkgo suppresses atherosclerosis through downregulating the
expression of connexin 43 in rabbits. Arch Med Sci. 9:340–346.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ren Q, Riquelme MA, Xu J, Yan X, Nicholson
BJ, Gu S and Jiang JX: Cataract-causing mutation of human connexin
46 impairs gap junction, but increases hemichannel function and
cell death. PLoS One. 8:e747322013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Retamal MA: Connexin and Pannexin
hemichannels are regulated by redox potential. Front Physiol.
5:802014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yuan D, Wang Q, Wu D, Yu M, Zhang S, Li L,
Tao L and Harris AL: Monocyte-endothelial adhesion is modulated by
Cx43-stimulated ATP release from monocytes. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 420:536–541. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ba J, Peng H, Chen Y and Gao Y: Effects
and mechanism analysis of vascular endothelial growth factor and
salvianolic acid B on 125I-low density lipoprotein permeability of
the rabbit aortary endothelial cells. Cell Biochem Biophys.
70:1533–1538. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Telo P, Lostaglio S and Dejana E:
Structure of intercellular junctions in the endothelium. Therapie.
52:395–398. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lehman DM, Leach RJ, Johnson-Pais T,
Hamlington J, Fowler S, Almasy L, Duggirala R, Stern MP and Abboud
