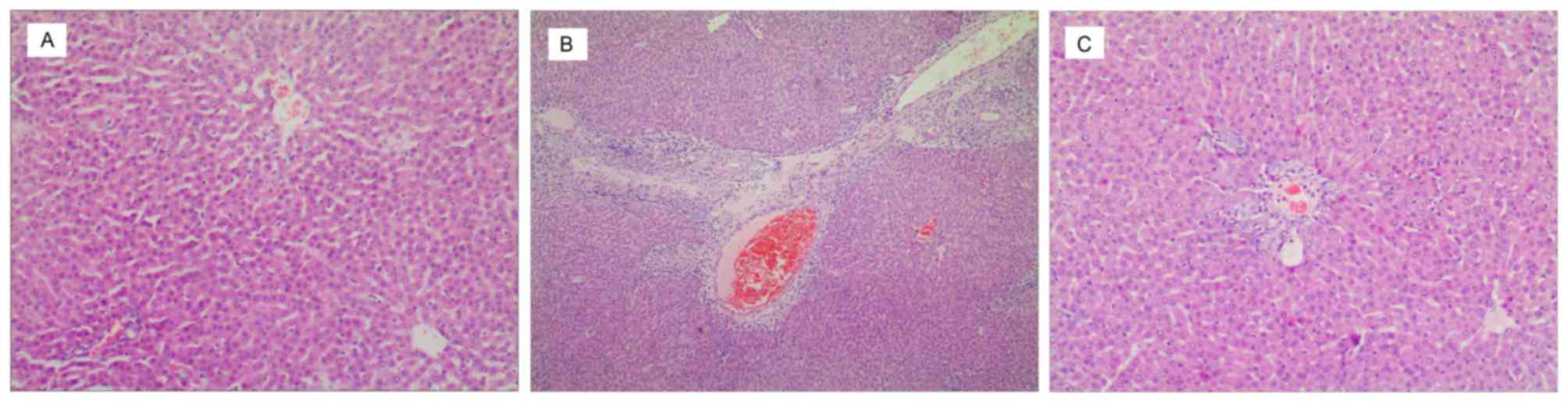
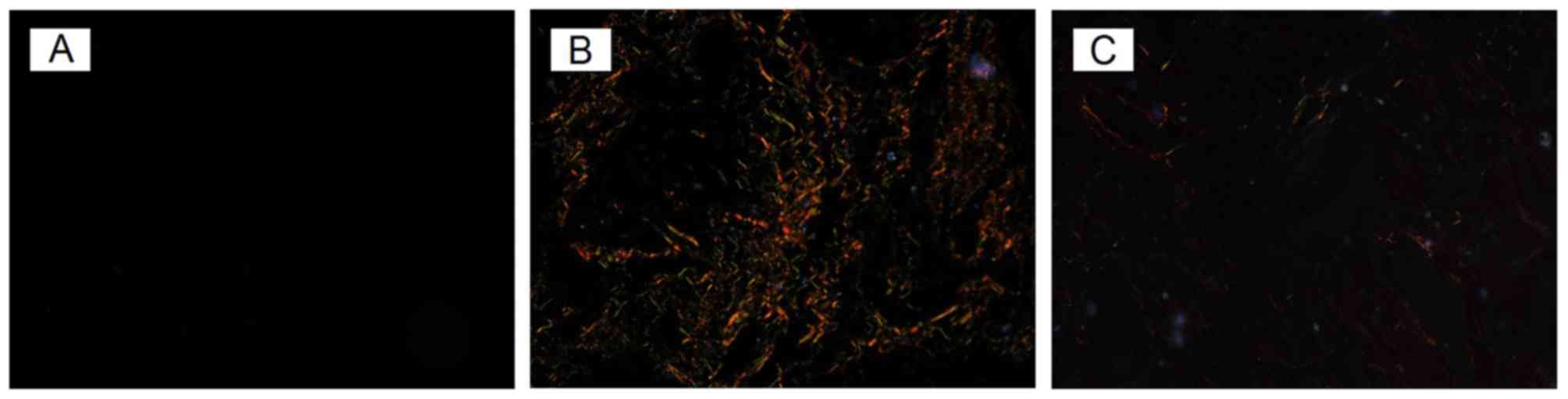
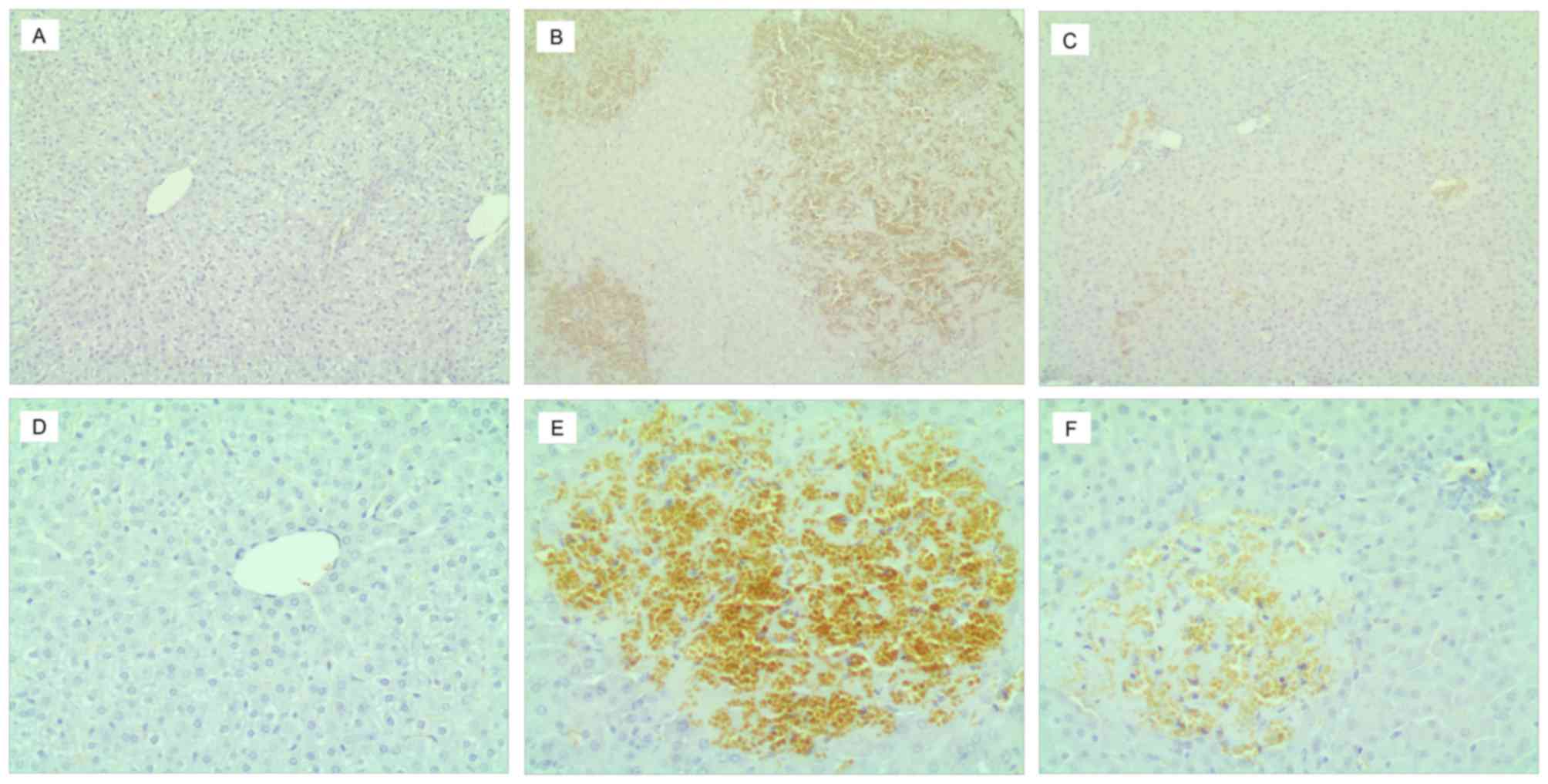
|
1
|
Fischler B and Lamireau T: Cholestasis in
the newborn and infant. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 38:263–267.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Catzola A and Vajro P: Management options
for cholestatic liver disease in children. Expert Rev Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 11:1019–1030. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hernandez-Gea V and Friedman SL:
Pathogenesis of liver fibrosis. Annu Rev Pathol. 6:425–456. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lindor KD, Gershwin ME, Poupon R, Kaplan
M, Bergasa NV and Heathcote EJ; American Association for Study of
Liver Diseases, : Primary biliary cirrhosis. Hepatology.
50:291–308. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
European Association for the Study of the
Liver, . EASL clinical practice guidelines: Management of
cholestatic liver diseases. J Hepatol. 51:237–267. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Orso G, Mandato C, Veropalumbo C, Cecchi
N, Garzi A and Vajro P: Pediatric parenteral nutrition-associated
liver disease and cholestasis: Novel advances in
pathomechanisms-based prevention and treatment. Dig Liver Dis.
