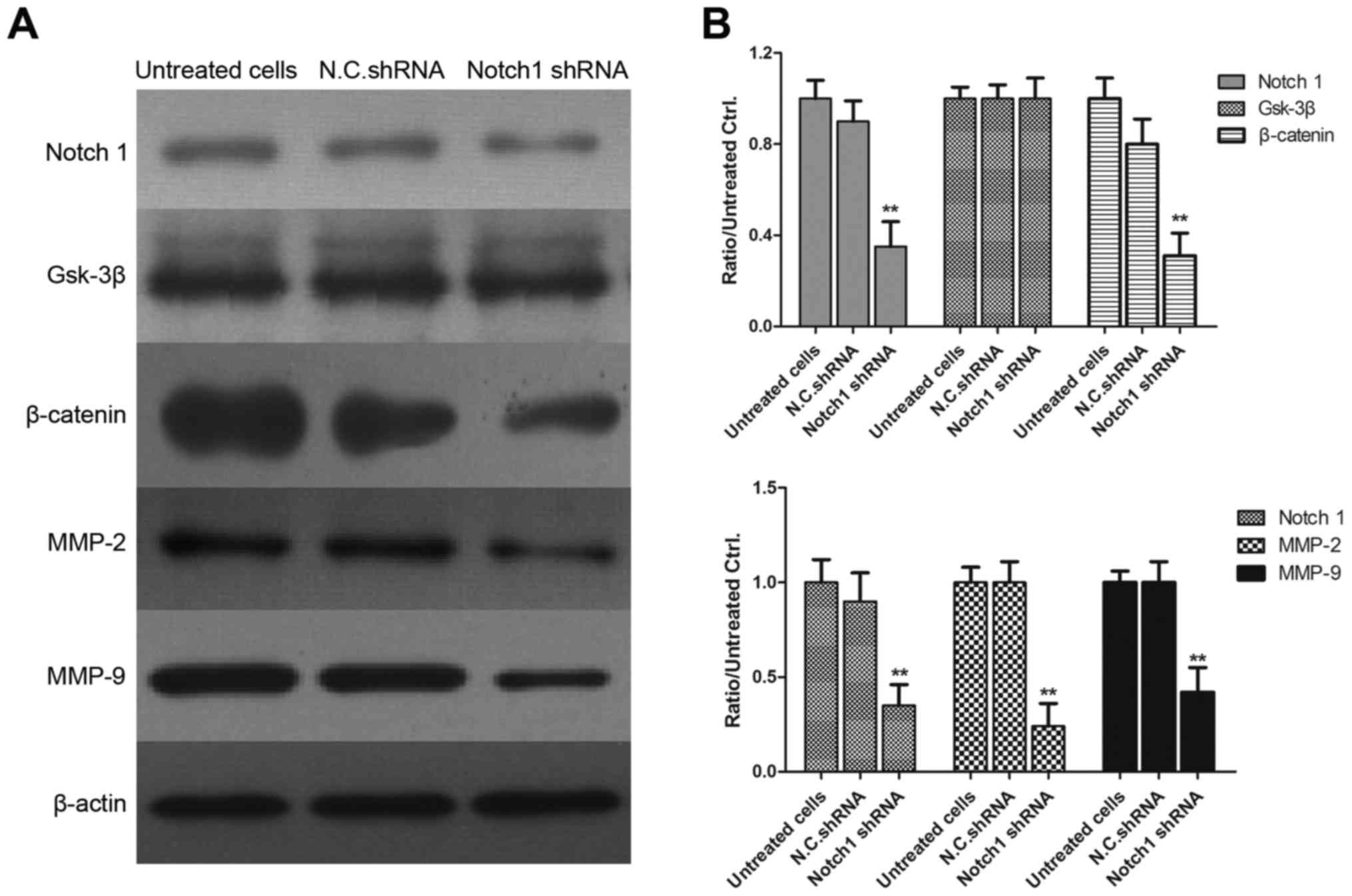
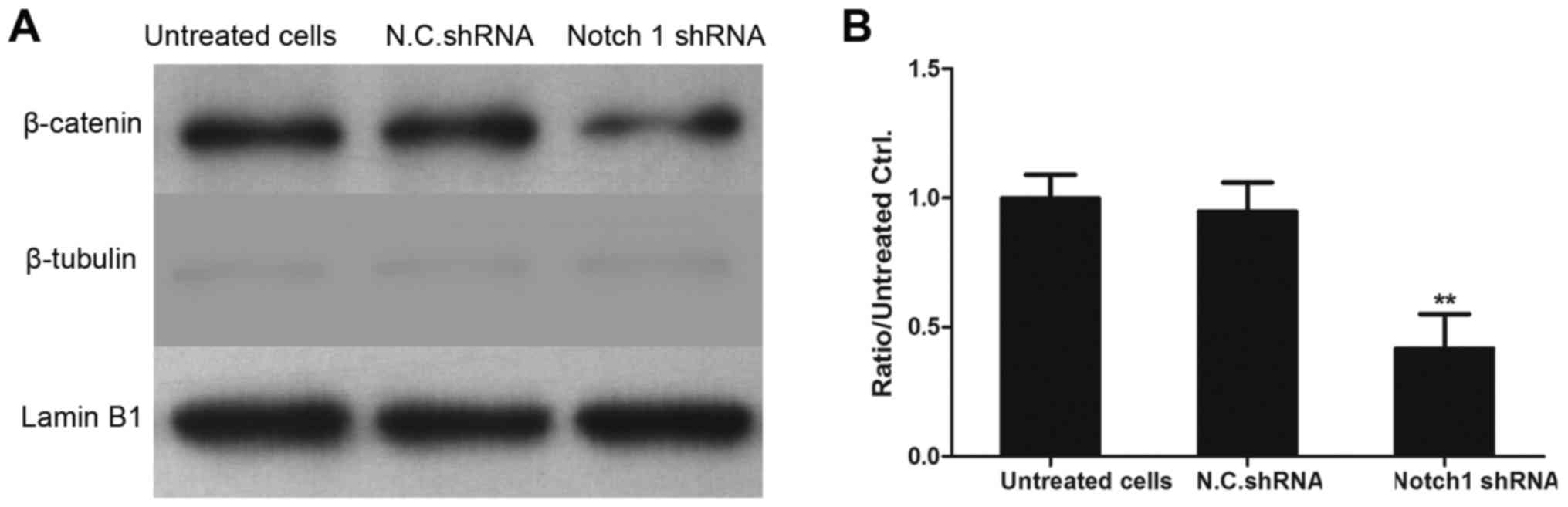
|
1
|
Wang Y, Yu J, Cui R, Lin J and Ding X:
Curcumin in treating breast cancer: A review. J Lab Autom.
21:723–731. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Asif HM, Sultana S, Ahmed S, Akhtar N and
Tariq M: HER-2 positive breast cancer - a mini-review. Asian Pac J
Cancer Prev. 17:1609–1615. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhu L, Li L, Li Y, Wang J and Wang Q:
Chinese herbal medicine as an adjunctive therapy for breast cancer:
A systematic review and meta-analysis. Evid Based Complement
Alternat Med. 2016:94692762016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
George BP and Abrahamse H: A review on
novel breast cancer therapies: Photodynamic therapy and plant
derived agent induced cell death mechanisms. Anticancer Agents Med
Chem. 16:793–801. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Nicolini A, Carpi A, Ferrari P, Biava PM
and Rossi G: Immunotherapy and hormone-therapy in metastatic breast
cancer: A review and an update. Curr Drug Targets. 17:1127–1139.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
van Nijnatten TJ, Schipper RJ, Lobbes MB,
Nelemans PJ, Beets-Tan RG and Smidt ML: The diagnostic performance
of sentinel lymph node biopsy in pathologically confirmed node
positive breast cancer patients after neoadjuvant systemic therapy:
A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Surg Oncol.
41:1278–1287. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bertozzi S, Londero AP, Cedolini C, Uzzau
