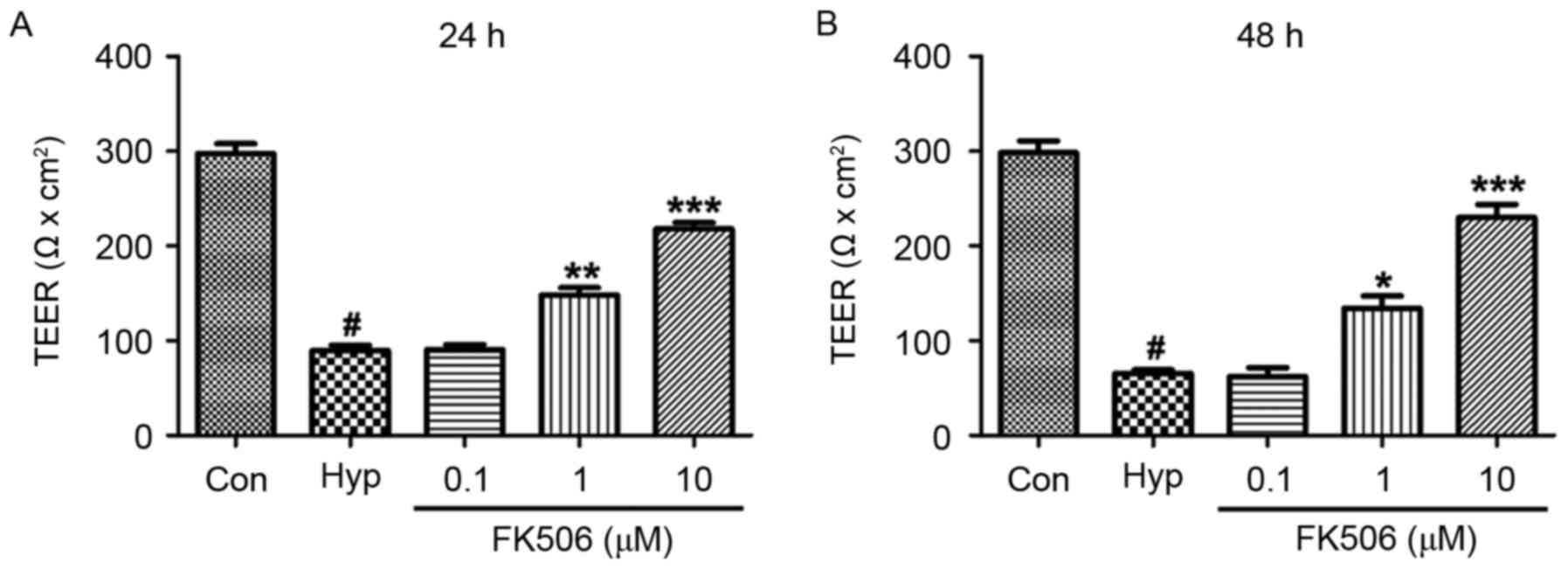
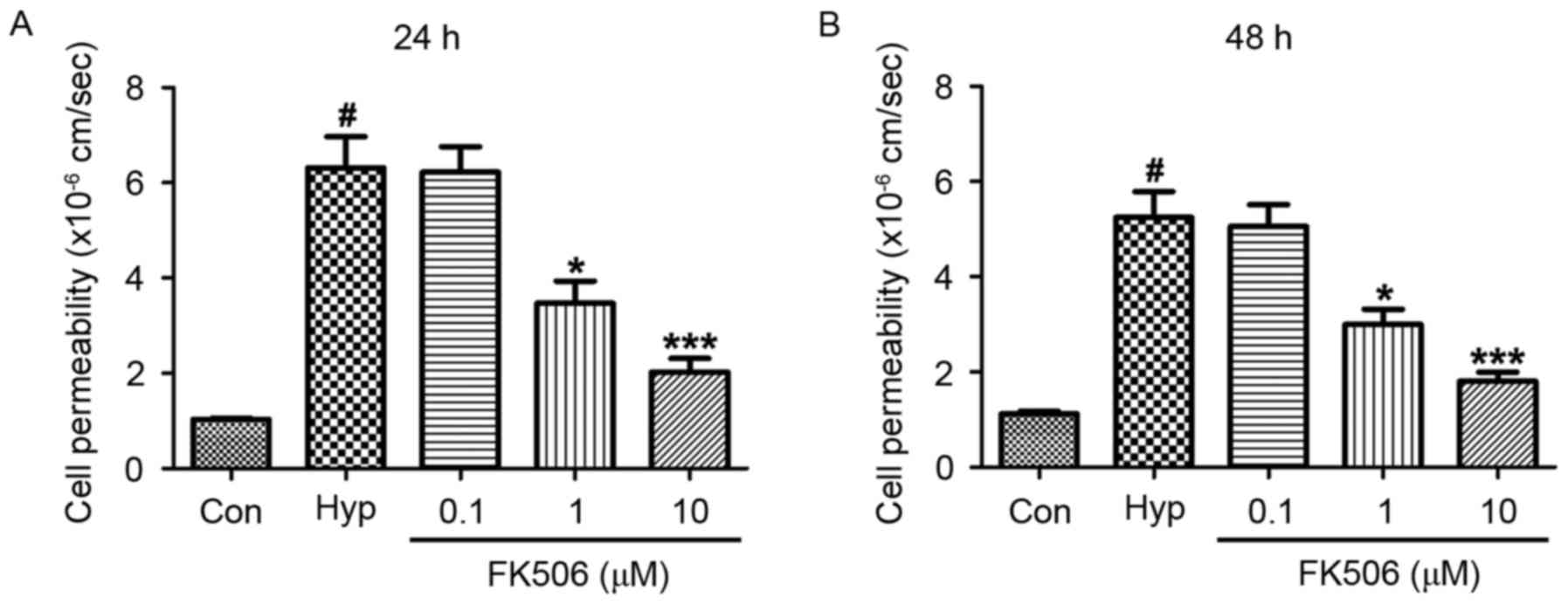
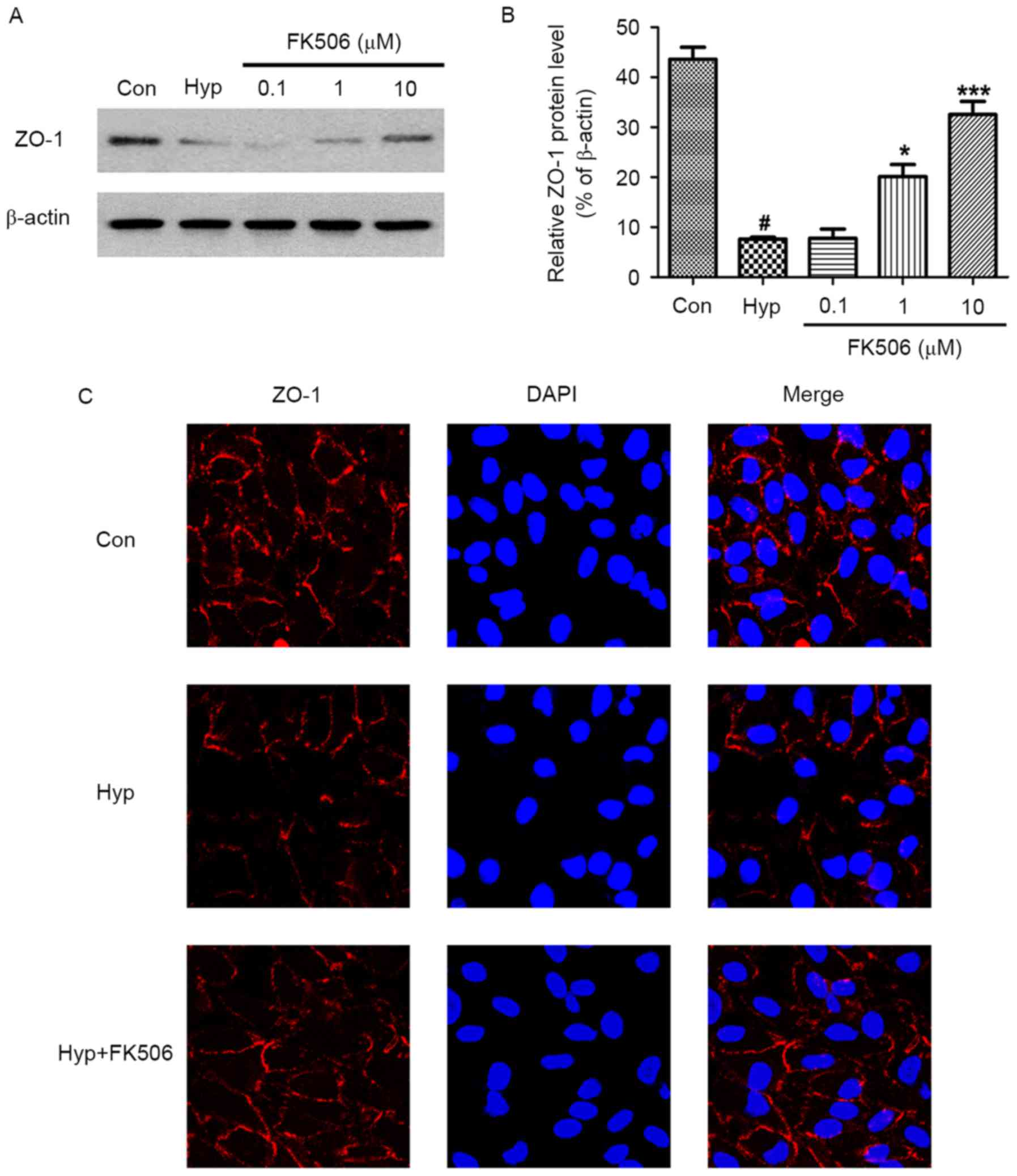
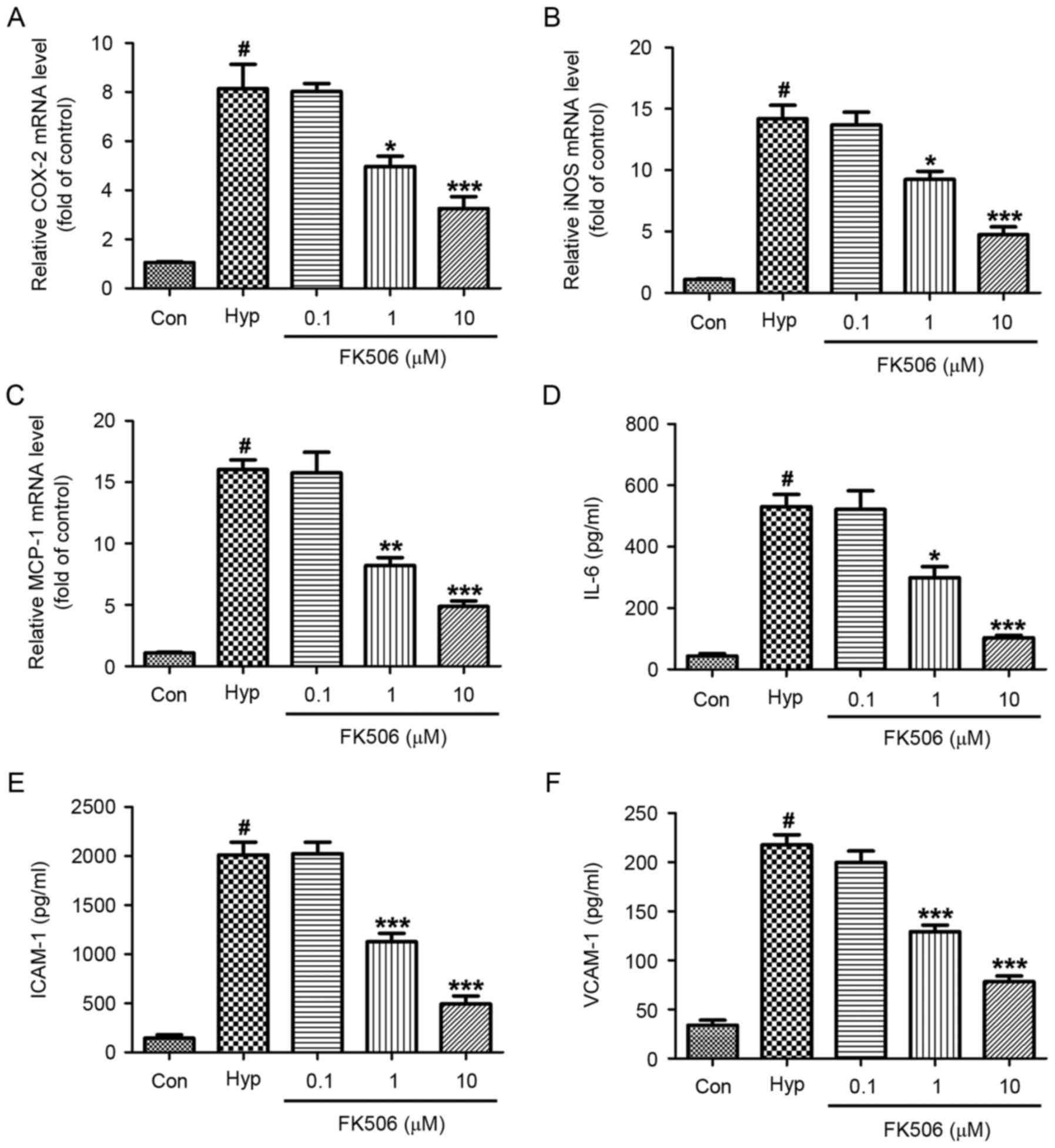
|
1
|
Gliem M, Finger RP, Fimmers R, Brinkmann
CK, Holz FG and Issa P Charbel: Treatment of choroidal
neovascularization due to angioid streaks: A comprehensive review.
Retina. 33:1300–1314. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
van Lookeren Campagne M, LeCouter J,
Yaspan BL and Ye W: Mechanisms of age-related macular degeneration
and therapeutic opportunities. J Pathol. 232:151–164. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mintz-Hittner HA, Kennedy KA and Chuang
