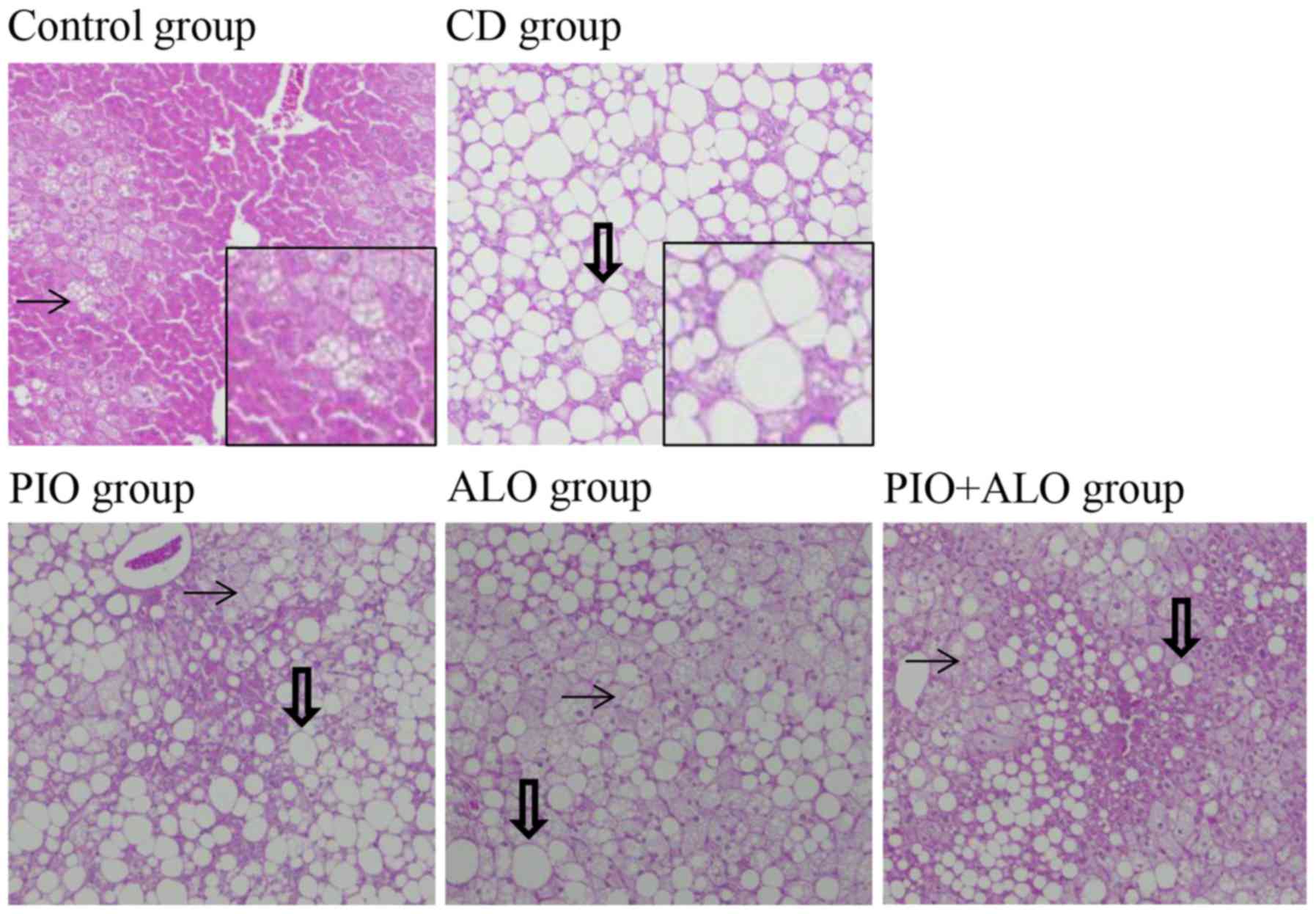
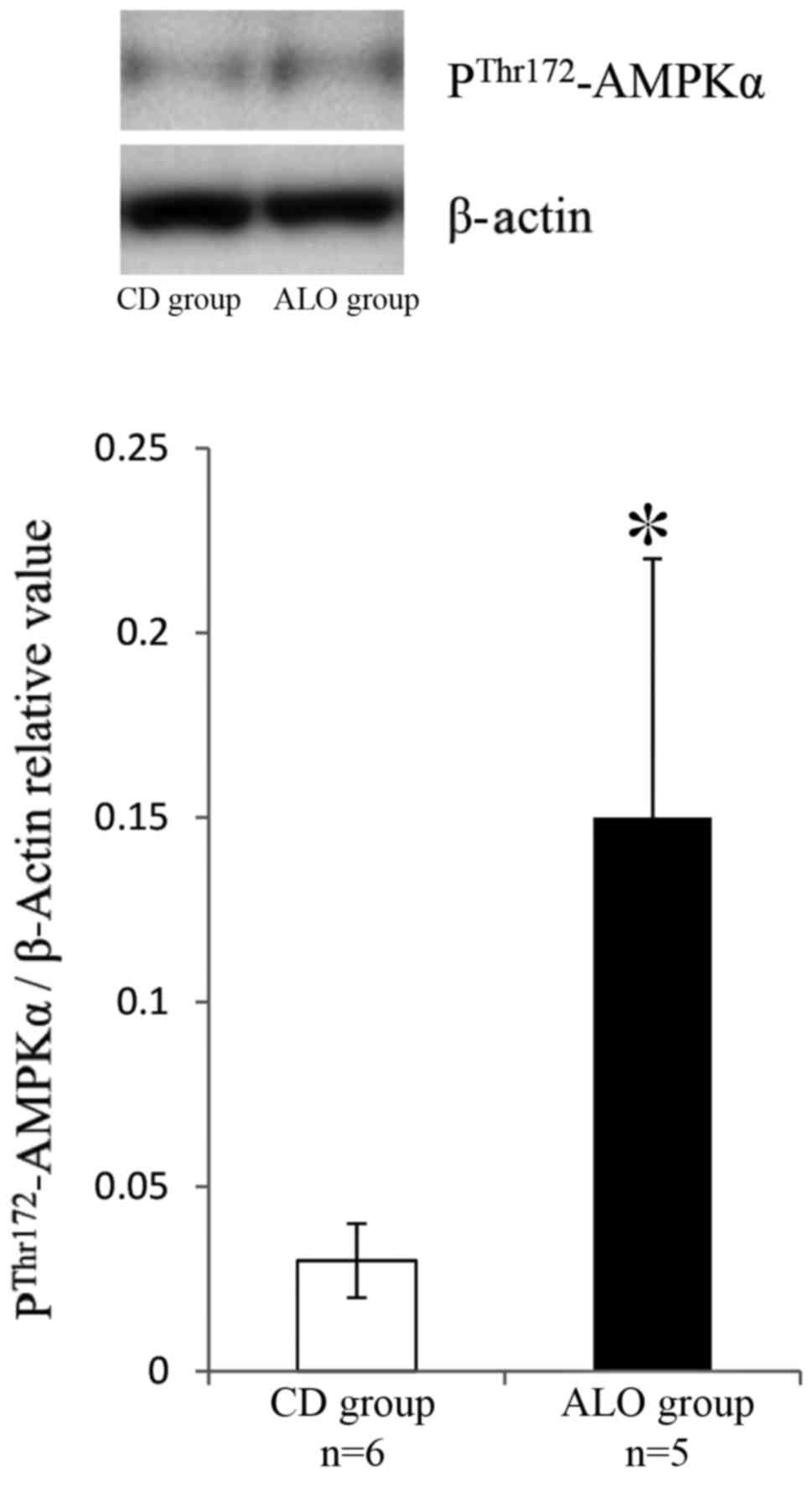
|
1
|
Bellentani S: The epidemiology of
non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Liver Int. 1:81–84. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Dai W, Ye L, Liu A, Wen SW, Deng J, Wu X
and Lai Z: Prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in
patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis. Medicine
(Baltimore). 96:e81792017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Angulo P, Kleiner DE, Dam-Larsen S, Adams
LA, Bjornsson ES, Charatcharoenwitthaya P, Mills PR, Keach JC,
Lafferty HD, Stahler A, et al: Liver fibrosis, but no other
histologic features, is associated with long-term outcomes of
patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology.
149:389–397. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Rafig N, Bai C, Fang Y, Srishord M,
McCullough A, Gramlich T and Younossi ZM: Long-term follow-up of
patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol.
7:234–238. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sanyal AJ, Chalasani N, Kowdley KV,
McCullough A, Diehl AM, Bass NM, Neuschwander-Tetri BA, Lavine JE,
Tonascia J, Unalp A, et al: Pioglitazone, vitamin E, or placebo for
nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. N Engl J Med. 362:1675–1685. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Da Silva Morais A, Lebrun V,
Abarca-Quinones J, Brichard S, Hue L, Guigas B, Viollet B and
Leclercq IA: Prevention of steatohepatitis by pioglitazone:
Implication of adiponectin-dependent inhibition of SREBP-1c and
inflammation. J Hepatol. 50:489–500. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yilmaz Y, Yonal O, Deyneli O, Celikel CA,
Kalayci C and Duman DG: Effects of sitagliptin in diabetic patients
with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Acta Gastroenterol Belg.
