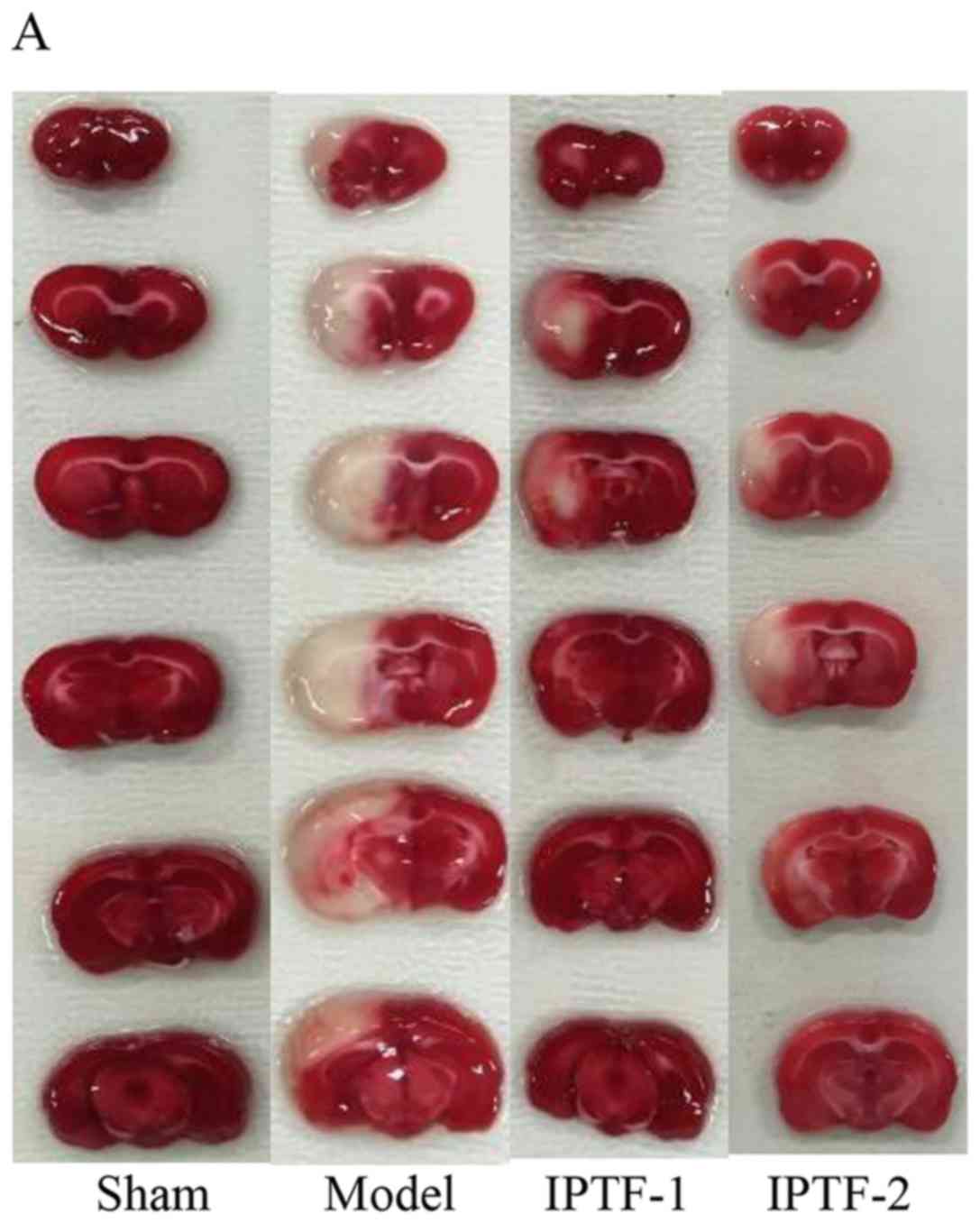
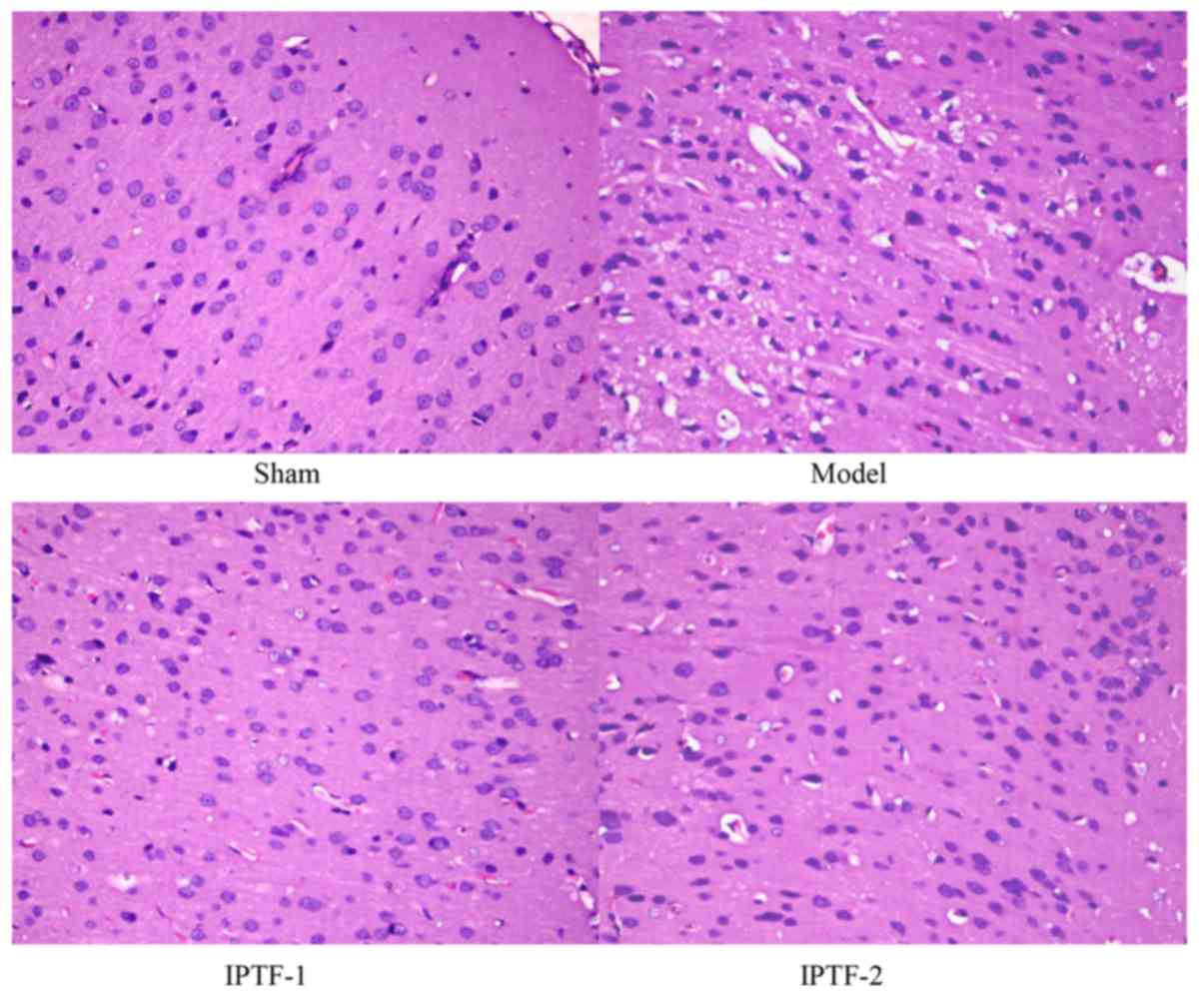
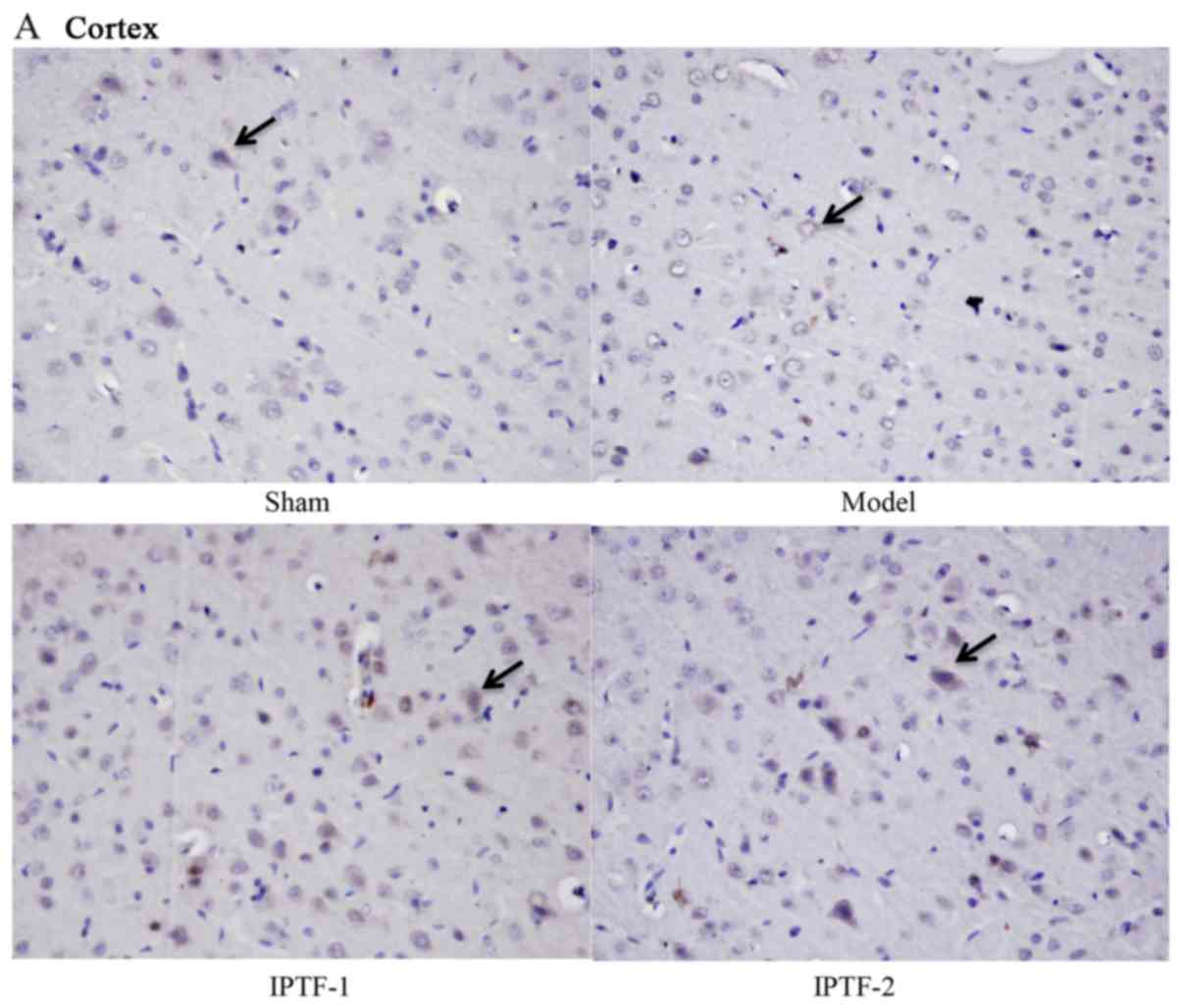
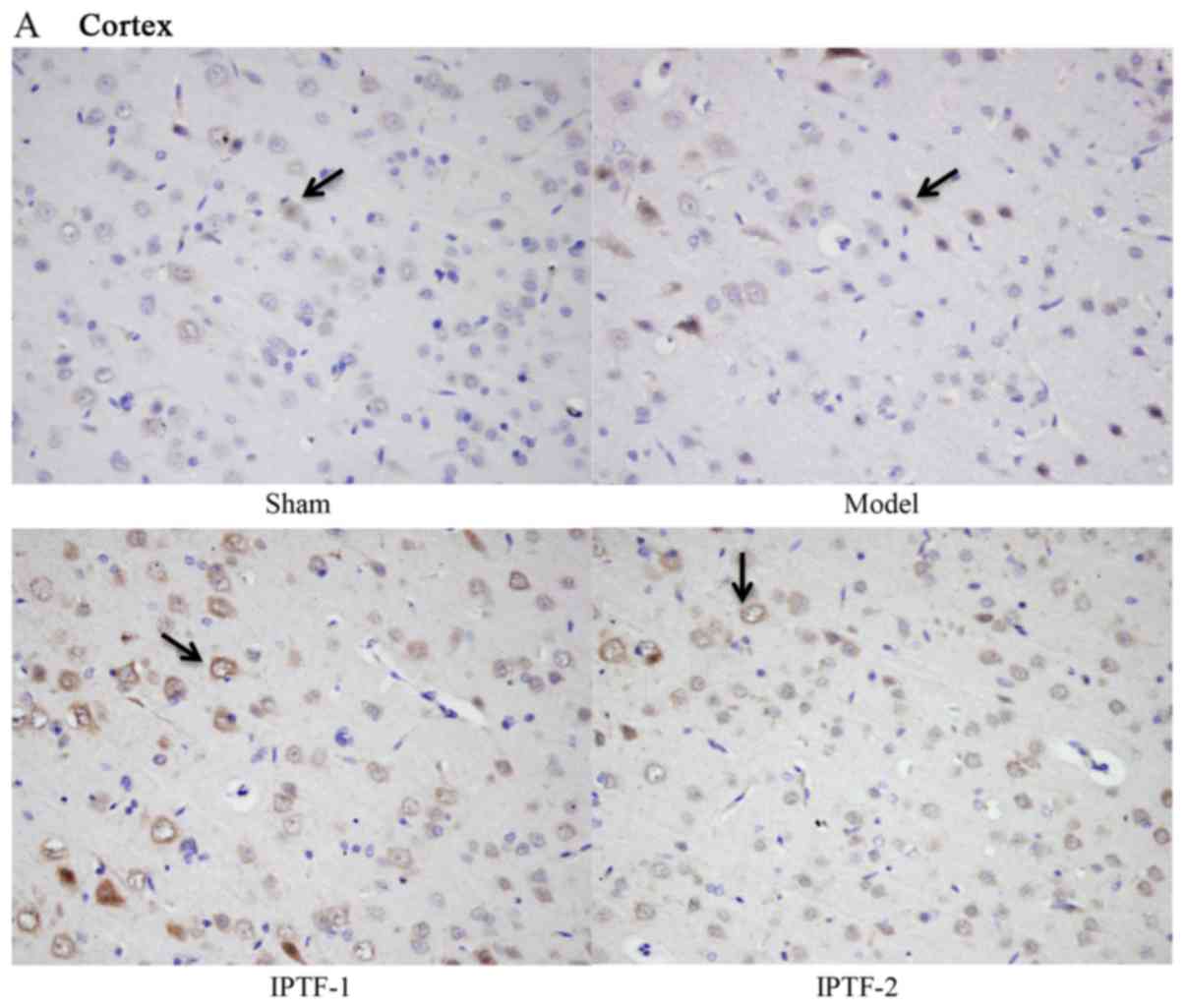
|
1
|
Zhang Y, Zhang S, Li H, Huang M, Xu W, Chu
K, Chen L and Chen X: Ameliorative effects of Gualou Guizhi
decoction on inflammation in focal cerebral ischemic-reperfusion
injury. Mol Med Rep. 12:988–994. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Duong TT, Chami B, McMahon AC, Fong GM,
Dennis JM, Freedman SB and Witting PK: Pre-treatment with the
synthetic antioxidant T-butyl bisphenol protects cerebral tissues
from experimental ischemia reperfusion injury. J Neurochem.
