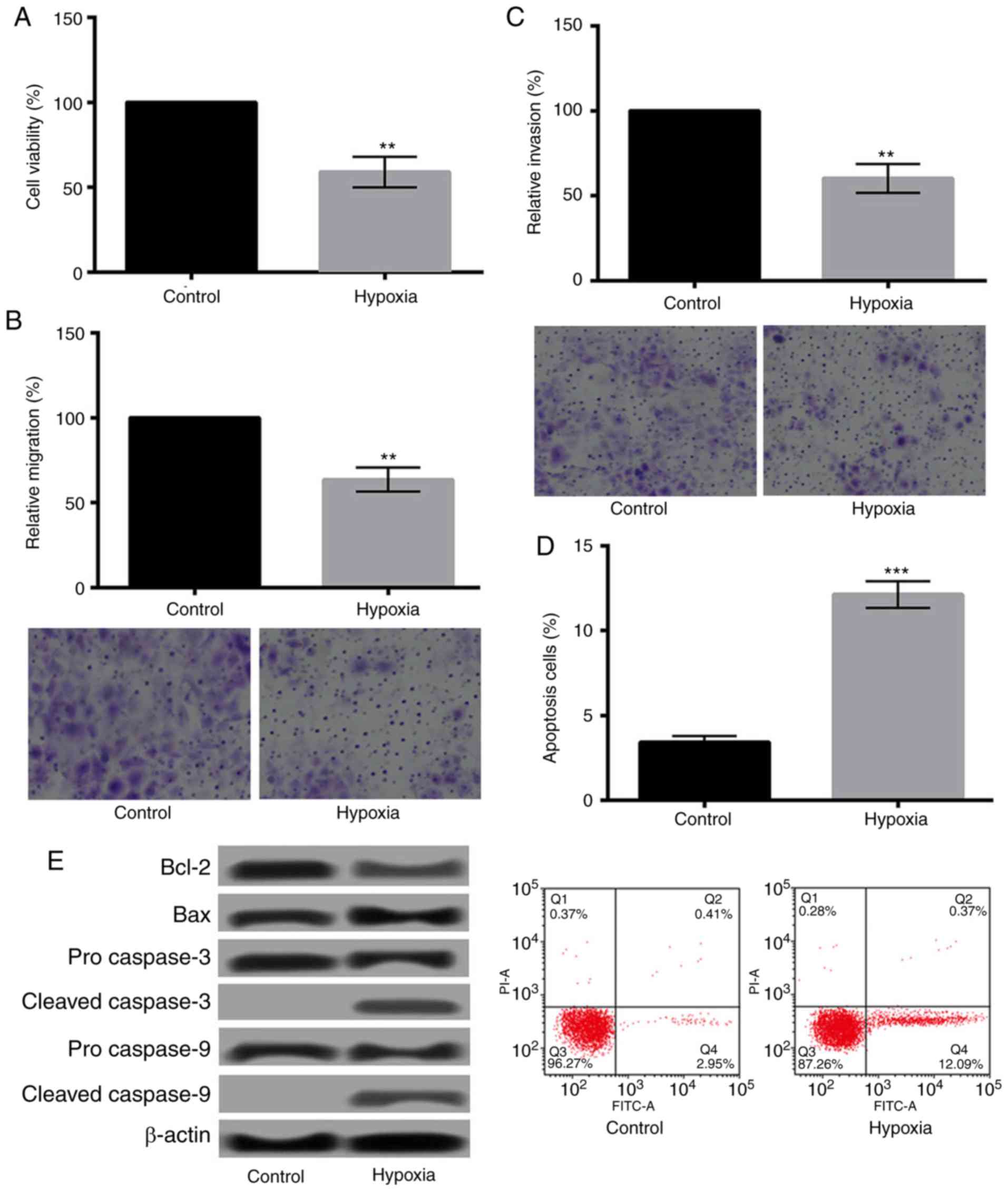
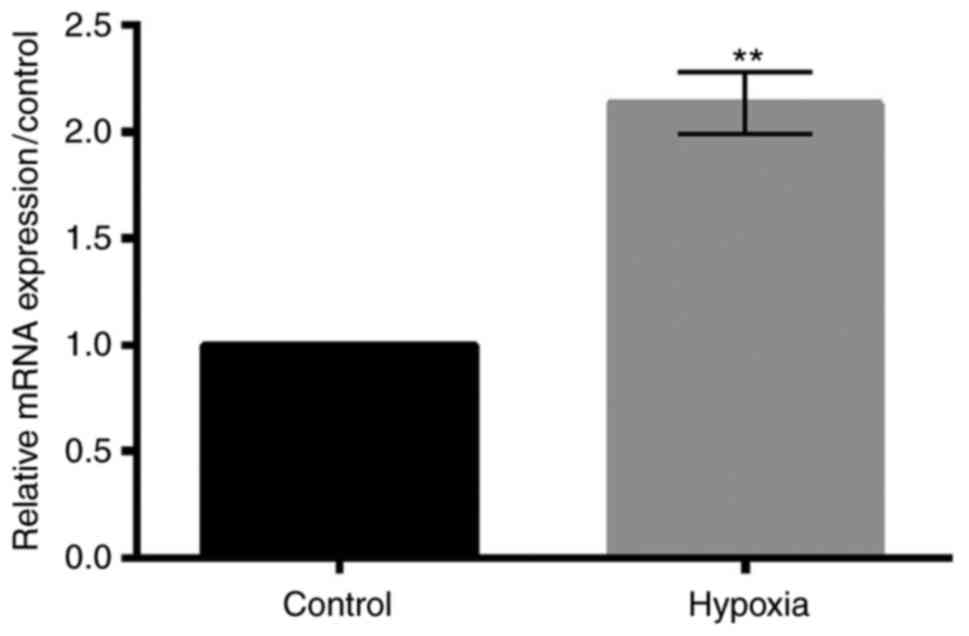
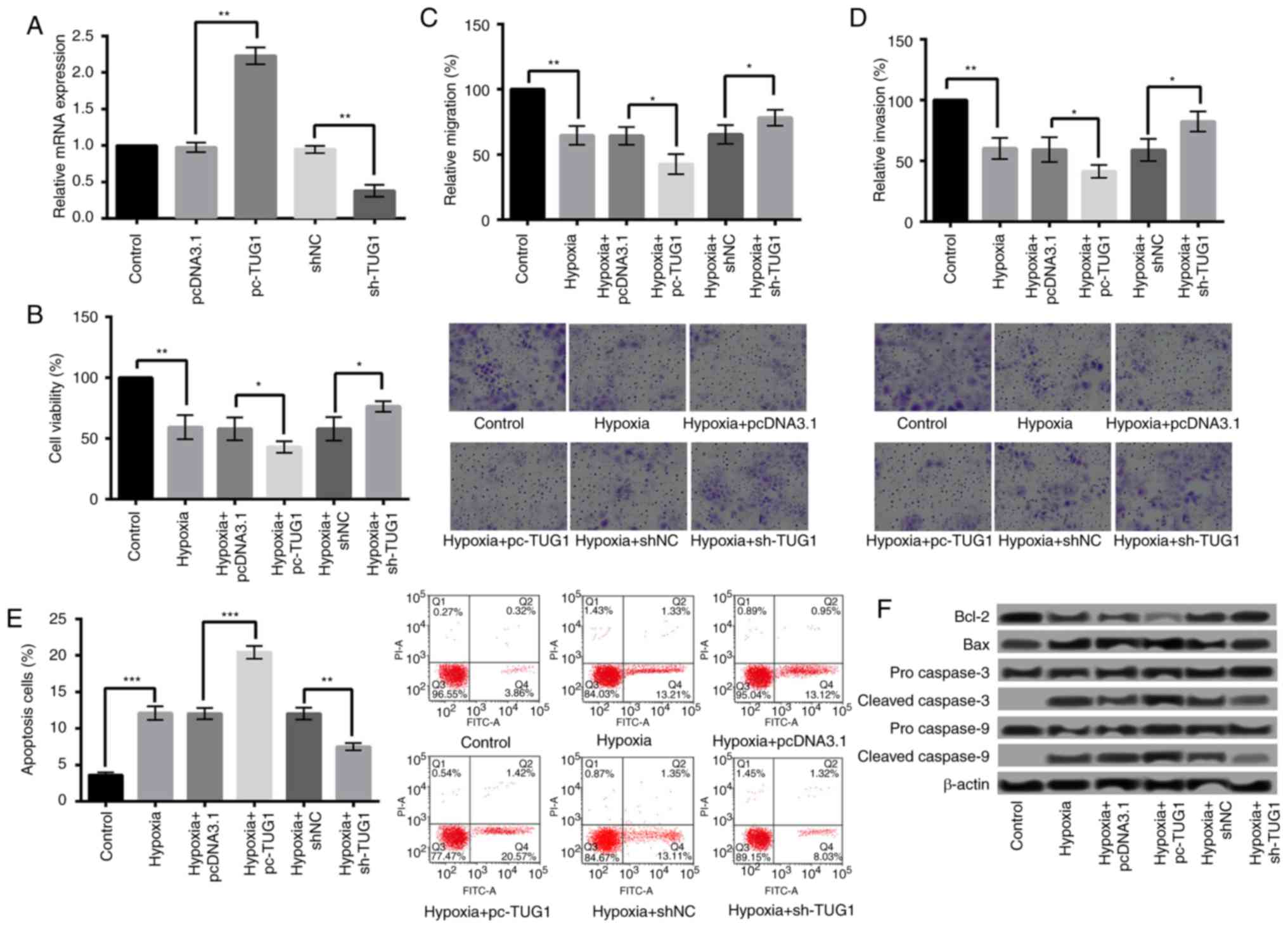
