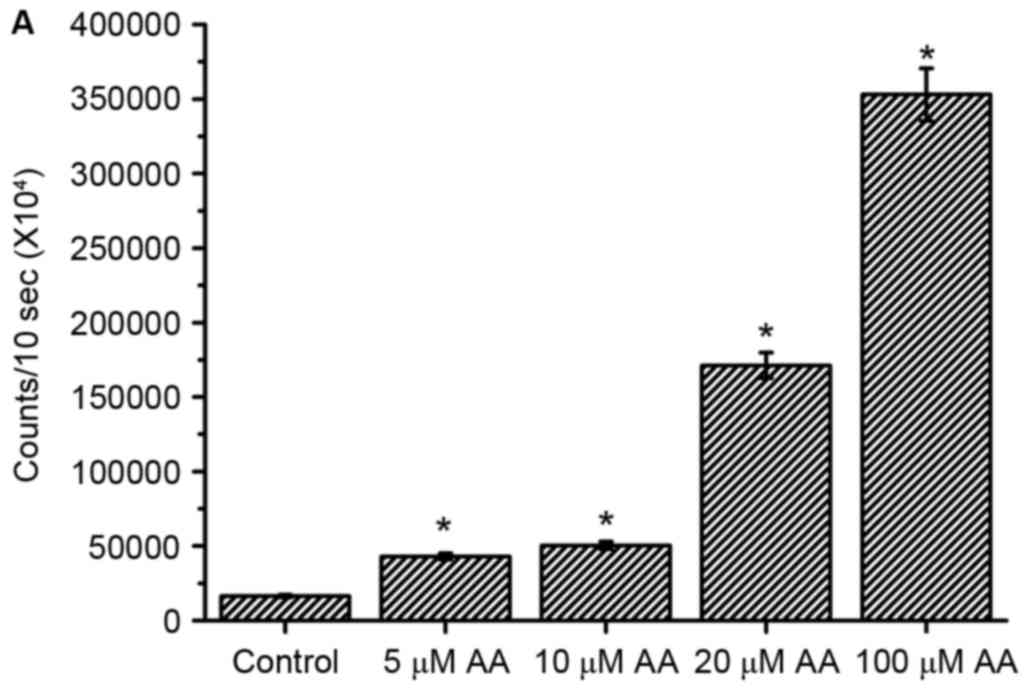
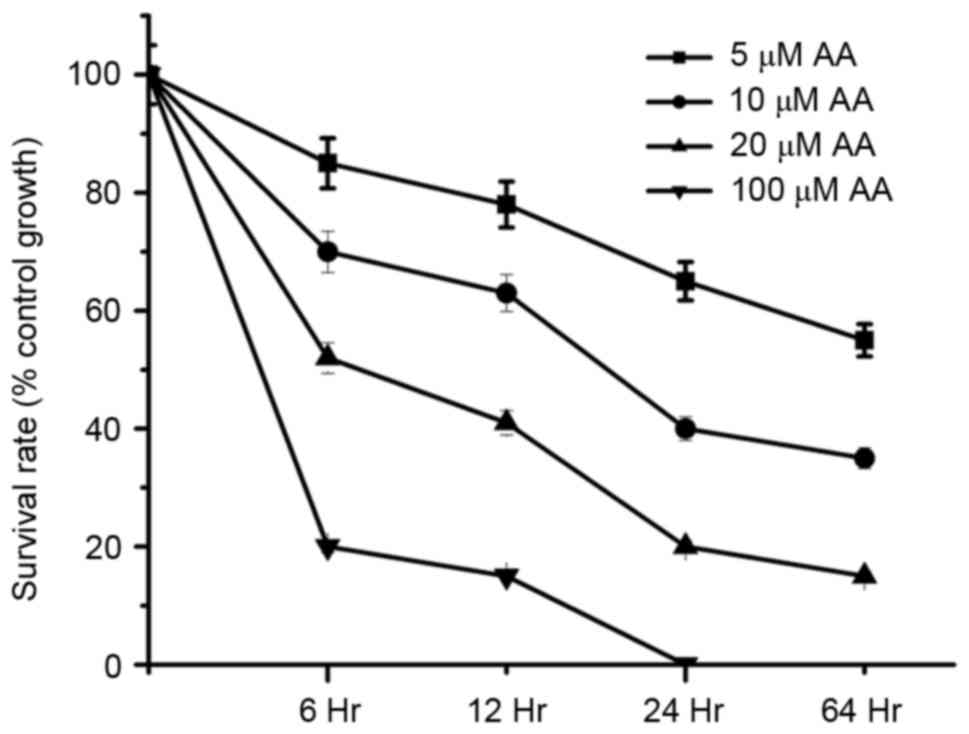
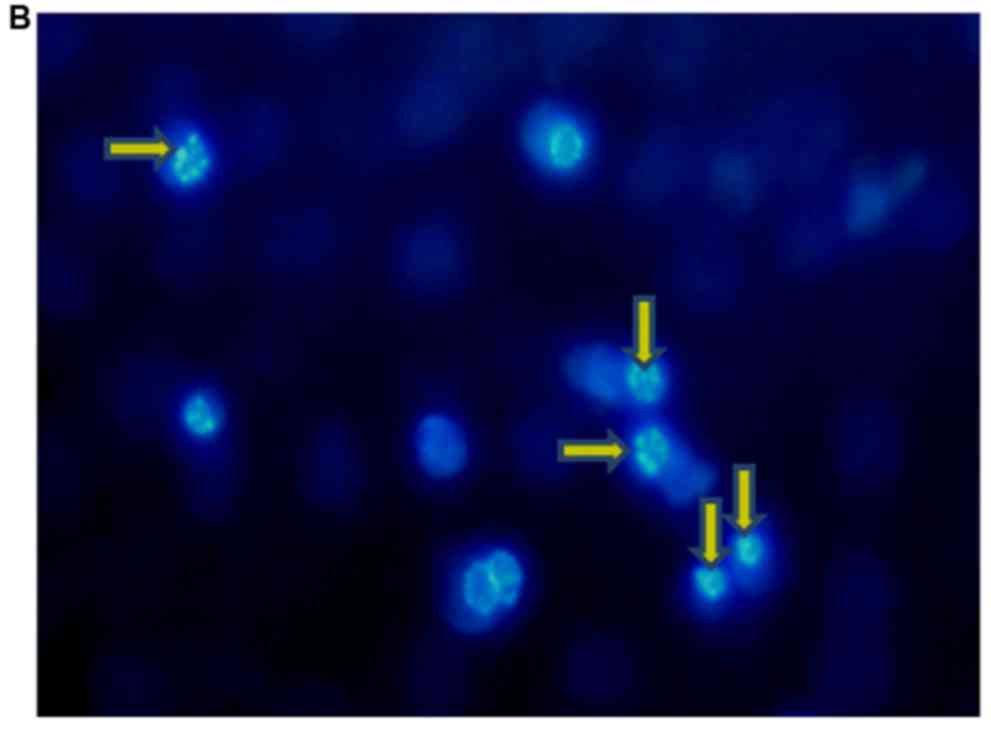
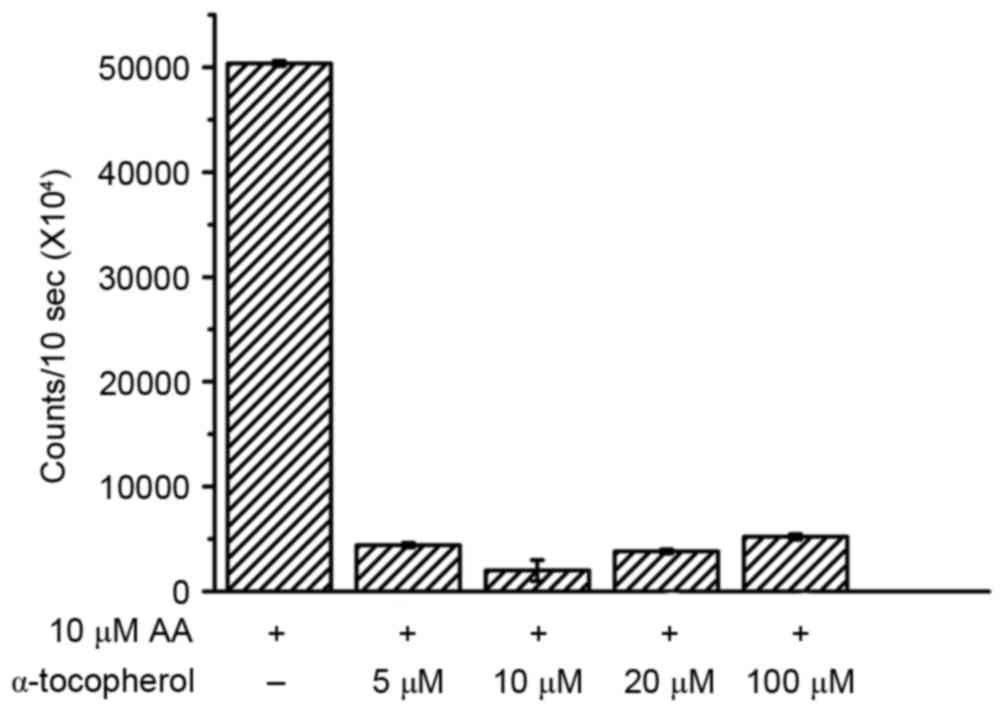
|
1
|
Schaneberg BT and Khan IA: Analysis of
products suspected of containing Aristolochia or
Asarum species. J Ethnopharmacol. 94:245–249. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Li XW, Morinaga O, Tian M, Uto T, Yu J,
Shang MY, Wang X, Cai SQ and Shoyama Y: Development of an Eastern
blotting technique for the visual detection of aristolochic acids
in Aristolochia and Asarum species by using a
monoclonal antibody against aristolochic acids I and II. Phytochem
Anal. 24:645–653. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Tsai DM, Kang JJ, Lee SS, Wang SY, Tsai
IL, Chen GY, Liao HW, Wei-Chu L, Kuo CH and Tseng YJ: Metabolomic
analysis of complex chinese remedies: Examples of induced
nephrotoxicity in the mouse from a series of remedies containing
aristolochic acid. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2013:2637572013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
4
|
Heinrich M, Chan J, Wanke S, Neinhuis C
and Simmonds MS: Local uses of Aristolochia species and
content of nephrotoxic aristolochic acid 1 and 2-a global
assessment based on bibliographic sources. J Ethnopharmacol.
125:108–144. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Feng C, Xie X, Wu M, Li C, Gao M, Liu M,
Qi X and Ren J: Tanshinone I protects mice from aristolochic acid
I-induced kidney injury by induction of CYP1A. Environ Toxicol
