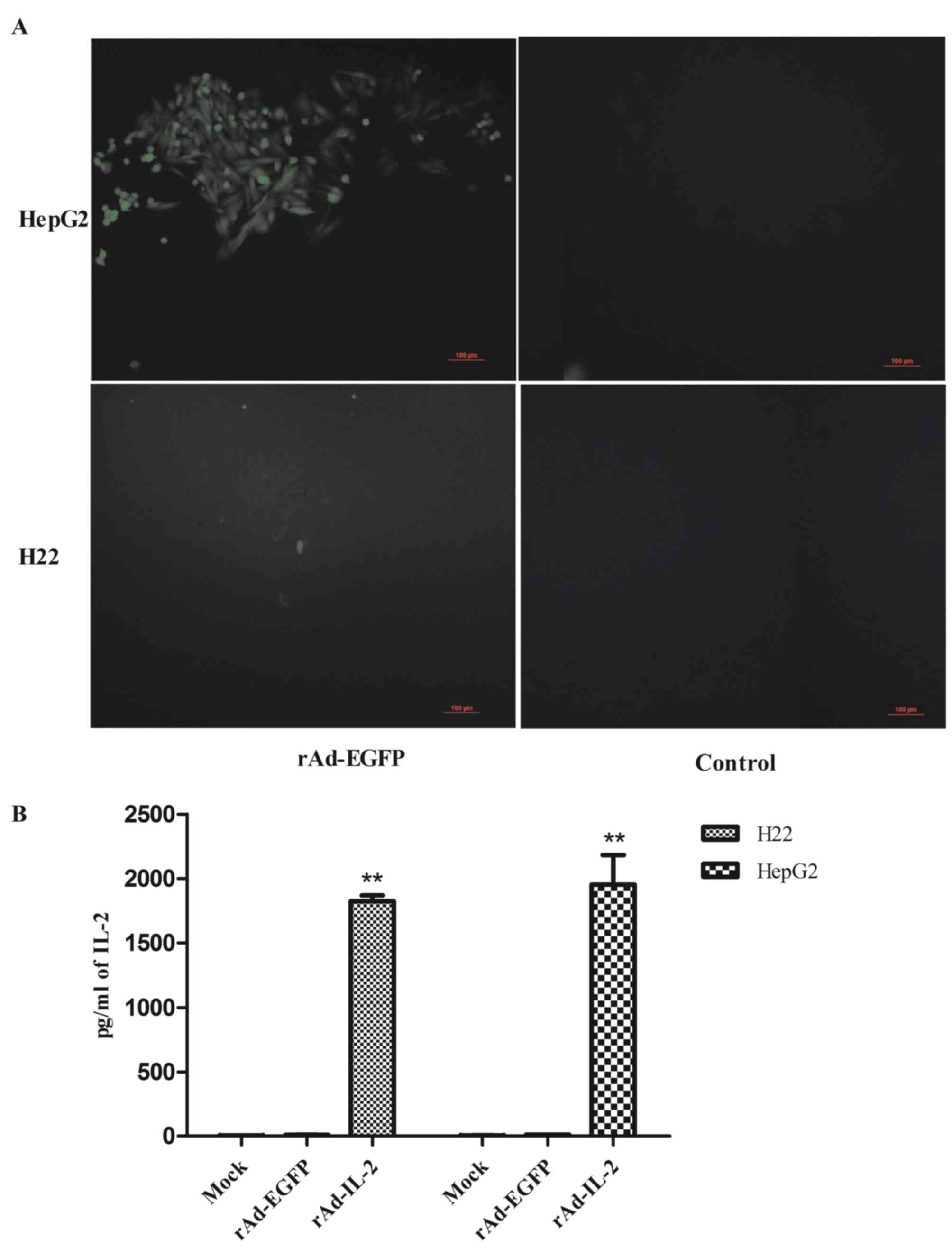
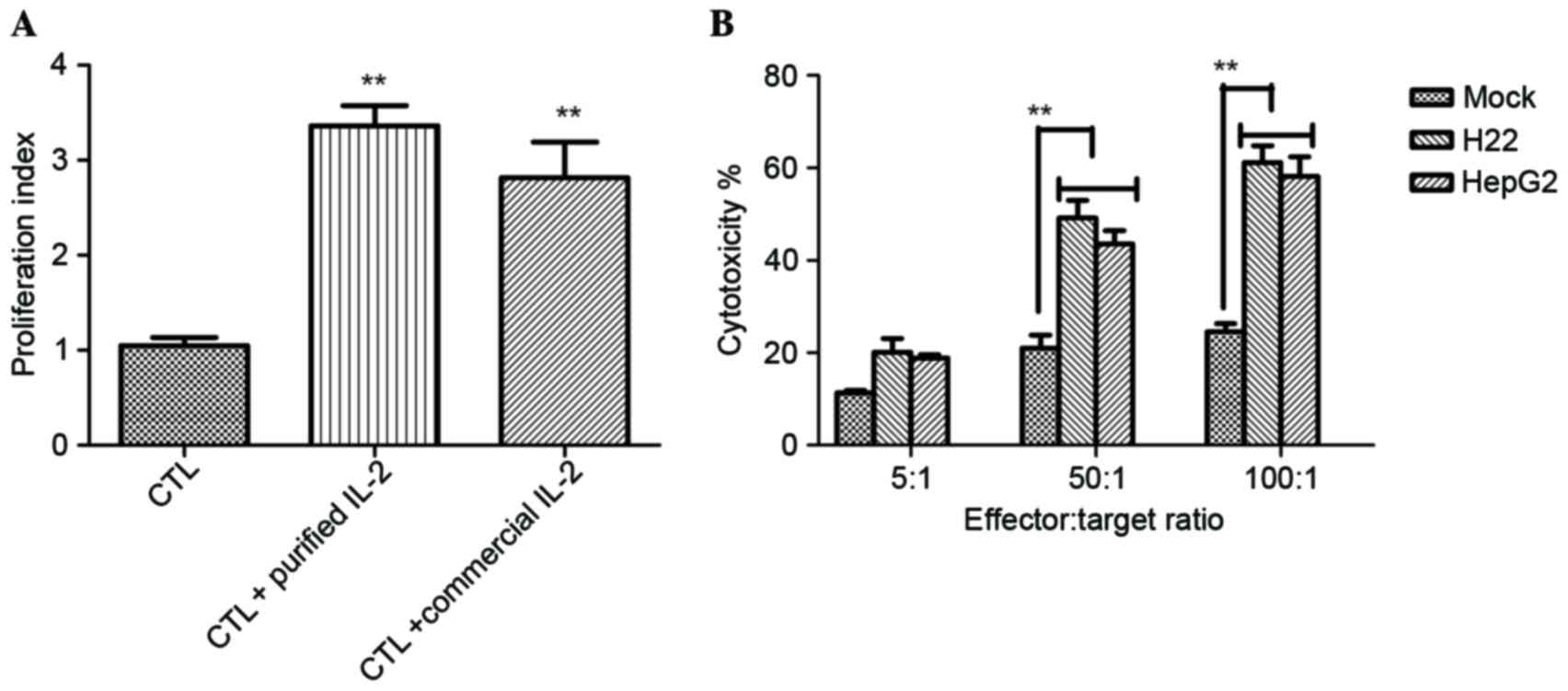
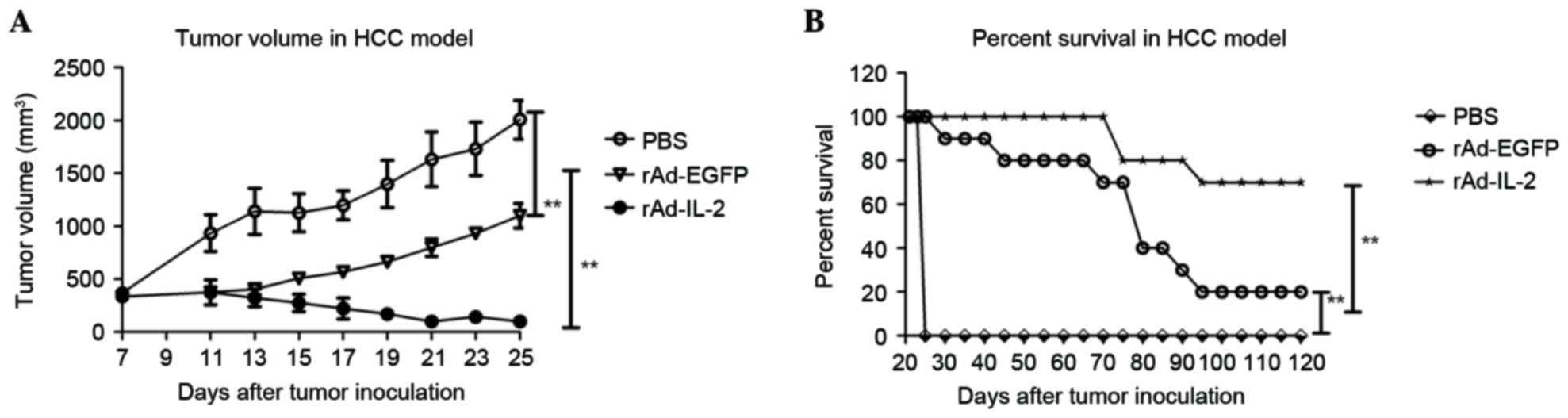
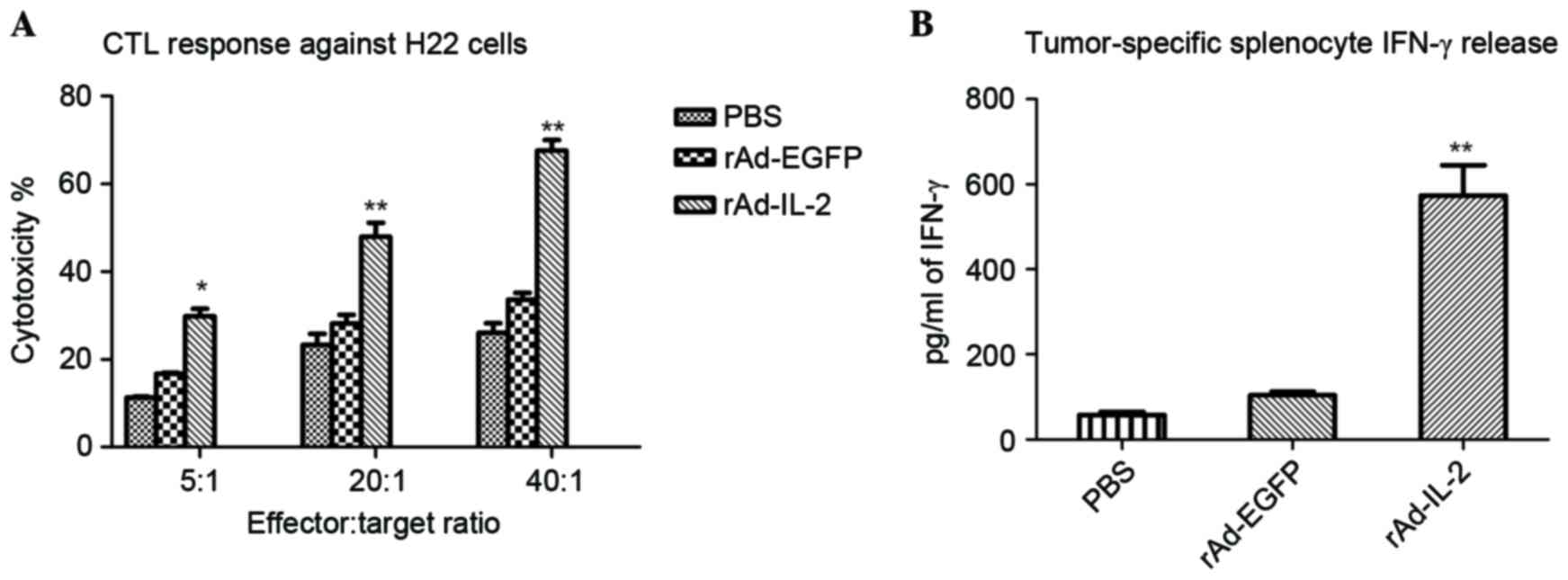
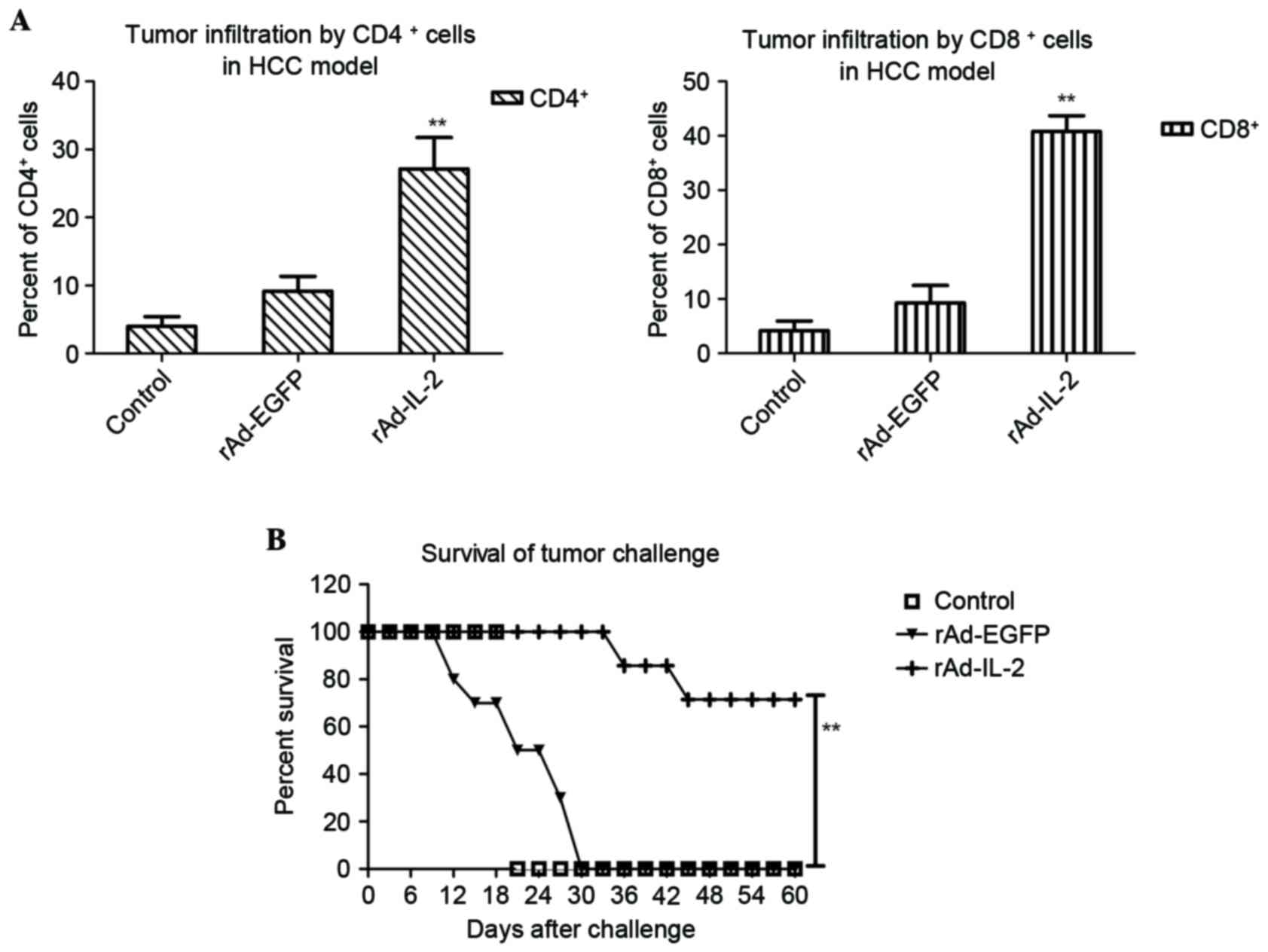
|
1
|
Fung SK and Lok AS: Management of patients
with hepatitis B virus-induced cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 42
Suppl:S54–S64. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Huang YH, Wu JC, Chen SC, Chen CH, Chiang
JH, Huo TI, Lee PC, Chang FY and Lee SD: Survival benefit of
transcatheter arterial chemoembolization in patients with
hepatocellular carcinoma larger than 10 cm in diameter. Aliment
Pharmacol Ther. 23:129–135. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lubienski A, Bitsch RG, Schemmer P,
Grenacher L, Düx M and Kauffmann GW: Long-term results of
interventional treatment of large unresectable hepatocellular
carcinoma (HCC): Significant survival benefit from combined
transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) and percutaneous
ethanol injection (PEI) compared to TACE monotherapy. Rofo.
