|
1
|
Nomori H, Watanabe K, Ohtsuka T, Naruke T,
Suemasu K and Uno K: Visual and semiquantitative analyses for F-18
fluorodeoxyglucose PET scanning in pulmonary nodules 1 to 3 cm in
size. Ann Thorac Surg. 79:984–989. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cronin P, Dwamena BA, Kelly AM and Carlos
RC: Solitary pulmonary nodules: Meta-analytic comparison of
cross-sectional imaging modalities for diagnosis of malignancy.
Radiology. 246:772–782. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wahidi MM, Govert JA, Goudar RK, Gould MK
and McCrory DC: American College of Chest Physicians: Evidence for
the treatment of patients with pulmonary nodules: When is it breast
cancer? ACCP evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest.
132 Suppl 3:S94–S107. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Wong N and Wang X: miRDB: An online
resource for microRNA target prediction and functional annotations.
Nucleic Acids Res. 43:(Database Issue). D146–D152. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Herder GJ, van Tinteren H, Golding RP,
Kostense PJ, Comans EF, Smit EF and Hoekstra OS: Clinical
prediction model to characterize pulmonary nodules: Validation and
added value of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography.
Chest. 128:2490–2496. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kim SH, Cho YR, Kim HJ, Oh JS, Ahn EK, Ko
HJ, Hwang BJ, Lee SJ, Cho Y, Kim YK, et al: Antagonism of
VEGF-A-induced increase in vascular permeability by an integrin
α3β1-Shp-1-cAMP/PKA pathway. Blood. 120:4892–4902. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yanokura M, Banno K, Kobayashi Y, Kisu I,
Ueki A, Ono A, Masuda K, Nomura H, Hirasawa A, Susumu N and Aoki D:
MicroRNA and endometrial cancer: Roles of small RNAs in human