Pharmacol. 36:850–857. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Luciano RL and Perazella MA: Aristolochic
acid nephropathy: Epidemiology, clinical presentation, and
treatment. Drug Saf. 38:55–64. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Zhang J, Zhang L, Wang W and Wang H: China
National Survey of Chronic Kidney Disease Working Group:
Association between aristolochic acid and CKD: A cross-sectional
survey in China. Am J Kidney Dis. 61:918–922. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
De Broe ME: Chinese herbs nephropathy and
Balkan endemic nephropathy: Toward a single entity, aristolochic
acid nephropathy. Kidney Int. 81:513–515. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Pozdzik AA, Salmon IJ, Debelle FD,
Decaestecker C, Van den Branden C, Verbeelen D, Deschodt-Lanckman
MM, Vanherweghem JL and Nortier JL: Aristolochic acid induces
proximal tubule apoptosis and epithelial to mesenchymal
transformation. Kidney Int. 73:595–607. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Lin TC, Lee TC, Hsu SL and Yang CS: The
molecular mechanism of leptin secretion and expression induced by
aristolochic acid in kidney fibroblast. PLoS One. 6:e166542011.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
11
|
Matsui K, Kamijo-Ikemorif A, Sugaya T,
Yasuda T and Kimura K: Renal liver-type fatty acid binding protein
(L-FABP) attenuates acute kidney injury in aristolochic acid
