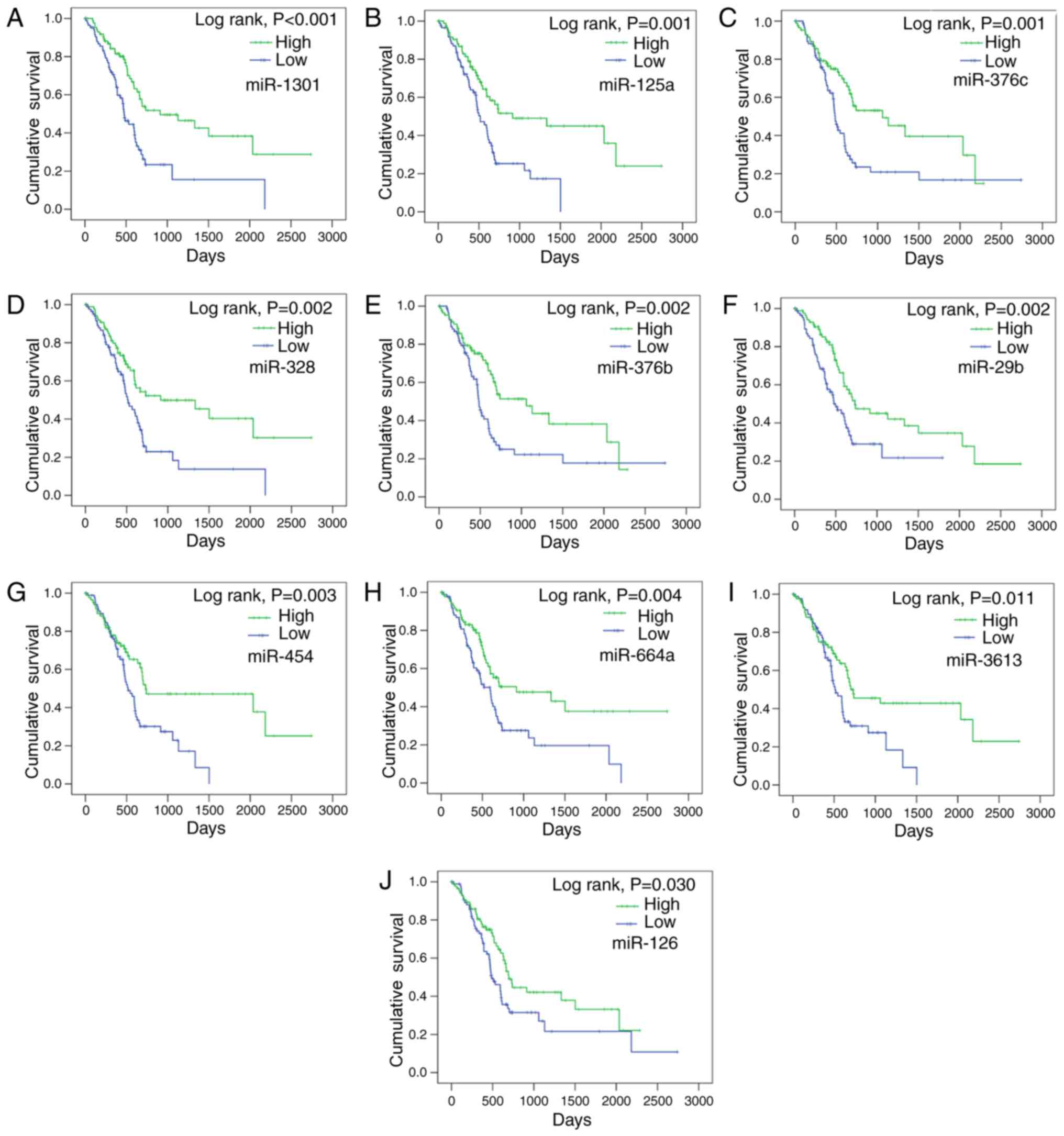
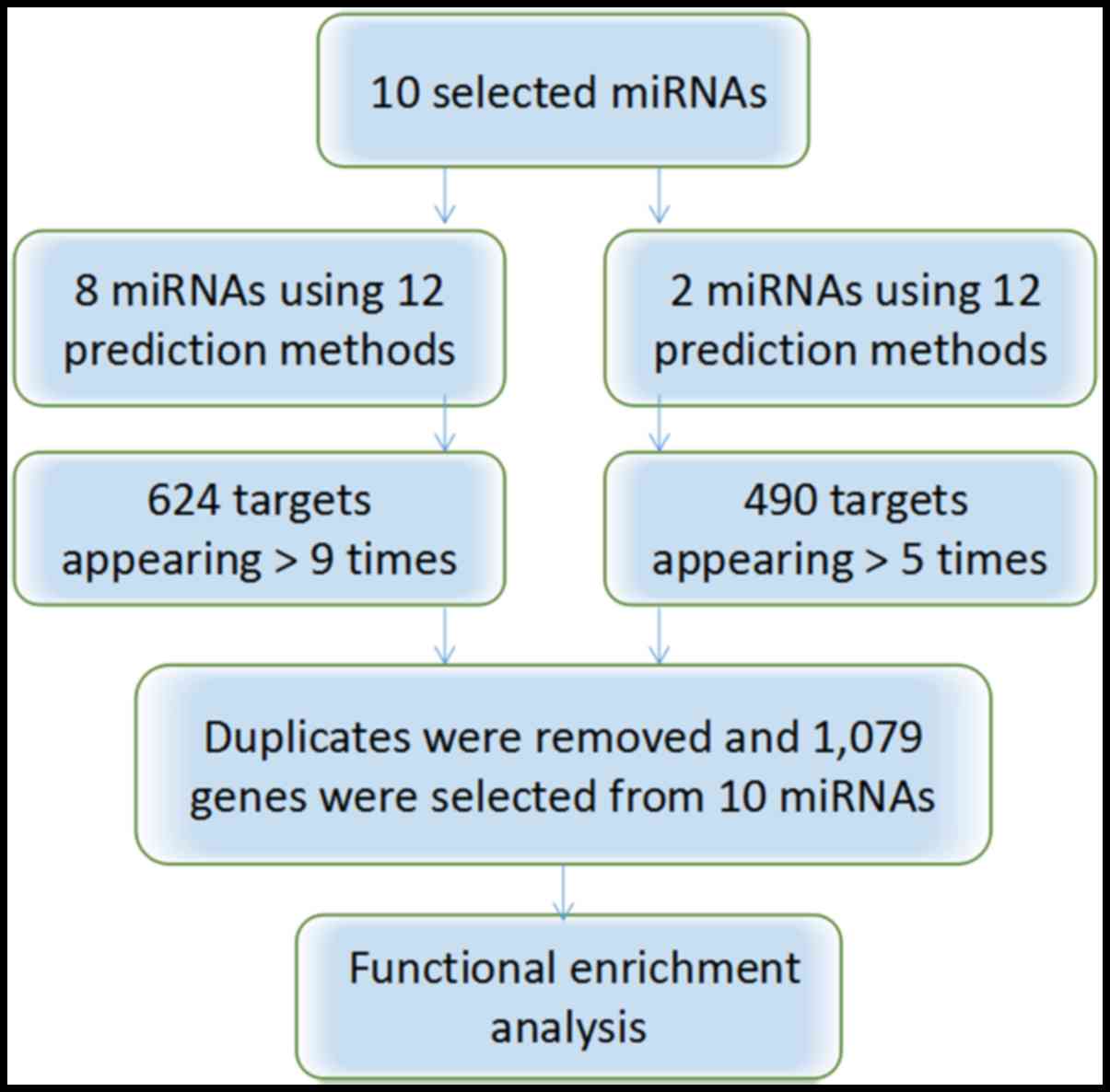
