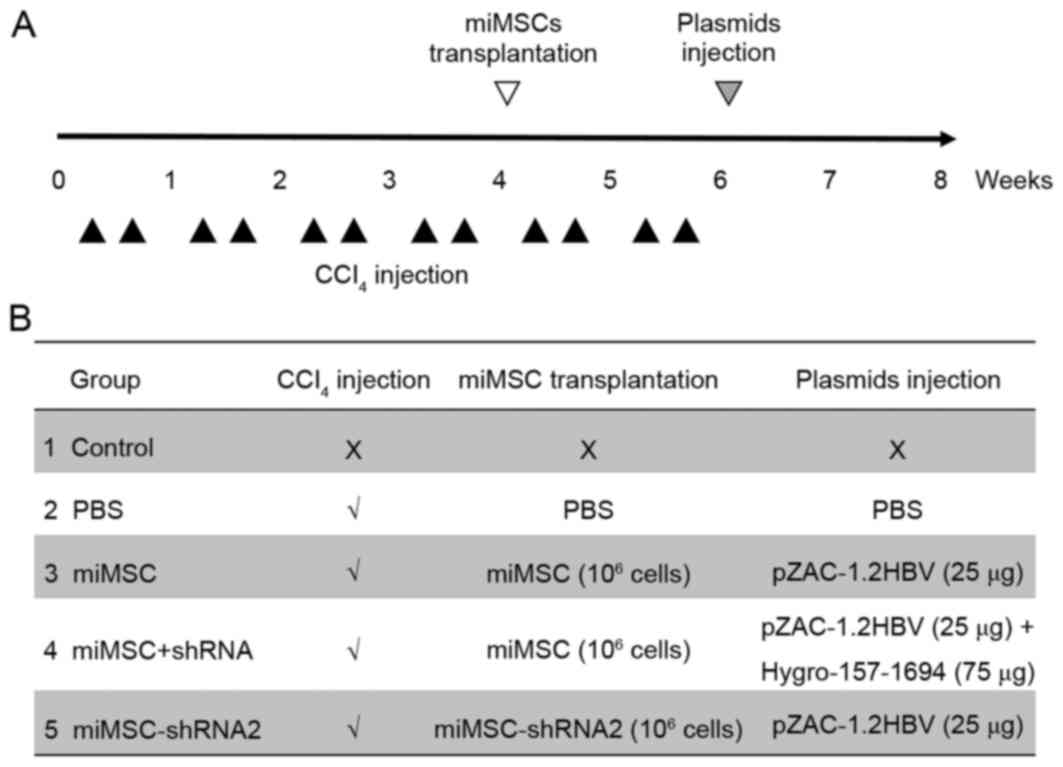
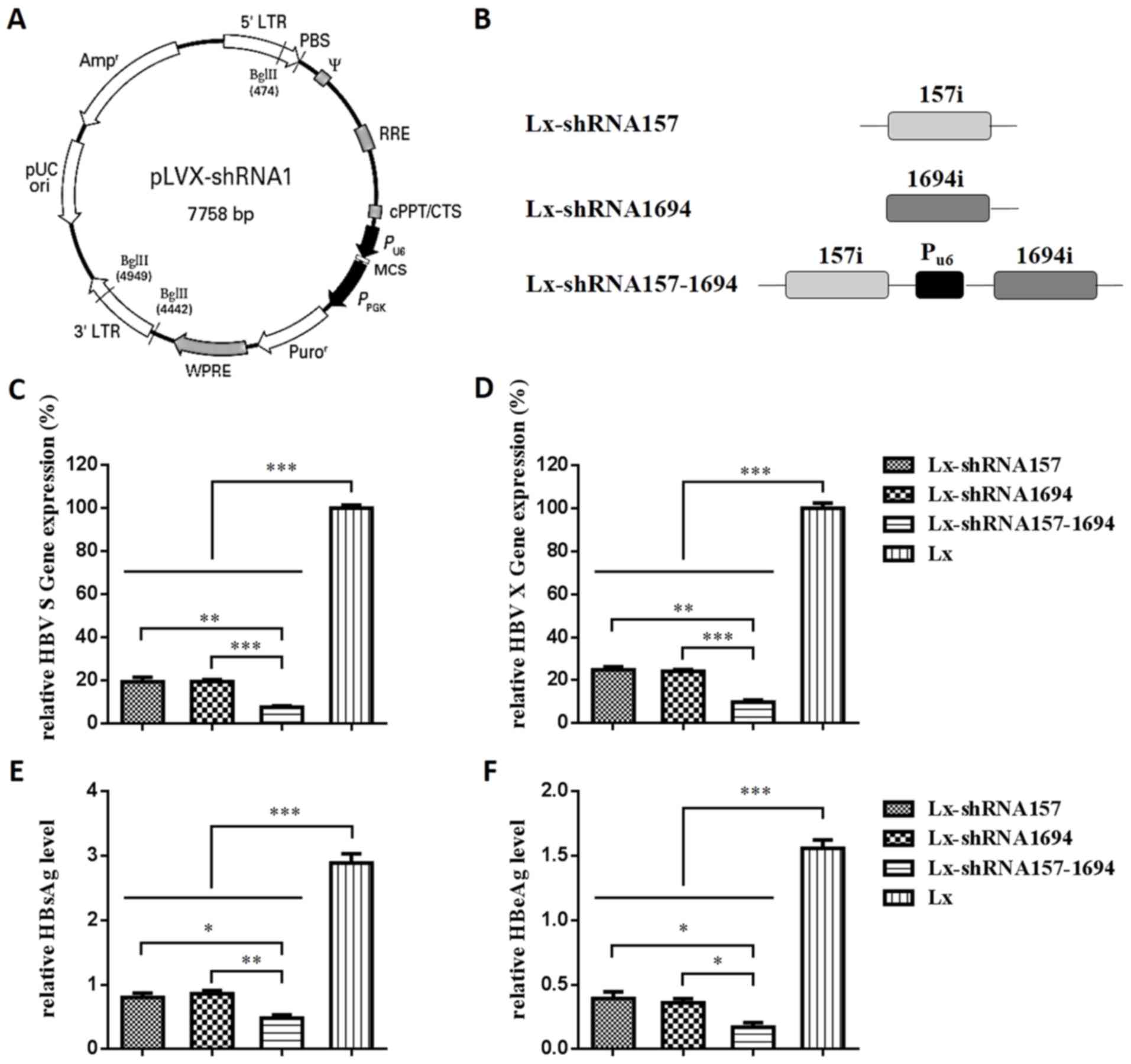
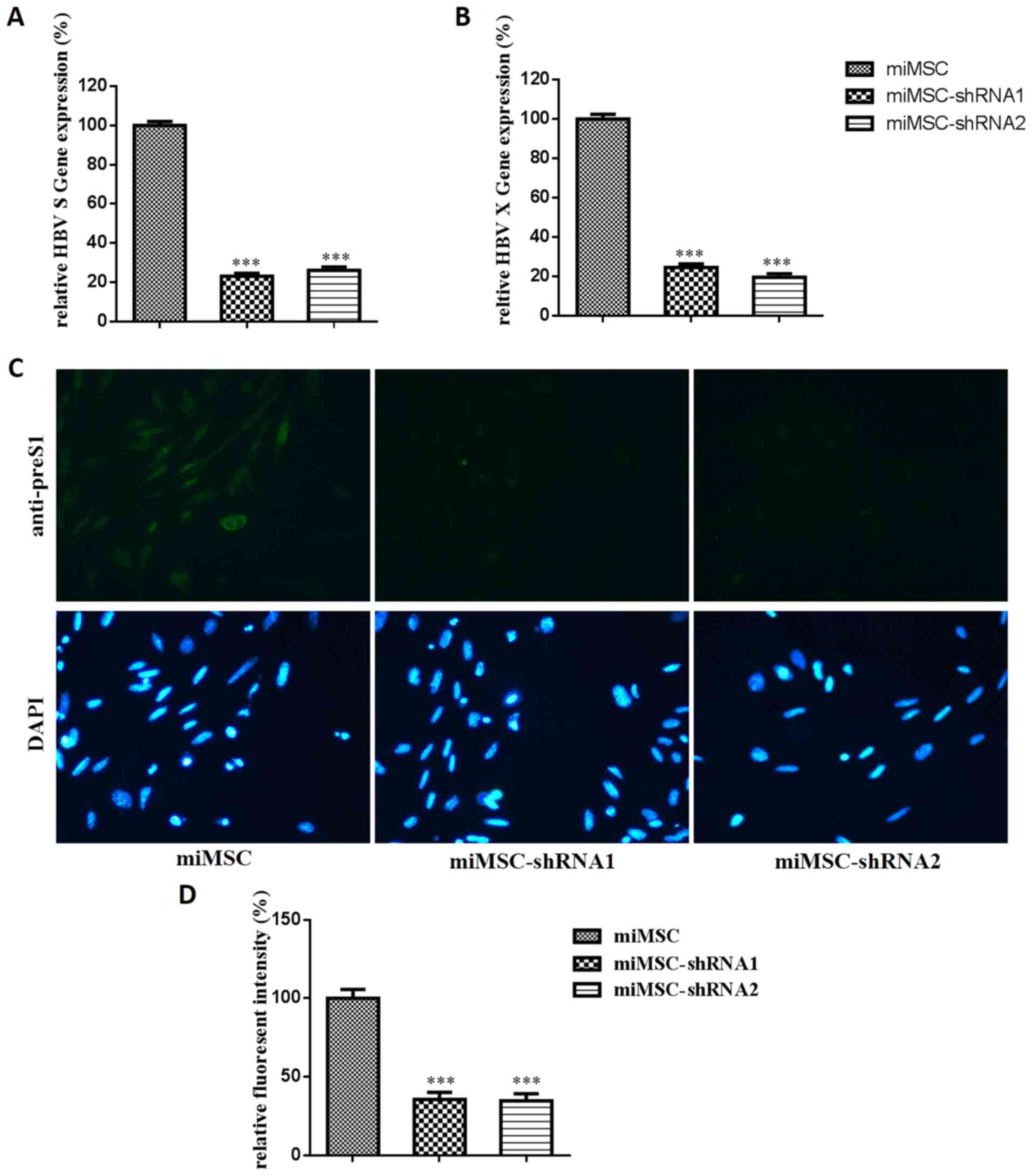
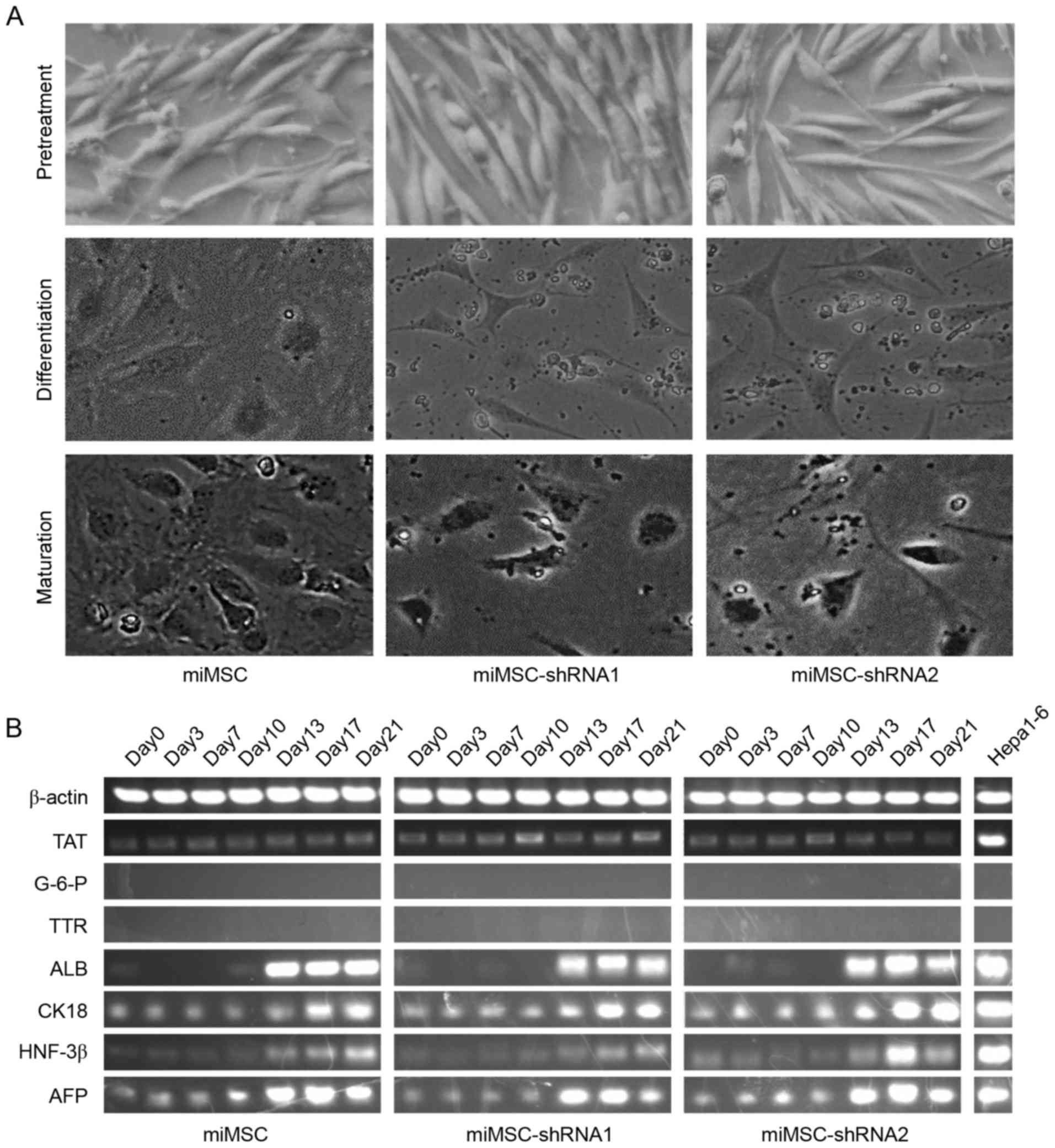
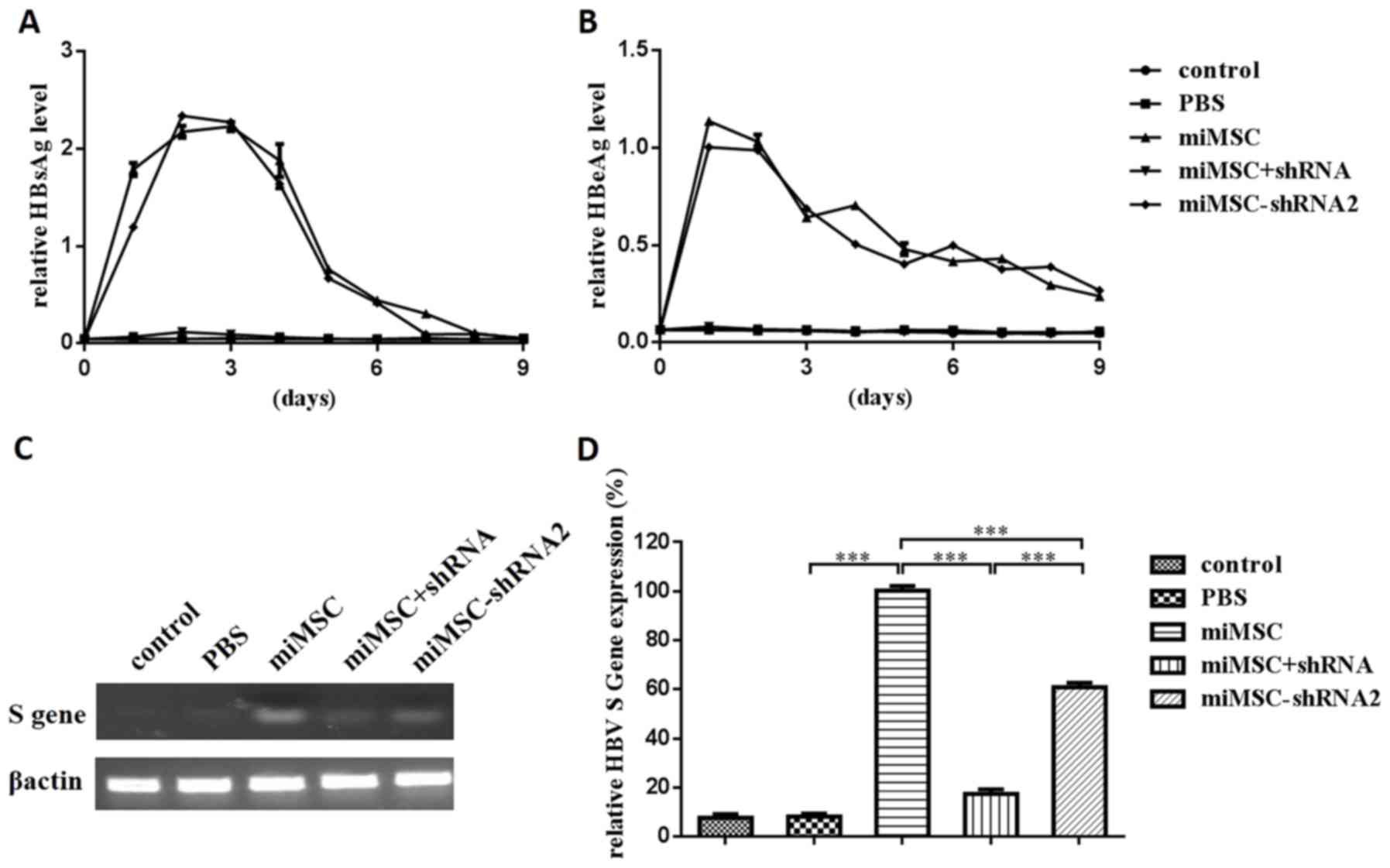
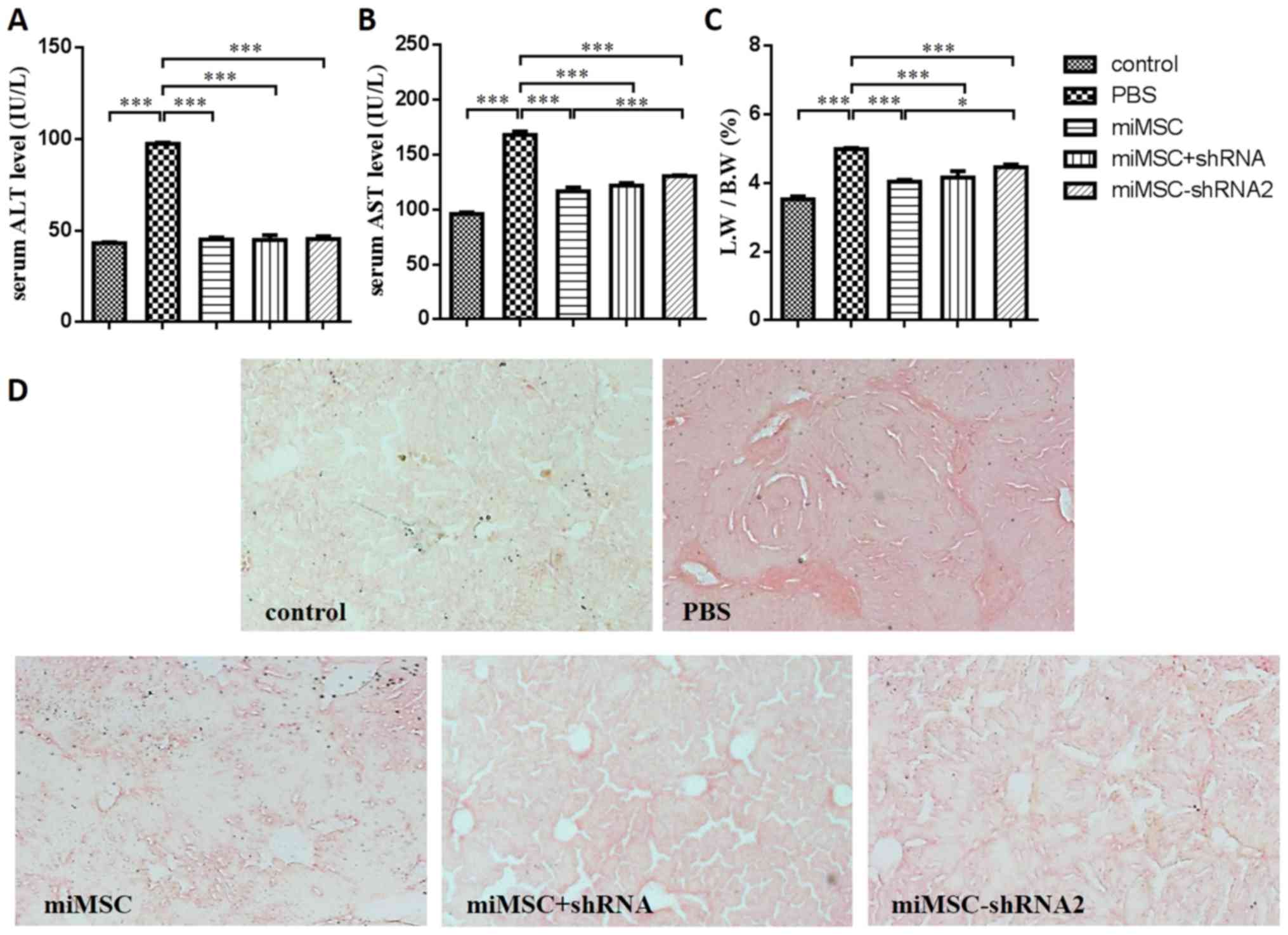
|
1
|
Lin GG, Zhang K and Li JM: Application of