nephrotoxicity. Am J Pathol. 178:1021–1032. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
12
|
Bunel V, Antoine MH, Nortier J, Duez P and
Stévigny C: In vitro effects of Panax ginseng in
aristolochic acid-mediated renal tubulotoxicity: Apoptosis versus
regeneration. Planta Med. 81:363–372. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Yu FY, Wu TS, Chen TW and Liu BH:
Aristolochic acid I induced oxidative DNA damage associated with
glutathione depletion and ERK1/2 activation in human cells. Toxicol
In Vitro. 25:810–816. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Singh M, Kapoor A and Bhatnagar A:
Oxidative and reductive metabolism of lipid-peroxidation derived
carbonyls. Chem Biol Interact. 234:261–273. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
15
|
Dur A, Kocaman O, Koçyiğit A, Türkdoğan
KA, Sönmez E, Keskin S, Yiğit M, Gülen B, Kılıç E and Uysal Ö:
Oxidative status and lymphocyte DNA damage in patients with acute
pancreatitis and its relationship with severity of acute
pancreatitis. Turk J Gastroenterol. 27:68–72. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Kruk J, Kubasik-Kladna K and Aboul-Enein
HY: The role oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of eye diseases:
Current status and a dual role of physical activity. Mini Rev Med
Chem. 16:241–257. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Yao CW, Piao MJ, Kim KC, Zheng J, Cha JW
and Hyun JW: 6′-o-galloylpaeoniflorin protects human keratinocytes
against oxidative stress-induced cell damage. Biomol Ther (Seoul).
