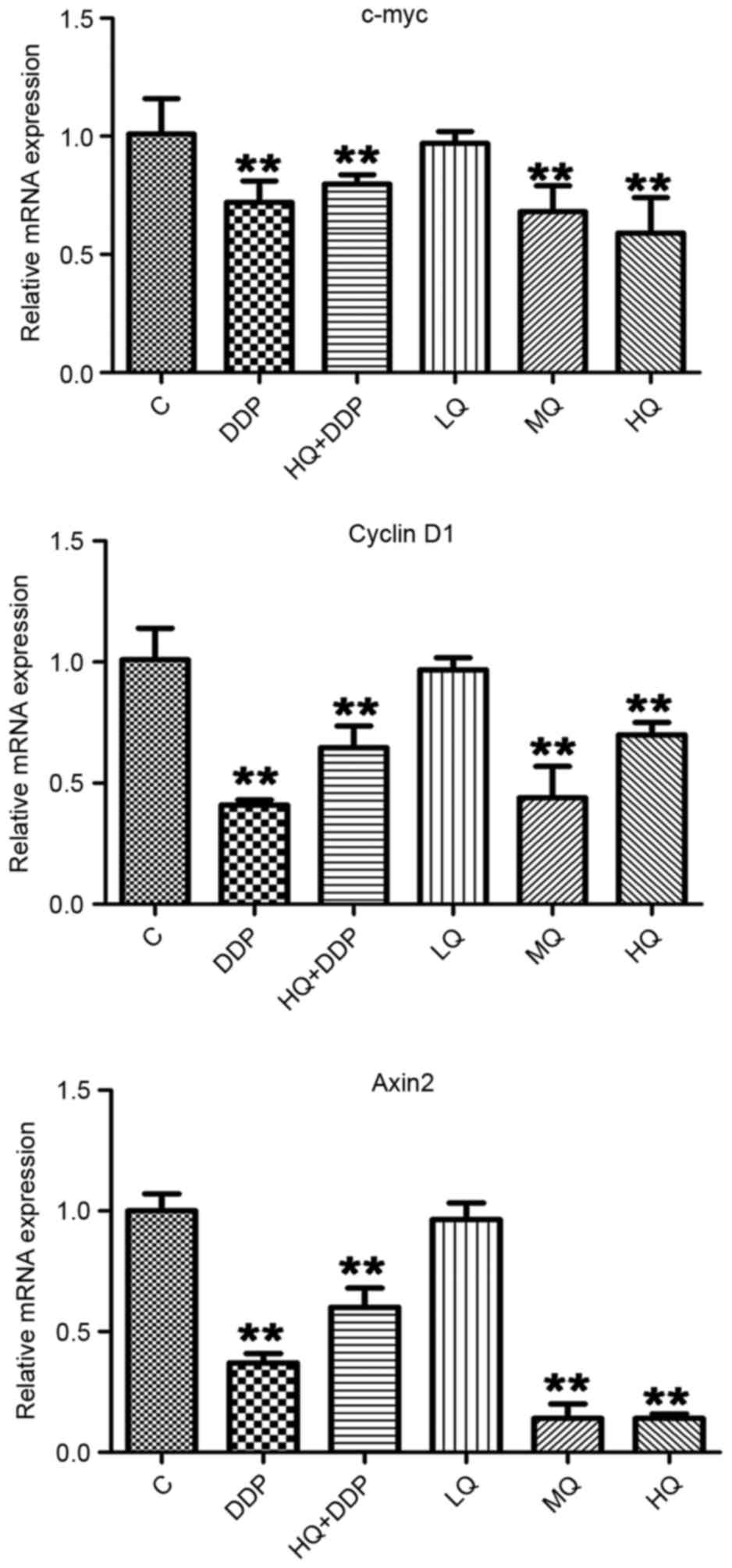
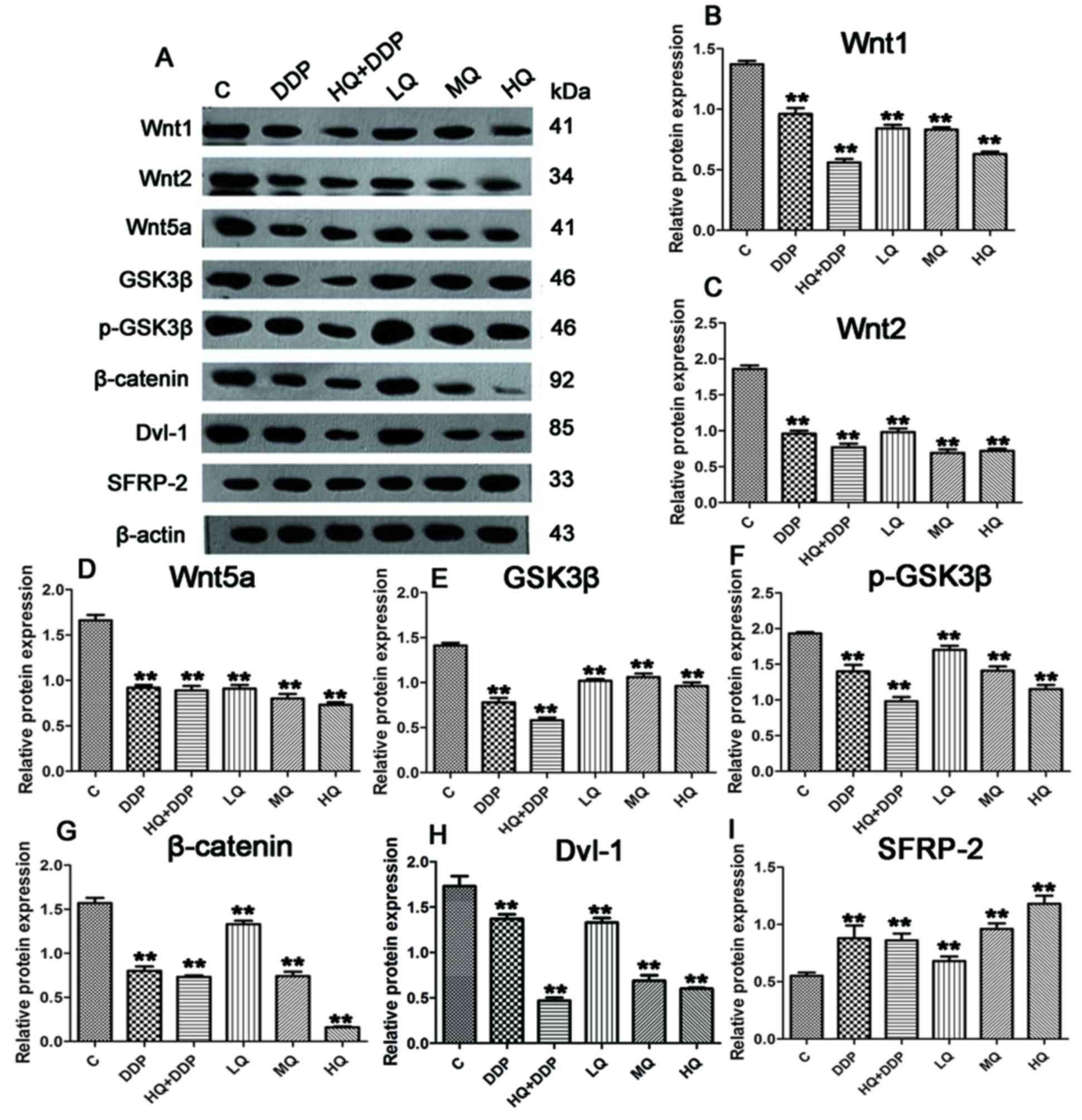
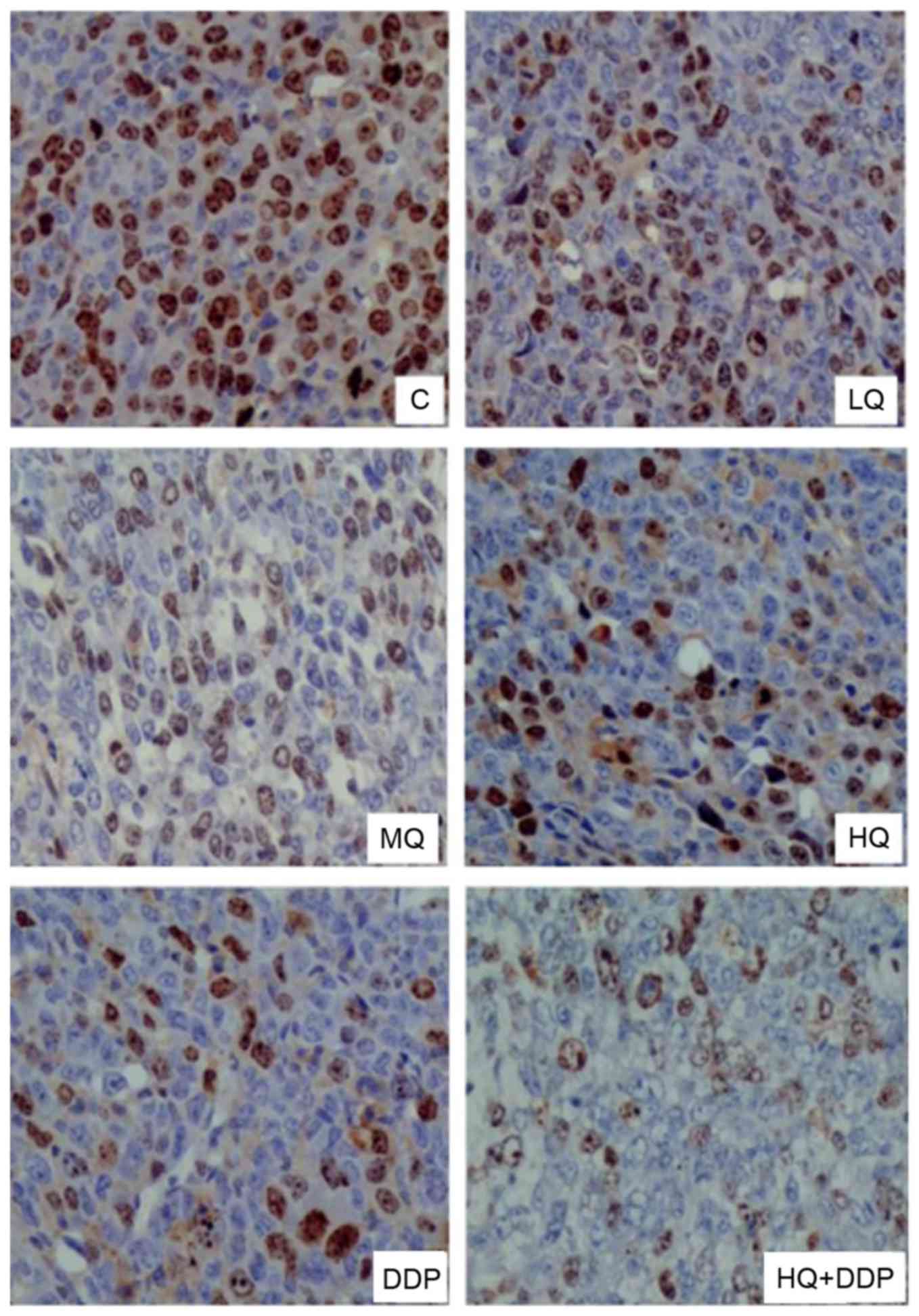
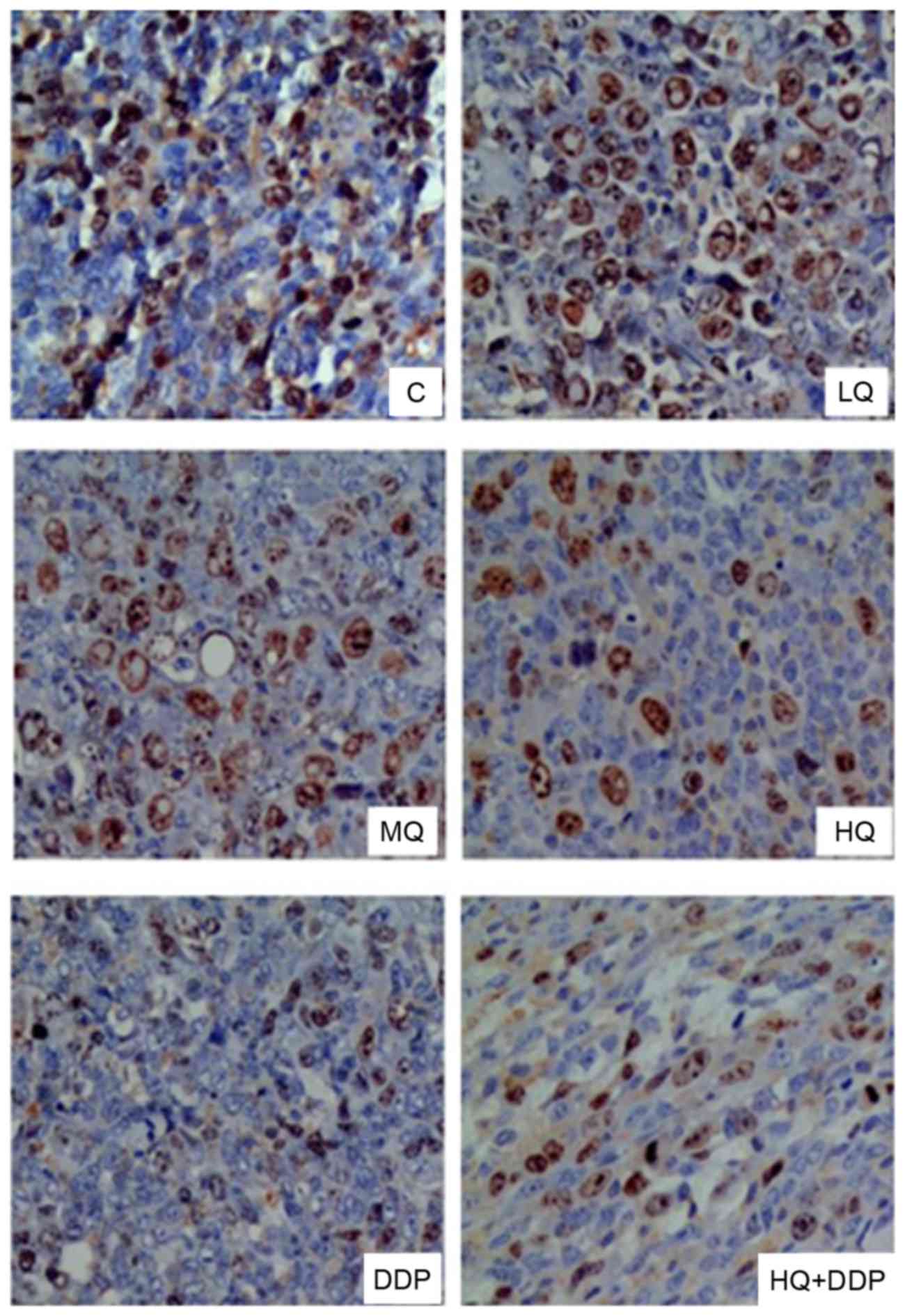
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hwang KE and Kim HR: Response evaluation
of chemotherapy for lung cancer. Tuberc Respir Dis (Seoul).
80:136–142. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yu N, Xiong Y and Wang C: Bu-Zhong-Yi-Qi
decoction, the water extract of chinese traditional herbal
medicine, enhances cisplatin cytotoxicity in A549/DDP cells through
induction of apoptosis and autophagy. Biomed Res Int.
2017:36927972017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Somasundaram A and Burns TF: The next
generation of immunotherapy: Keeping lung cancer in check. J
Hematol Oncol. 10:872017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ou Y, Zhai D, Wu N and Li X:
