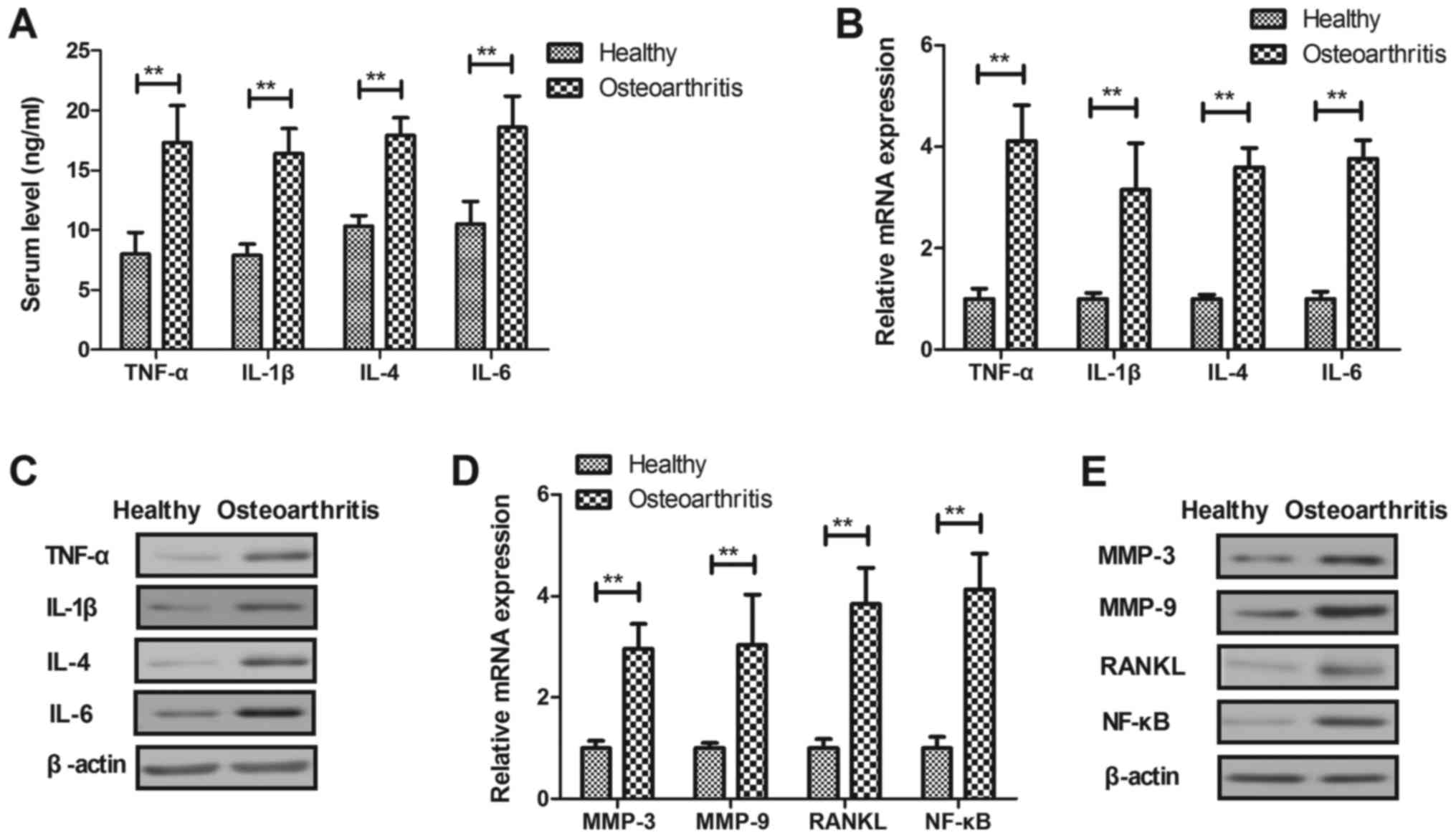
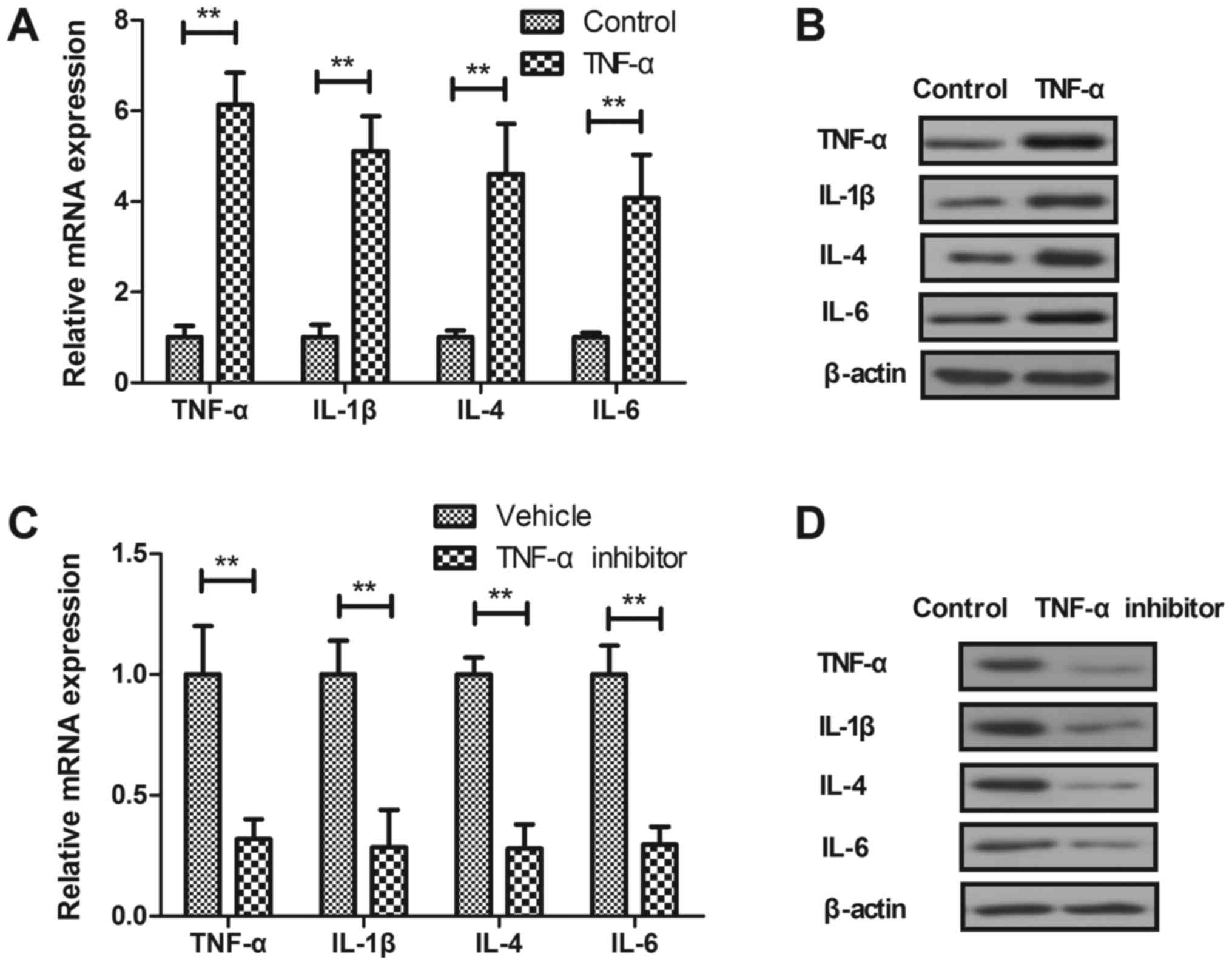
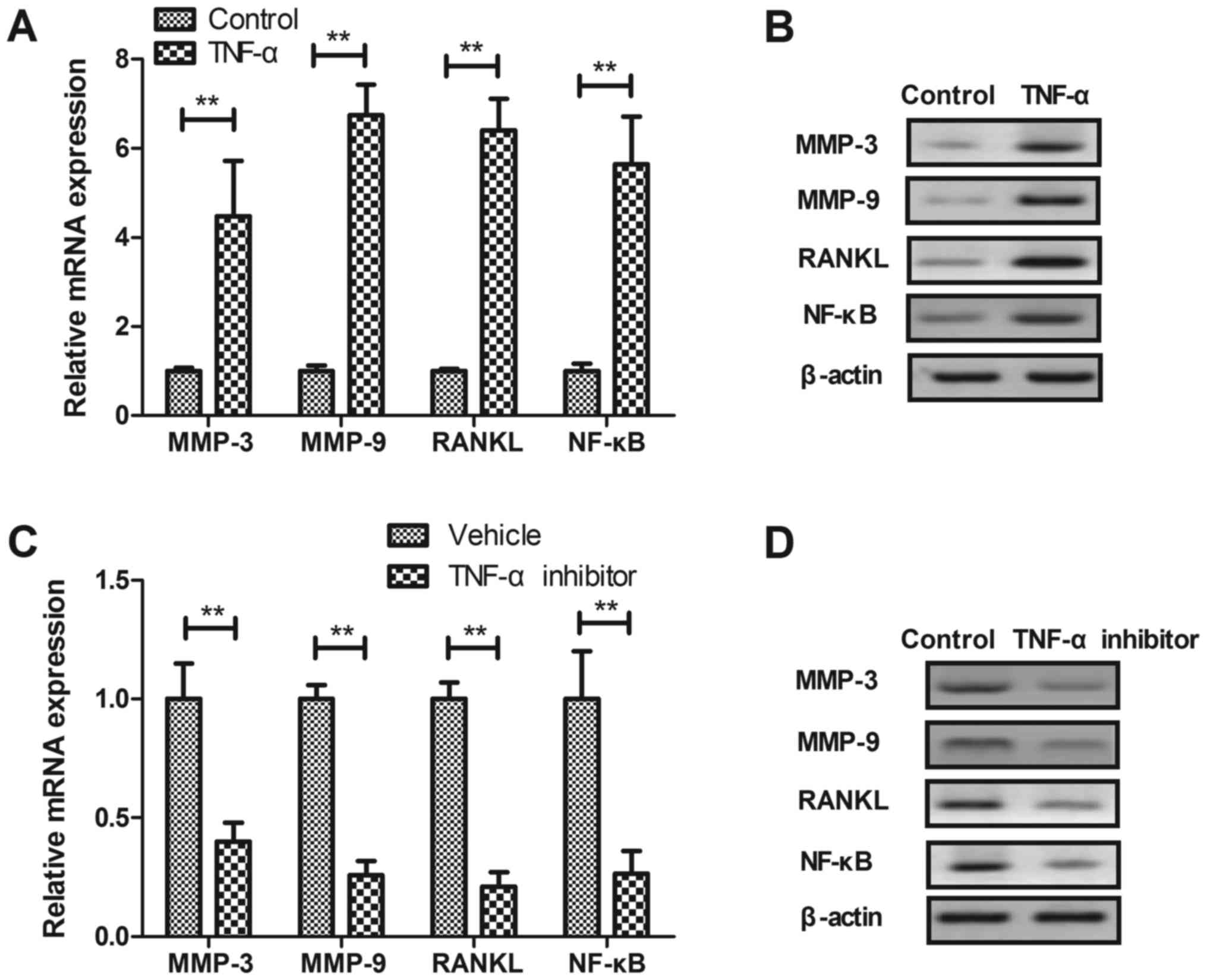
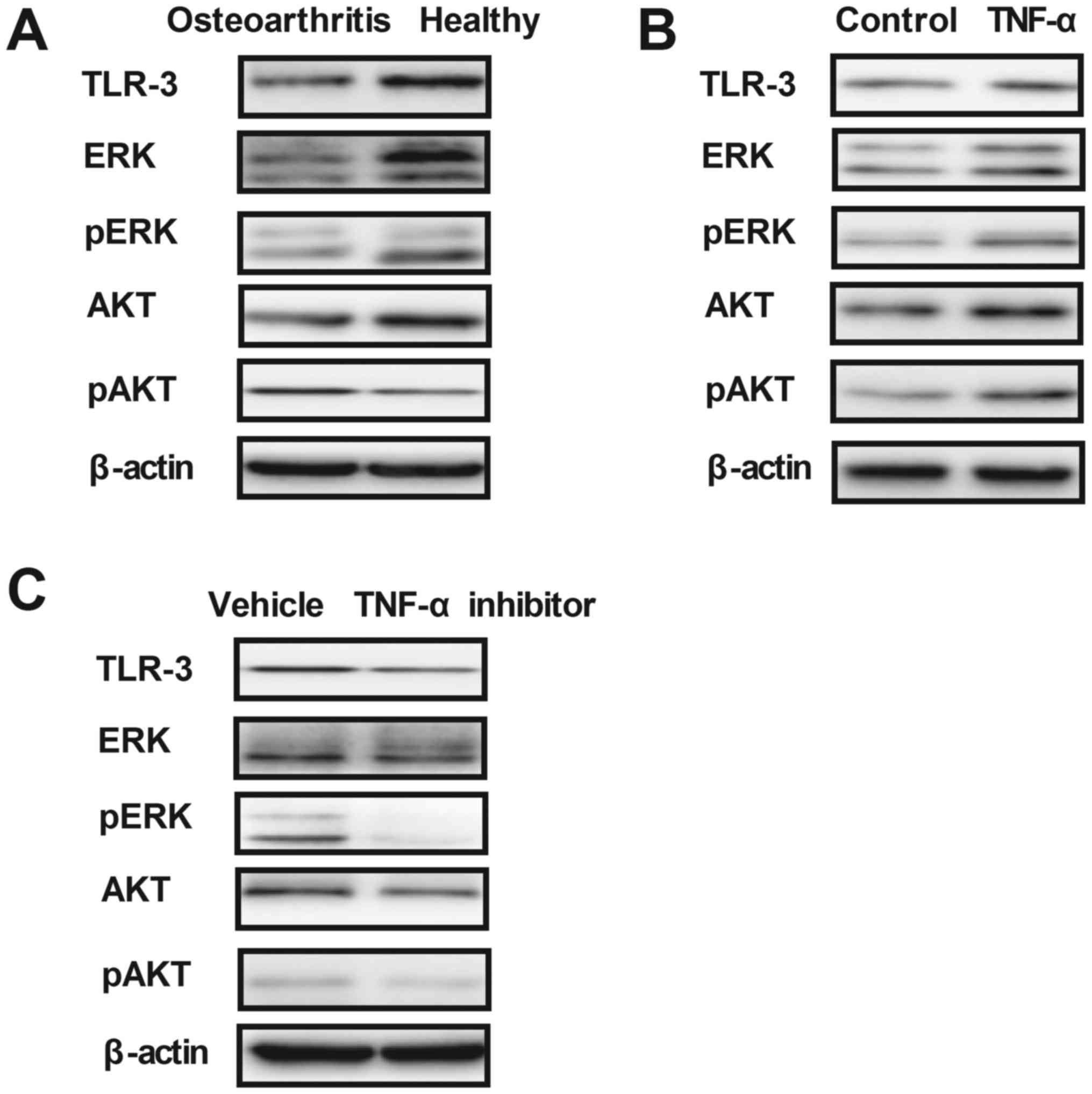
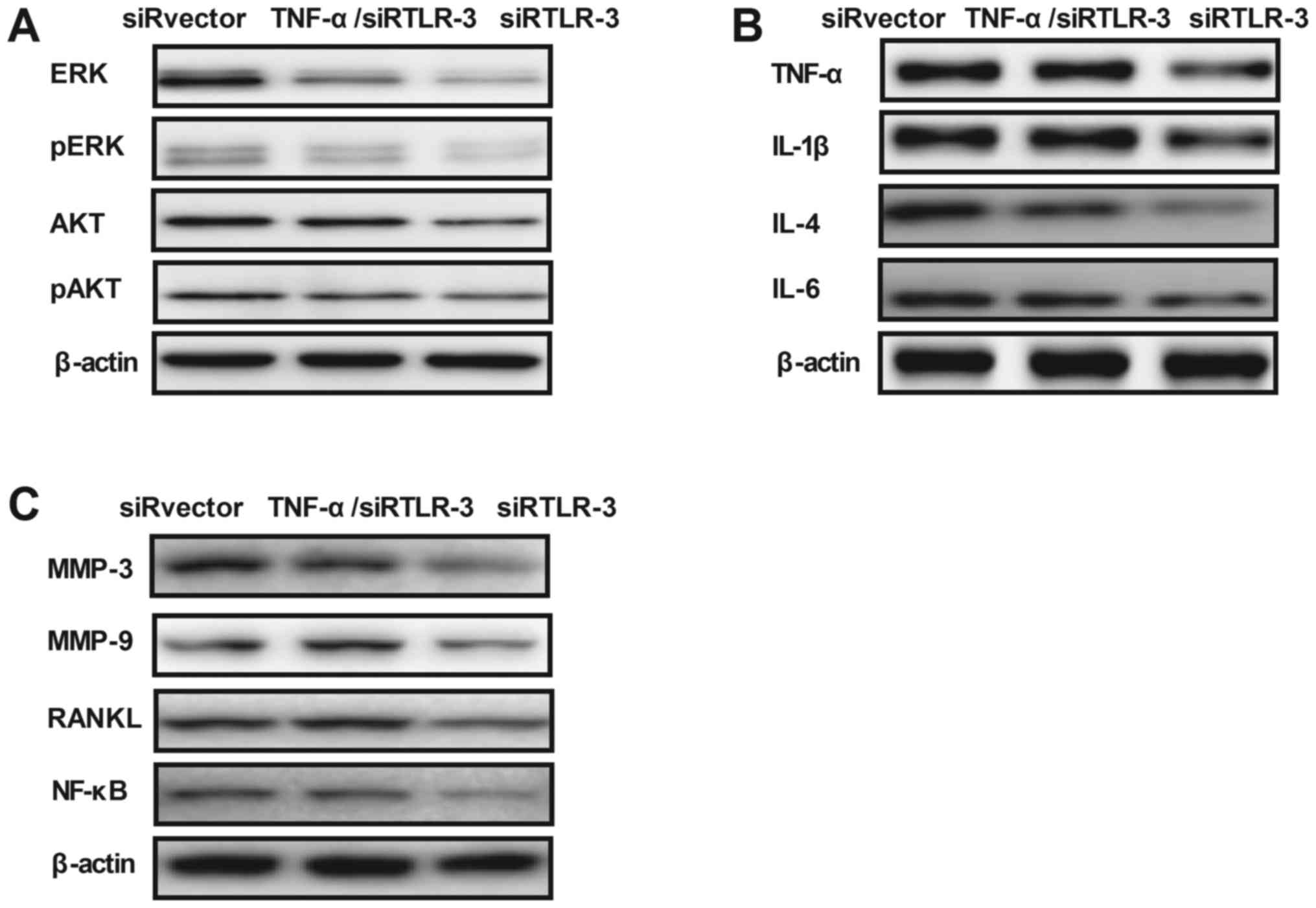
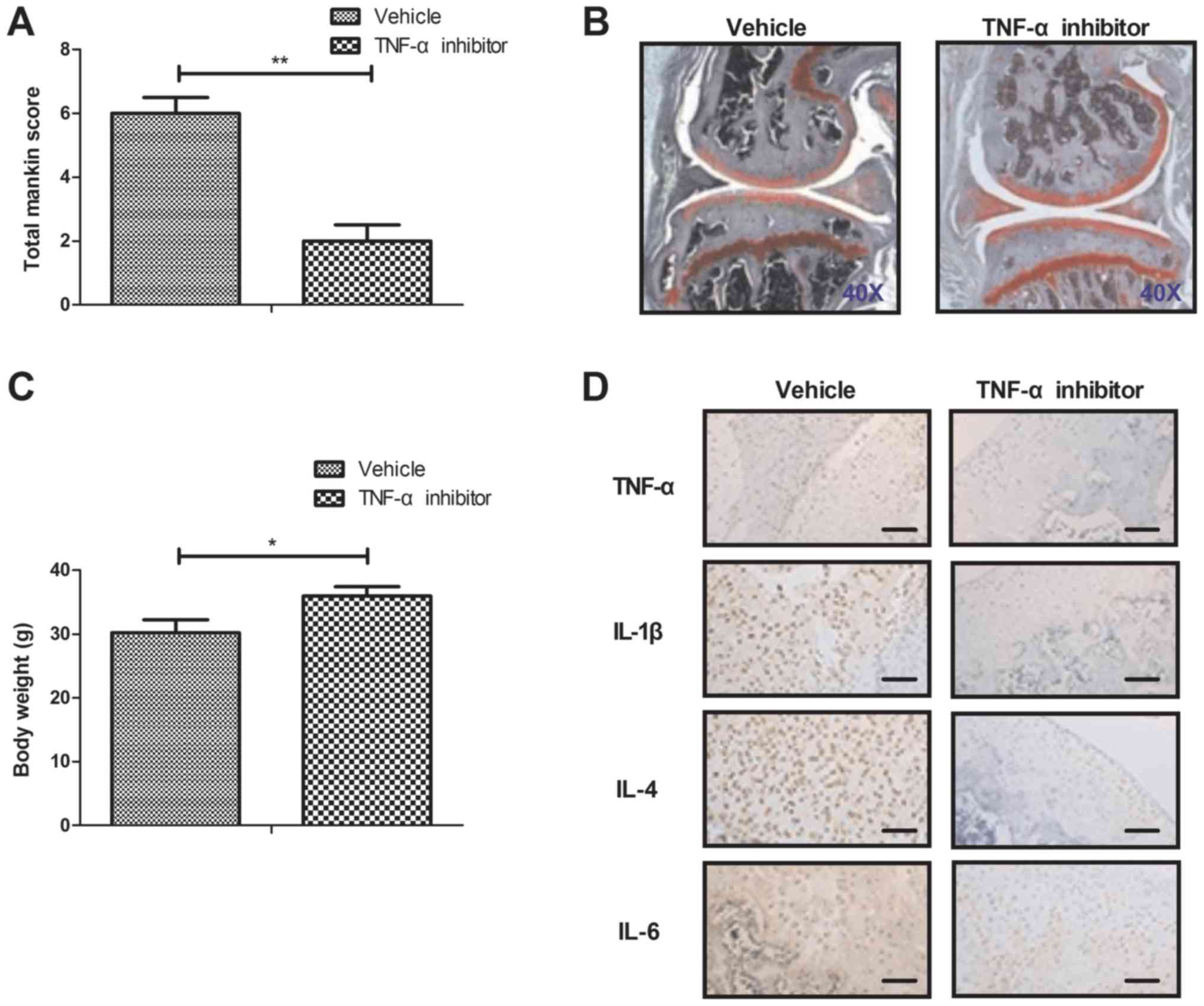
|
1
|
Xing F, Lu B, Kuang MJ, Wang Y, Zhao YL,
Zhao J, Sun L, Wang Y, Ma JX and Ma XL: A systematic review and