21:349–357. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
18
|
Sen S, Kawahara B, Fry NL, Farias-Eisner
R, Zhang D, Mascharak PK and Chaudhuri G: A light-activated NO
donor attenuates anchorage independent growth of cancer cells:
Important role of a cross talk between NO and other reactive oxygen
species. Arch Biochem Biophys. 540:33–40. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Goncalves RL, Quinlan CL, Perevoshchikova
IV, Hey-Mogensen M and Brand MD: Sites of superoxide and hydrogen
peroxide production by muscle mitochondria assessed ex vivo under
conditions mimicking rest and exercise. J Biol Chem. 290:209–227.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Goncalves RL, Rothschild DE, Quinlan CL,
Scott GK, Benz CC and Brand MD: Sources of
superoxide/H2O2 during mitochondrial proline
oxidation. Redox Biol. 2:901–909. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
21
|
Prasad AK and Mishra PC: Mechanism of
action of sulforaphane as a superoxide radical anion and hydrogen
peroxide scavenger by double hydrogen transfer: A model for iron
superoxide dismutase. J Phys Chem B. 119:7825–7836. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Ludwig E and Eyer P: Reactivity of
glutathione adducts of 4-(dimethylamino)phenol. Involvement of
reactive oxygen species during the interaction with oxyhemoglobin.
Chem Res Toxicol. 8:363–368. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Tulunoglu O, Alacam A, Bastug M and
Yavuzer S: Superoxide dismutase activity in healthy and inflamed
pulp tissues of permanent teeth in children. J Clin Pediatr Dent.
22:341–345. 1998.
|
|
24
|
Gölz L, Memmert S, Rath-Deschner B, Jäger
A, Appel T, Baumgarten G, Götz W and Frede S: LPS from P.
gingivalis and hypoxia increases oxidative stress in
periodontal ligament fibroblasts and contributes to periodontitis.
Mediators Inflamm. 2014:9862642014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
25
|
Magdalan J, Piotrowska A, Gomulkiewicz A,
Sozański T, Szelag A and Dziegiel P: Influence of commonly used
clinical antidotes on antioxidant systems in human hepatocyte
culture intoxicated with alpha-amanitin. Hum Exp Toxicol. 30:38–43.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Peng XL, Xu WT, Wang Y, Huang KL, Liang
ZH, Zhao WW and Luo YB: Mycotoxin Ochratoxin A-induced cell death
and changes in oxidative metabolism of Arabidopsis thaliana.