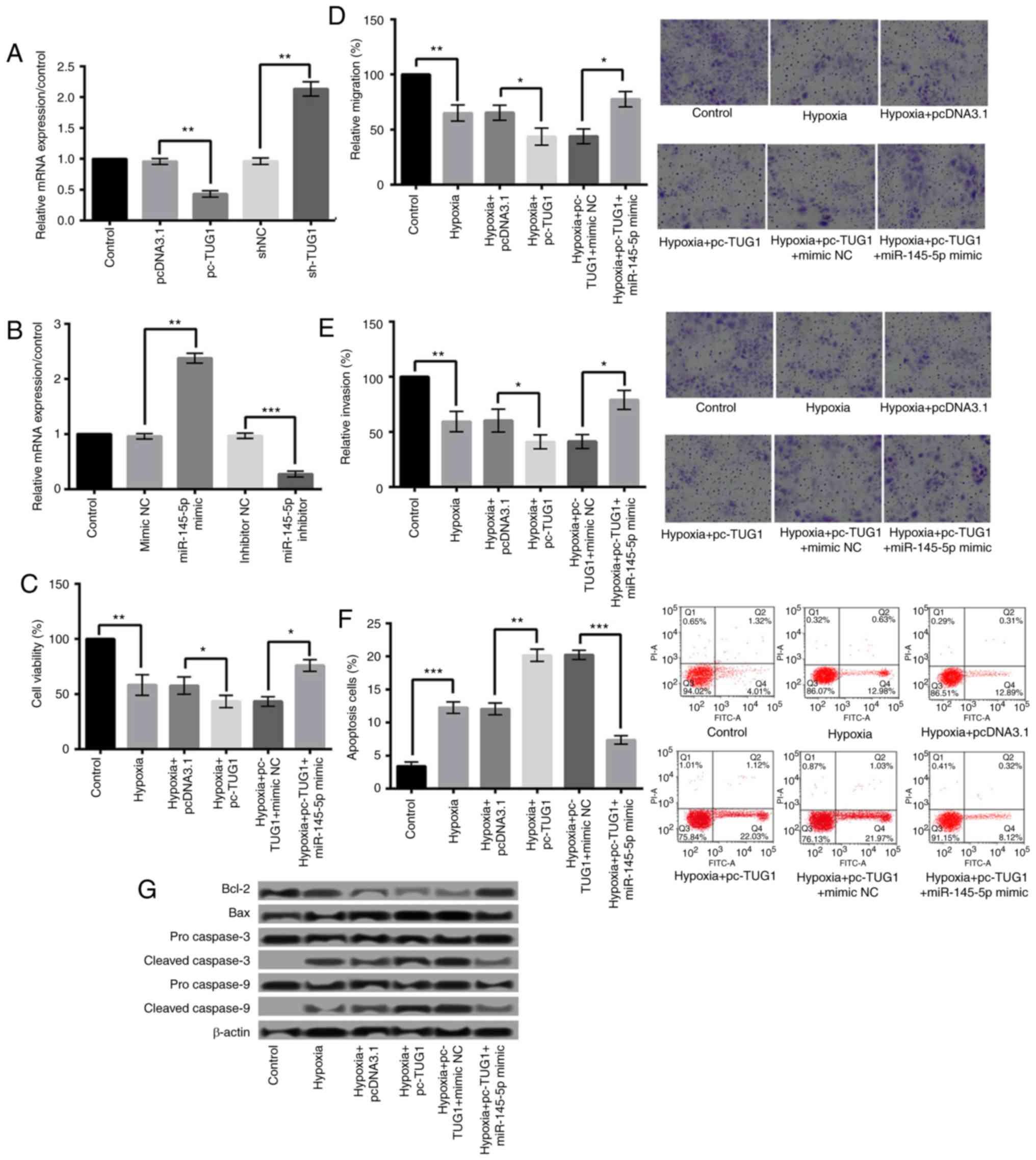
|
1
|
Reimer KA and Ideker RE: Myocardial
ischemia and infarction: Anatomic and biochemical substrates for
ischemic cell death and ventricular arrhythmias. Human Pathol.