130:733–747. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Liu LP, Xu AD, Wong LK, Wang DZ and Wang
YJ: and Expert consensus group of the evaluation & intervention
of collateral circulation for ischemic stroke: Chinese consensus
statement on the evaluation and intervention of collateral
circulation for ischemic stroke. CNS Neurosci Ther. 20:202–208.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Marmagkiolis K, Hakeem A, Cilingiroglu M,
Gundogdu B, Iliescu C, Tsitlakidou D and Katramados A: Safety and
efficacy of stent retrievers for the management of acute ischemic
stroke: Comprehensive review and meta-analysis. JACC Cardiovasc
Interv. 8:1758–1765. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Asdaghi N and Romano JG: Dual antiplatelet
therapy in acute ischemic stroke. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 17:372015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Niu PP, Guo ZN, Jin H, Xing YQ and Yang Y:
Antiplatelet regimens in the long-term secondary prevention of
transient ischaemic attack and ischaemic stroke: An updated network
meta-analysis. BMJ Open. 6:e0090132016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Brouns R and De Deyn PP: The complexity of
neurobiological processes in acute ischemic stroke. Clin Neurol
Neurosurg. 111:483–495. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hu XM, Zhou MM, Hu XM and Zeng FD:
Neuroprotective effects of scutellarin on rat neuronal damage
induced by cerebral ischemia/reperfusion. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
26:1454–1459. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jung YS, Park JH, Kim H, Kim SY, Hwang JY,
Hong KW, Bae SS, Choi BT, Lee SW and Shin HK: Probucol inhibits
LPS-induced microglia activation and ameliorates brain ischemic
injury in normal and hyperlipidemic mice. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
37:1031–1044. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang F, Li N, Jiang L, Chen L and Huang
M: Neuroprotective effects of (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate
against focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats through
attenuation of inflammation. Neurochem Res. 40:1691–1698. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mattson MP, Maudsley S and Martin B: BDNF
and 5-HT: A dynamic duo in age-related neuronal plasticity and
neurodegenerative disorders. Trends Neurosci. 27:589–594. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang Y, Lan R, Wang J, Li XY, Zhu DN, Ma
YZ, Wu JT and Liu ZH: Acupuncture reduced apoptosis and
up-regulated BDNF and GDNF expression in hippocampus following
hypoxia-ischemia in neonatal rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 172:124–132.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yang J, Guo L, Liu R and Liu H:
Neuroprotective effects of VEGF administration after focal cerebral
ischemia/reperfusion: Dose response and time window. Neurochem Int.
60:592–596. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Miao M, Zhang X and Wang L: Persimmon leaf
flavonoid induces brain ischemic tolerance in mice. Neural Regen
Res. 8:1376–1382. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hsu SC and Chung JG: Anticancer potential
of emodin. BioMedicine. 2:108–116. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Hao JX and Yang CZ: Research progress on
pharmacological action and clinical application of Ilex pubescens.
Heilongjiang Med J. 23:592–593. 2010.(In Chinese).
|
|
17
|
Xiong H, Zhao F, Bi J, Zhang Y, Zhao G,
Chen X, Li Y, Yan R, Zhao Q, Qiao H and Zhang G: Two new compounds
from the roots of Ilex pubescens and their cytotoxic activity. J
Nat Med. 70:673–678. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhonghuabencao SAoTCMotPsRoCECo:
Zhonghuabencao. Shanghai Science and Technology Press; Shanghai:
1997
|
|
19
|
Zhang F, Zhang XL and Miao MS: Effect of
flvonoids of Ilex pubescens on blood stasis with cerebral ischemia.
Chin J Exp Tradit Med Form. 18:187–191. 2012.(In Chinese).
|
|
20
|
Cheng X, Zhang XL and Miao MS: Effect of
total flvonoids from radix Ilecis pubescens on rat cerebral
ischemia models. Tradit Chin Drug Res Pharmacol. 23:640–643.