CRISPR/Cas9 Technology to HBV. Int J Mol Sci. 16:26077–26086. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
2
|
Hassan MM, Li D, El-Deeb AS, Wolff RA,
Bondy ML, Davila M and Abbruzzese JL: Association between hepatitis
B virus and pancreatic cancer. J Clin Oncol. 26:4557–4562. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
3
|
Suhail M, Abdel-Hafiz H, Ali A, Fatima K,
Damanhouri GA, Azhar E, Chaudhary AG and Qadri I: Potential
mechanisms of hepatitis B virus induced liver injury. World J
Gastroentero. 20:12462–12472. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Guidotti LG and Chisari FV: Immunobiology
and pathogenesis of viral hepatitis. Annu Rev Pathol. 1:23–61.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Stein LL and Loomba R: Drug targets in
hepatitis B virus infection. Infect Disord Drug Targets. 9:105–116.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Kayaaslan B and Guner R: Adverse effects
of oral antiviral therapy in chronic hepatitis B. World J Hepatol.
9:227–241. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
7
|
Yu HB, Liu EQ, Lu SM and Zhao SH:
Treatment with peginterferon versus interferon in Chinese patients
with hepatitis B. Biomed Pharmacother. 64:559–564. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Nasir GA, Mohsin S, Khan M, Shams S, Ali
G, Khan SN and Riazuddin S: Mesenchymal stem cells and
Interleukin-6 attenuate liver fibrosis in mice. J Transl Med.
11:782013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
9
|
Liu J, Pan G, Liang T and Huang P:
HGF/c-Met signaling mediated mesenchymal stem cell-induced liver
recovery in intestinal ischemia reperfusion model. Int J Med Sci.
