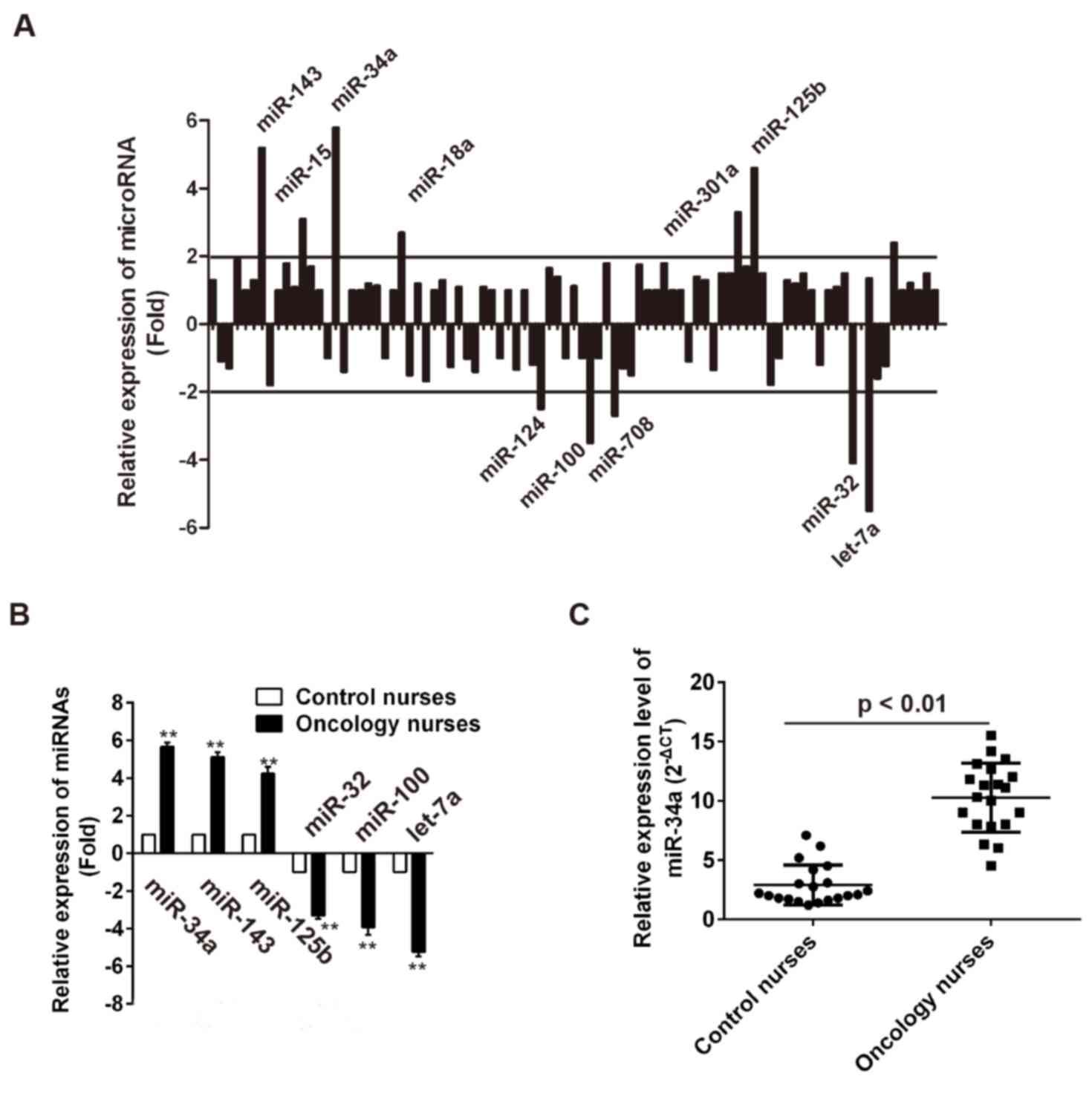
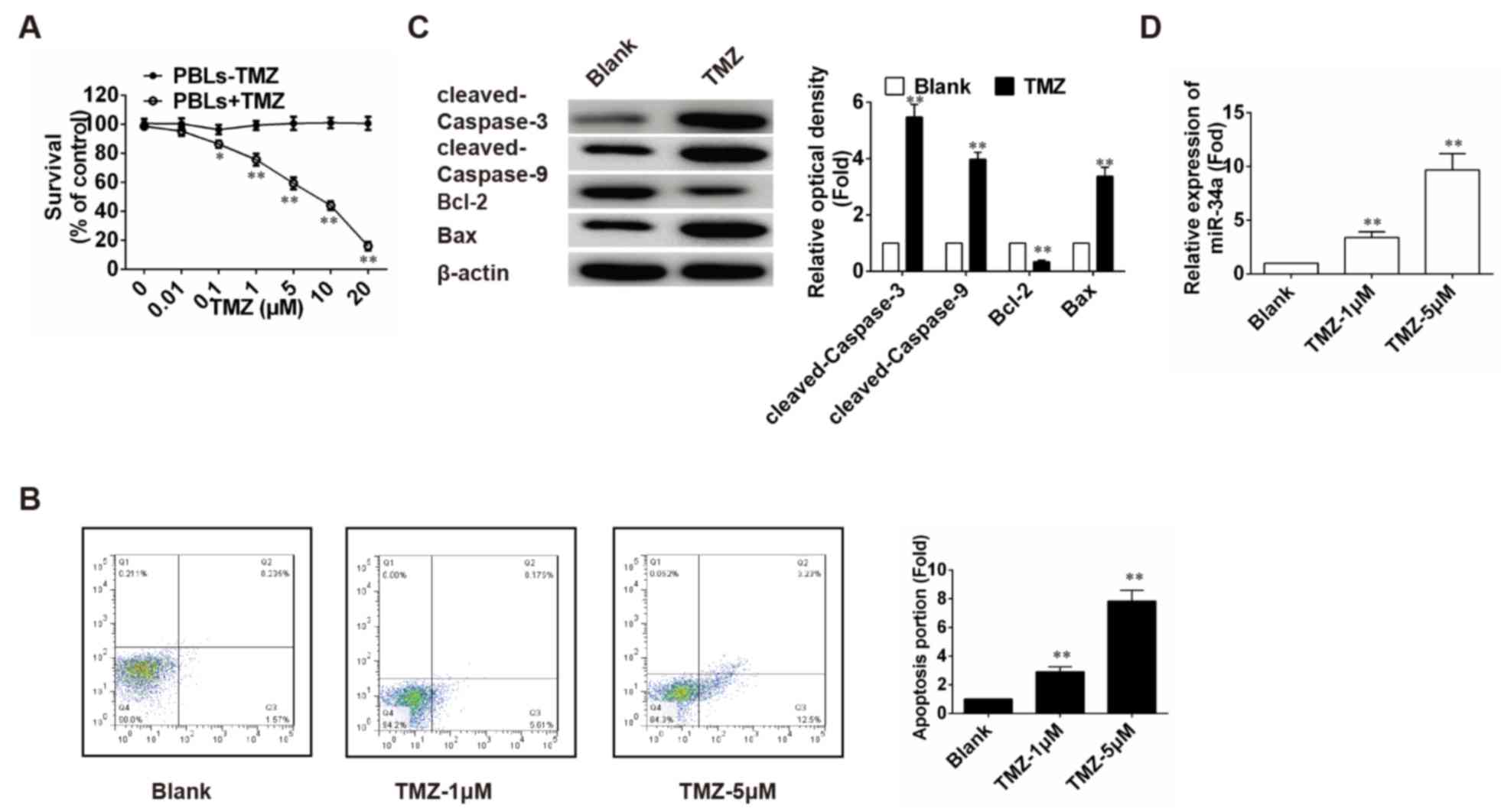
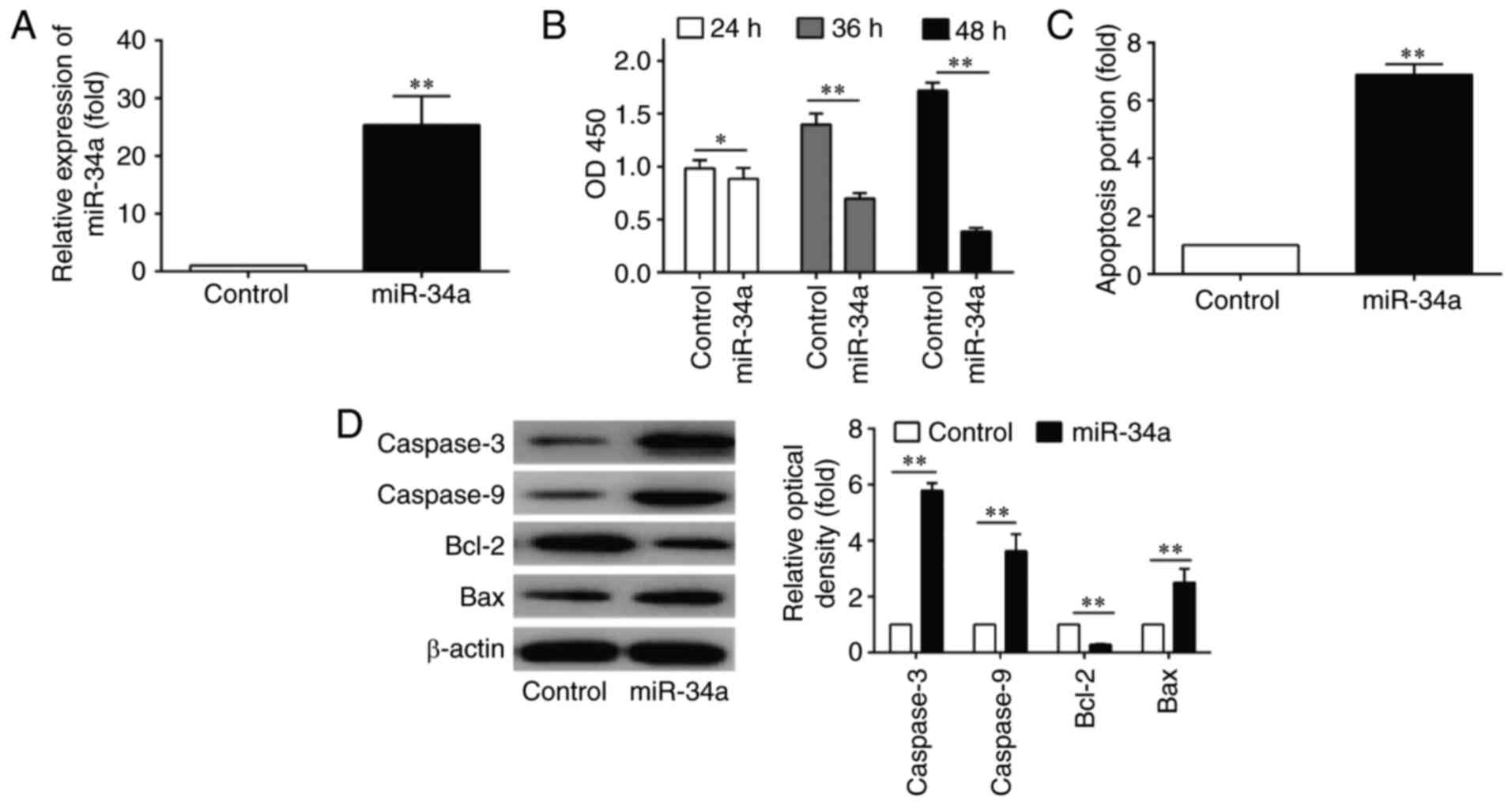
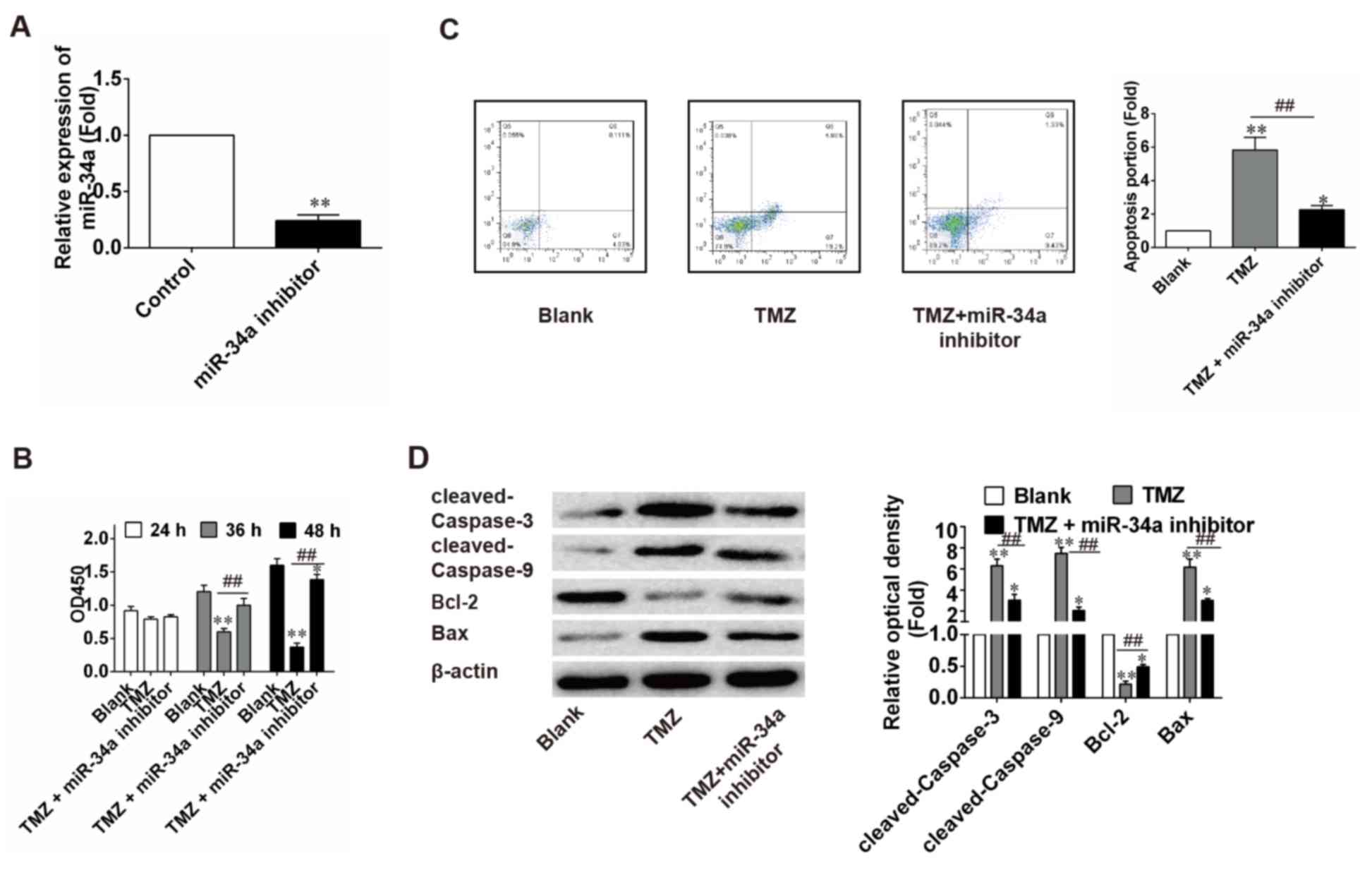
|
1
|
Rekhadevi PV, Sailaja N, Chandrasekhar M,
Mahboob M, Rahman MF and Grover P: Genotoxicity assessment in
oncology nurses handling anti-neoplastic drugs. Mutagenesis.
22:395–401. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cavallo D, Ursini CL, Omodeo-Salé E and
Iavicoli S: Micronucleus induction and FISH analysis in buccal
cells and lymphocytes of nurses administering antineoplastic drugs.
Mutat Res. 628:11–18. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mathias PI, Connor TH and B'Hymer C: A
review of high performance liquid chromatographic-mass
spectrometric urinary methods for anticancer drug exposure of
health care workers. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci.
1060:316–324. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Roland C, Caron N and Bussiéres JF:
Multicenter study of environmental contamination with
cyclophosphamide, ifosfamide, and methotrexate in 66 Canadian
hospitals: A 2016 follow-up study. J Occup Environ Hyg. 14:661–669.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Connor TH and Smith JP: New approaches to
wipe sampling methods for antineoplastic and other hazardous drugs
in healthcare settings. Pharm Technol Hosp Pharm. 1:107–114.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fukushima T, Hamada Y, Yamada H and Horii
I: Changes of micro-RNA expression in rat liver treated by