Plant Cell Rep. 29:153–161. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Maruf AA and O'Brien P:
Inflammation-enhanced drug-induced liver injury. Free Radic Biol
Med. 75 Suppl 1:S402014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Pisoschi AM and Pop A: The role of
antioxidants in the chemistry of oxidative stress: A review. Eur J
Med Chem. 97:55–74. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Wu TK, Wei CW, Pan YR, Cherng SH, Chang
WJ, Wang HF and Yu YL: Vitamin C attenuates the toxic effect of
aristolochic acid on renal tubular cells via decreasing oxidative
stress-mediated cell death pathways. Mol Med Rep. 12:6086–6092.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Gomez C, Martinez L, Mesa A, Duque JC,
Escobar LA, Pham SM and Vazquez-Padron RI: Oxidative stress induces
early-onset apoptosis of vascular smooth muscle cells and neointima
formation in response to injury. Biosci Rep. 35:pii: e00227. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
31
|
Hu XL, Niu YX, Zhang Q, Tian X, Gao LY,
Guo LP, Meng WH and Zhao QC: Neuroprotective effects of Kukoamine B
against hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis and potential
mechanisms in SH-SY5Y cells. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 40:230–240.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Zhang T, Zhang Y, Cui M, Jin L, Wang Y, Lv
F, Liu Y, Zheng W, Shang H, Zhang J, et al: CaMKII is a RIP3
substrate mediating ischemia- and oxidative stress-induced
myocardial necroptosis. Nat Med. 22:175–182. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Yang H, Dou Y, Zheng X, Tan Y, Cheng J, Li
L, Du Y, Zhu D and Lou Y: Cysteinyl leukotrienes synthesis is
involved in aristolochic acid I-induced apoptosis in renal proximal
tubular epithelial cells. Toxicology. 287:38–45. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Baudoux TE, Pozdzik AA, Arlt VM, De Prez
EG, Antoine MH, Quellard N, Goujon JM and Nortier JL: Probenecid
prevents acute tubular necrosis in a mouse model of aristolochic
acid nephropathy. Kidney Int. 82:1105–1113. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Yang L, Li X and Wang H: Possible
mechanisms explaining the tendency towards interstitial fibrosis in
aristolochic acid-induced acute tubular necrosis. Nephrol Dial
Transplant. 22:445–456. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Seo HS, Ku JM, Choi HS, Woo JK, Jang BH,
Go H, Shin YC and Ko SG: Apigenin induces caspase-dependent
apoptosis by inhibiting signal transducer and activator of
transcription 3 signaling in HER2-overexpressing SKBR3 breast
cancer cells. Mol Med Rep. 12:2977–2984. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Göke A, Göke R, Ofner A, Herbst A and
Lankat-Buttgereit B: The FGFR inhibitor NVP-BGJ398 induces NSCLC
cell death by activating caspase-dependent pathways as well as
caspase-independent apoptosis. Anticancer Res. 35:5873–5879.
2015.
|
|
38
|
Wang Y, Fu W, Wang H, Liang Y, Wang Y, Yao
W, Chen W, Li Q, Ying PH, Shi X and Peng W: Renal microvascular
injury in chronic aristolochic acid nephropathy and protective
effects of Cozaar. Ren Fail. 34:60–67. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Zhang L, Li J, Jiang Z, Sun L, Mei X, Yong
B and Zhang L: Inhibition of aquaporin-1 expression by RNAi
protects against aristolochic acid I-induced apoptosis in human
proximal tubular epithelial (HK-2) cells. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 405:68–73. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Yuan SY, Yang CR, Cheng CL, Hsu SL, Liao
JW, Lin CC, Chou YY and Cheng YW: Comparative nephrotoxicity of
aristolochic acid and tetrandrine in vitro and in vivo. Int J
Toxicol. 30:35–46. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Kwak DH, Park JH, Lee HS, Moon JS and Lee
S: Aristolochic acid I induces ovarian toxicity by inhibition of
akt phosphorylation. Chem Res Toxicol. 27:2128–35. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Qi X, Cai Y, Gong L, Liu L, Chen F, Xiao
Y, Wu X, Li Y, Xue X and Ren J: Role of mitochondrial permeability
transition in human renal tubular epithelial cell death induced by
aristolochic acid. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 222:105–110. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Cook-Mills JM: Isoforms of vitamin E
differentially regulate PKC α and inflammation: A review. J Clin
Cell Immunol. 4:pii: 1000137. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
44
|
Stanger O, Aigner I, Schimetta W and
Wonisch W: Antioxidant supplementation attenuates oxidative stress
in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass graft surgery. Tohoku
J Exp Med. 232:145–154. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Park OJ, Kim HY, Kim WK, Kim YJ and Kim
SH: Effect of vitamin E supplementation on antioxidant defense
systems and humoral immune responses in young, middle-aged and
elderly Korean women. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 49:94–99. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Kutlubay R, Oğuz EO, Güven C, Can B, Sinik
Z and Tuncay OL: Histological and ultrastructural evidence for
protective effects on aluminium-induced kidney damage by
intraperitoneal administration of alpha-tocopherol. Int J Toxicol.