11:626–633. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
10
|
Le Blanc K and Ringdén O: Immunobiology of
human mesenchymal stem cells and future use in hematopoietic stem
cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 11:321–334.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Parekkadan B, van Poll D, Megeed Z,
Kobayashi N, Tilles AW, Berthiaume F and Yarmush ML:
Immunomodulation of activated hepatic stellate cells by mesenchymal
stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 363:247–252. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
12
|
Seo KW, Sohn SY, Bhang DH, Nam MJ, Lee HW
and Youn HY: Therapeutic effects of hepatocyte growth
factor-overexpressing human umbilical cord blood-derived
mesenchymal stem cells on liver fibrosis in rats. Cell Biol Int.
38:106–116. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Paddison PJ, Caudy AA, Bernstein E, Hannon
GJ and Conklin DS: Short hairpin RNAs (shRNAs) induce
sequence-specific silencing in mammalian cells. Gene Dev.
16:948–958. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
14
|
Sun DX, Rösler C, Kidd-Ljunggren K and
Nassal M: Quantitative assessment of the antiviral potencies of 21
shRNA vectors targeting conserved, including structured, hepatitis
B virus sites. J Hepatol. 52:817–826. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Beck J and Nassal M: Hepatitis B virus
replication. World J Gastroentero. 13:48–64. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Wooddell CI, Yuen MF, Chan HL, Gish RG,
Locarnini SA, Chavez D, Ferrari C, Given BD, Hamilton J, Kanner SB,
et al: RNAi-based treatment of chronically infected patients and
chimpanzees reveals that integrated hepatitis B virus DNA is a
source of HBsAg. Sci Transl Med. 9:eaan02412017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Marimani M, Hean J, Bloom K, Ely A and
Arbuthnot P: Recent advances in developing nucleic acid-based HBV
therapy. Future Microbiol. 8:1489–1504. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Li Z, He ML, Yao H, Dong QM, Chen YC, Chan
CY, Zheng BJ, Yuen KY, Peng Y, Sun Q, et al: Inhibition of HBV
replication and gene expression in vitro and in vivo with a single
AAV vector delivering two shRNA molecules. BMB Rep. 42:59–64. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Zhao R, Wang TZ, Kong D, Zhang L, Meng HX,
Jiang Y, Wu YQ, Yu ZX and Jin XM: HHepatoma cell line HepG2.2.15
demonstrates distinct biological features compared with parental
HepG2. World J Gastroentero. 17:1152–1159. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Meier RP, Müller YD, Morel P,
Gonelle-Gispert C and Bühler LH: Transplantation of mesenchymal
stem cells for the treatment of liver diseases, is there enough
evidence? Stem Cell Res. 11:1348–1364. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Sarvandi SS, Joghataei MT, Parivar K,
Khosravi M, Sarveazad A and Sanadgol N: In vitro differentiation of
rat mesenchymal stem cells to hepatocyte lineage. Iran J Basic Med
Sci. 18:89–97. 2015.
|
|
23
|
Qu M, Yuan X, Liu D, Ma Y, Zhu J, Cui J,
Yu M, Li C and Guo D: Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells
attenuate immune-mediated liver injury and compromise virus control
during acute hepatitis B virus infection in mice. Stem Cells Dev.
26:818–827. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Saat TC, van den Engel S, Bijman-Lachger
W, Korevaar SS, Hoogduijn MJ, IJzermans JN and de Bruin RW: Fate
and effect of intravenously infused mesenchymal stem cells in a
mouse model of hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury and resection.
Stem Cells Int. 2016:57614872016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
25
|
Xie SR, An JY, Zheng LB, Huo XX, Guo J,
Shih D and Zhang XL: Effects and mechanism of adenovirus-mediated
phosphatase and tension homologue deleted on chromosome ten gene on
collagen deposition in rat liver fibrosis. World J Gastroentero.
