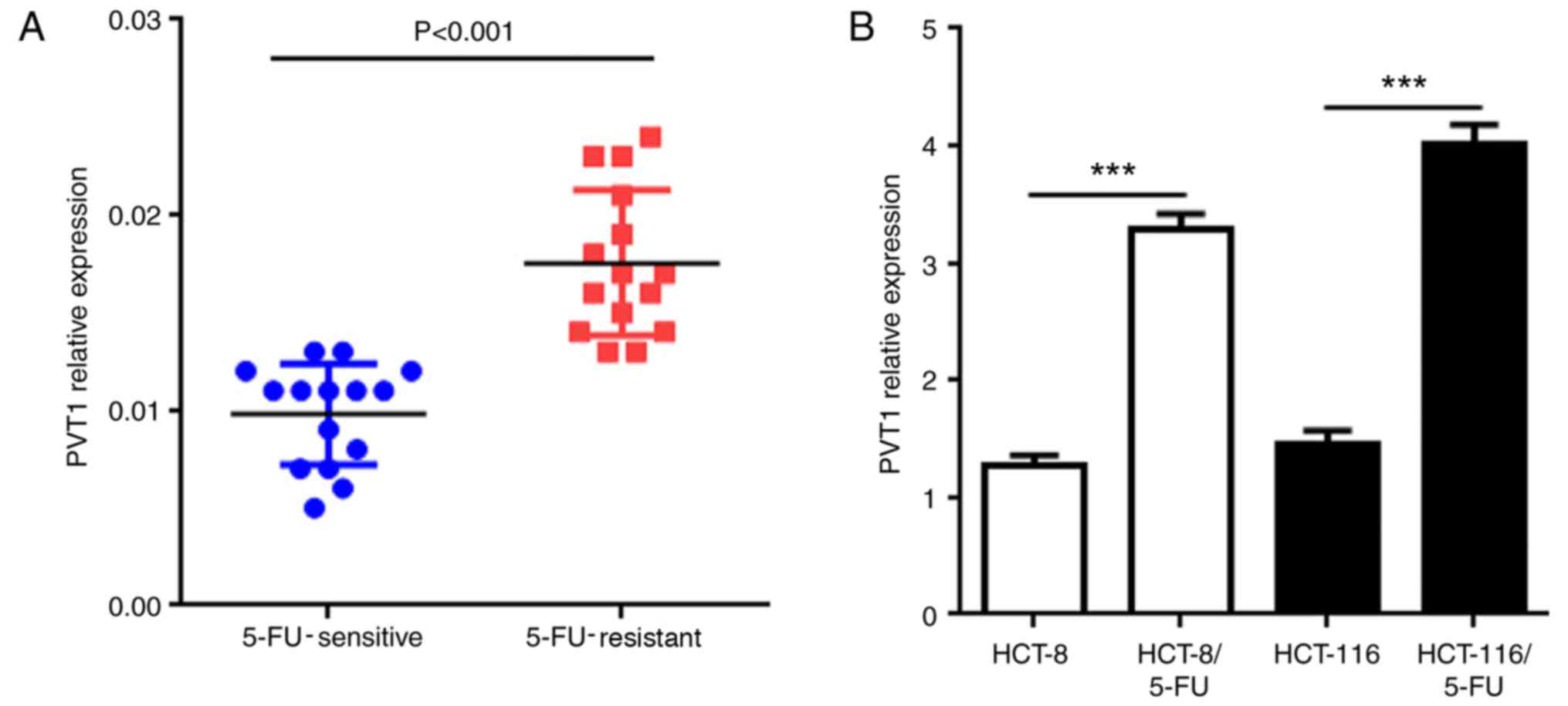
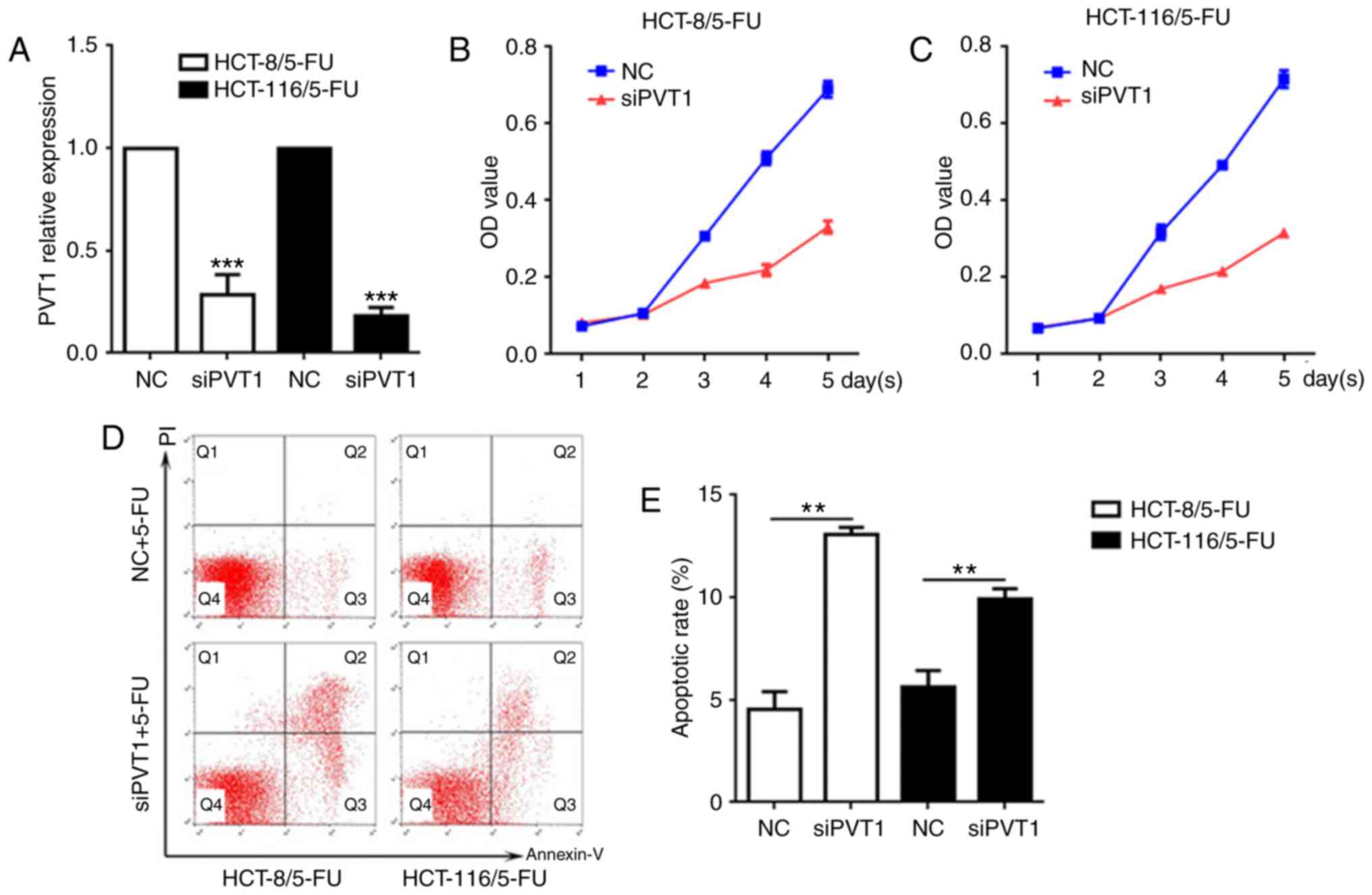
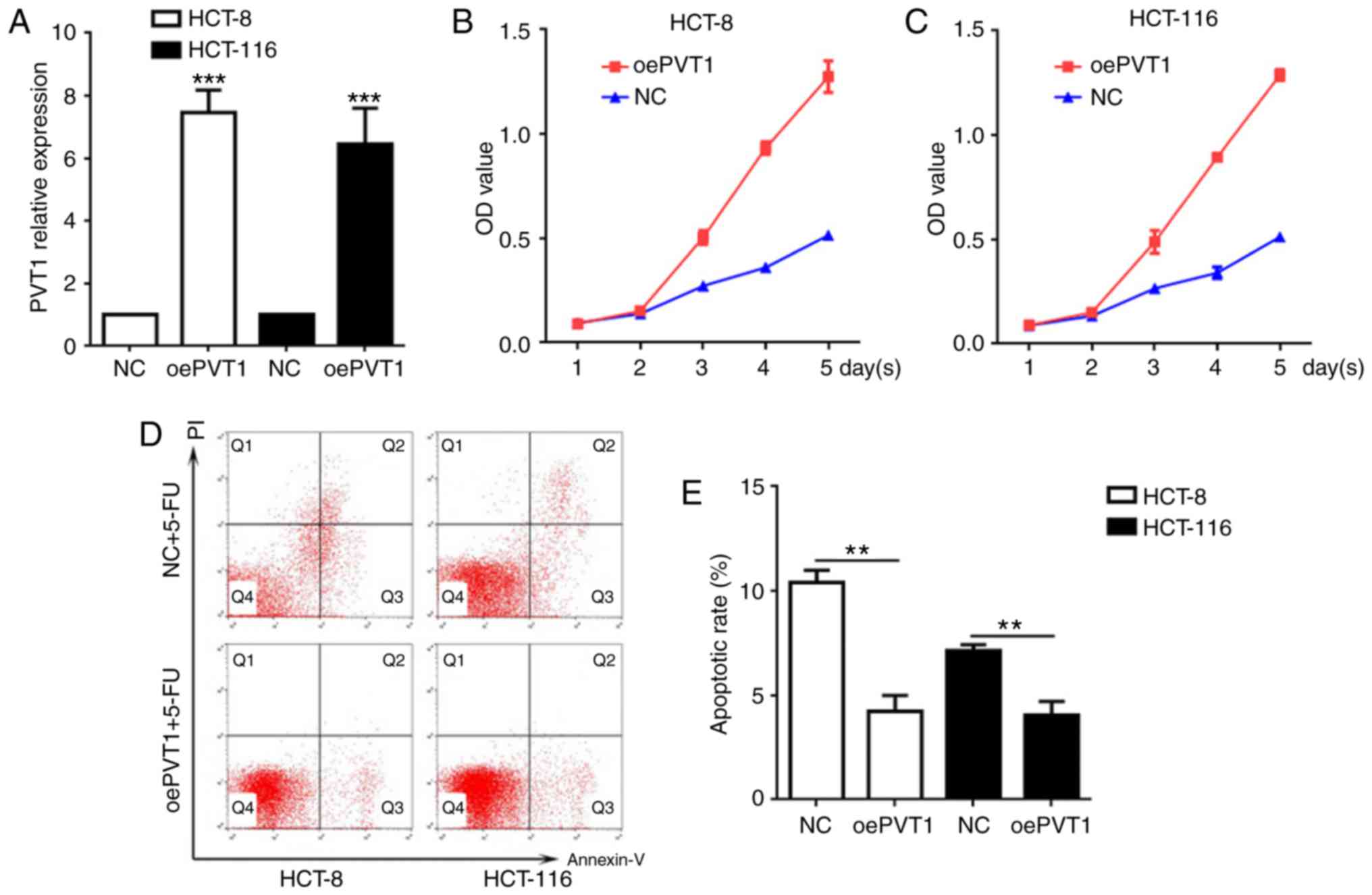
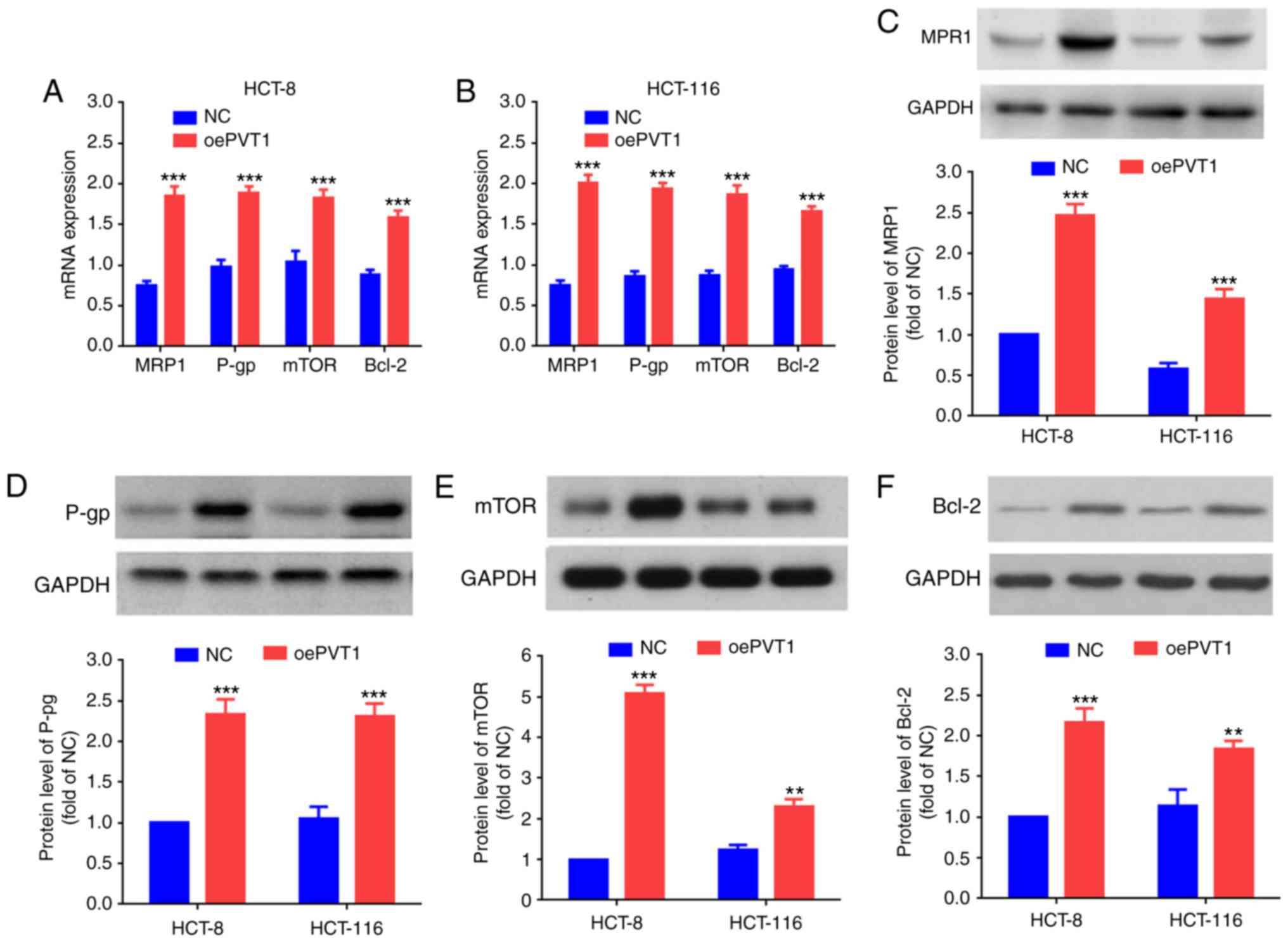
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Parkin DM and Steliarova-Foucher
E: Estimates of cancer incidence and mortality in Europe in 2008.
Eur J Cancer. 46:765–781. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Xu M, Chen YM, Huang J, Fang YJ, Huang WQ,
Yan B, Lu MS, Pan ZZ and Zhang CX: Flavonoid intake from vegetables
