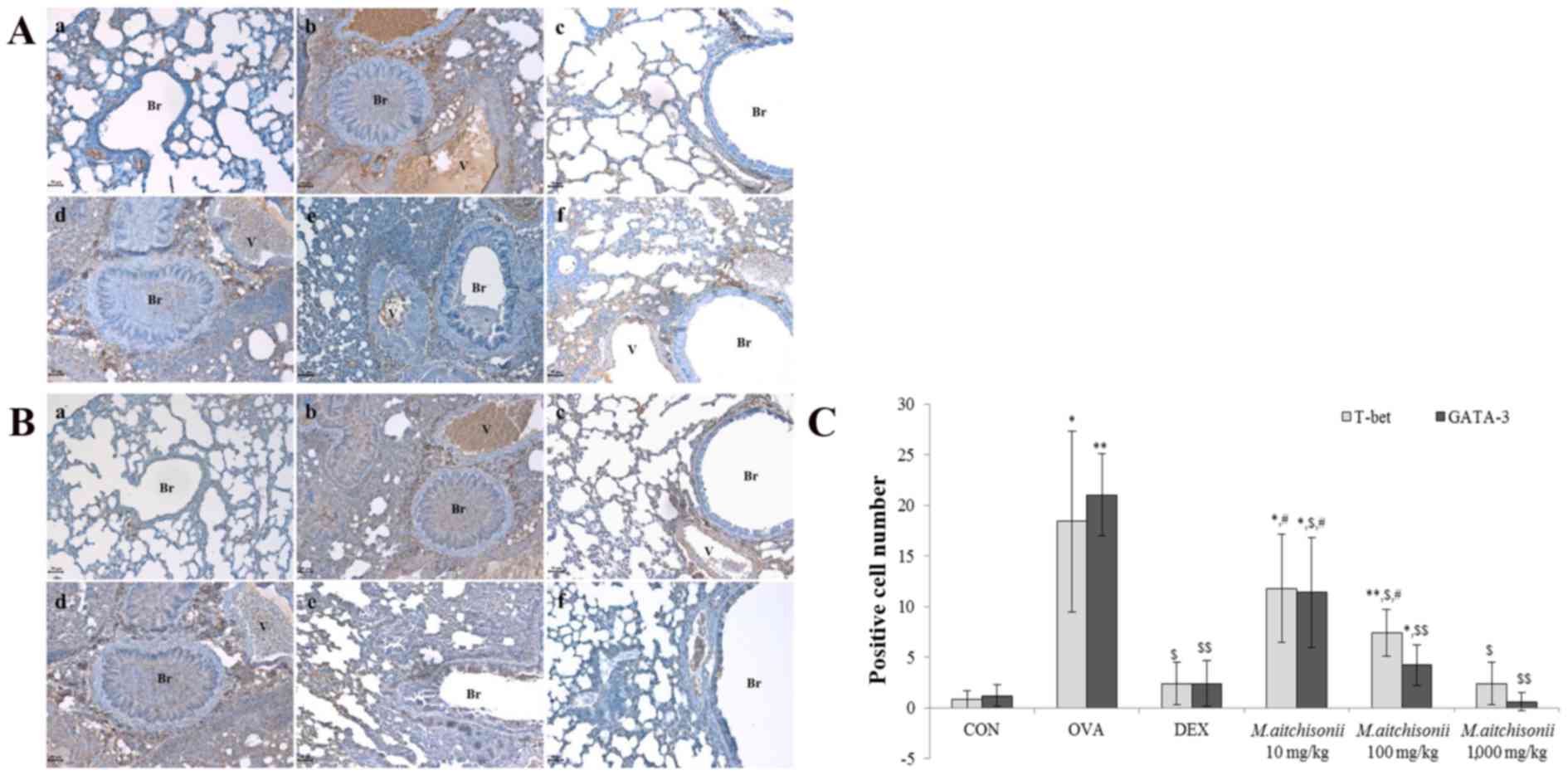
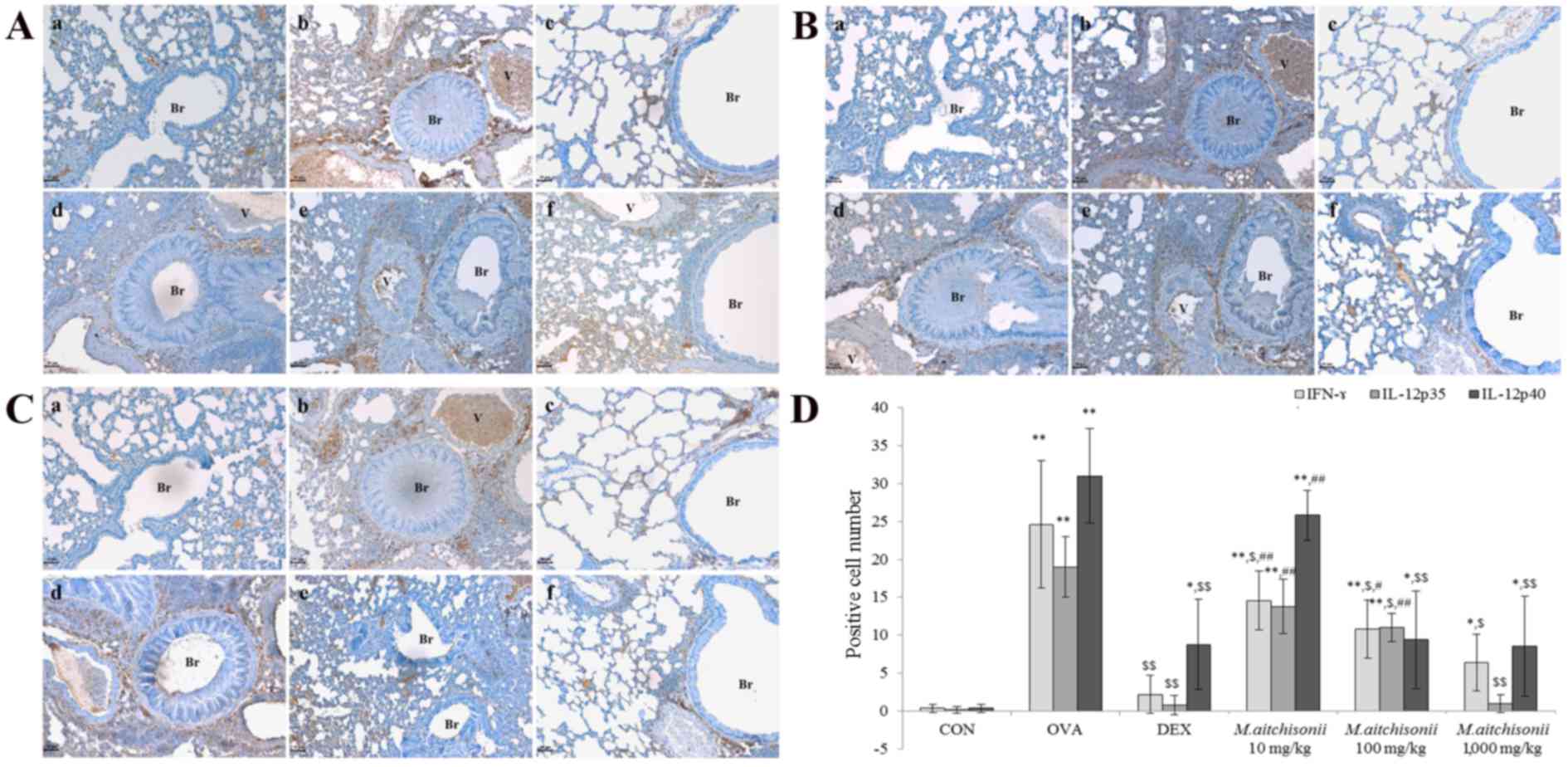