75:240–244. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mashitani T, Noguchi R, Okura Y, Namisaki
T, Mitoro A, Ishii H, Nakatani T, Kikuchi E, Moriyasu H, Matsumoto
M, et al: Efficacy of alogliptin in preventing non-alcoholic fatty
liver disease progression in patients with type 2 diabetes. Biomed
Rep. 4:183–187. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nonogaki K, Nozue K and Oka Y: Social
isolation affects the development of obesity and type 2 diabetes in
mice. Endocrinology. 148:4658–4666. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Haluzik MM, Lacinova Z, Dolinkova M,
Haluzikova D, Housa D, Horinek A, Vernerova Z, Kumstyrova T and
Haluzik M: Improvement of insulin sensitivity after peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor-alpha agonist treatment is
accompanied by paradoxical increase of circulating resistin levels.
Endocrinology. 147:4517–4524. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rinella ME, Elias MS, Smolak RR, Fu T,
Borensztajn J and Green RM: Mechanisms of hepatic steatosis in mice
fed a lipogenic methionine choline-deficient diet. J Lipid Res.
49:1068–1076. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rozen S and Skaletsky H: Primer3 on the
WWW for general users and for biologist programmers. Methods Mol
Biol. 132:365–386. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Raabe M, Véniant MM, Sullivan MA, Zlot CH,
Björkegren J, Nielsen LB, Wong JS, Hamilton RL and Young SG:
Analysis of the role of microsomal triglyceride transfer protein in
the liver of tissue-specific knockout mice. J Clin Invest.
103:1287–1298. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Okumura K, Ikejima K, Kon K, Abe W,
Yamashina S, Enomoto N, Takei Y and Sato N: Exacerbation of dietary
steatohepatitis and fibrosis in obese, diabetic KK-A(y) mice.
Hepatol Res. 36:217–228. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Boettcher E, Csako G, Pucino F, Wesley R
and Loomba R: Meta-analysis: Pioglitazone improves liver histology
and fibrosis in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.
Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 35:66–75. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gastaldelli A, Harrison S, Belfort-Aguiar
R, Hardies J, Balas B, Schenker S and Cusi K: Pioglitazone in the
treatment of NASH: The role of adiponectin. Aliment Pharmacol Ther.
32:769–775. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kon K, Ikejima K, Hirose M, Yoshikawa M,
Enomoto N, Kitamura T, Takei Y and Sato N: Pioglitazone prevents
early-phase hepatic fibrogenesis caused by carbon tetrachloride.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 291:55–61. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Klein T, Fujii M, Sandel J, Shibazaki Y,
Wakamatsu K, Mark M and Yoneyama H: Linagliptin alleviates hepatic
steatosis and inflammation in a mouse model of non-alcoholic
steatohepatitis. Med Mol Morphol. 47:137–149. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kern M, Klöting N, Niessen HG, Thomas L,
Stiller D, Mark M, Klein T and Blüher M: Linagliptin improves
insulin sensitivity and hepatic steatosis in diet-induced obesity.
PLoS One. 7:e387442012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Aroor AR, Habibi J, Ford DA, Nistala R,
Lastra G, Manrique C, Dunham MM, Ford KD, Thyfault JP, Parks EJ, et
al: Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibition ameliorates Western
diet-induced hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance through
hepatic lipid remodeling and modulation of hepatic mitochondrial
function. Diabetes. 64:1988–2001. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Orellana-Gavaldà JM, Herrero L, Malandrino
MI, Pañeda A, Sol Rodríguez-Peña M, Petry H, Asins G, Van Deventer
S, Hegardt FG and Serra D: Molecular therapy for obesity and
diabetes based on a long-term increase in hepatic fatty-acid
oxidation. Hepatology. 53:821–832. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ben-Shlomo S, Zvibel I, Shnell M, Shlomai
A, Chepurko E, Halpern Z, Barzilai N, Oren R and Fishman S:
Glucagon-like peptide-1 reduces hepatic lipogenesis via activation
of AMP-activated protein kinase. J Hepatol. 54:1214–1223. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Steinberg GR and Kemp BE: AMPK in health
and disease. Physiol Rev. 89:1025–1078. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kim JH, Kang SI, Shin HS, Yoon SA, Kang
SW, Ko HC and Kim SJ: Sasa quelpaertensis and p-coumaric acid
attenuate oleic acid-induced lipid accumulation in HepG2 cells.
Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 77:1595–1598. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dahlhoff C, Worsch S, Sailer M, Hummel BA,
Fiamoncini J, Uebel K, Obeid R, Scherling C, Geisel J, Bader BL and
Daniel H: Methyl-donor supplementation in obese mice prevents the
progression of NAFLD, activates AMPK and decreases acyl-carnitine
levels. Mol Metab. 3:565–580. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|