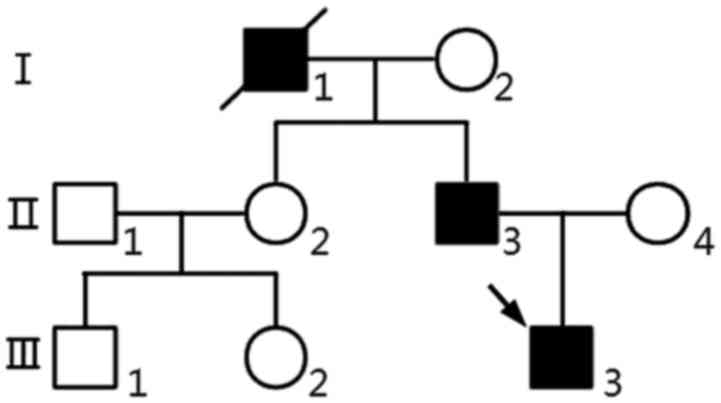
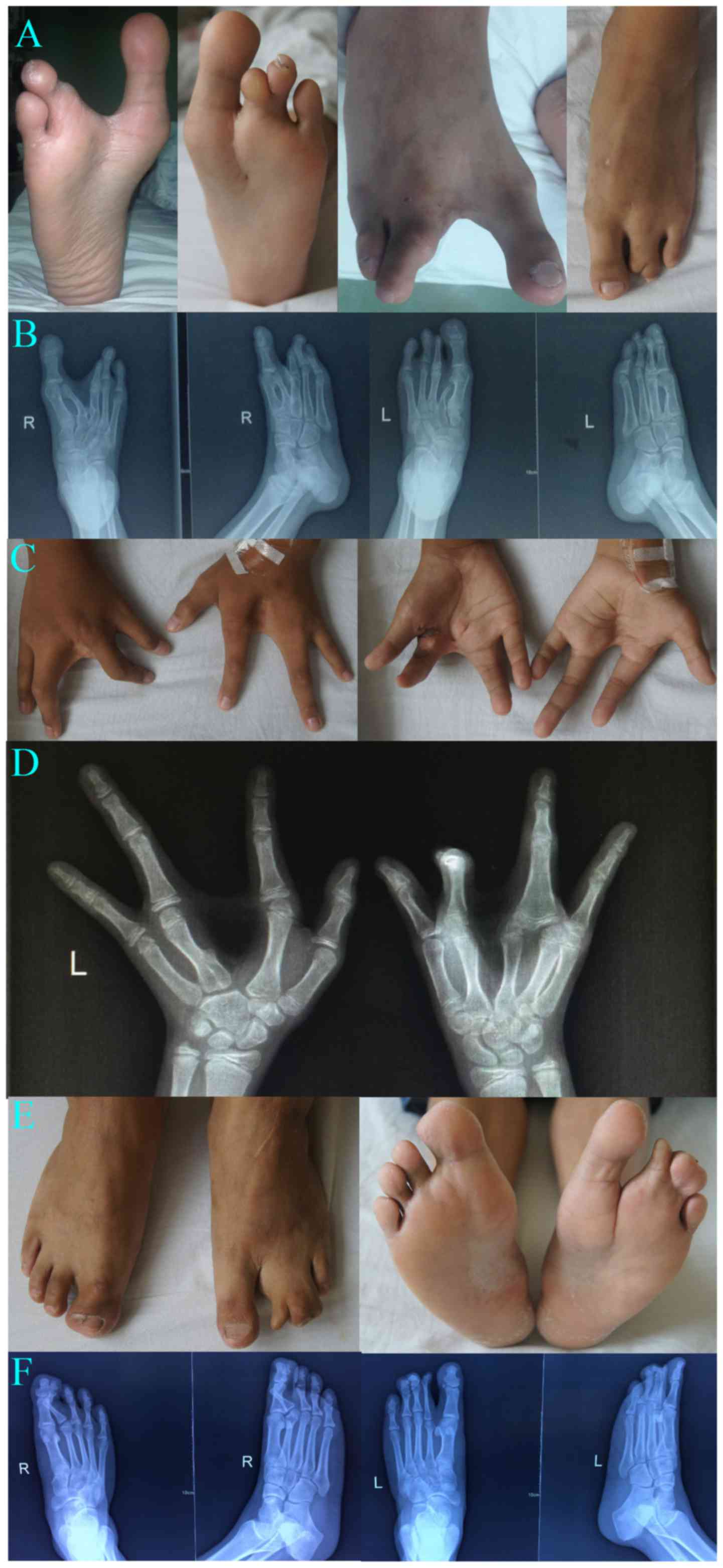
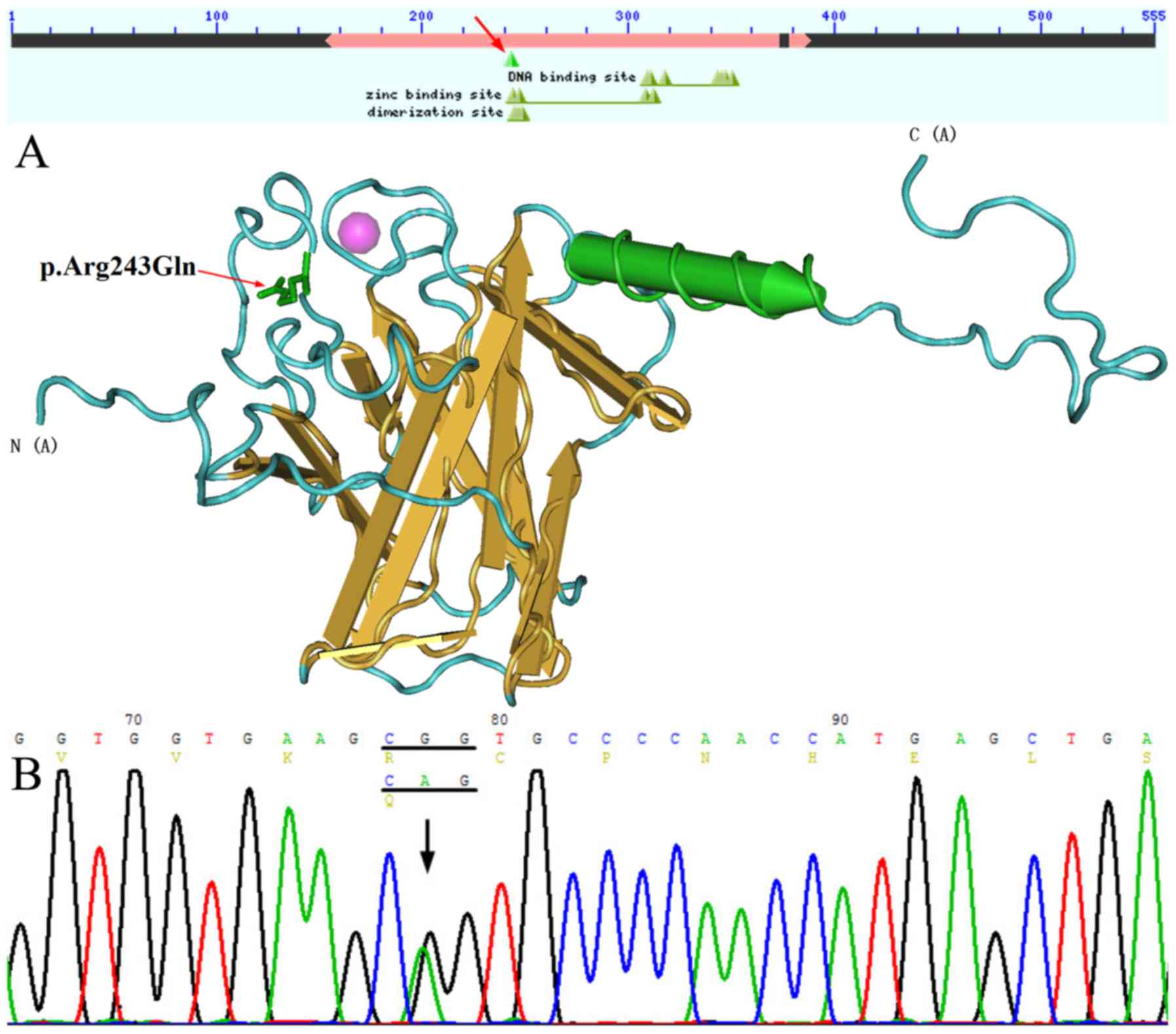
|
1
|
Basel D, Kilpatrick MW and Tsipouras P:
The expanding panorama of split hand foot malformation. Am J Med
Genet A. 140:1359–1365. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Duijf PH, van Bokhoven H and Brunner HG:
Pathogenesis of split-hand/split-foot malformation. Hum Mol Genet.