176:1794–1802. 2004.(In German). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yeh ML, Huang CI, Huang CF, Hsieh MY,
Huang JF, Dai CY, Lin ZY, Chen SC, Yu ML and Chuang WL: Neoadjuvant
transcatheter arterial chemoembolization does not provide survival
benefit compared to curative therapy alone in single hepatocellular
carcinoma. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 31:77–82. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Marabelle A and Gray J: Tumor-targeted and
immune-targeted monoclonal antibodies: Going from passive to active
immunotherapy. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 62:1317–1325. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nishimura Y, Tomita Y, Yuno A, Yoshitake Y
and Shinohara M: Cancer immunotherapy using novel tumor-associated
antigenic peptides identified by genome-wide cDNA microarray
analyses. Cancer Sci. 106:505–511. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hemminki O, Parviainen S, Juhila J, Turkki
R, Linder N, Lundin J, Kankainen M, Ristimäki A, Koski A, Liikanen
I, et al: Immunological data from cancer patients treated with
Ad5/3-E2F-Δ24-GMCSF suggests utility for tumor immunotherapy.
Oncotarget. 6:4467–4481. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Smith SG, Koppolu BP, Ravindranathan S,
Kurtz SL, Yang L, Katz MD and Zaharoff DA: Intravesical
chitosan/interleukin-12 immunotherapy induces tumor-specific
systemic immunity against murine bladder cancer. Cancer Immunol
Immunother. 64:689–696. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bai FL, Tian H, Yu QZ, Renl GP and Li DS:
Expressing foreign genes by Newcastle disease virus for cancer
therapy. Mol Biol (Mosk). 49:195–204. 2015.(In Russian). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Snyder A, Zamarin D and Wolchok JD:
Immunotherapy of Melanoma. Prog Tumor Res. 42:22–29.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bai FL, Yu YH, Tian H, Ren GP, Wang H,
Zhou B, Han XH, Yu QZ and Li DS: Genetically engineered Newcastle
disease virus expressing interleukin-2 and TNF-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand for cancer therapy. Cancer Biol Ther.
15:1226–1238. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shi L, Zhou Q, Wu J, Ji M, Li G, Jiang J
and Wu C: Efficacy of adjuvant immunotherapy with cytokine-induced
killer cells in patients with locally advanced gastric cancer.
Cancer Immunol Immunother. 61:2251–2259. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen Y, Guo ZQ, Shi CM, Zhou ZF, Ye YB and
Chen Q: Efficacy of adjuvant chemotherapy combined with
immunotherapy with cytokine-induced killer cells for gastric cancer
after d2 gastrectomy. Int J Clin Exp Med. 8:7728–7736.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lippitz BE: Cytokine patterns in patients
with cancer: A systematic review. Lancet Oncol. 14:e218–e228. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Guan YS, Liu Y, He Q, Li X, Yang L, Hu Y
and La Z: p53 gene therapy in combination with transcatheter
arterial chemoembolization for HCC: One-year follow-up. World J
Gastroenterol. 17:2143–2149. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Graepler F, Verbeek B, Graeter T, Smirnow
I, Kong HL, Schuppan D, Bauer M, Vonthein R, Gregor M and Lauer UM:
Combined endostatin/sFlt-1 antiangiogenic gene therapy is highly
effective in a rat model of HCC. Hepatology. 41:879–886. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zou W, Luo C, Zhang Z, Liu J, Gu J, Pei Z,
Qian C and Liu X: A novel oncolytic adenovirus targeting to
telomerase activity in tumor cells with potent. Oncogene.
23:457–464. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hernández-Alcoceba R, Sangro B and Prieto
J: Gene therapy of liver cancer. Ann Hepatol. 6:5–14.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yan F, Zheng Y and Huang L:
Adenovirus-mediated combined anti-angiogenic and pro-apoptotic gene
therapy enhances antitumor efficacy in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Oncol Lett. 5:348–354. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Greaves MF and Brown G: Purification of
human T and B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 112:420–423. 1974.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zamarin D, Vigil A, Kelly K, García-Sastre
A and Fong Y: Genetically engineered Newcastle disease virus for
malignant melanoma therapy. Gene Ther. 16:796–804. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sinkovics JG and Horvath JC: Natural and
genetically engineered viral agents for oncolysis and gene therapy
of human cancers. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 56 Suppl 1:3S–59S.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang MM, Yan LN, Li DH, Gou XH, Liu JW,
Su Z, Han L and Zhao LY: Inhibition of adenovirus-mediated gene
transfer of antisense matrix metalloproteinase-2 on hepatocellular
carcinoma growth in vivo. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi.