HE: Evaluation of tight junction protein 1 encoding zona occludens
1 as a candidate gene for albuminuria in a Mexican American
population. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 114:432–437. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gan H, Wang G, Hao Q, Wang QJ and Tang H:
Protein kinase D promotes airway epithelial barrier dysfunction and
permeability through down-regulation of claudin-1. J Biol Chem.
289:204892014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Polacek D, Bech F, McKinsey JF and Davies
PF: Connexin43 gene expression in the rabbit arterial wall: Effects
of hypercholesterolemia, balloon injury and their combination. J
Vasc Res. 34:19–30. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chadjichristos CE, Matter CM, Roth I,
Sutter E, Pelli G, Lüscher TF, Chanson M and Kwak BR: Reduced
connexin43 expression limits neointima formation after balloon
distension injury in hypercholesterolemic mice. Circulation.
113:2835–2843. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yuan D, Sun G, Zhang R, Luo C, Ge M, Luo G
and Hei Z: Connexin 43 expressed in endothelial cells modulates
monocyteendothelial adhesion by regulating cell adhesion proteins.
Mol Med Rep. 12:7146–7152. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kameritsch P, Pogoda K and Pohl U:
Channel-independent influence of connexin 43 on cell migration.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1818:1993–2001. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Morel S and Kwak BR: Roles of connexins in
