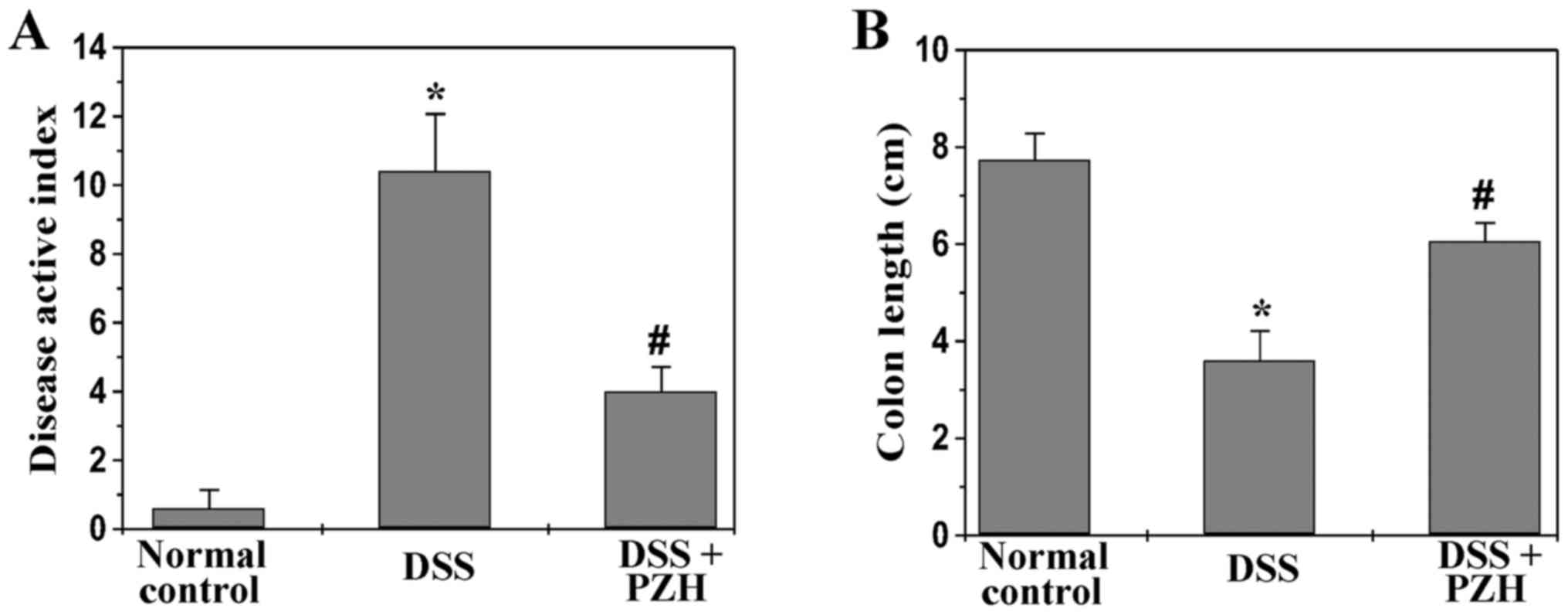
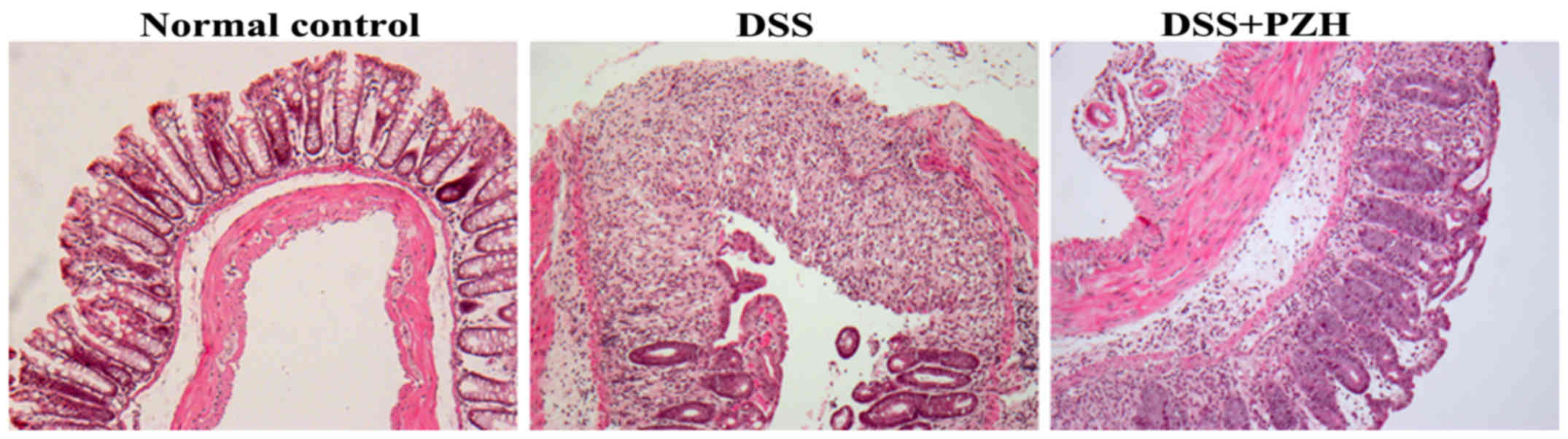
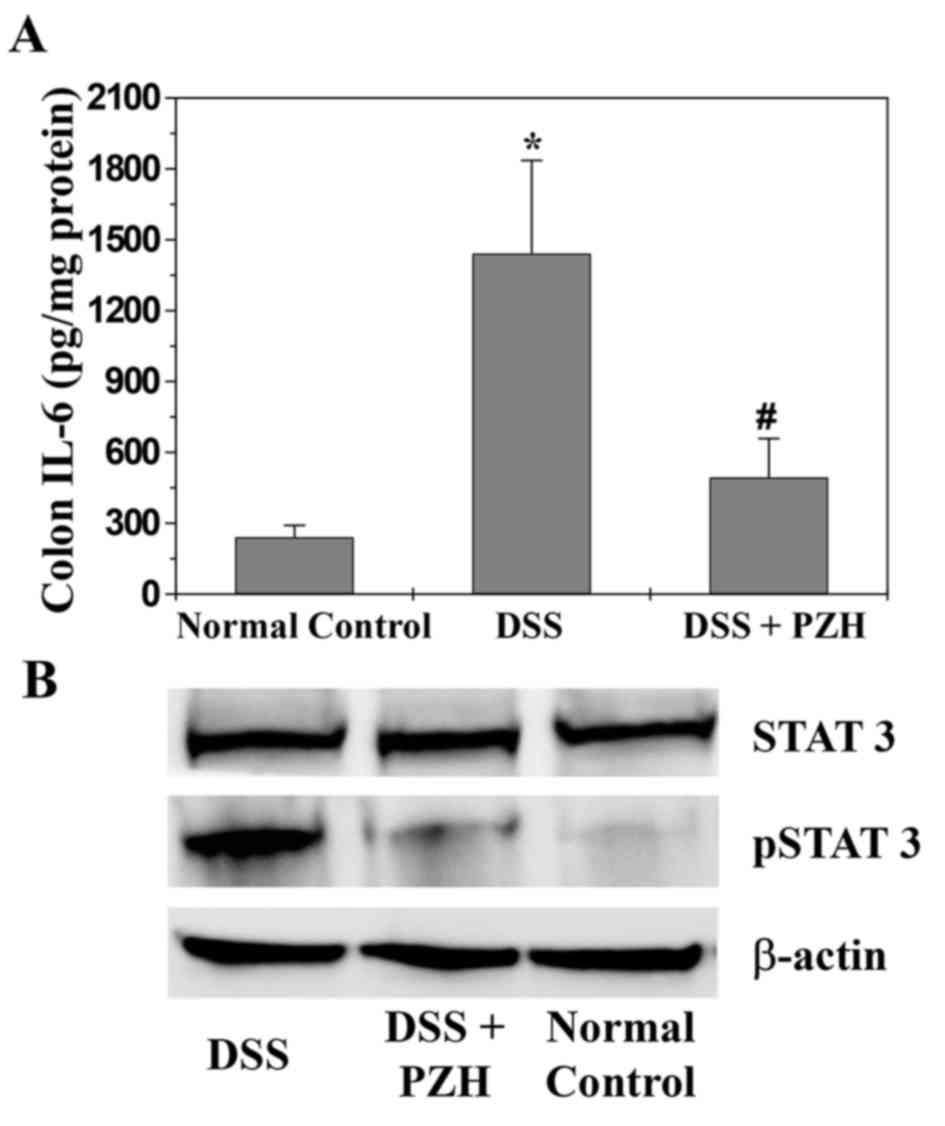
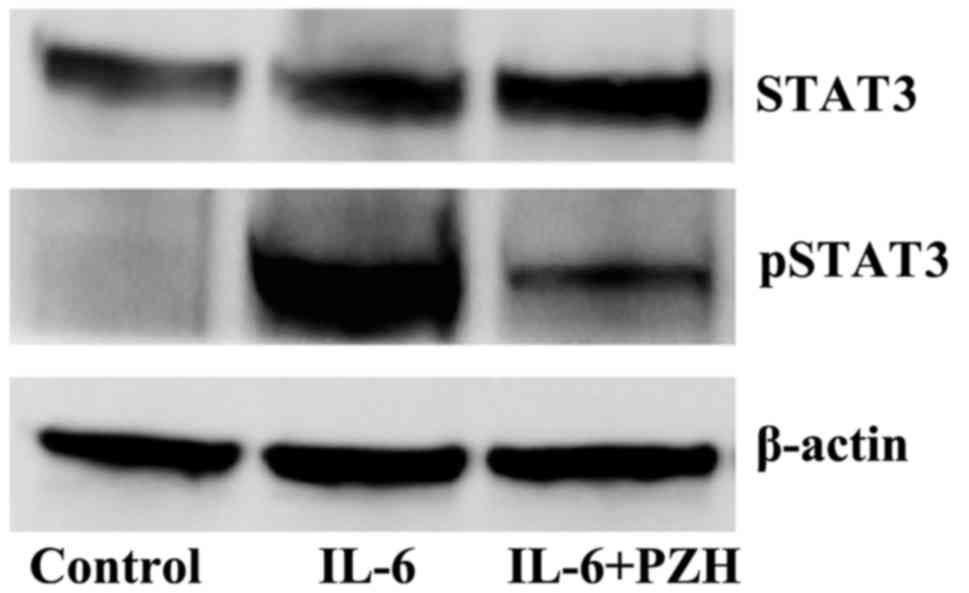
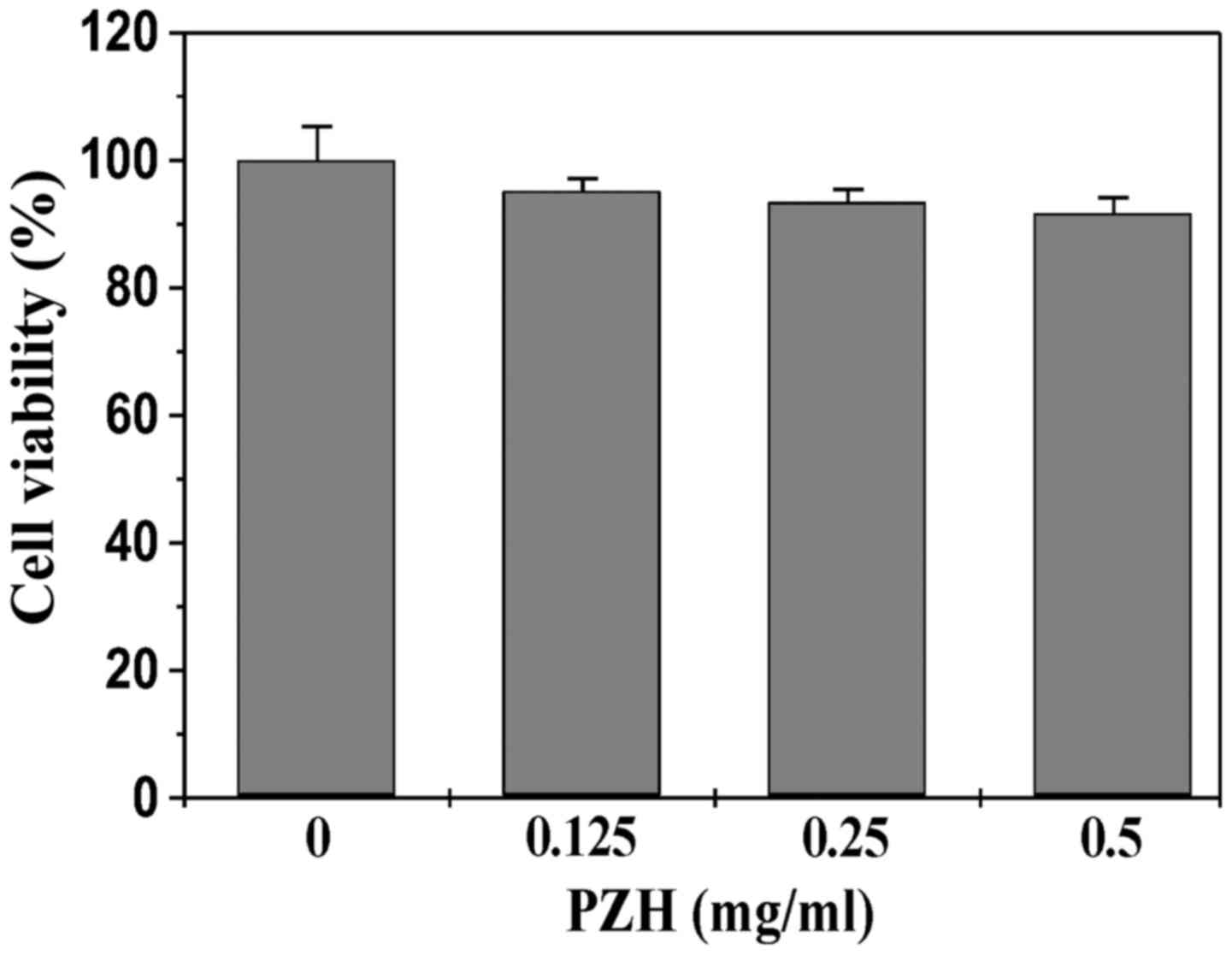
|
1
|
Baumgart DC and Carding SR: Inflammatory
bowel disease: Cause and immunobiology. The Lancet. 369:1627–1640.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Baumgart DC and Sandborn WJ: Inflammatory
bowel disease: Clinical aspects and established and evolving
therapies. The Lancet. 369:1641–1657. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Xavier RJ and Podolsky DK: Unravelling the
pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Nature. 448:427–434.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Podolsky DK: Inflammatory bowel disease. N