26:95–101. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Tasanarong A, Kongkham S, Duangchana S,
Thitiarchakul S and Eiam-Ong S: Vitamin E ameliorates renal
fibrosis by inhibition of TGF-beta/Smad2/3 signaling pathway in UUO
mice. J Med Assoc Thai 94 Suppl. 7:S1–S9. 2011.
|
|
48
|
Lin BR, Yu CJ, Chen WC, Lee HS, Chang HM,
Lee YC, Chien CT and Chen CF: Green tea extract supplement reduces
D-galactosamine-induced acute liver injury by inhibition of
apoptotic and proinflammatory signaling. J Biomed Sci. 16:352009.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
49
|
Yiang GT, Yu YL, Lin KT, Chen JN, Chang WJ
and Wei CW: Acetaminophen induces JNK/p38 signaling and activates
the caspase-9-3-dependent cell death pathway in human mesenchymal
stem cells. Int J Mol Med. 36:485–492. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Yu YL, Yiang GT, Chou PL, Tseng HH, Wu TK,
Hung YT, Lin PS, Lin SY, Liu HC, Chang WJ and Wei CW: Dual role of
acetaminophen in promoting hepatoma cell apoptosis and kidney
fibroblast proliferation. Mol Med Rep. 9:2077–2084. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Chen YY, Chung JG, Wu HC, Bau DT, Wu KY,
Kao ST, Hsiang CY, Ho TY and Chiang SY: Aristolochic acid
suppresses DNA repair and triggers oxidative DNA damage in human
kidney proximal tubular cells. Oncol Rep. 24:141–153.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Kataki A, Skandami V, Memos N,
Nikolopoulou M, Oikonomou V, Androulis A, Konstadoulakis MM and
Zografos CG: Similar immunity profiles in patients with meningioma
and glioma tumors despite differences in the apoptosis and necrosis
of circulating lymphocyte and monocyte populations. J Neurosurg
Sci. 58:9–15. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Song AS, Najjar AM and Diller KR:
Thermally induced apoptosis, necrosis and heat shock protein
expression in 3D culture. J Biomech Eng. 136:2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
54
|
Wang Q, Zeng P, Liu Y, Wen G, Fu X and Sun
X: Inhibition of autophagy ameliorates atherogenic inflammation by
augmenting apigenin-induced macrophage apoptosis. Int
Immunopharmacol. 27:24–31. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Martin KR, Ohayon D and Witko-Sarsat V:
Promoting apoptosis of neutrophils and phagocytosis by macrophages:
Novel strategies in the resolution of inflammation. Swiss Med Wkly.
145:w140562015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Yiang GT, Chou PL, Hung YT, Chen JN, Chang
WJ, Yu YL and Wei CW: Vitamin C enhances anticancer activity in
methotrexate-treated Hep3B hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncol
Rep. 32:1057–1063. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Valle A, Oliver J and Roca P: Role of
uncoupling proteins in cancer. Cancers (Basel). 2:567–591. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Cai H: Hydrogen peroxide regulation of
endothelial function: Origins, mechanisms, and consequences.
Cardiovasc Res. 68:26–36. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Zelko IN, Mariani TJ and Folz RJ:
Superoxide dismutase multigene family: A comparison of the CuZn-SOD
(SOD1), Mn-SOD (SOD2), and EC-SOD (SOD3) gene structures,
evolution, and expressio. Free Radic Biol Med. 33:337–349. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Flora SJ: Structural, chemical and
biological aspects of antioxidants for strategies against metal and
metalloid exposure. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2:191–206. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Costa A, Scholer-Dahirel A and
Mechta-Grigoriou F: The role of reactive oxygen species and
metabolism on cancer cells and their microenvironment. Semin Cancer
Biol. 25:23–32. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Anichini C, Lotti F, Pietrini A, Lo Rizzo
C, Longini M, Proietti F, Felici C and Buonocore G: Antioxidant
effects of potassium ascorbate with ribose in costello syndrome.
Anticancer Res. 33:691–695. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Moore DF, Ye F, Brennan ML, Gupta S,
Barshop BA, Steiner RD, Rhead WJ, Brady RO, Hazen SL and Schiffmann
R: Ascorbate decreases Fabry cerebral hyperperfusion suggesting a
reactive oxygen species abnormality: An arterial spin tagging
study. J Magn Reson Imaging. 20:674–683. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Packer L, Weber SU and Rimbach G:
Molecular aspects of alpha-tocotrienol antioxidant action and cell
signalling. J Nutr. 131:369S–373S. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Chaudière J and Ferrari-Iliou R:
Intracellular antioxidants: From chemical to biochemical
mechanisms. Food Chem Toxicol. 37:949–962. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Singh M, Singh S and Kale RK:
Chemomodulatory potential of Asparagus adscendens against
murine skin and forestomach papillomagenesis. Eur J Cancer Prev.
20:240–247. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|