tumors and clinical applications (Review). Oncol Lett. 1:935–940.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Engels BM and Hutvagner G: Principles and
effects of microRNA-mediated post-transcriptional gene regulation.
Oncogene. 25:6163–6169. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Philippe L, Alsaleh G, Bahram S, Pfeffer S
and Georgel P: The miR-17~92 cluster: A key player in the control
of inflammation during rheumatoid arthritis. Front Immunol.
4:702013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Dylla L, Moore C and Jedlicka P: MicroRNAs
in Ewing sarcoma. Front Oncol. 3:652013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Renner W, Kotschan S, Hoffmann C,
Obermayer-Pietsch B and Pilger E: A common 936 C/T mutation in the
gene for vascular endothelial growth factor is associated with
vascular endothelial growth factor plasma levels. J Vasc Res.
37:443–448. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wolf G, Aigner RM, Schaffler G,
Langsenlehner U, Renner W, Samonigg H, Yazdani-Biuki B and Krippl
P: The 936C> T polymorphism of the gene for vascular endothelial
growth factor is associated with 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose uptake.
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 88:205–208. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bae SJ, Kim JW, Kang H, Hwang SG, Oh D and
Kim NK: Gender-specific association between polymorphism of
vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF 936 C>T) gene and colon
cancer in Korea. Anticancer Res. 28:1271–1276. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li J, Li L, Li Z, Gong G, Chen P, Liu H,
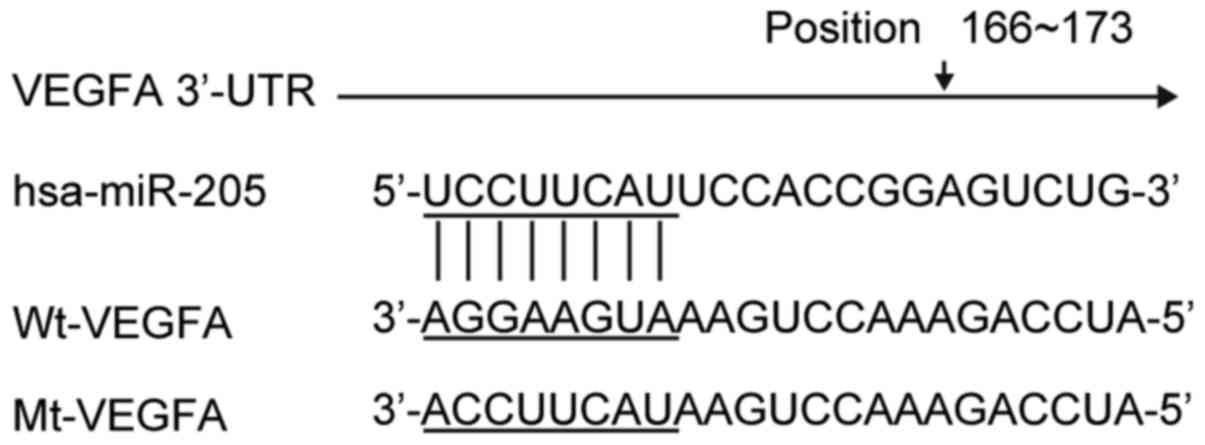
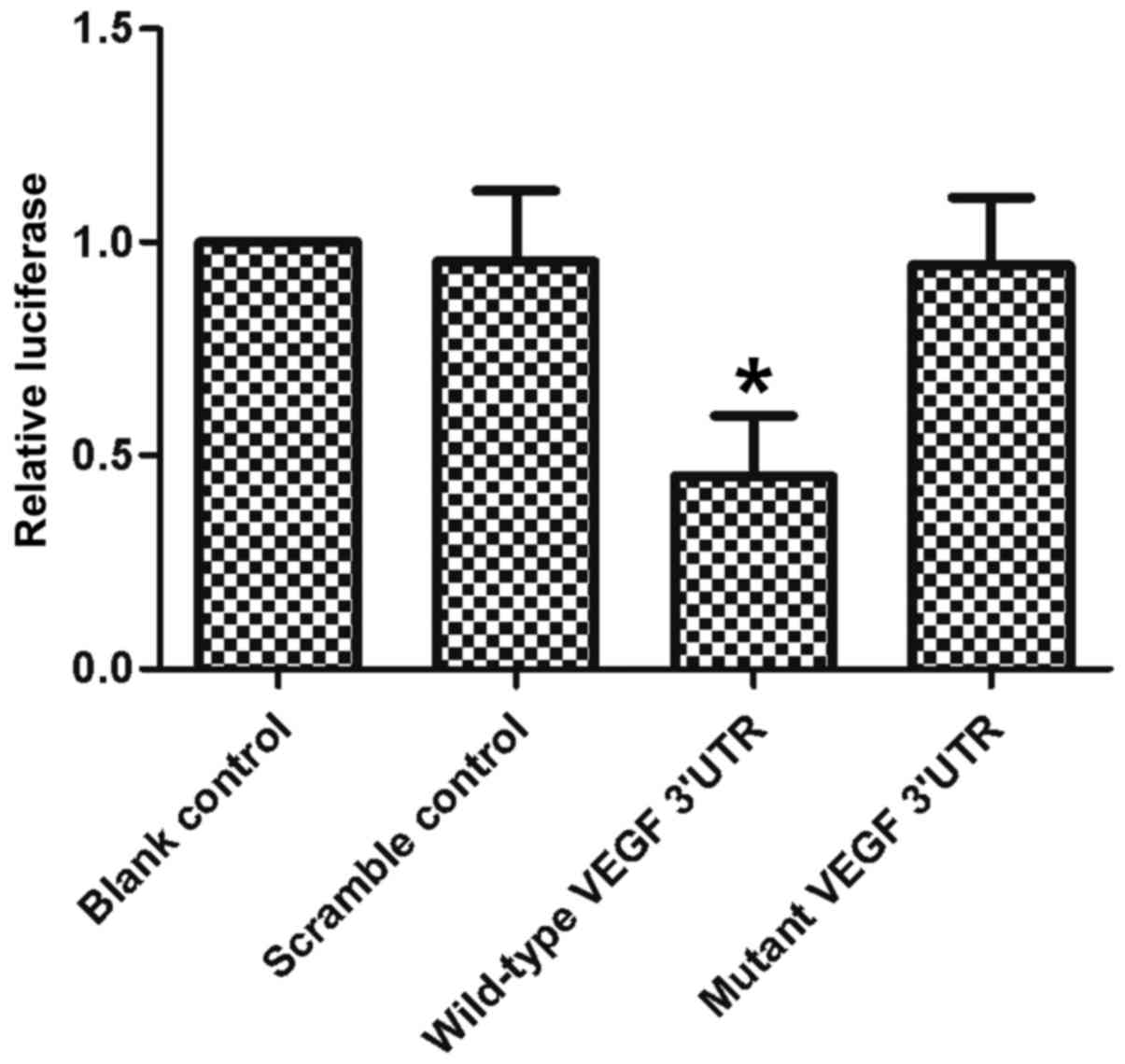
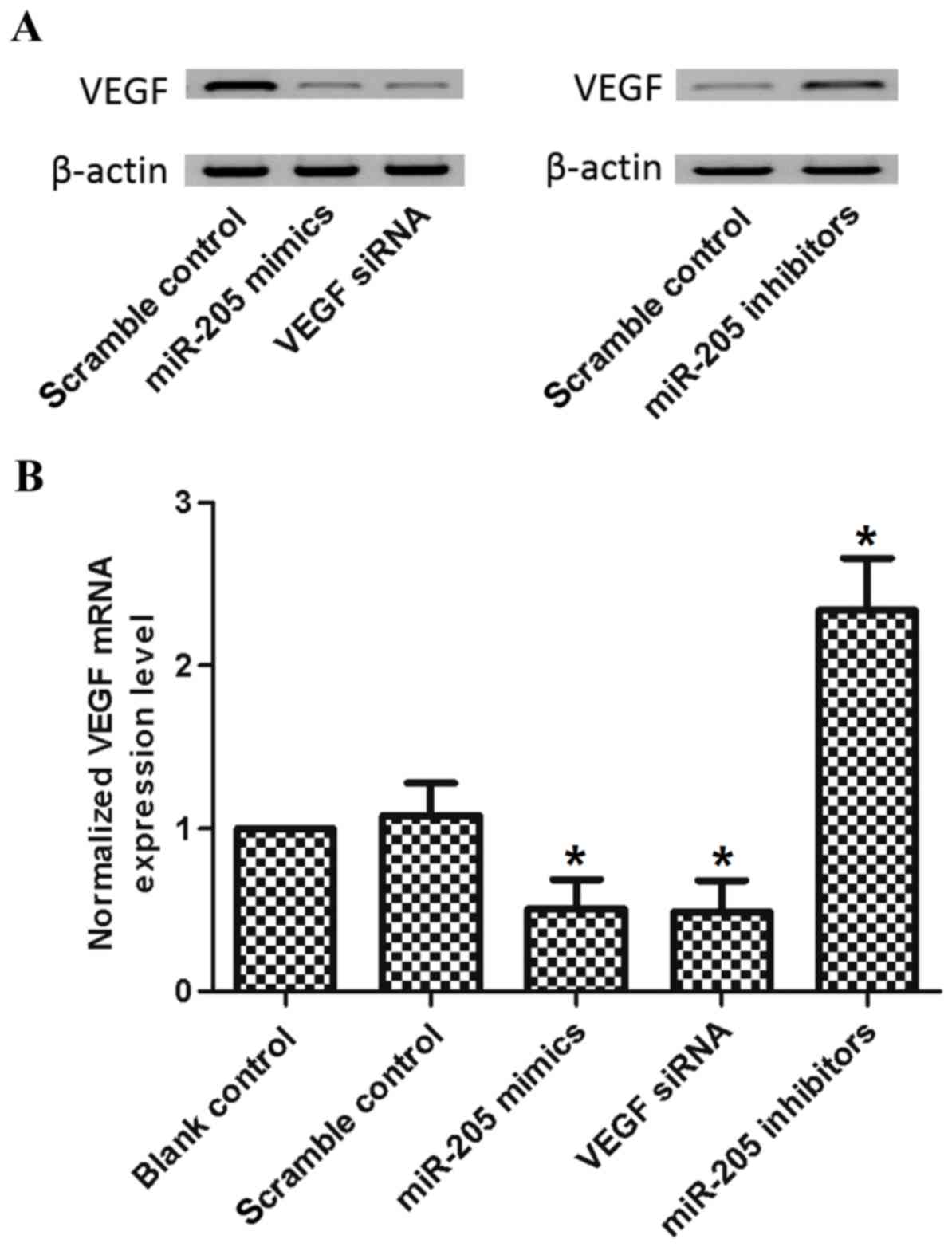
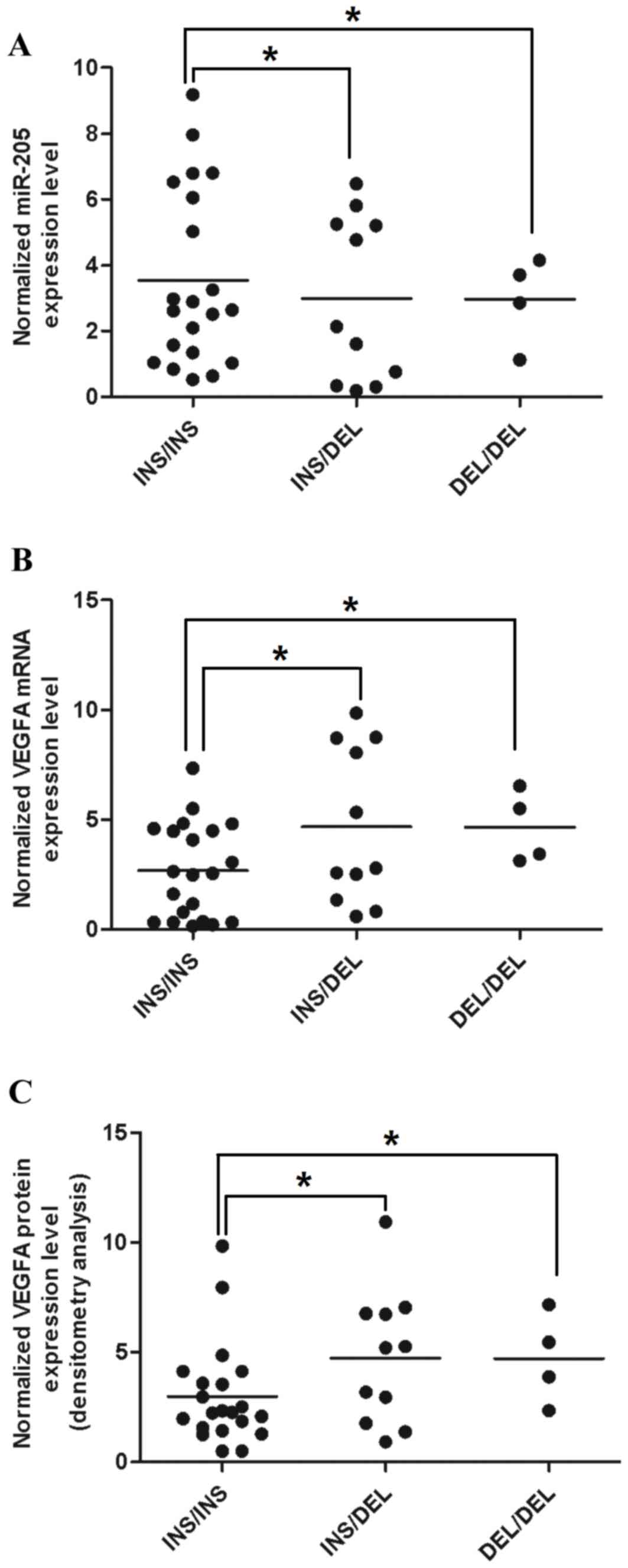
Wang J, Liu Y and Wu X: The role of miR-205 in the VEGF-mediated
promotion of human ovarian cancer cell invasion. Gynecol Oncol.