Engl J Med. 347:417–429. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rezaie A, Parker RD and Abdollahi M:
Oxidative stress and pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease: An
epiphenomenon or the cause? Dig Dis Sci. 52:2015–2021. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cho EJ, Shin JS, Noh YS, Cho YW, Hong SJ,
Park JH, Lee JY, Lee JY and Lee KT: Anti-inflammatory effects of
methanol extract of Patrinia scabiosaefolia in mice with
ulcerative colitis. J Ethnopharmacol. 136:428–435. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jani N and Regueiro MD: Medical therapy
for ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterol Clin N Am. 31:147–166. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Lakatos PL and Lakatos L: Ulcerative
proctitis: A review of pharmacotherapy and management. Expert Opin
Pharmacother. 9:741–749. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Treasure J: Herbal medicine and cancer: An
introductory overview. Semin Oncol Nurs. 21:177–1835. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Stickel F and Schuppan D: Herbal medicine
in the treatment of liver diseases. Dig Liver Dis. 39:293–304.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Langmead L and Rampton DS: Review article:
Complementary and alternative therapies for inflammatory bowel
disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 23:341–349. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bensoussan M, Jovenin N, Garcia B,
Vandromme L, Jolly D, Bouché O, Thiéfin G and Cadiot G:
Complementary and alternative medicine use by patients with
inflammatory bowel disease: Results from a postal survey.
Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 30:14–23. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gross V, Andus T, Cäsar I, Roth M and
Schölmerich J: Evidence for continuous stimulation of interleukin-6
production in Crohn's disease. Gastroenterol. 102:514–519. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Holub M C, Mako E, Devay T, Dank M, Szalai
C, Fenyvesi A and Falus A: Increased interleukin-6 levels,
interleukin-6 receptor and gp130 expression in peripheral
lymphocytes of patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Scand J
Gastroenterol Suppl. 228:47–50. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Isaacs KL, Sartor RB and Haskill S:
Cytokine messenger RNA profiles in inflammatory bowel disease
mucosa detected by polymerase chain reaction amplification.