acetaminophen or carbon tetrachloride-regulating role of micro-RNA
for RNA expression. J Toxicol Sci. 32:401–409. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Huang L, Gao D, Zhang Y, Wang C and Zuo Z:
Exposure to low dose benzo[a]pyrene during early life stages causes
symptoms similar to cardiac hypertrophy in adult zebrafish. J
Hazard Mater. 276:377–382. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Song MK, Lee HS and Ryu JC: Integrated
analysis of microRNA and mRNA expression profiles highlights
aldehyde-induced inflammatory responses in cells relevant for lung
toxicity. Toxicology. 334:111–121. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Song MK, Park YK and Ryu JC: Polycyclic
aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH)-mediated upregulation of hepatic
microRNA-181 family promotes cancer cell migration by targeting
MAPK phosphatase-5, regulating the activation of p38 MAPK. Toxicol
Appl Pharmacol. 273:130–139. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Cavenee
WK, Burger PC, Jouvet A, Scheithauer BW and Kleihues P: The 2007
WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. Acta
Neuropathol. 114:97–109. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Galanis E and Buckner J: Chemotherapy for
high-grade gliomas. Br J Cancer. 82:1371–1380. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller
M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, Belanger K, Brandes AA, Marosi C, Bogdahn
U, et al: Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide
for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 352:987–996. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rathod SS, Rani SB, Khan M, Muzumdar D and
Shiras A: Tumor suppressive miRNA-34a suppresses cell proliferation
and tumor growth of glioma stem cells by targeting Akt and Wnt
signaling pathways. FEBS Open Bio. 4:485–495. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li SZ, Hu YY, Zhao J, Zhao YB, Sun JD,
Yang YF, Ji CC, Liu ZB, Cao WD, Qu Y, et al: MicroRNA-34a induces
apoptosis in the human glioma cell line, A172, through enhanced ROS
production and NOX2 expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
444:6–12. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ward EM, Schulte PA, Straif K, Hopf NB,
Caldwell JC, Carreón T, DeMarini DM, Fowler BA, Goldstein BD,
Hemminki K, et al: Research recommendations for selected
IARC-classified agents. Environ Health Perspect. 118:1355–1362.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Crauste-Manciet S, Sessink PJ, Ferrari S,
Jomier JY and Brossard D: Environmental contamination with
cytotoxic drugs in healthcare using positive air pressure
isolators. Ann Occup Hyg. 49:619–628. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fransman W, Vermeulen R and Kromhout H:
Occupational dermal exposure to cyclophosphamide in Dutch
hospitals: A pilot study. Ann Occup Hyg. 48:237–244.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kopjar N, Garaj-Vrhovac V, Kasuba V,
Rozgaj R, Ramić S, Pavlica V and Zeljezić D: Assessment of
genotoxic risks in Croatian health care workers occupationally