12:R51–R60. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Amalnath SD, Gopalakrishnan M and Dutta
TK: Split-hand/feet malformation in three tamilian families and
review of the reports from India. Indian J Hum Genet. 20:92–95.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Klar AJ: Split hand/foot malformation
genetics supports the chromosome 7 copy segregation mechanism for
human limb development. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci.
371:201504152016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Celli J, Duijf P, Hamel BC, Bamshad M,
Kramer B, Smits AP, Newbury-Ecob R, Hennekam RC, Van Buggenhout G,
van Haeringen A, et al: Heterozygous germline mutations in the p53
homolog p63 are the cause of EEC syndrome. Cell. 99:143–153. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Khan S, Basit S, Zimri FK, Ali N, Ali G,
Ansar M and Ahmad W: A novel homozygous missense mutation in WNT10B
in familial split-hand/foot malformation. Clin Genet. 82:48–55.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Armour CM, Bulman DE, Jarinova O, Rogers
RC, Clarkson KB, DuPont BR, Dwivedi A, Bartel FO, McDonell L,
Schwartz CE, et al: 17p13.3 microduplications are associated with
split-hand/foot malformation and long-bone deficiency (SHFLD). Eur
J Hum Genet. 19:1144–1151. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Van Bokhoven H, Melino G, Candi E and
Declercq W: p63, a story of mice and men. J Invest Dermatol.
131:1196–1207. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
van Bokhoven H, Hamel BC, Bamshad M,
Sangiorgi E, Gurrieri F, Duijf PH, Vanmolkot KR, van Beusekom E,
van Beersum SE, Celli J, et al: p63 Gene mutations in EEC syndrome,
limb-mammary syndrome and isolated split hand-split foot
malformation suggest a genotype-phenotype correlation. Am J Hum
Genet. 69:481–492. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sowińska-Seidler A, Socha M and Jamsheer
A: Split-hand/foot malformation-molecular cause and implications in
genetic counseling. J Appl Genet. 55:105–115. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Celik TH, Buyukcam A, Simsek-Kiper PO,
Utine GE, Ersoy-Evans S, Korkmaz A, Yntema HG, Bodugroglu K and
Yurdakok M: A newborn with overlapping features of AEC and EEC
syndromes. Am J Med Genet A. 155A:3100–3103. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Robinson JT, Thorvaldsdóttir H, Winckler
W, Guttman M, Lander ES, Getz G and Mesirov JP: Integrative
genomics viewer. Nat Biotechnol. 29:24–26. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Thorvaldsdóttir H, Robinson JT and Mesirov
JP: Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV): High-performance genomics
data visualization and exploration. Brief Bioinform. 14:178–192.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lam HY, Clark MJ, Chen R, Chen R,
Natsoulis G, O'Huallachain M, Dewey FE, Habegger L, Ashley EA,
Gerstein MB, et al: Performance comparison of whole-genome
sequencing platforms. Nat Biotechnol. 30:78–82. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang Y, Addess KJ, Chen J, Geer LY, He J,
He S, Lu S, Madej T, Marchler-Bauer A, Thiessen PA, et al: MMDB:
annotating protein sequences with Entrez's 3D-structure database.