AZ: BEAT-ROP Cooperative Group: Efficacy of intravitreal
bevacizumab for stage 3+ retinopathy of prematurity. N Engl J Med.
364:603–615. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kollias AN and Ulbig MW: Diabetic
retinopathy: Early diagnosis and effective treatment. Dtsch Arztebl
Int. 107:75–83. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Todo S, Fung JJ, Starzl TE, Tzakis A,
Demetris AJ, Kormos R, Jain A, Alessiani M, Takaya S and Shapiro R:
Liver, kidney and thoracic organ transplantation under FK 506. Ann
Surg. 212:295–307. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Baumgart DC, Pintoffl JP, Sturm A,
Wiedenmann B and Dignass AU: Tacrolimus is safe and effective in
patients with severe steroid-refractory or steroid-dependent
inflammatory bowel disease-a long-term follow-up. Am J
Gastroenterol. 101:1048–1056. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Thestrup-Pedersen K: Tacrolimus treatment
of atopic eczema/dermatitis syndrome. Curr Opin Allergy Clin
Immunol. 3:359–362. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Weiwad M, Edlich F, Kilka S, Erdmann F,
Jarczowski F, Dorn M, Moutty MC and Fischer G: Comparative analysis
of calcineurin inhibition by complexes of immunosuppressive drugs
with human FK506 binding proteins. Biochemistry. 45:15776–15784.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Haydon GH and Hayes PC: New
immunosuppressive treatment in transplantation medicine. Baillieres
Clin Gastroenterol. 8:455–464. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tsuzuki S, Toyama-Sorimachi N, Kitamura F,
Tobita Y and Miyasaka M: FK506 (tacrolimus) inhibits extravasation
of lymphoid cells by abrogating VLA-4/VCAM-1 mediated
transendothelial migration. FEBS Lett. 430:414–418. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kahan BD: Cyclosporine. N Engl J Med.