exposed to cytotoxic drugs: A multi-biomarker approach. Int J Hyg
Environ Health. 212:414–431. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chen X, Ba Y, Ma L, Cai X, Yin Y, Wang K,
Guo J, Zhang Y, Chen J, Guo X, et al: Characterization of microRNAs
in serum: A novel class of biomarkers for diagnosis of cancer and
other diseases. Cell Res. 18:997–1006. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Schultz NA, Dehlendorff C, Jensen BV,
Bjerregaard JK, Nielsen KR, Bojesen SE, Calatayud D, Nielsen SE,
Yilmaz M, Holländer NH, et al: MicroRNA biomarkers in whole blood
for detection of pancreatic cancer. JAMA. 311:392–404. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kushwaha D, Ramakrishnan V, Ng K, Steed T,
Nguyen T, Futalan D, Akers JC, Sarkaria J, Jiang T, Chowdhury D, et
al: A genome-wide miRNA screen revealed miR-603 as a
MGMT-regulating miRNA in glioblastomas. Oncotarget. 5:4026–4039.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lan J, Xue Y, Chen H, Zhao S, Wu Z, Fang
J, Han C and Lou M: Hypoxia-induced miR-497 decreases glioma cell
sensitivity to TMZ by inhibiting apoptosis. FEBS Lett.
588:3333–3339. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu Q, Zou R, Zhou R, Gong C, Wang Z, Cai
T, Tan C and Fang J: miR-155 regulates glioma cells invasion and
chemosensitivity by p38 isforms in vitro. J Cell Biochem.
116:1213–1221. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Quintavalle C, Mangani D, Roscigno G,
Romano G, Diaz-Lagares A, Iaboni M, Donnarumma E, Fiore D, De