atherosclerosis and ischemia-reperfusion injury. Curr Pharm
Biotechnol. 13:17–26. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cheng X, Wang X, Wan Y, Zhou Q, Zhu H and
Wang Y: Myosin light chain kinase inhibitor ML7 improves vascular
endothelial dysfunction via tight junction regulation in a rabbit
model of atherosclerosis. Mol Med Rep. 12:4109–4116. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Decano JL, Mattson PC and Aikawa M:
Macrophages in Vascular Inflammation: Origins and Functions. Curr
Atheroscler Rep. 18:342016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rathouska J, Jezkova K, Nemeckova I and
Nachtigal P: Soluble endoglin, hypercholesterolemia and endothelial
dysfunction. Atherosclerosis. 243:383–388. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
van Laake LW, van den Driesche S, Post S,
Feijen A, Jansen MA, Driessens MH, Mager JJ, Snijder RJ, Westermann
CJ, Doevendans PA, et al: Endoglin has a crucial role in blood
cell-mediated vascular repair. Circulation. 114:2288–2297. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
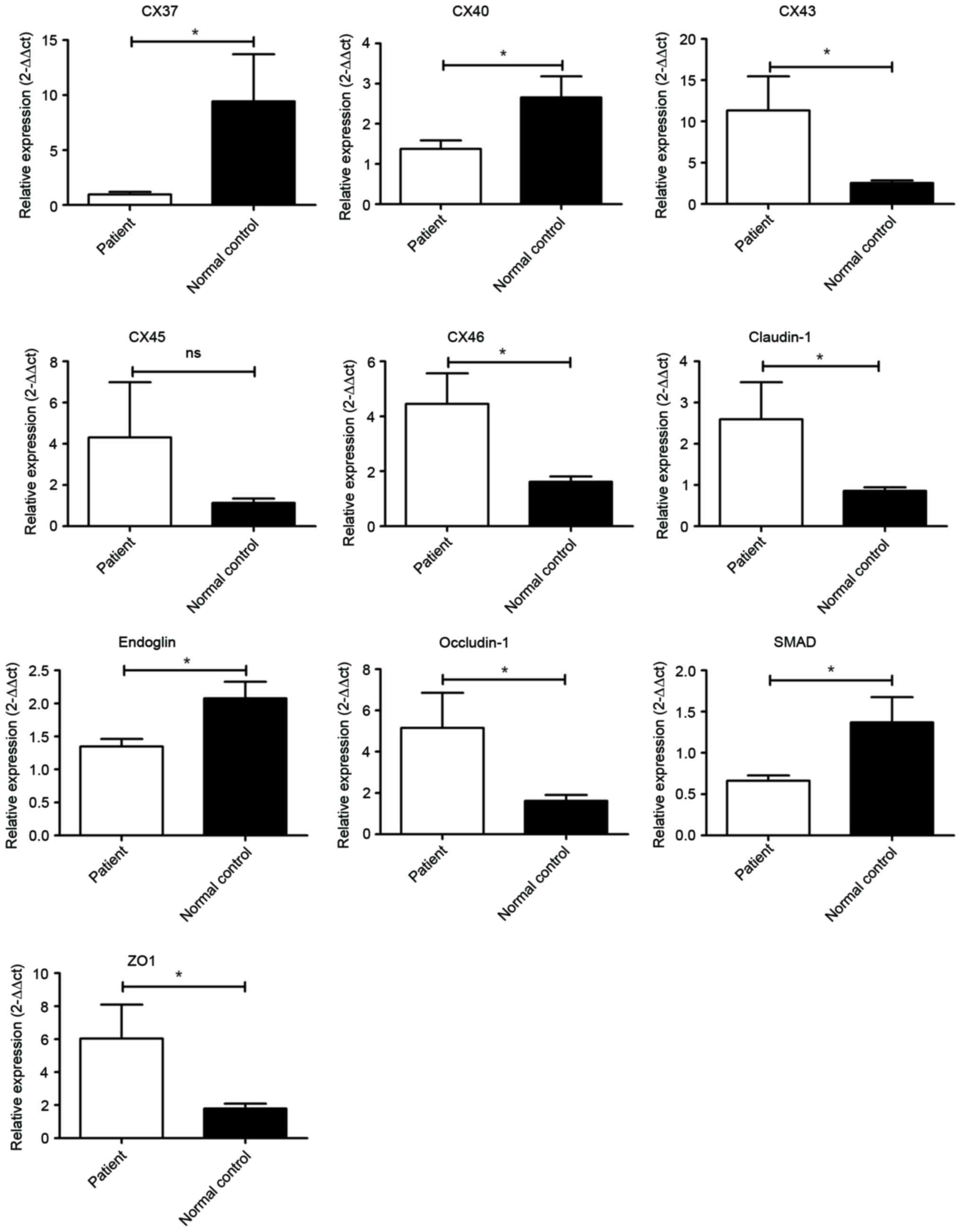
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
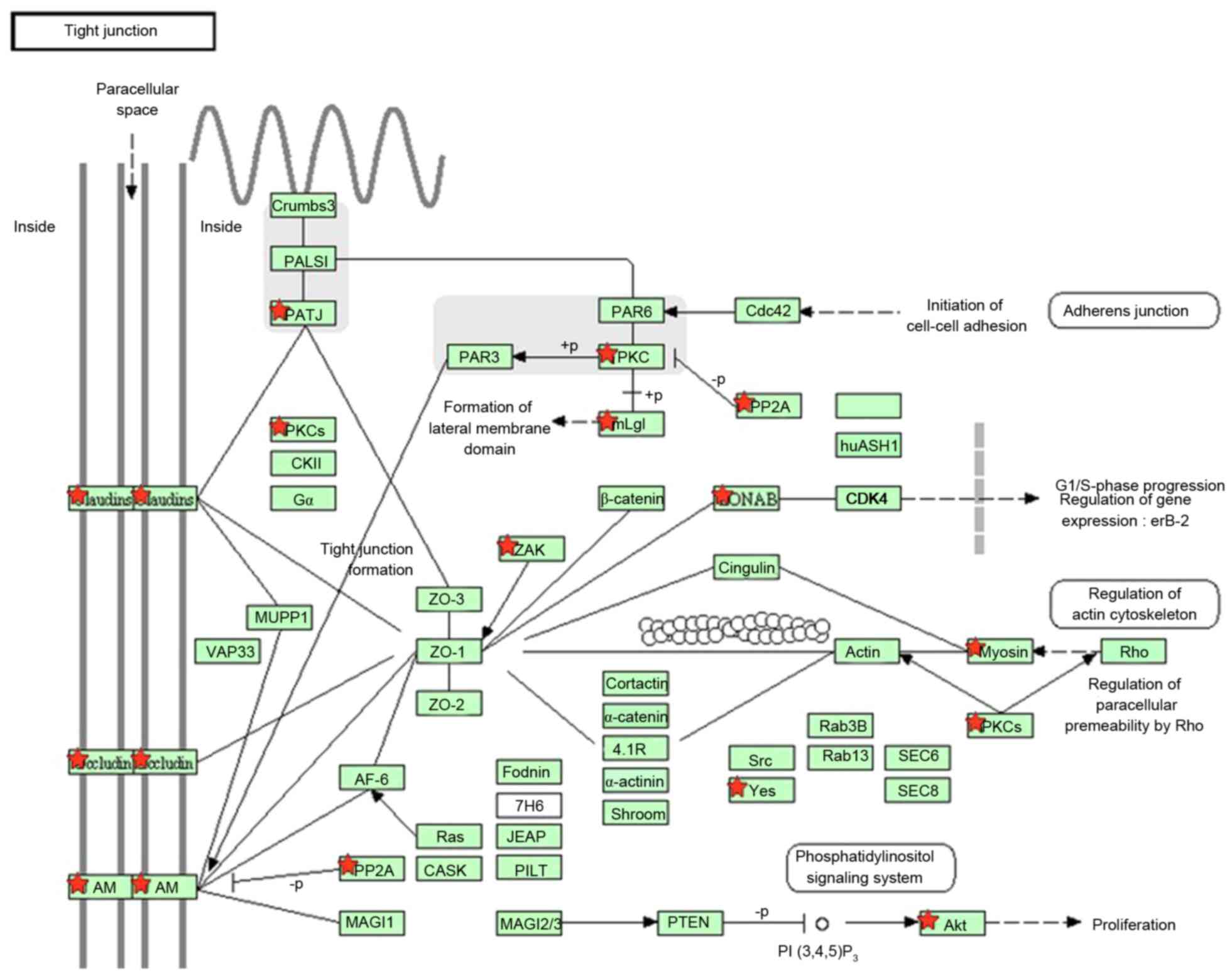
Haseloff RF, Dithmer S, Winkler L, Wolburg
H and Blasig IE: Transmembrane proteins of the tight junctions at
the blood-brain barrier: Structural and functional aspects. Semin