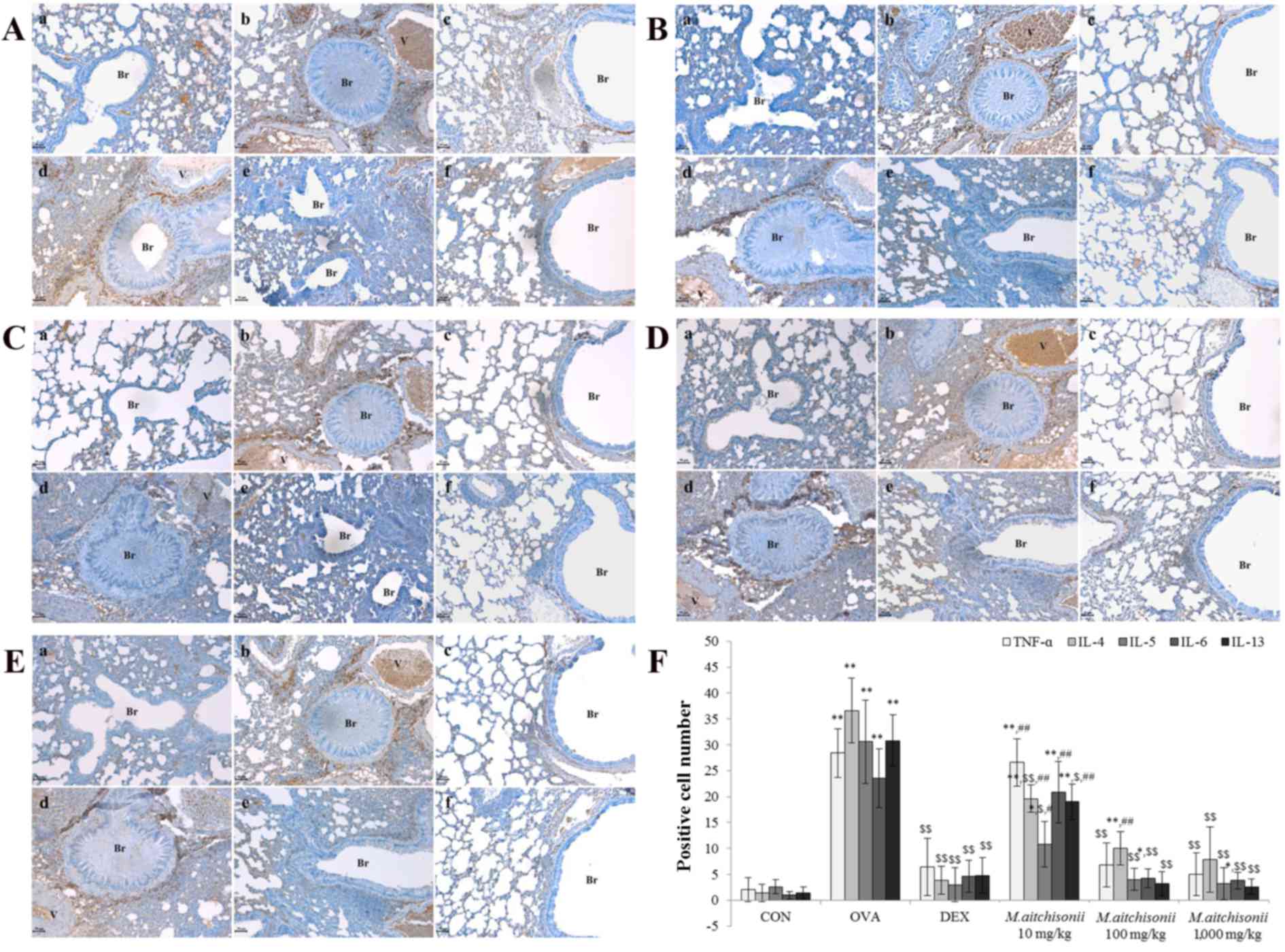
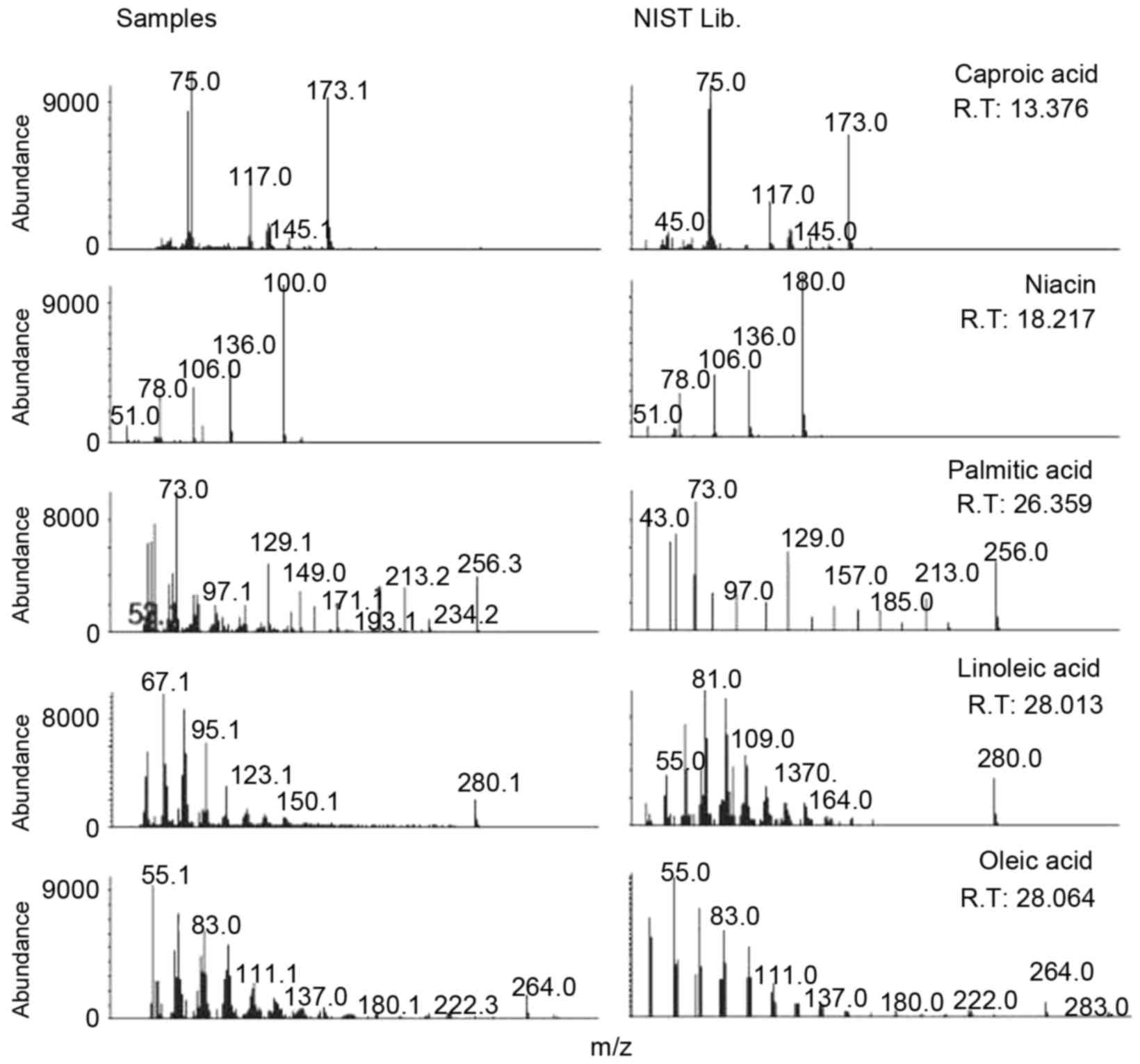
|
1
|
World Health Organization: Asthma Fact
Sheet No 307. November;2013.
|
|
2
|
United States Environmental Protection
Agency (EPA): Asthma Facts EPA-402-F-04-019. March;2013.
|
|
3
|
Kay AB: Allergy and allergic diseases.