48:215–222. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Qiu YL, Gong JY, Feng JY, Wang RX, Han J,
Liu T, Lu Y, Li LT, Zhang MH, Sheps JA, et al: Defects in myosin VB
are associated with a spectrum of previously undiagnosed low
γ-glutamyltransferase cholestasis. Hepatology. 65:1655–1669. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tang N, Zhang Y, Liu Z, Fu T, Liang Q and
Ai X: Correlation analysis between four serum biomarkers of liver
fibrosis and liver function in infants with cholestasis. Biomed
Rep. 5:107–112. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fang YQ, Lv DX, Jia W, Li J, Deng YQ, Wang
Y, Yu M and Wang GQ: Case-control study on prednisolone combined
with ursodeoxycholic acid and azathioprine in pure primary biliary
cirrhosis with high levels of immunoglobulin G and transaminases:
Efficacy and safety analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 93:e1042014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Rudic JS, Poropat G, Krstic MN, Bjelakovic
G and Gluud C: Ursodeoxycholic acid for primary biliary cirrhosis.
Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 12:CD0005512012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Simić D, Milojević I, Bogićević D,
Milenović M, Radlović V, Drasković B, Benka AU, Sindjić S and
Maksimović R: Preventive effect of ursodeoxycholic acid on
parenteral nutrition-associated liver disease in infants. Srp Arh
Celok Lek. 142:184–188. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hatano R, Kawaguchi K, Togashi F, Sugata
M, Masuda S and Asano S: Ursodeoxycholic acid ameliorates
intrahepatic cholestasis independent of biliary bicarbonate
secretion in Vil2kd/kd mice. Biol Pharm Bull. 40:34–42. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhou WC, Zhang QB and Qiao L: Pathogenesis
of liver cirrhosis. World J Gastroenterol. 20:7312–7324. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mizuochi T, Kimura A, Suzuki M, Ueki I,
Takei H, Nittono H, Kakiuchi T, Shigeta T, Sakamoto S, Fukuda A, et
al: Successful heterozygous living donor liver transplantation for
an oxysterol 7α-hydroxylase deficiency in a Japanese patient. Liver
Transpl. 17:1059–1065. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang L, Wu G, Wu F, Jiang N and Lin Y:
Geniposide attenuates ANIT-induced cholestasis through regulation
of transporters and enzymes involved in bile acids homeostasis in
rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 20:178–185. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Tang N, Zhang Y, Liu Z, Ai X and Liang Q:
Correlation of four potential biomarkers of liver fibrosis with
liver function and grade of hepatic fibrosis in a neonatal
cholestatic rat model. Mol Med Rep. 16:415–421. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Knodell RG, Ishak KG, Black WC, Chen TS,
Craig R, Kaplowitz N, Kiernan TW and Wollman J: Formulation and
application of a numerical scoring system for assessing
histological activity in asymptomatic chronic active hepatitis.
Hepatology. 1:431–435. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang T, Zhou ZX, Sun LX, Li X, Xu ZM, Chen
M, Zhao GL, Jiang ZZ and Zhang LY: Resveratrol effectively
attenuates α-naphthyl-isothiocyanate-induced acute cholestasis and
liver injury through choleretic and anti-inflammatory mechanisms.
Acta Pharmacol Sin. 35:1527–1536. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Connolly AK, Price SC, Connelly JC and
Hinton RH: Early changes in bile duct lining cells and hepatocytes
in rats treated with alpha-naphthylisothiocyanate. Toxicol Appl
Pharmacol. 93:208–219. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kossor DC, Meunier PC, Handler JA, Sozio
RS and Goldstein RS: Temporal relationship of changes in
hepatobiliary function and morphology in rats following
alpha-naphthylisothiocyanate (ANIT) administration. Toxico1 Appl
Pharmacol. 119:108–114. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Golbar HM, Izawa T, Yano R, Ichikawa C,
Sawamoto O, Kuwamura M, Lamarre J and Yamate J: Immunohistochemical
characterization of macrophages and myofibroblasts in
α-Naphthylisoth-iocyanate (ANIT)-induced bile duct injury and
subsequent fibrogenesis in rats. Toxicol Pathol. 39:795–808. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tarantino G, Finelli C, Colao A, Capone D,
Tarantino M, Grimaldi E, Chianese D, Gioia S, Pasanisi F, Contaldo
F, et al: Are hepatic steatosis and carotid intima media thickness
associated in obese patients with normal or slightly elevated
gamma-glutamyl-transferase? J Transl Med. 10:502012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tavian D, Degiorgio D, Roncaglia N,
Vergani P, Cameroni I, Colombo R and Coviello DA: A new splicing
site mutation of the ABCB4 gene in intrahepatic cholestasis of
pregnancy with raised serum gamma-GT. Dig Liver Dis. 41:671–675.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lurie Y, Webb M, Cytter-Kuint R,
Shteingart S and Lederkremer GZ: Non-invasive diagnosis of liver
fibrosis and cirrhosis. World J Gastroenterol. 21:11567–11583.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Matsui S, Yamane T, Takita T, Oishi Y and
Kobayashi-Hattori K: The hypocholesterolemic activity of Momordica
charantia fruit is mediated by the altered cholesterol- and bile
acid-regulating gene expression in rat liver. Nutr Res. 33:580–585.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Soroka CJ, Mennone A, Hagey LR, Ballatori
N and Boyer JL: Mouse organic solute transporter alpha deficiency
enhances renal excretion of bile acids and attenuates cholestasis.