Marinis P, Soini Y, et al: MiR-221/222 target the DNA
methyltransferase MGMT in glioma cells. PLoS One. 8:e744662013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sun YC, Wang J, Guo CC, Sai K, Wang J,
Chen FR, Yang QY, Chen YS, Wang J, To TS, et al: MiR-181b
sensitizes glioma cells to teniposide by targeting MDM2. BMC
Cancer. 14:6112014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wu H, Liu Q, Cai T, Chen YD, Liao F and
Wang ZF: MiR-136 modulates glioma cell sensitivity to temozolomide
by targeting astrocyte elevated gene-1. Diagn Pathol. 9:1732014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang W, Zhang J, Hoadley K, Kushwaha D,
Ramakrishnan V, Li S, Kang C, You Y, Jiang C, Song SW, et al:
miR-181d: A predictive glioblastoma biomarker that downregulates
MGMT expression. Neuro Oncol. 14:712–719. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Forrest MS, Lan Q, Hubbard AE, Zhang L,
Vermeulen R, Zhao X, Li G, Wu YY, Shen M, Yin S, et al: Discovery
of novel biomarkers by microarray analysis of peripheral blood
mononuclear cell gene expression in benzene-exposed workers.
Environ Health Perspect. 113:801–807. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
McHale CM, Zhang L, Lan Q, Li G, Hubbard
AE, Forrest MS, Vermeulen R, Chen J, Shen M, Rappaport SM, et al:
Changes in the peripheral blood transcriptome associated with
occupational benzene exposure identified by cross-comparison on two
microarray platforms. Genomics. 93:343–349. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|