Downregulation of miR-363 increases drug resistance in
cisplatin-treated HepG2 by dysregulating Mcl-1. Gene. 572:116–122.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lin HQ, Gong AG, Wang HY, Duan R, Dong TT,
Zhao KJ and Tsim KW: Danggui Buxue Tang (Astragali Radix and
Angelicae Sinensis Radix) for menopausal symptoms: A review. J
Ethnopharmacol. 199:205–210. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liu Z, Chen S, Cai J, Zhang E, Lan L,
Zheng J, Liao L, Yang X, Zhou C and Du J: Traditional Chinese
medicine syndrome-related herbal prescriptions in treatment of
malignant tumors. J Tradit Chin Med. 33:19–26. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang X, Tong J and Li Z: Qiyusanlong
decoction inhibits the level of PD-1/PD-L1 in mice bearing Lewis
lung carcinoma. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 32:770–774.
2016.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jiang Q, He M, Guan S, Ma M, Wu H, Yu Z,
Jiang L, Wang Y, Zong X, Jin F and Wei M: MicroRNA-100 suppresses
the migration and invasion of breast cancer cells by targeting
FZD-8 and inhibiting Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Tumour Biol.
37:5001–5011. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhan P, Zhang B, Xi GM, Wu Y, Liu HB, Liu
YF, Xu WJ, Zhu QQ, Cai F, Zhou ZJ, et al: PRC1 contributes to
tumorigenesis of lung adenocarcinoma in association with the
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Mol Cancer. 16:1082017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hu T and Li C: Convergence between
Wnt-β-catenin and EGFR signaling in cancer. Mol Cancer. 9:2362010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shang S, Hua F and Hu ZW: The regulation
of β-catenin activity and function in cancer: Therapeutic
opportunities. Oncotarget. 8:33972–33989. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Salahshor S, Naidoo R, Serra S, Shih W,
Tsao MS, Chetty R and Woodgett JR: Frequent accumulation of nuclear
E-cadherin and alterations in the Wnt signaling pathway in
esophageal squamous cell carcinomas. Mod Pathol. 21:271–281. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ponta H, Sherman L and Herrlich PA: CD44:
From adhesion molecules to signalling regulators. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 4:33–45. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang S, Zhu L, Zuo W, Zeng Z, Huang L, Lin
F, Lin R, Wang J, Lu J, Wang Q, et al: MicroRNA-mediated epigenetic
targeting of survivin significantly enhances the antitumor activity
of paclitaxel against non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget.