A, Seriau L, Bernardi S, Bacchetti S, Pasqual EM and Risaliti A:
Prevalence, risk factors, and prognosis of peritoneal metastasis
from breast cancer. Springerplus. 4:6882015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Petekkaya I, Ayyildiz V, Kizilarslanoglu
MC, Sahin U, Gezgen G, Roach EC, Karcaaltincaba M and Altundag K:
Prognosis of breast cancer in patients with peritoneal metastasis.
Breast. 21:420–421. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yasuoka H, Tsujimoto M, Yoshidome K,
Nakahara M, Kodama R, Sanke T and Nakamura Y: Cytoplasmic CXCR4
expression in breast cancer: Induction by nitric oxide and
correlation with lymph node metastasis and poor prognosis. BMC
Cancer. 8:3402008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wu MQ, Hu P, Gao J, Wei WD, Xiao XS, Tang
HL, Li X, Ge QD, Jia WH, Liu RB and Xie XM: Low expression of
tyrosine-protein phosphatase nonreceptor type 12 is associated with
lymph node metastasis and poor prognosis in operable
triple-negative breast cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 14:287–292.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Venkitaraman R, Joseph T, Dhadda A,
Chaturvedi A and Upadhyay S: Prognosis of patients with
triple-negative breast cancer and brain metastasis. Clin Oncol (R
Coll Radiol). 21:729–730. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wikman H, Westphal L, Schmid F, Pollari S,
Kropidlowski J, Sielaff-Frimpong B, Glatzel M, Matschke J, Westphal
M, Iljin K, et al: Loss of CADM1 expression is associated with poor
prognosis and brain metastasis in breast cancer patients.