First of two parts. N Engl J Med. 344:30–37. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
National Asthma Education and Prevention
Program: National asthma education and prevention program, . Expert
panel report: Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of asthma
update on selected topics-2002. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 110 5
Suppl:S141–S219. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lazarevic V and Glimcher LH: T-bet in
disease. Nature Immunol. 12:597–606. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Zhu J, Jankovic D, Oler AJ, Wei G, Sharma
S, Hu G, Guo L, Yagi R, Yamane H, Punkosdy G, et al: The
transcription factor T-bet is induced by multiple pathways and
prevents an endogenous T helper-2 program during T helper-1
responses. Immunity. 37:660–673. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zedan MM, El-Chennawi FA and Fouda AE:
Interleukin-12 and peripheral blood invariant natural killer T
cells as an axis in childhood asthma pathogenesis. Iran J Allergy
Asthma Immunol. 9:43–48. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Trinchieri G: Interleukin-12: A cytokine
at the interface of inflammation and immunity. Adv Immunol.
70:83–243. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hamza T, Barnett JB and Li B: Interleukin
12 a key immunoregulatory cytokine in infection applications. Int J
Mol Sci. 11:789–806. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yagi R, Zhu J and Paul WE: An updated view
on transcription factor GATA3-mediated regulation of Th1 and Th2
cell differentiation. Int Immunol. 23:415–420. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Uhm TG, Kim BS and Chung IY: Eosinophil
development, regulation of eosinophil-specific genes and role of
eosinophils in the pathogenesis of asthma. Allergy Asthma Immunol
Res. 4:68–79. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Platts-Mills TA: The role of
immunoglobulin E in allergy and asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
164:S1–S5. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kamimura D, Ishihara K and Hirano T: IL-6
signal transduction and its physiological roles: The signal
orchestration model. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 149:1–38. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Neveu WA, Allard JL, Raymond DM, Bourassa
LM, Burns SM, Bunn JY, Irvin CG, Kaminsky DA and Rincon M:
Elevation of IL-6 in the allergic asthmatic airway is independent
of inflammation but associates with loss of central airway
function. Respir Res. 11:282010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Berry M, Brightling C, Pavord I and
Wardlaw A: TNF-alpha in asthma. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 7:279–282.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lukacs NW, Strieter RM, Chensue SW, Widmer
M and Kunkel SL: TNF-alpha mediates recruitment of neutrophils and
eosinophils during airway inflammation. J Immunol. 154:5411–5417.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Scheurich P, Thoma B, Ucer U and
Pfizenmaier K: Immunoregulatory activity of recombinant human tumor
necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha: Induction of TNF receptors on human T
cells and TNF-alpha-mediated enhancement of T cell responses. J
Immunol. 138:1786–1790. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bosnjak B, Stelzmueller B, Erb KJ and
Epstein MM: Treatment of allergic asthma: Modulation of Th2 cells
and their responses. Respir Res. 12:1142011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Barnes PJ: Current issues for establishing
inhaled corticosteroids as the anti-inflammatory agents of choice
in asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 101:S427–S433. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wise J: Corticosteroids for asthma may
suppress growth in children in first year of treatment, researchers
say. BMJ. 349:g46232014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ciriaco M, Ventrice P, Russo G,
Scicchitano M, Mazzitello G, Scicchitano F and Russo E:
Corticosteroid-related central nervous system side effects. J
Pharmacol Pharmacother. 4 Suppl 1:S94–S98. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Seo JW, Cho SC, Park SJ, Lee EJ, Lee JH,
Han SS, Pyo BS, Park DH and Kim BH: 1′-Acetoxychavicol acetate
isolated from Alpinia galangal ameliorates ovalbumin-induced asthma
in mice. PLoS One. 8:e564472013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bang MA, Seo JH, Seo JW, Jo GH, Jung SK,
Yu R, Park DH and Park SJ: Bacillus subtilis KCTC 11782BP-produced
alginate oligosaccharide effectively suppresses asthma via T-helper
cell type 2-related cytokines. PLoS One. 10:e01175242015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chandrasekaran G, Oh DS and Shin HJ:
Versatile applications of the culinary-medicinal mushroom
Mycoeptodonoides aitchisonii (Berk.) Maas G. (Higher
Basidiomycetes): A review. Int J Med Mushrooms. 14:395–401. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Okuyama S, Lam NV, Hatakeyama T, Terashima
T, Yamagata K and Yokogoshi H: Mycoleptodonoides aitchisonii
affects brain nerve growth factor concentration in newborn rats.