Nucleic Acids Res. 35:(Database issue). D298–D300. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Var view Protein 3D, . https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/cblast/cblast.cgi?client=snp&master_gi=169234657&neighbor_gi=212374861
|
|
17
|
Rinne T, Brunner HG and van Bokhoven H:
p63-associated disorders. Cell Cycle. 6:262–268. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Berdón-Zapata V, Granillo-Alvarez M,
Valdés-Flores M, García-Ortiz JE, Kofman-Alfaro S and Zenteno JC:
p63 gene analysis in Mexican patients with syndromic and
non-syndromic ectrodactyly. J Orthop Res. 22:1–5. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zenteno JC, Berdón-Zapata V, Kofman-Alfaro
S and Mutchinick OM: Isolated ectrodactyly caused by a heterozygous
missense mutation in the transactivation domain of TP63. Am J Med
Genet A. 134A:74–76. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ianakiev P, Kilpatrick MW, Toudjarska I,
Basel D, Beighton P and Tsipouras P: Split-hand/split-foot
malformation is caused by mutations in the p63 gene on 3q27. Am J
Hum Genet. 67:59–66. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rinne T, Hamel B, van Bokhoven H and
Brunner HG: Pattern of p63 mutations and their phenotypes-update.
Am J Med Genet A. 140:1396–1406. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mangiulli M, Valletti A, Caratozzolo MF,
Tullo A, Sbisà E, Pesole G and D'Erchia AM: Identification and
functional characterization of two new transcriptional variants of
the human p63 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 37:6092–6104. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gonfloni S, Caputo V and Iannizzotto V:
P63 in health and cancer. Int J Dev Biol. 59:87–93. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Thanos CD and Bowie JU: p53 Family members
p63 and p73 are SAM domain-containing proteins. Protein Sci.
8:1708–1710. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Enthart A, Klein C, Dehner A, Coles M,
Gemmecker G, Kessler H and Hagn F: Solution structure and binding
specificity of the p63 DNA binding domain. Sci Rep. 6:267072016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Stiewe T, Zimmermann S, Frilling A, Esche
H and Pützer BM: Transactivation-deficient DeltaTA-p73 acts as an
oncogene. Cancer Res. 62:3598–3602. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yang A, Schweitzer R, Sun D, Kaghad M,
Walker N, Bronson RT, Tabin C, Sharpe A, Caput D, Crum C, et al:
p63 is essential for regenerative proliferation in limb,
craniofacial and epithelial development. Nature. 398:714–718. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Vincek V, Knowles J, Li J and Nassiri M:
Expression of p63 mRNA isoforms in normal human tissue. Anticancer
Res. 23:3945–3948. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Koster MI, Dai D, Marinari B, Sano Y,
Costanzo A, Karin M and Roop DR: p63 induces key target genes
required for epidermal morphogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
104:3255–3260. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Koster MI and Roop DR: Mechanisms
regulating epithelial stratification. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol.
23:93–113. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Koster MI, Dai D and Roop DR: Conflicting
roles for p63 in skin development and carcinogenesis. Cell Cycle.
6:269–273. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sommer M, Poliak N, Upadhyay S, Ratovitski
E, Nelkin BD, Donehower LA and Sidransky D: DeltaNp63alpha
overexpression induces downregulation of Sirt1 and an accelerated
aging phenotype in the mouse. Cell Cycle. 5:2005–2011. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yan W and Chen X: GPX2, a direct target of
p63, inhibits oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in a p53-dependent
manner. J Biol Chem. 281:7856–7862. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Restelli M, Lopardo T, Lo Iacono N,
Garaffo G, Conte D, Rustighi A, Napoli M, Del Sal G, Perez-Morga D,
Costanzo A, et al: DLX5, FGF8 and the Pin1 isomerase control ΔNp63α
protein stability during limb development: A regulatory loop at the
basis of the SHFM and EEC congenital malformations. Hum Mol Genet.
23:3830–3842. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lo Iacono N, Mantero S, Chiarelli A,
Garcia E, Mills AA, Morasso MI, Costanzo A, Levi G, Guerrini L and
Merlo GR: Regulation of Dlx5 and Dlx6 gene expression by p63 is
involved in EEC and SHFM congenital limb defects. Development.
135:1377–1388. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|