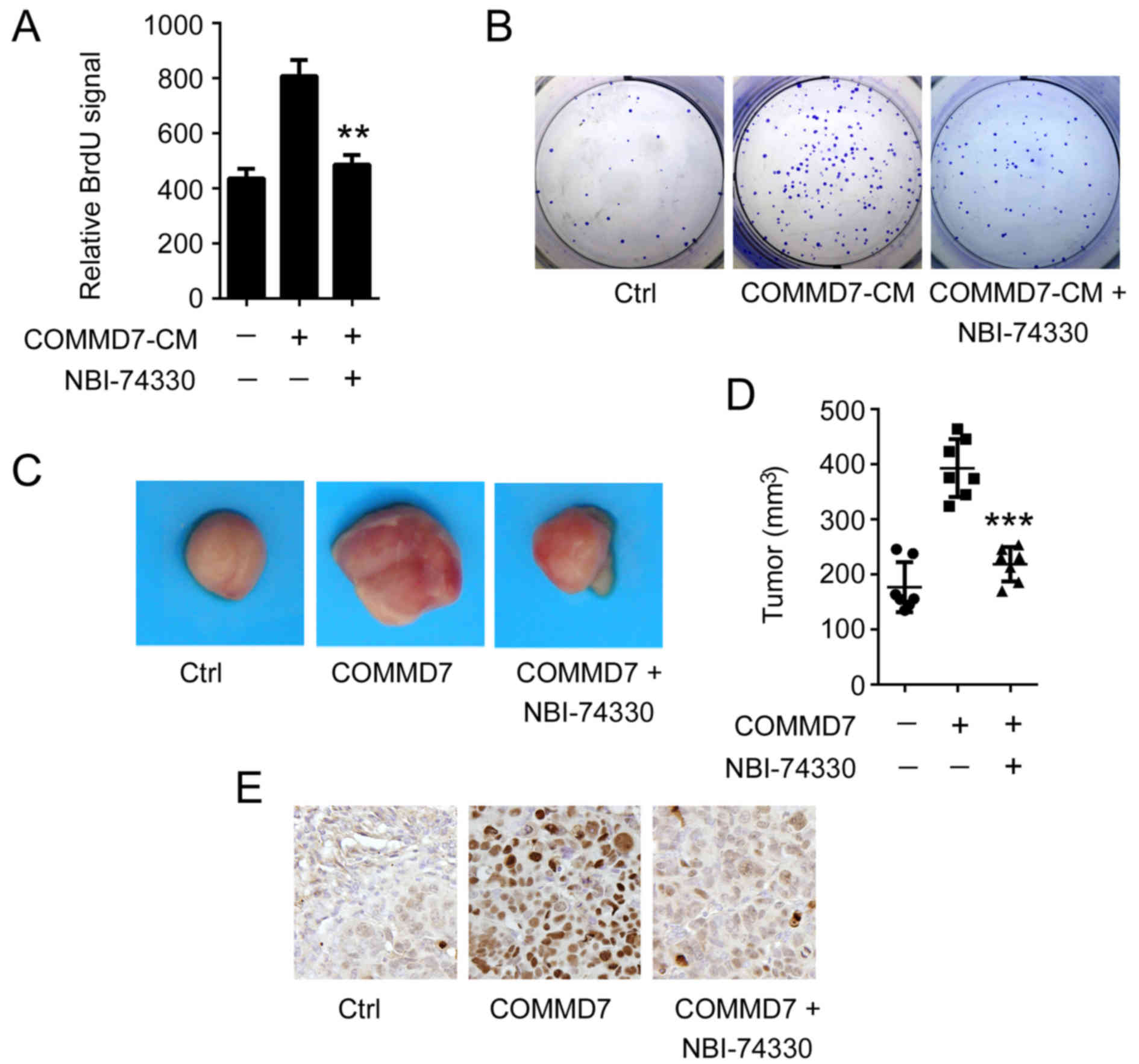
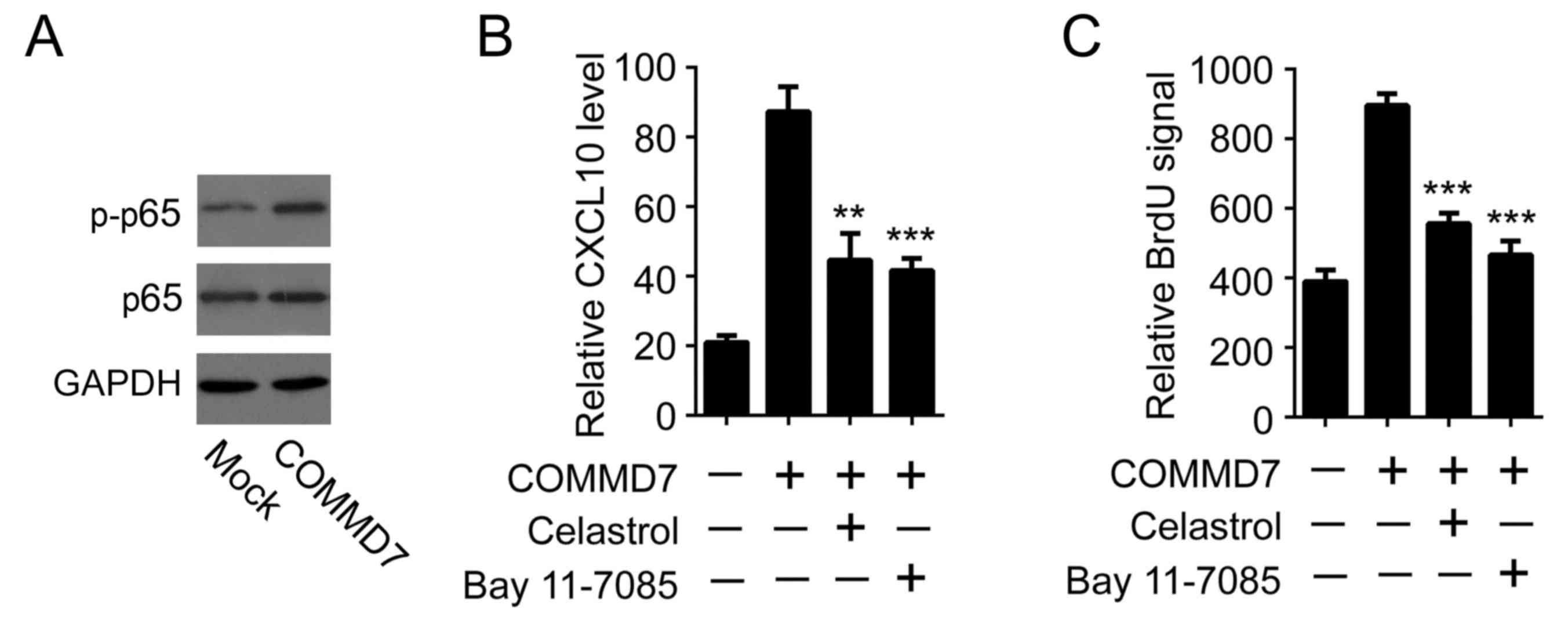
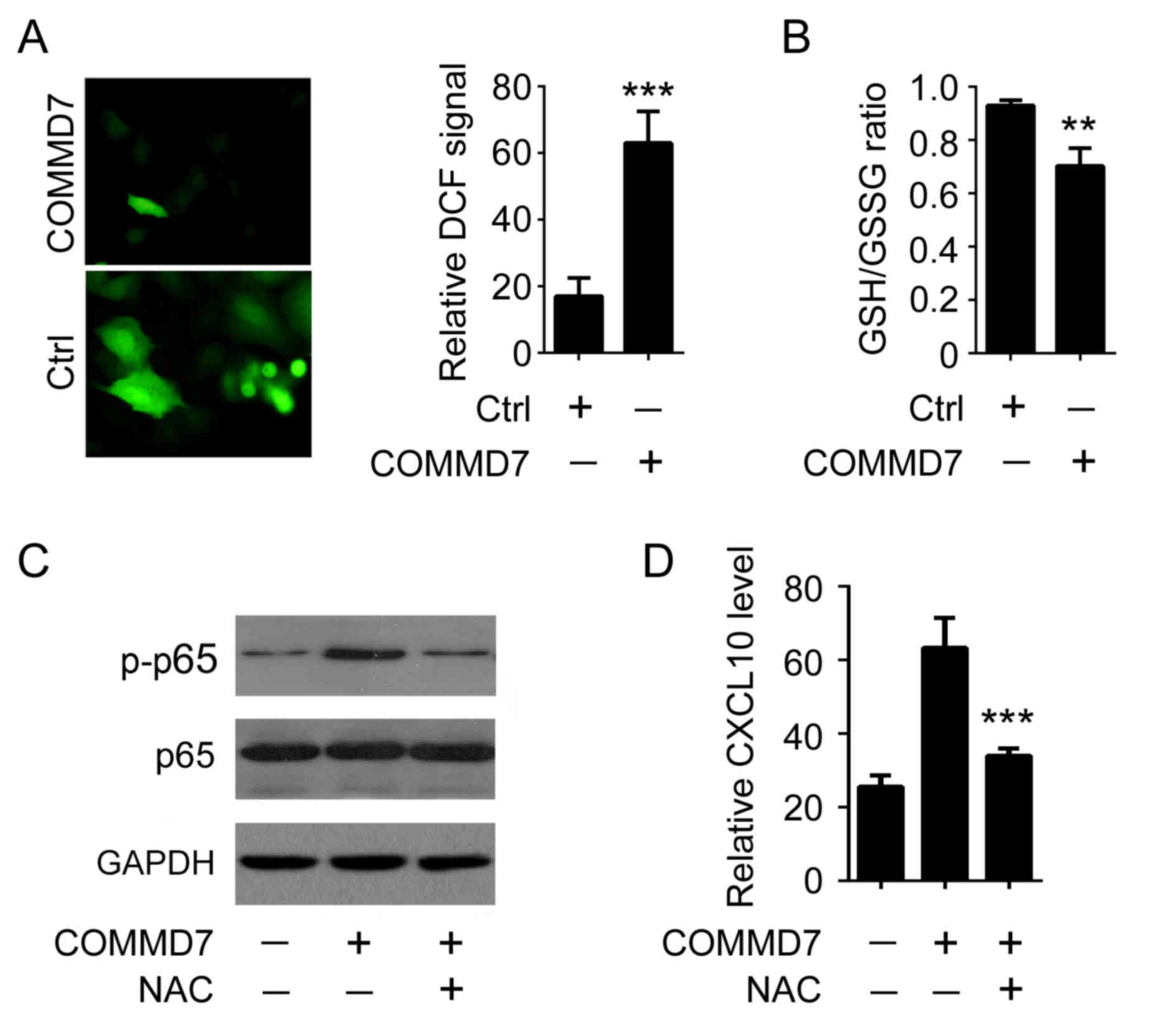
|
1
|
El-Serag HB: Epidemiology of viral
hepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology.
142:1264–1273.e1. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bruix J, Gores GJ and Mazzaferro V:
Hepatocellular carcinoma: Clinical frontiers and perspectives. Gut.
63:844–855. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Arzumanyan A, Reis HM and Feitelson MA:
Pathogenic mechanisms in HBV- and HCV-associated hepatocellular
carcinoma. Nat Rev Cancer. 13:123–135. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Morgan RL, Baack B, Smith BD, Yartel A,
Pitasi M and Falck-Ytter Y: Eradication of hepatitis C virus
infection and the development of hepatocellular carcinoma: A
meta-analysis of observational studies. Ann Intern Med.