Hepatology. 51:181–190. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Geenes V, Lövgren-Sandblom A, Benthin L,
Lawrance D, Chambers J, Gurung V, Thornton J, Chappell L, Khan E,
Dixon P, et al: The reversed feto-maternal bile acid gradient in
intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy is corrected by
ursodeoxycholic acid. PLoS One. 9:e838282014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Poupon R: Ursodeoxycholic acid and
bile-acid mimetics as therapeutic agents for cholestatic liver
diseases: An overview of their mechanisms of action. Clin Res
Hepatol Gastroenterol. 36 Suppl 1:S3–S12. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ozel Coskun BD, Yucesoy M, Gursoy S,
Baskol M, Yurci A, Yagbasan A, Doğan S and Baskol G: Effects of
ursodeoxycholic acid therapy on carotid intima media thickness,
apolipoprotein A1, apolipoprotein B, and apolipoprotein B/A1 ratio
in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
27:142–149. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kim MD, Kim SS, Cha HY, Jang SH, Chang DY,
Kim W, Suh-Kim H and Lee JH: Therapeutic effect of hepatocyte
growth factor-secreting mesenchymal stem cells in a rat model of
liver fibrosis. Exp Mol Med. 46:e1102014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Friedman SL: Hepatic fibrosis-overview.
Toxicology. 254:120–129. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Suk KT, Kim DY, Sohn KM and Kim DJ:
Biomarkers of liver fibrosis. Adv Clin Chem. 62:33–122. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
El-Mezayen HA, Habib S, Marzok HF and Saad
MH: Diagnostic performance of collagen IV and laminin for the
prediction of fibrosis and cirrhosis in chronic hepatitis C
patients: A multicenter study. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
27:378–385. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lee HH, Seo YS, Um SH, Won NH, Yoo H, Jung
ES, Kwon YD, Park S, Keum B, Kim YS, et al: Usefulness of
non-invasive markers for predicting significant fibrosis in
patients with chronic liver disease. J Korean Med Sci. 25:67–74.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
El-Shabrawi MH, Zein El Abedin MY, Omar N,
Kamal NM, Elmakarem SA, Khattab S, El-Sayed HM, El-Hennawy A and
Ali AS: Predictive accuracy of serum hyaluronic acid as a
non-invasive marker of fibrosis in a cohort of multi-transfused
Egyptian children with β-thalassaemia major. Arab J Gastroenterol.
13:45–48. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Nath NC, Rahman MA, Khan MR, Hasan MS,
Bhuiyan TM, Hoque MN, Kabir MM, Raha AK and Jahan B: Serum
hyaluronic acid as a predictor of fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B
and C virus infection. Mymensingh Med J. 20:614–619.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Nobili V, Alisi A, Torre G, De Vito R,
Pietrobattista A, Morino G, De Ville De Goyet J, Bedogni G and
Pinzani M: Hyaluronic acid predicts hepatic fibrosis in children
with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Transl Res. 156:229–234.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Li ZX, He Y, Wu J, Liang DM, Zhang BL,
Yang H, Wang LL, Ma Y and Wei KL: Noninvasive evaluation of hepatic
fibrosis in children with infant hepatitis syndrome. World J
Gastroenterol. 12:7155–7160. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Paumgartner G and Beuers U:
Ursodeoxycholic acid in cholestatic liver disease: Mechanisms of
action and therapeutic use revisited. Hepatology. 36:525–531. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Alaca N, Özbeyli D, Uslu S, Şahin HH,
Yiğittürk G, Kurtel H, Öktem G and Çağlayan Yeğen B: Treatment with
milk thistle extract (Silybum marianum), ursodeoxycholic acid, or
their combination attenuates cholestatic liver injury in rats: Role
of the hepatic stem cells. Turk J Gastroenterol. 28:476–484. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|