13:671–674. 2005.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ye Z, Wang X, Hao S, Zhong J, Xiang J and
Yang J: Oncolytic adenovirus-mediated E1A gene therapy induces
tumor-cell apoptosis and reduces tumor angiogenesis leading to
inhibition of hepatocellular carcinoma growth in animal model.
Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 21:225–234. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hu HY, Xue XB, Chen K, Wang CJ, Li Y,
Zheng JW, Yu Y, Ji WW and Wu ZD: Inhibition of hepatocellular
carcinoma growth by adenovirus-mediated mda-7 with adriamycin.
Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 16:461–462. 2008.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
He L, Gong HX, Li XP, Wang YD, Li Y, Huang
JJ, Xie D, Kung HF and Peng Y: Inhibition of hepatocellular
carcinoma growth by adenovirus-mediated expression of human
telomerase reverse transcriptase COOH-27 terminal polypeptide in
mice. Oncol Lett. 6:748–752. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Thomas AA, Ernstoff MS and Fadul CE:
Immunotherapy for the treatment of glioblastoma. Cancer J.
18:59–68. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Larsen CJ: Cellular immunotherapy and
glioblastoma: A hopeful treatment? Bull Cancer. 98:4572011.(In
French). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Varghese S, Rabkin SD, Nielsen GP,
MacGarvey U, Liu R and Martuza RL: Systemic therapy of spontaneous
prostate cancer in transgenic mice with oncolytic herpes simplex
viruses. Cancer Res. 67:9371–9379. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Husain SR, Behari N, Kreitman RJ, Pastan I
and Puri RK: Complete regression of established human glioblastoma
tumor xenograft by interleukin-4 toxin therapy. Cancer Res.
58:3649–3653. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Debinski W, Gibo DM, Obiri NI, Kealiher A
and Puri RK: Novel anti-brain tumor cytotoxins specific for cancer
cells. Nat Biotechnol. 16:449–453. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bera TK, Viner J, Brinkmann E and Pastan
I: Pharmacokinetics and antitumor activity of a bivalent
disulfide-stabilized Fv immunotoxin with improved antigen binding
to erbB2. Cancer Res. 59:4018–4022. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ghetie MA, Richardson J, Tucker T, Jones
D, Uhr JW and Vitetta ES: Antitumor activity of Fab' and
IgG-anti-CD22 immunotoxins in disseminated human B lymphoma grown
in mice with severe combined immunodeficiency disease: Effect on
tumor cells in extranodal sites. Cancer Res. 51:5876–5880.
1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang X, Bayer ME, Chen X, Fredrickson C,
Cornforth AN, Liang G, Cannon J, He J, Fu Q, Liu J, et al: Phase I
trial of active specific immunotherapy with autologous dendritic
cells pulsed with autologous irradiated tumor stem cells in
hepatitis B-positive patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. J Surg
Oncol. 111:862–867. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kusnierczyk H, Pajtasz-Piasecka E, Koten
JW, Bijleveld C, Krawczyk K and Den Otter W: Further development of
local IL-2 therapy of cancer: Multiple versus single IL-2 treatment
of transplanted murine colon carcinoma. Cancer Immunol Immunother.
53:445–452. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Pantuck AJ and Belldegrun AS: Phase I
clinical trial of interleukin 2 (IL-2) gene therapy for prostate
cancer. Curr Urol Rep. 2:332001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Baek S, Kim YM, Kim SB, Kim CS, Kwon SW,
Kim Y, Kim H and Lee H: Therapeutic DC vaccination with IL-2 as a
consolidation therapy for ovarian cancer patients: A phase I/II
trial. Cell Mol Immunol. 12:87–95. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Tan Y, Xu M, Wang W, Zhang F, Li D, Xu X,
Gu J and Hoffman RM: IL-2 gene therapy of advanced lung cancer
patients. Anticancer Res. 16:1993–1998. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Bai F, Niu Z, Tian H, Li S, Lv Z, Zhang T,
Ren G and Li D: Genetically engineered Newcastle disease virus
expressing interleukin 2 is a potential drug candidate for cancer
immunotherapy. Immunol Lett. 159:36–46. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|