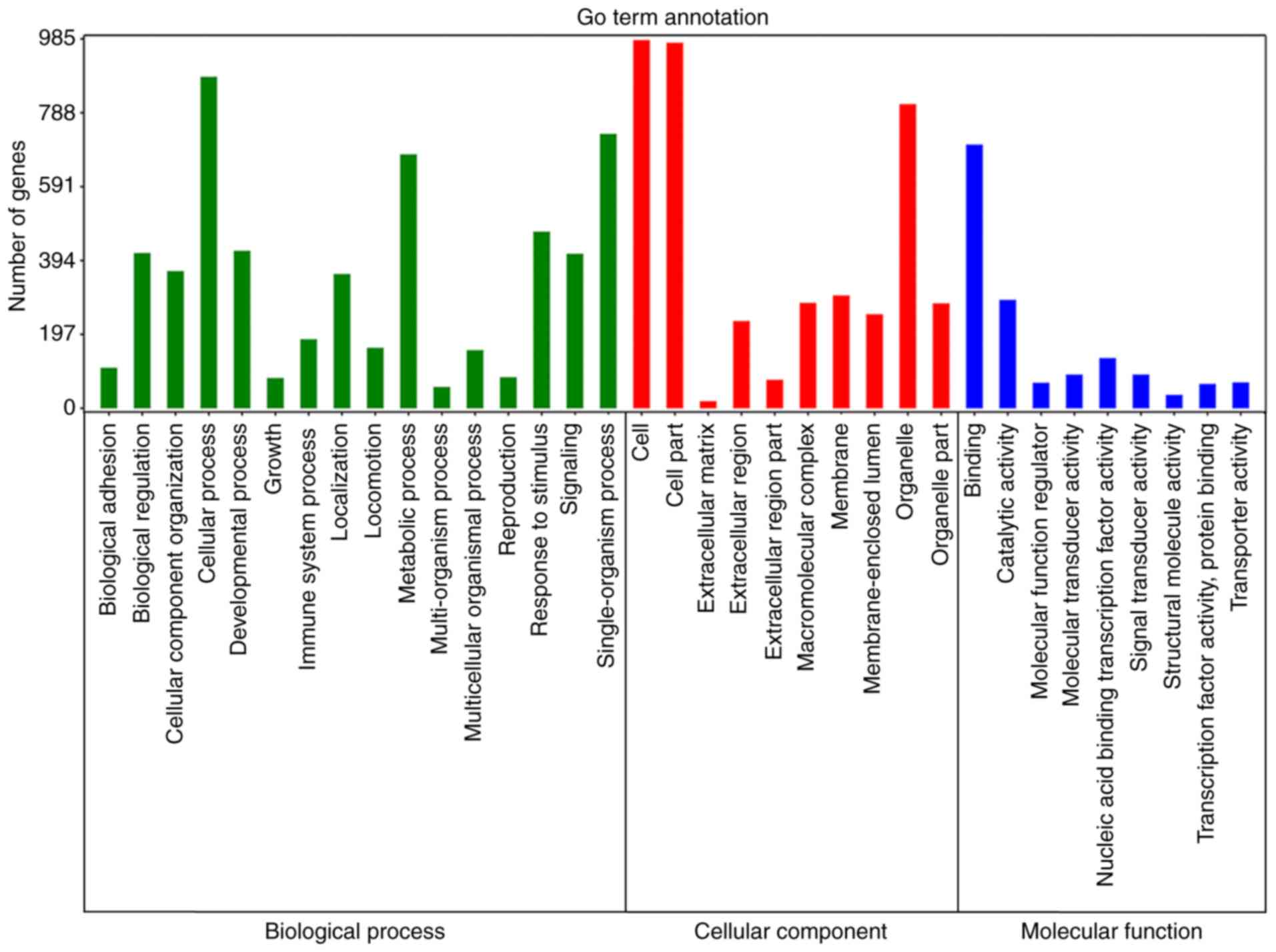
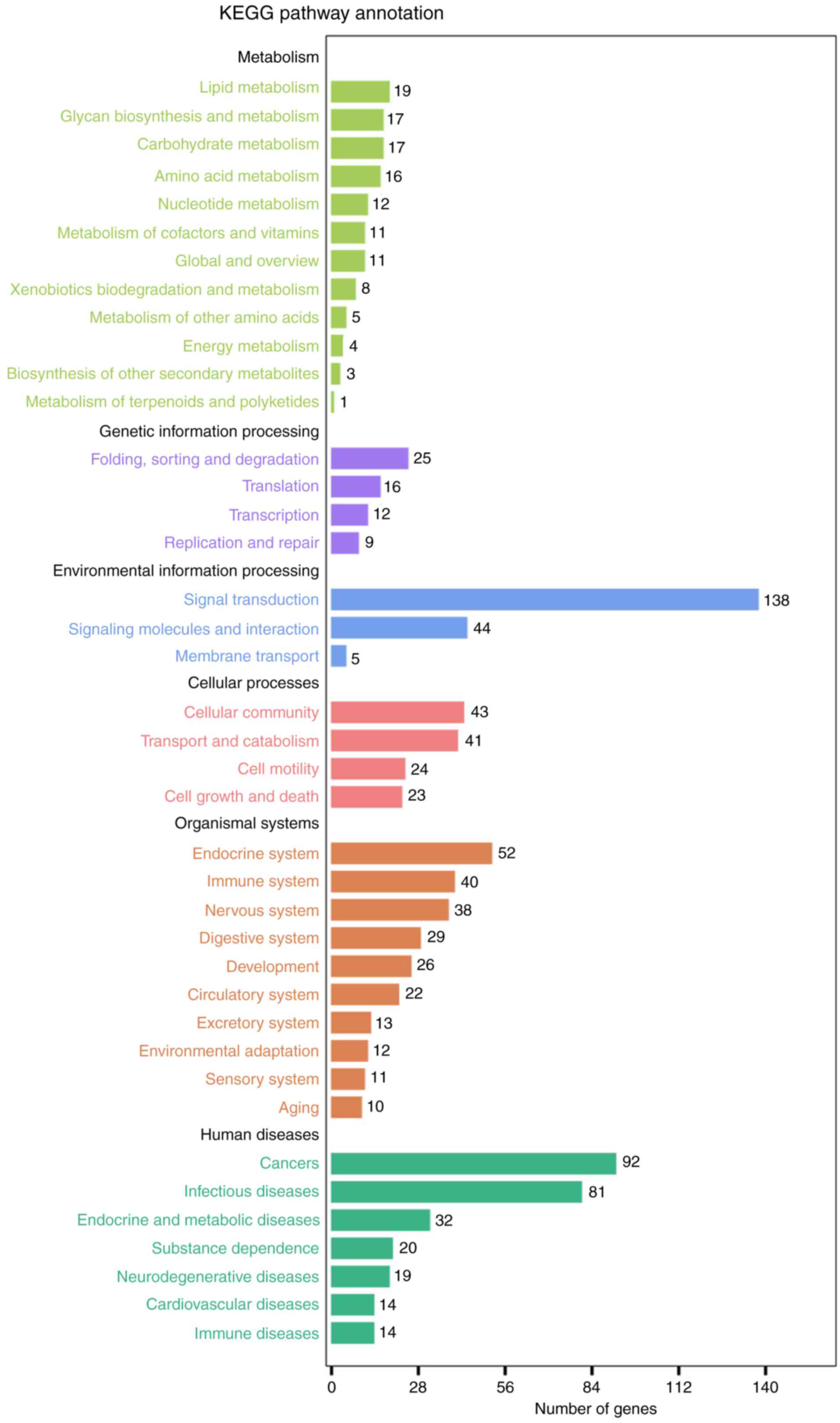
|
1
|
Yu J, Ohuchida K, Mizumoto K, Fujita H,
Nakata K and Tanaka M: MicroRNA miR-17-5p is overexpressed in
pancreatic cancer, associated with a poor prognosis, and involved
in cancer cell proliferation and invasion. Cancer Biol Ther.