meta-analysis into the effect of lateral wedge arch support insoles
for reducing knee joint load in patients with medial knee
osteoarthritis. Medicine (Baltimore). 96:e71682017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Aujla RS and Esler CN: Total knee
arthroplasty for osteoarthritis in patients less than fifty-five
years of age: A systematic review. J Arthroplasty. 32:2598–2603.e1.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Alrushud AS, Rushton AB, Kanavaki AM and
Greig CA: Effect of physical activity and dietary restriction
interventions on weight loss and the musculoskeletal function of
overweight and obese older adults with knee osteoarthritis: A
systematic review and mixed method data synthesis. BMJ Open.
7:e0145372017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Alentorn-Geli E, Samuelsson K, Musahl V,
Green CL, Bhandari M and Karlsson J: The association of
recreational and competitive running with hip and knee
osteoarthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Orthop
Sports Phys Ther. 47:373–390. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Veenhof C, Huisman PA, Barten JA, Takken T
and Pisters MF: Factors associated with physical activity in
patients with osteoarthritis of the hip or knee: A systematic
review. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 20:6–12. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Davis AM: Osteoarthritis year in review:
Rehabilitation and outcomes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 20:201–206.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Stannus O, Jones G, Cicuttini F,
Parameswaran V, Quinn S, Burgess J and Ding C: Circulating levels
of IL-6 and TNF-α are associated with knee radiographic
osteoarthritis and knee cartilage loss in older adults.
Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 18:1441–1447. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yuan PW, Liu DY, Chu XD, Hao YQ, Zhu C and
Qu Q: Effects of preventive administration of juanbi capsules on
TNF-alpha, IL-1 and IL-6 contents of joint fluid in the rabbit with
knee osteoarthritis. J Tradit Chin Med. 30:254–258. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Güler-Yüksel M, Allaart CF, Watt I,
Goekoop-Ruiterman YP, de Vries-Bouwstra JK, van Schaardenburg D,
van Krugten MV, Dijkmans BA, Huizinga TW, Lems WF and Kloppenburg
M: Treatment with TNF-α inhibitor infliximab might reduce hand
osteoarthritis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 18:1256–1262. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Qin J, Shang L, Ping AS, Li J, Li XJ, Yu
H, Magdalou J, Chen LB and Wang H: TNF/TNFR signal transduction
pathway-mediated anti-apoptosis and anti-inflammatory effects of
sodium ferulate on IL-1β-induced rat osteoarthritis chondrocytes in
vitro. Arthritis Res Ther. 14:R2422012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li ZC, Han N, Li X, Li G, Liu YZ, Sun GX,
Wang Y, Chen GT and Li GF: Decreased expression of microRNA-130a
correlates with TNF-α in the development of osteoarthritis. Int J
Clin Exp Pathol. 8:2555–2564. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Latourte A, Cherifi C, Maillet J, Ea HK,
Bouaziz W, Funck-Brentano T, Cohen-Solal M, Hay E and Richette P:
Systemic inhibition of IL-6/Stat3 signalling protects against
experimental osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 76:748–755. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lee SY, Yoon BY, Kim JI, Heo YM, Woo YJ,
Park SH, Kim HY, Kim SI and Cho ML: Interleukin-17 increases the
expression of Toll-like receptor 3 via the STAT3 pathway in
rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Immunology.
141:353–361. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ospelt C, Brentano F, Rengel Y, Stanczyk
J, Kolling C, Tak PP, Gay RE, Gay S and Kyburz D: Overexpression of
toll-like receptors 3 and 4 in synovial tissue from patients with
early rheumatoid arthritis: Toll-like receptor expression in early
and longstanding arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 58:3684–3692. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhu W, Meng L, Jiang C, He X, Hou W, Xu P,
Du H, Holmdahl R and Lu S: Arthritis is associated with
T-cell-induced upregulation of Toll-like receptor 3 on synovial
fibroblasts. Arthritis Res Ther. 13:R1032011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Domagala F, Martin G, Bogdanowicz P,
Ficheux H and Pujol JP: Inhibition of interleukin-1beta-induced
activation of MEK/ERK pathway and DNA binding of NF-kappaB and
AP-1: Potential mechanism for diacerein effects in osteoarthritis.
Biorheology. 43:577–587. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Klosowska K, Volin MV, Huynh N, Chong KK,
Halloran MM and Woods JM: Fractalkine functions as a
chemoattractant for osteoarthritis synovial fibroblasts and
stimulates phosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein kinases and
Akt. Clin Exp Immunol. 156:312–319. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mohan G, Perilli E, Kuliwaba JS, Humphries
JM, Parkinson IH and Fazzalari NL: Application of in vivo
micro-computed tomography in the temporal characterisation of
subchondral bone architecture in a rat model of low-dose monosodium
iodoacetate-induced osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther.