18:462–475. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Buja LM, Hagler HK and Willerson JT:
Altered calcium homeostasis in the pathogenesis of myocardial
ischemic and hypoxic injury. Cell Calcium. 9:205–217. 1988.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Farber JL, Chien KR and Mittnacht S Jr:
Myocardial ischemia: The pathogenesis of irreversible cell injury
in ischemia. Am J Pathol. 102:271–281. 1981.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Buja LM: Myocardial ischemia and
reperfusion injury. Cardiovasc Pathol. 14:1–175. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
American College of Emergency Physicians,
; Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, ;
O'Gara PT, Kushner FG, Ascheim DD, Casey DE Jr, Chung MK, de Lemos
JA, Ettinger SM, Fang JC, et al: 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the
management of ST-elevation myocardial infarction: Executive
summary: A report of the american college of cardiology
foundation/american heart association task force on practice
guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 61:485–510. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gartler SM and Riggs AD: Mammalian
X-chromosome inactivation. Annu Rev Genet. 17:155–190. 1983.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shi X, Sun M, Liu H, Yao Y and Song Y:
Long non-coding RNAs: A new frontier in the study of human
diseases. Cancer Lett. 339:159–166. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wapinski O and Chang HY: Long noncoding
RNAs and human disease. Trends Cell Biol. 21:354–361. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li J, Xuan Z and Liu C: Long non-coding
RNAs and complex human diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 14:18790–18808.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Grote P, Wittler L, Hendrix D, Koch F,
Währisch S, Beisaw A, Macura K, Bläss G, Kellis M, Werber M and
Herrmann BG: The tissue-specific lncRNA Fendrr is an essential
regulator of heart and body wall development in the mouse. Dev
Cell. 24:206–214. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ishii N, Ozaki K, Sato H, Mizuno H, Saito
S, Takahashi A, Miyamoto Y, Ikegawa S, Kamatani N, Hori M, et al:
Identification of a novel non-coding RNA, MIAT, that confers risk
of myocardial infarction. J Hum Genet. 51:1087–1099. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yin DD, Zhang EB, You LH, Wang N, Wang LT,
Jin FY, Zhu YN, Cao LH, Yuan QX, De W and Tang W: Downregulation of
lncRNA TUG1 affects apoptosis and insulin secretion in mouse
pancreatic β cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 35:1892–1904. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang Q, Geng PL, Yin P, Wang XL, Jia JP
and Yao J: Down-regulation of long non-coding RNA TUG1 inhibits
osteosarcoma cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis. Asian Pac J
Cancer Prev. 14:2311–2315. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Han Y, Liu Y, Gui Y and Cai Z: Long
intergenic non-coding RNA TUG1 is overexpressed in urothelial
carcinoma of the bladder. J Surg Oncol. 107:555–559. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lomonosova E and Chinnadurai G: BH3-only
proteins in apoptosis and beyond: An overview. Oncogene. 27 Suppl
1:S2–S19. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kubli DA, Quinsay MN, Huang C, Lee Y and
Gustafsson AB: Bnip3 functions as a mitochondrial sensor of
oxidative stress during myocardial ischemia and reperfusion. Am J
Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 295:H2025–H2031. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kubasiak LA, Hernandez OM, Bishopric NH
and Webster KA: Hypoxia and acidosis activate cardiac myocyte death
through the Bcl-2 family protein BNIP3. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
99:pp. 1–12830. 2002; PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Guo K, Searfoss G, Krolikowski D, Pagnoni
M, Franks C, Clark K, Yu KT, Jaye M and Ivashchenko Y: Hypoxia
induces the expression of the pro-apoptotic gene BNIP3. Cell Death
Differ. 8:367–376. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Young TL, Matsuda T and Cepko CL: The
noncoding RNA taurine upregulated gene 1 is required for
differentiation of the murine retina. Curr Biol. 15:501–512. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tan J, Qiu K, Li M and Liang Y:
Double-negative feedback loop between long non-coding RNA TUG1 and
miR-145 promotes epithelial to mesenchymal transition and
radioresistance in human bladder cancer cells. FEBS Lett.