321:1725–1738. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jacobson P, Uberti J, Davis W and
Ratanatharathorn V: Tacrolimus: A new agent for the prevention of
graft-versus-host disease in hematopoietic stem cell
transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 22:217–225. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zeyda M, Geyeregger R, Poglitsch M,
Weichhart T, Zlabinger GJ, Koyasu S, Hörl WH, Stulnig TM,
Watschinger B and Saemann MD: Impairment of T cell interactions
with antigen-presenting cells by immunosuppressive drugs reveals
involvement of calcineurin and NF-kappaB in immunological synapse
formation. J Leukoc Biol. 81:319–327. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Du S, Hiramatsu N, Hayakawa K, Kasai A,
Okamura M, Huang T, Yao J, Takeda M, Araki I, Sawada N, et al:
Suppression of NF-kappaB by cyclosporin a and tacrolimus (FK506)
via induction of the C/EBP family: Implication for unfolded protein
response. J Immunol. 182:7201–7211. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yoshino T, Nakase H, Honzawa Y, Matsumura
K, Yamamoto S, Takeda Y, Ueno S, Uza N, Masuda S, Inui K and Chiba
T: Immunosuppressive effects of tacrolimus on macrophages
ameliorate experimental colitis. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 16:2022–2033.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Nakamura-Yanagidaira T, Takahashi Y, Sano
K, Murata T and Hayashi T: Development of spontaneous neuropathy in
NF-κBp50-deficient mice by calcineurin-signal involving impaired
NF-κB activation. Mol Vis. 17:2157–2170. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Xia W, Xia J, Zhang XF, Zhong L, Sun ZT
and Wang YM: Inhibition of FK506 on the expression of vascular
endothelial growth factor in retinal Müller cells cultured by high
concentration glucose. Chin J Exp Ophthalmol. 32:998–1003.
2014.
|
|
19
|
Xiao ZX, Xie YY and Zhen RD: Effect of
FK506 on injured vascular wall. Hainan Med J. 4:1–3. 2009.(In
Chinese).
|
|
20
|
Larkin DF: Longitudinal changes to tight
junction expression and endothelial cell integrity in a mouse model
of sterile corneal inflammation. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
57:34852016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cannon AR, Akhtar S, Hammer AM, Morris NL,
Javorski MJ, Li X, Kennedy RH, Gamelli RL and Choudhry MA: Effects
of mesalamine treatment on gut barrier integrity after burn injury.
J Burn Care Res. 37:283–292. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Rao A, Luo C and Hogan PG: Transcription
factors of the NFAT family: Regulation and function. Annu Rev
Immunol. 15:707–747. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hogan PG, Chen L, Nardone J and Rao A:
Transcriptional regulation by calcium, calcineurin, and NFAT. Genes
Dev. 17:2205–2232. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mancini M and Toker A: NFAT proteins:
Emerging roles in cancer progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 9:810–820.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chang CP, Neilson JR, Bayle JH, Gestwicki
JE, Kuo A, Stankunas K, Graef IA and Crabtree GR: A field of
myocardial-endocardial NFAT signaling underlies heart valve
morphogenesis. Cell. 118:649–663. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Graef IA, Chen F, Chen L, Kuo A and
Crabtree GR: Signals transduced by Ca(2+)/calcineurin and NFATc3/c4
pattern the developing vasculature. Cell. 105:863–875. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bretz CA, Savage S, Capozzi M and Penn JS:
The role of the NFAT signaling pathway in retinal
neovascularization. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 54:7020–7027. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Minami T, Jiang S, Schadler K, Suehiro J,
Osawa T, Oike Y, Miura M, Naito M, Kodama T and Ryeom S: The
calcineurin-NFAT-angiopoietin-2 signaling axis in lung endothelium
is critical for the establishment of lung metastases. Cell Rep.
4:709–723. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|