Cell Dev Biol. 38:16–25. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tornavaca O, Chia M, Dufton N, Almagro LO,
Conway DE, Randi AM, Schwartz MA, Matter K and Balda MS: ZO-1
controls endothelial adherens junctions, cell-cell tension,
angiogenesis, and barrier formation. J Cell Biol. 208:821–838.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
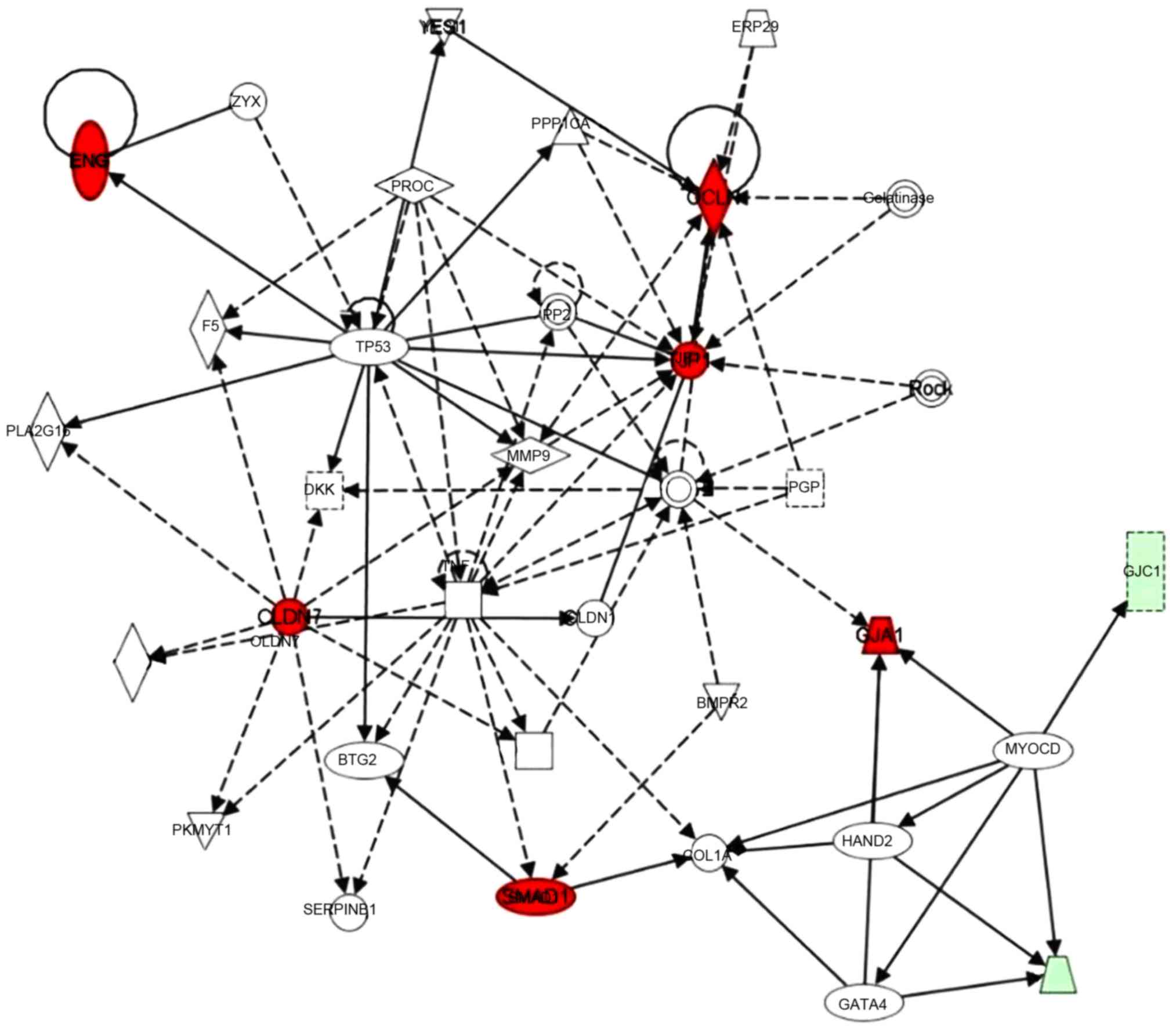
Chadjichristos CE and Kwak BR: Connexins:
New genes in atherosclerosis. Ann Med. 39:402–411. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Rennick RE, Connat JL, Burnstock G,
Rothery S, Severs NJ and Green CR: Expression of connexin43 gap
junctions between cultured vascular smooth muscle cells is
dependent upon phenotype. Cell Tissue Res. 271:323–332. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Collins NT, Cummins PM, Colgan OC,
Ferguson G, Birney YA, Murphy RP, Meade G and Cahill PA: Cyclic
strain-mediated regulation of vascular endothelial occludin and
ZO-1: Influence on intercellular tight junction assembly and
function. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 26:62–68. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhu HQ, Wang XB, Han JX, Hu ZP and Wang Y,
Zhou Q, Gui SY and Wang Y: Myosin light chain kinase inhibitor
attenuates atherosclerosis and permeability via reduced endothelial
tight junction in rabbits. Int J Cardiol. 168:5042–5043. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|