Oncotarget. 5:3076–3087. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yamamura J, Masuda N, Yasojima H, Mizutani
M, Kuriyama K, Nakamori S, Sekimoto M, Mano M, Tanaka E and Nonaka
M: Clinicopathological factors related to the prognosis of
metastatic breast cancer patients after development of brain
metastasis. Breast Care (Basel). 10:387–392. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li Y, Jin K, van Pelt GW, van Dam H, Yu X,
Mesker WE, Ten Dijke P, Zhou F and Zhang L: c-Myb enhances breast
cancer invasion and metastasis through the Wnt/β-Catenin/Axin2
pathway. Cancer Res. 76:3364–3375. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shi M, Cao M, Song J, Liu Q, Li H, Meng F,
Pan Z, Bai J and Zheng J: PinX1 inhibits the invasion and
metastasis of human breast cancer via suppressing NF-κB/MMP-9
signaling pathway. Mol Cancer. 14:662015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
D'Angelo RC, Ouzounova M, Davis A, Choi D,
Tchuenkam SM, Kim G, Luther T, Quraishi AA, Senbabaoglu Y, Conley
SJ, et al: Notch reporter activity in breast cancer cell lines
identifies a subset of cells with stem cell activity. Mol Cancer
Ther. 14:779–787. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang W and Grivennikov SI: Top Notch
cancer stem cells by paracrine NF-κB signaling in breast cancer.
Breast Cancer Res. 15:3162013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang Q, Yuan Y, Cui J, Xiao T and Jiang
D: Paeoniflorin inhibits proliferation and invasion of breast
cancer cells through suppressing Notch-1 signaling pathway. Biomed
Pharmacother. 78:197–203. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Pei J and Wang B: Notch-1 promotes breast
cancer cells proliferation by regulating LncRNA GAS5. Int J Clin
Exp Med. 8:14464–14471. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xu J, Song F, Jin T, Qin J, Wu J, Wang M,
Wang Y and Liu J: Prognostic values of Notch receptors in breast
cancer. Tumour Biol. 37:1871–1877. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Vinson KE, George DC, Fender AW, Bertrand
FE and Sigounas G: The Notch pathway in colorectal cancer. Int J
Cancer. 138:1835–1842. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pant S, Jones SF, Kurkjian CD, Infante JR,
Moore KN, Burris HA, McMeekin DS, Benhadji KA, Patel BK, Frenzel
MJ, et al: A first-in-human phase I study of the oral Notch
inhibitor, LY900009, in patients with advanced cancer. Eur J
Cancer. 56:1–9. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Mizuma M, Rasheed ZA, Yabuuchi S, Omura N,
Campbell NR, de Wilde RF, De Oliveira E, Zhang Q, Puig O, Matsui W,
et al: The gamma secretase inhibitor MRK-003 attenuates pancreatic
cancer growth in preclinical models. Mol Cancer Ther. 11:1999–2009.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jiang X, Li T and Liu RH:
2α-Hydroxyursolic acid inhibited cell proliferation and induced
apoptosis in MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells through the
p38/MAPK signal transduction pathway. J Agric Food Chem.
64:1806–1816. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang HT and Wang CQ: 27-O-(E)-p-coumaric
acyl ursolic acid via JNK/SAPK signal pathway regulates apoptosis
of human breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cell line. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za
Zhi. 40:722–726. 2015.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang Y, Song M, Cui ZS, Li CY, Xue XX, Yu
M, Lu Y, Zhang SY, Wang EH and Wen YY: Down-regulation of TSG101 by
small interfering RNA inhibits the proliferation of breast cancer
cells through the MAPK/ERK signal pathway. Histol Histopathol.
26:87–94. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lin YJ, Huang YH, Zhen YZ, Liu XJ and Zhen
YS: Rhein lysinate induces apoptosis in breast cancer SK-Br-3 cells
by inhibiting HER-2 signal pathway. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 43:1099–1105.
2008.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhou X, Teng L and Wang M: Distinct
prognostic values of four-Notch-receptor mRNA expression in ovarian
cancer. Tumour Biol. 37:6979–6985. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ranogajec I, Jakić-Razumović J, Puzović V
and Gabrilovac J: Prognostic value of matrix metalloproteinase-2
(MMP-2), matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) and aminopeptidase
N/CD13 in breast cancer patients. Med Oncol. 29:561–569. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yi SJ, Li LL and Tu WB: MiR-214 negatively
regulates proliferation and WNT/β-catenin signaling in breast
cancer. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 20:5148–5154. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Huang Y, Zhao K, Hu Y, Zhou Y, Luo X, Li
X, Wei L, Li Z, You Q, Guo Q and Lu N: Wogonoside inhibits
angiogenesis in breast cancer via suppressing Wnt/β-catenin
pathway. Mol Carcinog. 55:1598–1612. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|