2012.(In Chinese).
|
|
21
|
Zhang F, Zhang XL and Miao MS: Effect on
total flvonoids of radix Ilicis pubescentis in mice models of
cerebral ischemia. Tradit Chin Drug Res Pharmacol. 23:409–412.
2012.(In Chinese).
|
|
22
|
Feng SX, Miao MS, Miao JX, Xu P, Shao P
and Hou CJ: Simultaneous separation and purification technology of
total flavonoids and total saponins from Ilex pubescens by AB-8
macroporous resin. Chin J Exper Trad Med Form. 1–8. 2012.
|
|
23
|
Xu YH, Miao MS, Xu P and Feng SX:
Determination on content of total flavoniods in the effective
fraction of Ilex pubescens Hook. Chin J Chin Med. 1–827. 2011.
|
|
24
|
Koizumi J, Yoshida Y, Nakazawa T and
Ooneda G: Experimental studies of ischemic brain edema: I. A new
experiment model of cerebral embolism in rats in which
recirculation can be introduced in the ischemic area. Jpn J Stroke.
8:1–8. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Nagasawa H and Kogure K: Correlation
between cerebral blood flow and histologic changes in a new rat
model of middle cerebral artery occlusion. Stroke. 20:1037–1043.
1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S and
Cummins R: Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without
craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 20:84–91. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Belayev L, Alonso OF, Busto R, Zhao W and
Ginsberg MD: Middle cerebral artery occlusion in the rat by
intraluminal suture. Neurological and pathological evaluation of an
improved model. Stroke. 27:1616–1622. 1996.discussion 1623.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yang Y, Shuaib A and Li Q: Quantification
of infarct size on focal cerebral ischemia model of rats using a
simple and economical method. J Neurosci Methods. 84:9–16. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kato H, Liu Y, Araki T and Kogure K:
Temporal profile of the effects of pretreatment with brief cerebral
ischemia on the neuronal damage following secondary ischemic insult
in the gerbil: Cumulative damage and protective effects. Brain Res.
553:238–242. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Rodrigo J, Fernández AP, Serrano J,
Peinado MA and Martínez A: The role of free radicals in cerebral
hypoxia and ischemia. Free Radic Biol Med. 39:26–50. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang JR, Zhou H, Jiang ZH, Wong YF and Liu
L: In vivo anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities of a purified
saponin fraction derived from the root of Ilex pubescens. Biol
Pharm Bull. 31:643–650. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Fujimoto T, Fujimura K and Kuramoto A:
Electrophysiological evidence that glycoprotein IIb-IIIa complex is
involved in calcium channel activation on human platelet plasma
membrane. J Biol Chem. 266:16370–16375. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Xing XD, Zhang Q, Feng F and Liu WY:
Chemical constituents from stems of Ilex pubescens. Zhong Yao Cai.
35:1429–1431. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yang ML and Pang PK: The vascular effects
of Ilex pubescens. Planta Med. 4:262–265. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Muir KW, Tyrrell P, Sattar N and Warburton
E: Inflammation and ischaemic stroke. Current opinion in neurology.
20:334–342. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Han HS and Yenari MA: Cellular targets of
brain inflammation in stroke. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 4:522–529.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hansel G, Tonon AC, Guella FL, Pettenuzzo
LF, Duarte T, Duarte MMMF, Oses JP, Achaval M and Souza DO:
Guanosine protects against cortical focal ischemia. Mol Neurobiol.