158:329–337. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zheng L, Liang P, Li J, Huang XB, Liu SC,
Zhao HZ, Han KQ and Wang Z: ShRNA-targeted COMMD7 suppresses
hepatocellular carcinoma growth. PLoS One. 7:e454122012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
van Wanrooij EJ, de Jager SC, van Es T, de
Vos P, Birch HL, Owen DA, Watson RJ, Biessen EA, Chapman GA, van
Berkel TJ and Kuiper J: CXCR3 antagonist NBI-74330 attenuates
atherosclerotic plaque formation in LDL receptor-deficient mice.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 28:251–257. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ni H, Zhao W, Kong X, Li H and Ouyang J:
NF-kappa B modulation is involved in celastrol induced human
multiple myeloma cell apoptosis. PLoS One. 9:e958462014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Matteucci C, Minutolo A, Marino-Merlo F,
Grelli S, Frezza C, Mastino A and Macchi B: Characterization of the
enhanced apoptotic response to azidothymidine by pharmacological
inhibition of NF-kB. Life Sci. 127:90–97. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gilmore TD: Introduction to NF-kappaB:
Players, pathways, perspectives. Oncogene. 25:6680–6684. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Meimaridou E, Kowalczyk J, Guasti L,
Hughes CR, Wagner F, Frommolt P, Nürnberg P, Mann NP, Banerjee R,
Saka HN, et al: Mutations in NNT encoding nicotinamide nucleotide
transhydrogenase cause familial glucocorticoid deficiency. Nat
Genet. 44:740–742. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chang JH, Kim YJ, Han SH and Kang CY:
IFN-gamma-STAT1 signal regulates the differentiation of inducible
Treg: Potential role for ROS-mediated apoptosis. Eur J Immunol.
39:1241–1251. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Altekruse SF, McGlynn KA and Reichman ME:
Hepatocellular carcinoma incidence, mortality, and survival trends
in the United States from 1975 to 2005. J Clin Oncol. 27:1485–1491.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Farazi PA and DePinho RA: Hepatocellular
carcinoma pathogenesis: From genes to environment. Nat Rev Cancer.
6:674–687. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lazennec G and Richmond A: Chemokines and
chemokine receptors: New insights into cancer-related inflammation.
Trends Mol Med. 16:133–144. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Datta D, Flaxenburg JA, Laxmanan S, Geehan
C, Grimm M, Waaga-Gasser AM, Briscoe DM and Pal S: Ras-induced
modulation of CXCL10 and its receptor splice variant CXCR3-B in
MDA-MB-435 and MCF-7 cells: Relevance for the development of human
breast cancer. Cancer Res. 66:9509–9518. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kawada K, Hosogi H, Sonoshita M, Sakashita
H, Manabe T, Shimahara Y, Sakai Y, Takabayashi A, Oshima M and
Taketo MM: Chemokine receptor CXCR3 promotes colon cancer
metastasis to lymph nodes. Oncogene. 26:4679–4688. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ding Q, Xia Y, Ding S, Lu P, Sun L and Liu
M: An alternatively spliced variant of CXCR3 mediates the
metastasis of CD133+ liver cancer cells induced by CXCL9.
Oncotarget. 7:14405–14414. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ling CC, Ng KT, Shao Y, Geng W, Xiao JW,
Liu H, Li CX, Liu XB, Ma YY, Yeung WH, et al: Post-transplant
endothelial progenitor cell mobilization via CXCL10/CXCR3 signaling
promotes liver tumor growth. J Hepatol. 60:103–109. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhu Y, Wang Z, Zhu Y, Wang J, Cai L, Shen
H, Kong Y and Qiu Y: CXCR3 monoclonal antibody inhibits the
proliferation and migration of MCF-7 cells and HepG2 cells in
vitro. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 31:1544–1548. 2015.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Helbig KJ, Ruszkiewicz A, Semendric L,
Harley HA, McColl SR and Beard MR: Expression of the CXCR3 ligand
I-TAC by hepatocytes in chronic hepatitis C and its correlation
with hepatic inflammation. Hepatology. 39:1220–1229. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Guo JQ, Chen L, Ai HW, Jing JN, Zhou JY,
Zhang CY and You SY: A novel fusion protein of IP10-scFv retains
antibody specificity and chemokine function. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 320:506–513. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Huang YT, Chen YY, Lai YH, Cheng CC, Lin
TC, Su YS, Liu CH and Lai PC: Resveratrol alleviates the
cytotoxicity induced by the radiocontrast agent, ioxitalamate, by
reducing the production of reactive oxygen species in HK-2 human
renal proximal tubule epithelial cells in vitro. Int J Mol Med.
37:83–91. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Karthik S, Sankar R, Varunkumar K, Anusha
C and Ravikumar V: Blocking NF-κB sensitizes non-small cell lung
cancer cells to histone deacetylase inhibitor induced extrinsic
apoptosis through generation of reactive oxygen species. Biomed
Pharmacother. 69:337–344. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|