23:5904–5912. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Oh IS and Park SH: Immune-mediated liver
injury in hepatitis B virus infection. Immune Netw. 15:191–198.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
27
|
Shi M, Zhang Z, Xu R, Lin H, Fu J, Zou Z,
Zhang A, Shi J, Chen L, Lv S, et al: Human mesenchymal stem cell
transfusion is safe and improves liver function in acute-on-chronic
liver failure patients. Stem Cell Transl Med. 1:725–731. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Pamecha V, Kumar S and Bharathy KG: Liver
transplantation in acute on chronic liver failure: Challenges and
an algorithm for patient selection and management. Hepatol Int.
9:534–542. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Lin BL, Chen JF, Qiu WH, Wang KW, Xie DY,
Chen XY, Liu QL, Peng L, Li JG, Mei YY, et al: Allogeneic bone
marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells for hepatitis B
virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure: A randomized
controlled trial. Hepatology. 66:209–219. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Rabani V, Shahsavani M, Gharavi M, Piryaei
A, Azhdari Z and Baharvand H: Mesenchymal stem cell infusion
therapy in a carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis model
affects matrix metalloproteinase expression. Cell Biol Int.
34:601–605. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Chang YJ, Liu JW, Lin PC, Sun LY, Peng CW,
Luo GH, Chen TM, Lee RP, Lin SZ, Harn HJ and Chiou TW: Mesenchymal
stem cells facilitate recovery from chemically induced liver damage
and decrease liver fibrosis. Life Sci. 85:517–525. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
van Poll D, Parekkadan B, Cho CH,
Berthiaume F, Nahmias Y, Tilles AW and Yarmush ML: Mesenchymal stem
cell-derived molecules directly modulate hepatocellular death and
regeneration in vitro and in vivo. Hepatology. 47:1634–1643. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Terai S, Ishikawa T, Omori K, Aoyama K,
Marumoto Y, Urata Y, Yokoyama Y, Uchida K, Yamasaki T, Fujii Y, et
al: Improved liver function in patients with liver cirrhosis after
autologous bone marrow cell infusion therapy. Stem Cells.
24:2292–2298. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Peng L, Xie DY, Lin BL, Liu J, Zhu HP, Xie
C, Zheng YB and Gao ZL: Autologous bone marrow mesenchymal stem
cell transplantation in liver failure patients caused by hepatitis
B: Short-term and long-term outcomes. Hepatology. 54:820–828. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Buti M, Rodriguez-Frias F, Jardi R and
Esteban R: Hepatitis B virus genome variability and disease
progression: The impact of pre-core mutants and HBV genotypes. J
Clin Virol. 34 Suppl 1:S79–S82. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Tillmann HL: Antiviral therapy and
resistance with hepatitis B virus infection. World J Gastroentero.
13:125–140. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Yan H, Zhong G, Xu G, He W, Jing Z, Gao Z,
Huang Y, Qi Y, Peng B, Wang H, et al: Sodium taurocholate
cotransporting polypeptide is a functional receptor for human
hepatitis B and D virus. Elife. 1:e000492012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
38
|
Schulze A, Schieck A, Ni Y, Mier W and
Urban S: Fine mapping of pre-S sequence requirements for hepatitis
B virus large envelope protein-mediated receptor interaction. J
Virol. 84:1989–2000. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Chen CC, Sun CP, Ma HI, Fang CC, Wu PY,
Xiao X and Tao MH: Comparative study of anti-hepatitis B virus RNA
interference by double-stranded adeno-associated virus serotypes 7,
8, and 9. Mol Ther. 17:352–359. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Yang PL, Althage A, Chung J and Chisari
FV: Hydrodynamic injection of viral DNA: A mouse model of acute
hepatitis B virus infection. P Natl Acad Sci USA. 99:13825–13830.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Higashiyama R, Inagaki Y, Hong YY, Kushida
M, Nakao S, Niioka M, Watanabe T, Okano H, Matsuzaki Y, Shiota G
and Okazaki I: Bone marrow-derived cells express matrix
metalloproteinases and contribute to regression of liver fibrosis
in mice. Hepatology. 45:213–222. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Huang LR, Wu HL, Chen PJ and Chen DS: An
immunocompetent mouse model for the tolerance of human chronic
hepatitis B virus infection. P Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:17862–17867.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|