and fruits is inversely associated with colorectal cancer risk: A
case-control study in China. Br J Nutr. 116:1275–1287. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rebucci M and Michiels C: Molecular
aspects of cancer cell resistance to chemotherapy. Biochem
Pharmacol. 85:1219–1226. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Beck-Engeser GB, Lum AM, Huppi K, Caplen
NJ, Wang BB and Wabl M: Pvt1-encoded microRNAs in oncogenesis.
Retrovirology. 5:42008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yang X, Xie X, Xiao YF, Xie R, Hu CJ, Tang
B, Li BS and Yang SM: The emergence of long non-coding RNAs in the
tumorigenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett.
360:119–124. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liu E, Liu Z and Zhou Y:
Carboplatin-docetaxel-induced activity against ovarian cancer is
dependent on up-regulated lncRNA PVT1. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
8:3803–3810. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Paci P, Colombo T and Farina L:
Computational analysis identifies a sponge interaction network
between long non-coding RNAs and messenger RNAs in human breast
cancer. BMC Syst Biol. 8:832014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xu MD, Wang Y, Weng W, Wei P, Qi P, Zhang
Q, Tan C, Ni SJ, Dong L, Yang Y, et al: A positive feedback loop of
lncRNA-PVT1 and FOXM1 facilitates gastric cancer growth and
invasion. Clin Cancer Res. 23:2071–2080. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fang XY, Pan HF, Leng RX and Ye DQ: Long
noncoding RNAs: Novel insights into gastric cancer. Cancer Lett.