52:1791–1803. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhu Y, Chen X, Liu Z, Peng YP and Qiu YH:
Interleukin-10 protection against lipopolysaccharide-induced
neuro-inflammation and neurotoxicity in ventral mesencephalic
cultures. Int J Mol Sci. 17(pii): E252015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Moncada S, Palmer RM and Higgs EA: Nitric
oxide: Physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacol
Rev. 43:109–142. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Hibbs JB Jr, Taintor RR, Vavrin Z and
Rachlin EM: Nitric oxide: A cytotoxic activated macrophage effector
molecule. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 157:87–94. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Förstermann U, Schmidt HH, Pollock JS,
Sheng H, Mitchell JA, Warner TD, Nakane M and Murad F: Isoforms of
nitric oxide synthase. Characterization and purification from
different cell types. Biochem Pharmacol. 42:1849–1857. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Bredt DS and Snyder SH: Isolation of
nitric oxide synthase, a calmodulin requiring enzyme. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 87:682–685. 1990; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Knowles RG, Palacios M, Palmer RM and
Moncada S: Kinetic characteristics of nitric oxide synthase from
rat brain. Biochem J. 269:207–210. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Hashiguchi A, Yano S, Morioka M, Hamada J,
Ushio Y, Takeuchi Y and Fukunaga K: Up-regulation of endothelial
nitric oxide synthase via phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway
contributes to ischemic tolerance in the CA1 subfield of gerbil
hippocampus. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 24:271–279. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Koh PO: Ferulic acid modulates nitric
oxide synthase expression in focal cerebral ischemia. Lab Anim Res.
28:273–278. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Jiang Z, Li C, Arrick DM, Yang S, Baluna
AE and Sun H: Role of nitric oxide synthases in early blood-brain
barrier disruption following transient focal cerebral ischemia.
PLoS One. 9:e931342014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Iadecola C, Zhang F, Casey R, Nagayama M
and Ross ME: Delayed reduction of ischemic brain injury and
neurological deficits in mice lacking the inducible nitric oxide
synthase gene. J Neurosci. 17:9157–9164. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Kitagawa H, Hayashi T, Mitsumoto Y, Koga
N, Itoyama Y and Abe K: Reduction of ischemic brain injury by
topical application of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor
after permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. Stroke.
29:1417–1422. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Sheikh MA, Malik YS, Xing Z, Guo Z, Tian
H, Zhu X and Chen X: Polylysine-modified polyethylenimine (PEI-PLL)
mediated VEGF gene delivery protects dopaminergic neurons in cell
culture and in rat models of Parkinson's Disease (PD). Acta
Biomater. 54:58–68. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Sarkar S, Raymick J and Imam S:
Neuroprotective and therapeutic strategies against parkinson's
disease: Recent perspectives. Int J Mol Sci. 17(pii): E9042016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Echeverria V, Barreto GE, Ávila-Rodriguez
M, Tarasov VV and Aliev G: Is VEGF a key target of cotinine and
other potential therapies against Alzheimer disease? Curr Alzheimer
Res. Mar 29–2017.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Nigam SM, Xu S, Kritikou JS, Marosi K,
Brodin L and Mattson MP: Exercise and BDNF reduce Aβ production by
enhancing α-secretase processing of APP. J Neurochem. 142:286–296.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Wei S: Potential therapeutic action of
natural products from traditional Chinese medicine on Alzheimer's
disease animal models targeting neurotrophic factors. Fundam Clin
Pharmacol. 30:490–501. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Shimamura M, Sato N and Morishita R:
Experimental and clinical application of plasmid DNA in the field
of central nervous diseases. Curr Gene Ther. 11:491–500. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Choi Y, Kang SG and Kam KY: Changes in the
BDNF-immunopositive cell population of neocortical layers I and
II/III after focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Brain Res.
1605:76–82. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Nicole O, Ali C, Docagne F, Plawinski L,
MacKenzie ET, Vivien D and Buisson A: Neuroprotection mediated by
glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor: Involvement of a
reduction of NMDA-induced calcium influx by the mitogen-activated
protein kinase pathway. J Neurosci. 21:3024–3033. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Deng HL and Zhang JT: Anti-lipid
peroxidative effect of ginsenoside Rb1 and Rg1. Chin Med J (Engl).