7:37693–37713. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhuang B, Du L, Xu H, Xu X, Wang C, Fan Y,
Cong M, Yin J, Li H and Guan H: Self-assembled Micelle Loading
Cabazitaxel for therapy of Lung Cancer. Int J Pharm. 499:146–155.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Taixiang W, Munro AJ and Guanjian L:
Chinese medical herbs for chemotherapy side effects in colorectal
cancer patients. Cochrane Database Syst Rev: CD004540. 2005.
|
|
19
|
Xiao WL, Motley TJ, Unachukwu UJ, Lau CB,
Jiang B, Hong F, Leung PC, Wang QF, Livingston PO, Cassileth BR and
Kennelly EJ: Chemical and genetic assessment of variability in
commercial Radix Astragali (Astragalus spp.) by ion trap LC-MS and
nuclear ribosomal DNA barcoding sequence analyses. J Agric Food
Chem. 59:1548–1556. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tai Y, Sun YM, Zou X, Pan Q, Lan YD, Huo
Q, Zhu JW, Guo F, Zheng CQ, Wu CZ and Liu H: Effect of Polygonatum
odoratum extract on human breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cell
proliferation and apoptosis. Exp Ther Med. 12:2681–2687. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wu L, Liu T, Xiao Y, Li X, Zhu Y, Zhao Y,
Bao J and Wu C: Polygonatum odoratum lectin induces apoptosis and
autophagy by regulation of microRNA-1290 and microRNA-15a-3p in
human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells. Int J Biol Macromol.
85:217–226. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ma W, Liu R, Qi J and Zhang Y: Extracts of
centipede Scolopendra subspinipes mutilans induce cell cycle arrest
and apoptosis in A375 human melanoma cells. Oncol Lett. 8:414–420.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yang MY, Hung CH, Chang CH, Tseng TH and
Wang CJ: Solanum nigrum suppress angiogenesis-mediated tumor growth
through inhibition of the AKT/mTOR pathway. Am J Chin Med.
44:1273–1288. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liu X, Xu F, Wang G, Diao X and Li Y:
Kanglaite injection plus chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for
non-small cell lung cancer patients: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 69:381–411. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cheng J, Han W, Wang Z, Shao Y, Wang Y and
Zhang Y, Li Z, Xu X and Zhang Y: Hepatocellular carcinoma growth is
inhibited by euphorbia helioscopia L. Extract in nude mice
xenografts. Biomed Res Int. 2015:6010152015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kocaadam B and Şanlier N: Curcumin, an
active component of turmeric (Curcuma longa), and its effects on
health. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 57:2889–2895. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
MacDonald BT, Tamai K and He X:
Wnt/beta-catenin signaling: Components, mechanisms, and diseases.
Dev Cell. 17:9–26. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhao Y, Yang ZQ, Wang Y, Miao Y, Liu Y,
Dai SD, Han Y and Wang EH: Dishevelled-1 and dishevelled-3 affect
cell invasion mainly through canonical and noncanonical Wnt
pathway, respectively and associate with poor prognosis in nonsmall
cell lung cancer. Mol Carcinog. 49:760–770. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liu Y, Zhou Q, Zhou D, Huang C, Meng X and
Li J: Secreted frizzled-related protein 2-mediated cancer events:
Friend or foe? Pharmacol Rep. 69:403–408. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang J, Xiao L, Luo CH, Zhou H, Zeng L,
Zhong J, Tang Y, Zhao XH, Zhao M and Zhang Y: CD44v6 promotes
β-catenin and TGF-β expression, inducing aggression in ovarian
cancer cells. Mol Med Rep. 11:3505–3510. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sun W and Chen G: Impact and mechanism of
non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs combined with
chemotherapeutic drugs on human lung cancer-nude mouse transplanted
tumors. Oncol Lett. 11:4193–4199. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Garg H, Suri P, Gupta JC, Talwar GP and
Dubey S: Survivin: A unique target for tumor therapy. Cancer Cell
Int. 16:492016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|