13:R2102011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zimmermann T, Kunisch E, Pfeiffer R, Hirth
A, Stahl HD, Sack U, Laube A, Liesaus E, Roth A, Palombo-Kinne E,
et al: Isolation and characterization of rheumatoid arthritis
synovial fibroblasts from primary culture-primary culture cells
markedly differ from fourth-passage cells. Arthritis Res. 3:72–76.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kurien BT and Scofield RH: Western
blotting. Methods. 38:283–293. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bar-Yehuda S, Rath-Wolfson L, Del Valle L,
Ochaion A, Cohen S, Patoka R, Zozulya G, Barer F, Atar E,
Piña-Oviedo S, et al: Induction of an antiinflammatory effect and
prevention of cartilage damage in rat knee osteoarthritis by CF101
treatment. Arthritis Rheum. 60:3061–3071. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ma CH, Lv Q, Yu YX, Zhang Y, Kong D, Niu
KR and Yi CQ: Protective effects of tumor necrosis factor-α
blockade by adalimumab on articular cartilage and subchondral bone
in a rat model of osteoarthritis. Braz J Med Biol Res. 48:863–870.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chevalier X, Ravaud P, Maheu E, Baron G,
Rialland A, Vergnaud P, Roux C, Maugars Y, Mulleman D, Lukas C, et
al: Adalimumab in patients with hand osteoarthritis refractory to
analgesics and NSAIDs: A randomised, multicentre, double-blind,
placebo-controlled trial. Ann Rheum Dis. 74:1697–1705. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Fioravanti A, Fabbroni M, Cerase A and
Galeazzi M: Treatment of erosive osteoarthritis of the hands by
intra-articular infliximab injections: A pilot study. Rheumatol
Int. 29:961–965. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gratchev A, Schmuttermaier C, Mamidi S,
Gooi L, Goerdt S and Kzhyshkowska J: Expression of osteoarthritis
marker YKL-39 is stimulated by transforming growth factor beta
(TGF-beta) and IL-4 in differentiating macrophages. Biomark
Insights. 3:39–44. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Huang J, Zhuo LS, Wang YY, Peng ZL, Huang
YR, Wang Y and Yang L: Effects of electroacupuncture on synovia
IL-1beta and TNF-alpha contents in the rabbit with knee
osteoarthritis. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 32:115–118. 2007.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mahmoud RK, El-Ansary AK, El-Eishi HH,
Kamal HM and El-Saeed NH: Matrix metalloproteinases MMP-3 and MMP-1
levels in sera and synovial fluids in patients with rheumatoid
arthritis and osteoarthritis. Ital J Biochem. 54:248–257.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sun R, Huang Y, Zhang H and Liu R: MMP-2,
TNF-α and NLRP1 polymorphisms in Chinese patients with ankylosing
spondylitis and rheumatoid arthritis. Mol Biol Rep. 40:6303–6308.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Crotti TN, Smith MD, Weedon H, Ahern MJ,
Findlay DM, Kraan M, Tak PP and Haynes DR: Receptor activator
NF-kappaB ligand (RANKL) expression in synovial tissue from
patients with rheumatoid arthritis, spondyloarthropathy,
osteoarthritis, and from normal patients: Semiquantitative and
quantitative analysis. Ann Rheum Dis. 61:1047–1054. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yang HY, Lee HS, Lee CH, Fang WH, Chen HC,
Salter DM and Su SL: Association of a functional polymorphism in
the promoter region of TLR-3 with osteoarthritis: A two-stage
case-control study. J Orthop Res. 31:680–685. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Fu D, Shang X, Ni Z and Shi G: Shikonin
inhibits inflammation and chondrocyte apoptosis by regulation of
the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in a rat model of osteoarthritis.
Exp Ther Med. 12:2735–2740. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ballak DB, van Asseldonk EJ, van Diepen
JA, Jansen H, Hijmans A, Joosten LA, Tack CJ, Netea MG and
Stienstra R: TLR-3 is present in human adipocytes, but its
signalling is not required for obesity-induced inflammation in
adipose tissue in vivo. PLoS One. 10:e01231522015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Roelofs MF, Wenink MH, Brentano F,
Abdollahi-Roodsaz S, Oppers-Walgreen B, Barrera P, van Riel PL,
Joosten LA, Kyburz D, van den Berg WB and Radstake TR: Type I
interferons might form the link between Toll-like receptor (TLR)
3/7 and TLR4-mediated synovial inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis
(RA). Ann Rheum Dis. 68:1486–1493. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|