104:395–398. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Kobayashi T, Ahlenius H, Thored P,
Kobayashi R, Kokaia Z and Lindvall O: Intracerebral infusion of
glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor promotes striatal
neurogenesis after stroke in adult rats. Stroke. 37:2361–2367.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Liu Y, Wang S, Luo S, Li Z, Liang F, Zhu
Y, Pei Z and Huang R: Intravenous PEP-1-GDNF is protective after
focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Neurosci Lett. 617:150–155. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Lin TN, Te J, Lee M, Sun GY and Hsu CY:
Induction of basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) expression
following focal cerebral ischemia. Brain Res Mol Brain Res.
49:255–265. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Raber J, Fan Y, Matsumori Y, Liu Z,
Weinstein PR, Fike JR and Liu J: Irradiation attenuates
neurogenesis and exacerbates ischemia-induced deficits. Ann Neurol.
55:381–389. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Huang Z, Huang PL, Ma J, Meng W, Ayata C,
Fishman MC and Moskowitz MA: Enlarged infarcts in endothelial
nitric oxide synthase knockout mice are attenuated by
nitro-l-arginine. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 16:981–987. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Nagayama M, Aber T, Nagayama T, Ross ME
and Iadecola C: Age-dependent increase in ischemic brain injury in
wild-type mice and in mice lacking the inducible nitric oxide
synthase gene. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 19:661–666. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Zhu DY, Liu SH, Sun HS and Lu YM:
Expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase after focal cerebral
ischemia stimulates neurogenesis in the adult rodent dentate gyrus.
J Neurosci. 23:223–229. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Zhang ZG, Zhang L, Tsang W,
Soltanian-Zadeh H, Morris D, Zhang R, Goussev A, Powers C, Yeich T
and Chopp M: Correlation of VEGF and angiopoietin expression with
disruption of blood-brain barrier and angiogenesis after focal
cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 22:379–392. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Ogunshola OO, Stewart WB, Mihalcik V,
Solli T, Madri JA and Ment LR: Neuronal VEGF expression correlates
with angiogenesis in postnatal developing rat brain. Brain Res Dev
Brain Res. 119:139–153. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Krum JM, Mani N and Rosenstein JM:
Angiogenic and astroglial responses to vascular endothelial growth
factor administration in adult rat brain. Neuroscience.
110:589–604. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Zhang ZG, Zhang L, Jiang Q, Zhang R,
Davies K, Powers C, Bruggen Nv and Chopp M: VEGF enhances
angiogenesis and promotes blood-brain barrier leakage in the
ischemic brain. J Clin Invest. 106:829–838. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Ishii T, Ueyama T, Shigyo M, Kohta M,
Kondoh T, Kuboyama T, Uebi T, Hamada T, Gutmann DH, Aiba A, et al:
A novel Rac1-GSPT1 signaling pathway controls astrogliosis
following central nervous system injury. J Biol Chem.
292:1240–1250. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Sulaiman WA: Transforming growth factor-β
promotes axonal regeneration after chronic nerve injury. Spine
(Phila Pa 1976). 41 Suppl 7:S292016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Lin Q, Wong HL, Tian FR, Huang YD, Xu J,
Yang JJ, Chen PP, Fan ZL, Lu CT and Zhao YZ: Enhanced
neuroprotection with decellularized brain extracellular matrix
containing bFGF after intracerebral transplantation in Parkinson's
disease rat model. Int J Pharm. 517:383–394. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Lei C, Wu B, Cao T, Liu M and Hao Z: Brain
recovery mediated by toll-like receptor 4 in rats after
intracerebral hemorrhage. Brain Res. 1632:1–8. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Furukawa S: Basic research on neurotrophic
factors and its application to medical uses. Yakugaku Zasshi.
135:1213–1226. 2015.(In Japanese). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Stetler RA, Gao Y, Leak RK, Weng Z, Shi Y,
Zhang L, Pu H, Zhang F, Hu X, Hassan S, et al: APE1/Ref-1
facilitates recovery of gray and white matter and neurological
function after mild stroke injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
113:E3558–E3567. 2016; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|