356:357–366. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Uchibori K, Kasamatsu A, Sunaga M, Yokota
S, Sakurada T, Kobayashi E, Yoshikawa M, Uzawa K, Ueda S, Tanzawa H
and Sato N: Establishment and characterization of two
5-fluorouracil-resistant hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. Int J
Oncol. 40:1005–1010. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang Y, Zhou J, Wang Z, Wang P and Li S:
Upregulation of SOX2 activated LncRNA PVT1 expression promotes
breast cancer cell growth and invasion. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
493:429–436. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Farhana L, Antaki F, Anees MR,
Nangia-Makker P, Judd S, Hadden T, Levi E, Murshed F, Yu Y, Van
Buren E, et al: Role of cancer stem cells in racial disparity in
colorectal cancer. Cancer Med. 5:1268–1278. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wu Q, Yang Z, Nie Y, Shi Y and Fan D:
Multi-drug resistance in cancer chemotherapeutics: Mechanisms and
lab approaches. Cancer Lett. 347:159–166. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Iden M, Fye S, Li K, Chowdhury T,
Ramchandran R and Rader JS: The lncRNA PVT1 contributes to the
cervical cancer phenotype and associates with poor patient
prognosis. PLoS One. 11:e01562742016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhou Q, Chen J, Feng J and Wang J: Long
noncoding RNA PVT1 modulates thyroid cancer cell proliferation by
recruiting EZH2 and regulating thyroid-stimulating hormone receptor
(TSHR). Tumour Biol. 37:3105–3113. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kong R, Zhang EB, Yin DD, You LH, Xu TP,
Chen WM, Xia R, Wan L, Sun M, Wang ZX, et al: Long noncoding RNA
PVT1 indicates a poor prognosis of gastric cancer and promotes cell
proliferation through epigenetically regulating p15 and p16. Mol
Cancer. 14:822015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu E, Liu Z, Zhou Y, Mi R and Wang D:
Overexpression of long non-coding RNA PVT1 in ovarian cancer cells
promotes cisplatin resistance by regulating apoptotic pathways. Int
J Clin Exp Med. 8:20565–20572. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wan L, Sun M, Liu GJ, Wei CC, Zhang EB,
Kong R, Xu TP, Huang MD and Wang ZX: Long non-coding RNA PVT1
promotes non-small cell lung cancer cell proliferation through
epigenetically regulating LATS2 expression. Mol Cancer Ther.
15:1082–1094. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang XW, Bu P, Liu L, Zhang XZ and Li J:
Overexpression of long non-coding RNA PVT1 in gastric cancer cells
promotes the development of multidrug resistance. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 462:227–232. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Duarte N, Varga A, Cherepnev G, Radics R,
Molnár J and Ferreira MJ: Apoptosis induction and modulation of
P-glycoprotein mediated multidrug resistance by new macrocyclic
lathyrane-type diterpenoids. Bioorg Med Chem. 15:546–554. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wobst I, Ebert L, Birod K, Wegner MS,
Hoffmann M, Thomas D, Angioni C, Parnham MJ, Steinhilber D, Tegeder
I, et al: R-flurbiprofen traps prostaglandins within cells by
inhibition of multidrug resistance-associated protein-4. Int J Mol
Sci. 18:pii: E68. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang MZ, Qiu CZ, Yu WS, Guo YT, Wang CX
and Chen ZX: GOLPH3 expression promotes the resistance of HT29
cells to 5-fluorouracil by activating multiple signaling pathways.
Mol Med Rep. 17:542–548. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Takahashi Y, Sawada G, Kurashige J, Uchi
R, Matsumura T, Ueo H, Takano Y, Eguchi H, Sudo T, Sugimachi K, et
al: Amplification of PVT-1 is involved in poor prognosis via
apoptosis inhibition in colorectal cancers. Br J Cancer.
110:164–171. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Weerasinghe P, Hallock S, Tang SC, Trump B
and Liepins A: Sanguinarine overcomes p-glycoprotein-mediated
multidrug-resistance via induction of apoptosis and oncosis in
CEM-VLB 1,000 cells. Exp Toxicol Pathol. 58:21–30. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Xie Y, Yu N, Chen Y, Zhang K, Ma HY and Di
Q: HMGB1 regulates P-glycoprotein expression in status epilepticus
rat brains via the RAGE/NF-κB signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep.
16:1691–1700. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gottesman MM and Pastan IH: The role of
multidrug resistance efflux pumps in cancer: Revisiting a JNCI
publication exploring expression of the MDR1 (P-glycoprotein) gene.
J Natl Cancer Inst. 107:pii: djv222. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yan LH, Wei WY, Cao WL, Zhang XS, Xie YB
and Xiao Q: Overexpression of CDX2 in gastric cancer cells promotes
the development of multidrug resistance. Am J Cancer Res.
5:321–332. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|