10:748–757. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wang Z, Li J, Chen X, Duan W, Ma Q and Li
X: Disrupting the balance between tumor epithelia and stroma is a
possible therapeutic approach for pancreatic cancer. Med Sci Monit.
20:2002–2006. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Liang S, Yang Z, Li D, Miao X, Yang L, Zou
Q and Yuan Y: The clinical and pathological significance of
Nectin-2 and DDX3 expression in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas.
Dis Markers. 2015:3795682015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lee SH, Kang CM, Kim H, Hwang HK, Song SY,
Seong J, Kim MJ and Lee WJ: Pathological complete remission of
pancreatic cancer following neoadjuvant chemoradiation therapy; not
the end of battles. Medicine (Baltimore). 94:e21682015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chen Y, Wang X, Ke N, Mai G and Liu X:
Inferior mesenteric vein serves as an alternative guide for
transection of the pancreatic body during pancreaticoduodenectomy
with concomitant vascular resection: A comparative study evaluating
perioperative outcomes. Eur J Med Res. 19:422014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yang YF, Cao XH, Bao CE and Wan X:
Concurrent radiotherapy with oral fluoropyrimidine versus
gemcitabine in locally advanced pancreatic cancer: A systematic
review and meta-analysis. Onco Targets Ther. 8:3315–3322.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hezel AF, Kimmelman AC, Stanger BZ,
Bardeesy N and Depinho RA: Genetics and biology of pancreatic
ductal adenocarcinoma. Genes Dev. 20:1218–1249. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ali S, Dubaybo H, Brand RE and Sarkar FH:
Differential expression of MicroRNAs in tissues and plasma
co-exists as a biomarker for pancreatic cancer. J Cancer Sci Ther.
7:336–346. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Loosen SH, Neumann UP, Trautwein C,
Roderburg C and Luedde T: Current and future biomarkers for
pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Tumour Biol. 39:10104283176922312017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lewis BP, Burge CB and Bartel DP:
Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that
thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 120:15–20.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pillai RS: MicroRNA function: Multiple
mechanisms for a tiny RNA? RNA. 11:1753–1761. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Xiao J, Peng F, Yu C, Wang M, Li X, Li Z,
Jiang J and Sun C: microRNA-137 modulates pancreatic cancer cells
tumor growth, invasion and sensitivity to chemotherapy. Int J Clin
Exp Pathol. 7:7442–7450. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lin MS, Chen WC, Huang JX, Gao HJ and
Sheng HH: Aberrant expression of microRNAs in serum may identify
individuals with pancreatic cancer. Int J Clin Exp Med.
7:5226–5234. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kai Y, Qiang C, Xinxin P, Miaomiao Z and
Kuailu L: Decreased miR-154 expression and its clinical
significance in human colorectal cancer. World J Surg Oncol.
13:1952015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hou LJ and Zhai JJ: Aberrant expression
profile of translationally controlled tumor protein and
tumor-suppressive microRNAs in cervical cancer. J BUON.
20:1504–1509. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lu Y, Hu J, Sun W, Li S, Deng S and Li M:
MiR-29c inhibits cell growth, invasion, and migration of pancreatic
cancer by targeting ITGB1. Onco Targets Ther. 9:99–109.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Dong Q, Li C, Che X, Qu J, Fan Y, Li X, Li
Y, Wang Q, Liu Y, Yang X and Qu X: MicroRNA-891b is an independent
prognostic factor of pancreatic cancer by targeting Cbl-b to
suppress the growth of pancreatic cancer cells. Oncotarget.
7:82338–82353. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li BS, Liu H and Yang WL: Reduced
miRNA-218 expression in pancreatic cancer patients as a predictor
of poor prognosis. Genet Mol Res. 14:16372–16378. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Brunetti O, Russo A, Scarpa A, Santini D,
Reni M, Bittoni A, Azzariti A, Aprile G, Delcuratolo S, Signorile
M, et al: MicroRNA in pancreatic adenocarcinoma:
Predictive/prognostic biomarkers or therapeutic targets?