Nutr Neurosci. 7:341–349. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lee MR, Begum S, Oh DS, Wee AJ, Yun BS and
Sung CK: Ameliorating effect of Mycoleptodonoides aitchisonii on
high-fat diet-induced obese mice. Prev Nutr Food Sci. 19:69–74.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Choi JH, Suzuki T, Okumura H, Noguchi K,
Kondo M, Nagai K, Hirai H and Kawagishi H: Endoplasmic reticulum
stress suppressive compounds from the edible mushroom
Mycoleptodonoides aitchisonii. J Nat Prod. 77:1729–1733. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Burrows B, Martinez FD, Halonen M, Barbee
RA and Cline MG: Association of asthma with serum IgE levels and
skin-test reactivity to allergens. N Engl J Med. 320:271–277. 1989.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Shamri R, Xenakis JJ and Spencer LA:
Eosinophils in innate immunity: An evolving story. Cell Tissue Res.
343:57–83. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Galioto AM, Hess JA, Nolan TJ, Schad GA,
Lee JJ and Abraham D: Role of eosinophils and neutrophils in innate
and adaptive protective immunity to larval Strongyloides
stercoralis in mice. Infect Immun. 74:5730–5738. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kouro T and Takatsu K: IL-5- and
eosinophil-mediated inflammation: From discovery to therapy. Int
Immunol. 21:1303–1309. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Young B, Lowe JS, Stevens A, et al:
Wheater's functional histology; a text and colour atlas. 5th
edition. Edinburg: Elsevier; 2006, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Holling TM, Schooten E and van Den Elsen
PJ: Function and regulation of MHC class II molecules in
T-lymphocytes: Of mice and men. Human Immunol. 65:282–290. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Kim YK: Th1/Th2 imbalance vs. T cell
priming in asthma. BioWave. 7:SubNo.12005.
|
|
35
|
Airoldi I, Guglielmino R, Carra G,
Corcione A, Gerosa F, Taborelli G, Trinchieri G and Pistoia V: The
interleukin-12 and interleukin-12 receptor system in normal and
transformed human B lymphocytes. Haematologica. 87:434–442.
2002.
|
|
36
|
Singh A, Yamamoto M, Ruan J, Choi JY,
Gauvreau GM, Olek S, Hoffmueller U, Carlsten C, FitzGerald JM,
Boulet LP, et al: Th17/Treg ratio derived using DNA methylation
analysis is associated with the late phase asthmatic response.
Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 10:322014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
37
|
Melton G: Treatment of Asthma by Nicotinic
Acid. Br Med J. 1:600–601. 1943. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
38
|
Carrillo C, Mdel Cavia M and Alonso-Torre
S: Role of oleic acid in immune system; mechanism of action; a
review. Nutr Hosp. 27:978–990. 2012.
|
|
39
|
Wendell SG, Baffi C and Holguin F: Fatty
acids, inflammation, and asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol.
133:1255–1264. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|