137:125–133. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang L, Shan M, Liu Y, Yang F, Qi H, Zhou
L, Qiu L and Li Y: miR-205 suppresses the proliferative and
migratory capacity of human osteosarcoma Mg-63 cells by targeting
VEGFA. Onco Targets Ther. 16:2635–2642. 2015.
|
|
16
|
Leng S, Bernauer AM, Zhai R, Tellez CS, Su
L, Burki EA, Picchi MA, Stidley CA, Crowell RE, Christiani DC and
Belinsky SA: Discovery of common SNPs in the miR-205/200
family-regulated epithelial to mesenchymal transition pathway and
their association with risk for non-small cell lung cancer. Int J
Mol Epidemiol Genet. 2:145–155. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Carthew RW and Sontheimer EJ: Origins and
mechanisms of miRNAs and siRNAs. Cell. 136:642–655. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Schmittgen TD: Regulation of microRNA
processing in development, differentiation and cancer. J Cell Mol
Medicine. 12:1811–1819. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Rosenfeld N, Aharonov R, Meiri E,
Rosenwald S, Spector Y, Zepeniuk M, Benjamin H, Shabes N, Tabak S,
Levy A, et al: MicroRNAs accurately identify cancer tissue origin.
Nat Biotechnol. 26:462–469. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Croce CM: Causes and consequences of
microRNA dysregulation in cancer. Nat Rev Genet. 10:704–714. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mathé EA, Nguyen GH, Bowman ED, Zhao Y,
Budhu A, Schetter AJ, Braun R, Reimers M, Kumamoto K, Hughes D, et
al: MicroRNA expression in squamous cell carcinoma and
adenocarcinoma of the esophagus: Associations with survival. Clin
Cancer Res. 15:6192–6200. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kimura S, Naganuma S, Susuki D, Hirono Y,
Yamaguchi A, Fujieda S, Sano K and Itoh H: Expression of microRNAs
in squamous cell carcinoma of human head and neck and the
esophagus: miR-205 and miR-21 are specific markers for HNSCC and
ESCC. Oncol Rep. 23:1625–1633. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ferrara N: VEGF and the quest for tumour
angiogenesis factors. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:795–803. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Takahashi S: Vascular endothelial growth
factor (VEGF), VEGF receptors and their inhibitors for
antiangiogenic tumor therapy. Biol Pharm Bull. 34:1785–1788. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Omuro AM, Faivre S and Raymond E: Lessons
learned in the development of targeted therapy for malignant
gliomas. Mol Cancer Ther. 6:1909–1919. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Thomas G, Jacobs KB, Kraft P, Yeager M,
Wacholder S, Cox DG, Hankinson SE, Hutchinson A, Wang Z, Yu K, et
al: A multistage genome-wide association study in breast cancer
identifies two new risk alleles at 1p11. 2 and 14q24. 1 (RAD51L1).
Nat Genet. 41:579–584. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Goldstein DB: Common genetic variation and
human traits. N Engl J Med. 360:1696–1698. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Esquela-Kerscher A and Slack FJ:
Oncomirs-microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
6:259–269. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chen K and Rajewsky N: Natural selection
on human microRNA binding sites inferred from SNP data. Nat Genet.
38:1452–1456. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Liu CG, Veronese A,
Spizzo R, Sabbioni S, Magri E, Pedriali M, Fabbri M, Campiglio M,
et al: MicroRNA gene expression deregulation in human breast
cancer. Cancer Res. 65:7065–7070. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Duan R, Pak C and Jin P: Single nucleotide
polymorphism associated with mature miR-125a alters the processing
of pri-miRNA. Hum Mol Genet. 16:1124–1131. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Abelson JF, Kwan KY, O'Roak BJ, Baek DY,
Stillman AA, Morgan TM, Mathews CA, Pauls DL, Rasin MR, Gunel M, et
al: Sequence variants in SLITRK1 are associated with Tourette's
syndrome. Science. 310:317–320. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Landi D, Gemignani F, Barale R and Landi
S: A catalog of polymorphisms falling in microRNA-binding regions
of cancer genes. DNA Cell Biol. 27:35–43. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
He H, Jazdzewski K, Li W, Liyanarachchi S,
Nagy R, Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, Franssila K, Suster S, et al:
The role of microRNA genes in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USAmerica. 102:19075–19080. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Domigan CK, Warren CM, Antanesian V,
Happel K, Ziyad S, Lee S, Krall A, Duan L, Torres-Collado AX,
Castellani LW, et al: Autocrine VEGF maintains endothelial survival
through regulation of metabolism and autophagy. J Cell Sci.
128:2236–2248. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|