Oncotarget. 6:23323–23341. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang C, Sun Y, Wu H, Yu S, Zhang L, Meng
Y, Liu M, Yang H, Liu P, Mao X, et al: Elevated miR-483-3p
expression is an early event and indicates poor prognosis in
pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Tumour Biol. 36:9447–9456. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bai Z, Sun J, Wang X, Wang H, Pei H and
Zhang Z: MicroRNA-153 is a prognostic marker and inhibits cell
migration and invasion by targeting SNAI1 in human pancreatic
ductal adenocarcinoma. Oncol Rep. 34:595–602. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Shi H, Chen J, Li Y, Li G, Zhong R, Du D,
Meng R, Kong W and Lu M: Identification of a six microRNA signature
as a novel potential prognostic biomarker in patients with head and
neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget. 7:21579–21590. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang M, Wen TF, He LH, Li C, Zhu WJ and
Trishul NM: A six-microRNA set as prognostic indicators for bile
duct cancer. Int J Clin Exp Med. 8:17261–17270. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zheng H, Guo X, Tian Q, Li H and Zhu Y:
Distinct role of Tim-3 in systemic lupus erythematosus and clear
cell renal cell carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Med. 8:7029–7038.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dweep H and Gretz N: miRWalk2.0: A
comprehensive atlas of microRNA-target interactions. Nat Methods.
12:6972015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kanehisa M, Furumichi M, Tanabe M, Sato Y
and Morishima K: KEGG: New perspectives on genomes, pathways,
diseases and drugs. Nucleic Acids Res. 45:D353–D361. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang SW, Wang J and Pan J: Identification
of altered pathways in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy based on
combined data of protein-protein interactions and molecular
pathways. Genet Mol Res. 15:2016.
|
|
28
|
Jiang M, Zeng Q, Dai S, Liang H, Dai F,
Xie X, Lu K and Gao C: Comparative analysis of hepatocellular
carcinoma and cirrhosis gene expression profiles. Mol Med Rep.
15:380–386. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gu Y, Lu L, Wu L, Chen H, Zhu W and He Y:
Identification of prognostic genes in kidney renal clear cell
carcinoma by RNA-seq data analysis. Mol Med Rep. 15:1661–1667.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Uhlen M, Oksvold P, Fagerberg L, Lundberg
E, Jonasson K, Forsberg M, Zwahlen M, Kampf C, Wester K, Hober S,
et al: Towards a knowledge-based human protein atlas. Nat
Biotechnol. 28:1248–1250. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Uhlén M, Fagerberg L, Hallström BM,
Lindskog C, Oksvold P, Mardinoglu A, Sivertsson Å, Kampf C,
Sjöstedt E, Asplund A, et al: Proteomics. Tissue-based map of the
human proteome. Science. 347:12604192015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ma MZ, Kong X, Weng MZ, Cheng K, Gong W,
Quan ZW and Peng CH: Candidate microRNA biomarkers of pancreatic
ductal adenocarcinoma: Meta-analysis, experimental validation and
clinical significance. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 32:712013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Frampton AE, Krell J, Jamieson NB, Gall
TM, Giovannetti E, Funel N, Mato Prado M, Krell D, Habib NA,
Castellano L, et al: microRNAs with prognostic significance in
pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: A meta-analysis. Eur J Cancer.
51:1389–1404. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cheng PF, Dummer R and Levesque MP: Data
mining The Cancer Genome Atlas in the era of precision cancer
medicine. Swiss Med Wkly. 145:w141832015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Fang L, Yang N, Ma J, Fu Y and Yang GS:
microRNA-1301-mediated inhibition of tumorigenesis. Oncol Rep.