589:3175–3181. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liu Y, Yang S and Zhang X: WITHDRAWN:
Down-regulation of long non-coding RNA TUG1 suppresses melanoma
cell proliferation and induces apoptosis via up-regulating
microRNA-9. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013.
|
|
22
|
Buja LM: Modulation of the myocardial
response to ischemia. Lab Invest. 78:1345–1373. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Buja LM and Entman ML: Modes of myocardial
cell injury and cell death in ischemic heart disease. Circulation.
98:1355–1357. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chen S, Wang M, Yang H, Mao L, He Q, Jin
H, Ye ZM, Luo XY, Xia YP and Hu B: LncRNA TUG1 sponges microRNA-9
to promote neurons apoptosis by up-regulated Bcl2l11 under
ischemia. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 485:167–173. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Spizzo R, Nicoloso MS, Lupini L, Lu Y,
Fogarty J, Rossi S, Zagatti B, Fabbri M, Veronese A, Liu X, et al:
miR-145 participates with TP53 in a death-promoting regulatory loop
and targets estrogen receptor-alpha in human breast cancer cells.
Cell Death Differ. 17:246–254. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xu Q, Liu LZ, Qian X, Chen Q, Jiang Y, Li
D, Lai L and Jiang BH: MiR-145 directly targets p70S6K1 in cancer
cells to inhibit tumor growth and angiogenesis. Nucleic Acids Res.
40:761–774. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lei H, Gao Y and Xu X: LncRNA TUG1
influences papillary thyroid cancer cell proliferation, migration
and EMT formation through targeting miR-145: Acta. Biochim Biophys
Sin (Shsnghai). 49:1–597. 2017.
|
|
28
|
Jia L, Hao F, Wang W and Qu Y: Circulating
miR-145 is associated with plasma high-sensitivity C-reactive
protein in acute ischemic stroke patients. Cell Biochem Funct.
33:314–319. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li R, Yan G, Li Q, Sun H, Hu Y, Sun J and
Xu B: MicroRNA-145 protects cardiomyocytes against hydrogen
peroxide (H2O2)-induced apoptosis through targeting the
mitochondria apoptotic pathway. PLoS One. 7:e449072012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ray R, Chen G, Vande Velde C, Cizeau J,
Park JH, Reed JC, Gietz RD and Greenberg AH: BNIP3 heterodimerizes
with Bcl-2/Bcl-X(L) and induces cell death independent of a Bcl-2
homology 3 (BH3) domain at both mitochondrial and nonmitochondrial
sites. J Biol Chem. 275:1439–1448. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yasuda M, Theodorakis P, Subramanian T and
Chinnadurai G: Adenovirus E1B-19K/BCL-2 interacting protein BNIP3
contains a BH3 domain and a mitochondrial targeting sequence. J
Biol Chem. 273:12415–12421. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bruick RK: Expression of the gene encoding
the proapoptotic Nip3 protein is induced by hypoxia. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 97:pp. 9082–9087. 2000; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Graham RM, Frazier DP, Thompson JW, Haliko
S, Li H, Wasserlauf BJ, Spiga MG, Bishopric NH and Webster KA: A
unique pathway of cardiac myocyte death caused by hypoxia-acidosis.
J Exp Biol. 207:3189–3200. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Deb A: Cell-cell interaction in the heart
via Wnt/β-catenin pathway after cardiac injury. Cardiovasc Res.
102:214–223. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Bergmann MW: WNT signaling in adult
cardiac hypertrophy and remodeling: Lessons learned from cardiac
development. Circ Res. 107:1198–1208. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gessert S and Kühl M: The multiple phases
and faces of wnt signaling during cardiac differentiation and
development. Circ Res. 107:186–199. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|