27:929–934. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lin TY, Chen KC, Liu HJ, Liu AJ, Wang KL
and Shih CM: MicroRNA-1301-Mediated RanGAP1 Downregulation Induces
BCR-ABL nuclear entrapment to enhance imatinib efficacy in chronic
myeloid leukemia cells. PLoS One. 11:e01562602016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Bi D, Ning H, Liu S, Que X and Ding K:
miR-1301 promotes prostate cancer proliferation through directly
targeting PPP2R2C. Biomed Pharmacother. 81:25–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhang Y, Xue C, Zhu X, Zhu X, Xian H and
Huang Z: Suppression of microRNA-125a-5p upregulates the TAZ-EGFR
signaling pathway and promotes retinoblastoma proliferation. Cell
Signal. 28:850–860. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Li LJ, Huang Q, Zhang N, Wang GB and Liu
YH: miR-376b-5p regulates angiogenesis in cerebral ischemia. Mol
Med Rep. 10:527–535. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Xiong H, Li Q, Liu S, Wang F, Xiong Z,
Chen J, Chen H, Yang Y, Tan X, Luo Q, et al: Integrated microRNA
and mRNA transcriptome sequencing reveals the potential roles of
miRNAs in stage I endometrioid endometrial carcinoma. PLoS One.
9:e1101632014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Leidinger P, Brefort T, Backes C, Krapp M,
Galata V, Beier M, Kohlhaas J, Huwer H, Meese E and Keller A:
High-throughput qRT-PCR validation of blood microRNAs in non-small
cell lung cancer. Oncotarget. 7:4611–4623. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Mishra S, Srivastava AK, Suman S, Kumar V
and Shukla Y: Circulating miRNAs revealed as surrogate molecular
signatures for the early detection of breast cancer. Cancer Lett.
369:67–75. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Shao N, Wang L, Xue L, Wang R and Lan Q:
Plasma miR-454-3p as a potential prognostic indicator in human
glioma. Neurol Sci. 36:309–313. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Wu X, Ding N, Hu W, He J, Xu S, Pei H, Hua
J, Zhou G and Wang J: Down-regulation of BTG1 by miR-454-3p
enhances cellular radiosensitivity in renal carcinoma cells. Radiat
Oncol. 9:1792014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhang JX, Chen ZH, Xu Y, Chen JW, Weng HW,
Yun M, Zheng ZS, Chen C, Wu BL, Li EM, et al: Downregulation of
MicroRNA-644a promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
aggressiveness and stem cell-like phenotype via dysregulation of
PITX2. Clin Cancer Res. 23:298–310. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Chen Q, Hu H, Jiao D, Yan J, Xu W, Tang X,
Chen J and Wang J: miR-126-3p and miR-451a correlate with
clinicopathological features of lung adenocarcinoma: The underlying
molecular mechanisms. Oncol Rep. 36:909–917. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wu XJ, Zhao ZF, Kang XJ, Wang HJ, Zhao J
and Pu XM: MicroRNA-126-3p suppresses cell proliferation by
targeting PIK3R2 in Kaposi's sarcoma cells. Oncotarget.
7:36614–36621. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Ji H, Chen M, Greening DW, He W, Rai A,
Zhang W and Simpson RJ: Deep sequencing of RNA from three different
extracellular vesicle (EV) subtypes released from the human LIM1863
colon cancer cell line uncovers distinct miRNA-enrichment
signatures. PLoS One. 9:e1103142014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Suresh R, Sethi S, Ali S, Giorgadze T and
Sarkar FH: Differential expression of microRNAs in papillary
thyroid carcinoma and their role in racial disparity. J Cancer Sci
Ther. 7:145–154. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Pullen TJ, da Silva Xavier G, Kelsey G and
Rutter GA: miR-29a and miR-29b contribute to pancreatic
beta-cell-specific silencing of monocarboxylate transporter 1
(Mct1). Mol Cell Biol. 31:3182–3194. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Sulpizio S, Franceschini N, Piattelli A,
Di Sebastiano P, Innocenti P and Selvaggi F: Cathepsins and
pancreatic cancer: The 2012 update. Pancreatology. 12:395–401.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Zhou X, Huang Z, Xu L, Zhu M, Zhang L,
Zhang H, Wang X, Li H, Zhu W, Shu Y and Liu P: A panel of 13-miRNA
signature as a potential biomarker for predicting survival in
pancreatic cancer. Oncotarget. 7:69616–69624. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|