Gastroenterol. 103:1587–1595. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Reinecker HC, Steffen M, Witthöft T,
Pflüger I, Schreiber S, MacDermott RP and Rädler A: Enhanced
secretion of tumour necrosis factor-alpha, IL-6, and IL-1 beta by
isolated lamina propria mononuclear cells from patients with
ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. Clin Exp Immunol.
94:174–181. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Reinisch W, Gasche C, Tillinger W, Wyatt
J, Lichtenberger C, Willheim M, Dejaco C, Waldhör T, Bakos S,
Vogelsang H, Gangl A and Lochs H: Clinical relevance of serum
interleukin-6 in Crohn's disease: single point measurements,
therapy monitoring, and prediction of clinical relapse. Am J
Gastroenterol. 94:2156–2164. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Belaiche J, Van Kemseke C and Louis E: Use
of the enteroscope for colo-ileoscopy: Low yield in unexplained
lower gastrointestinal bleeding. Endoscopy. 31:298–301. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Louis E, Belaiche J, van Kemseke C,
Franchimont D, deGroote D, Gueenen V and Mary JY: A high serum
concentration of interleukin-6 is predictive of relapse in
quiescent Crohn's disease. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 9:939–944.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kusugami K, Fukatsu A, Tanimoto M, Shinoda
M, Haruta J, Kuroiwa A, Ina K, Kanayama K, Ando T and Matsuura T:
Elevation of interleukin-6 in inflammatory bowel disease is
macrophage- and epithelial cell-dependent. Digestive Dis Sci.
40:949–959. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Atreya R, Mudter J, Finotto S, Müllberg J,
Jostock T, Wirtz S, Schütz M, Bartsch B, Holtmann M, Becker C, et
al: Blockade of interleukin 6 trans signaling suppresses T-cell
resistance against apoptosis in chronic intestinal inflammation:
Evidence in Crohn disease and experimental colitis in vivo. Nat
Med. 6:583–588. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Desreumaux P, Brandt E, Gambiez L, Emilie
D, Geboes K, Klein O, Ectors N, Cortot A, Capron M and Colombel JF:
Distinct cytokine patterns in early and chronic ileal lesions of
Crohn's disease. Gastroenterol. 113:118–126. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Brown KA, Back SJ, Ruchelli ED, Markowitz
J, Mascarenhas M, Verma R, Piccoli DA and Baldassano RN: Lamina
propria and circulating interleukin-6 in newly diagnosed pediatric
inflammatory bowel disease patients. Am J Gastroenterol.
97:2603–2608. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Becker C, Fantini MC, Schramm C, Lehr HA,
Wirtz S, Nikolaev A, Burg J, Strand S, Kiesslich R, Huber S, et al:
TGF-beta suppresses tumor progression in colon cancer by inhibition
of IL-6 trans-signaling. Immunity. 2:491–501. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Becker C, Fantini MC, Wirtz S, Nikolaev A,
Lehr HA, Galle PR, Rose-John S and Neurath MF: IL-6 signaling
promotes tumor growth in colorectal cancer. Cell Cycle. 4:217–220.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Dowdall JF, Winter DC, Andrews E, Laug WE,
Wang JH and Redmond HP: Soluble interleukin 6 receptor (sIL-6R)
mediates colonic tumor cell adherence to the vascular endothelium:
A mechanism for metastatic initiation? J Surg Res. 107:1–6. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Heinrich PC, Behrmann I, Haan S, Hermanns
HM, Müller-Newen G and Schaper F: Principles of interleukin
(IL)-6-type cytokine signalling and its regulation. Biochem J.
374:1–20. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bromberg J and Darnell JE Jr: The role of
STATs in transcriptional control and their impact on cellular
function. Oncogene. 19:2468–2473. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Aggarwal BB, Kunnumakkara AB, Harikumar
KB, Gupta SR, Tharakan ST, Koca C, Dey S and Sung B: Signal
transducer and activator of transcription-3, inflammation, and
cancer: How intimate is the relationship? Ann NY Acad Sci.
1171:59–76. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lovato P, Brender C, Agnholt J, Kelsen J,
Kaltoft K, Svejgaard A, Eriksen KW, Woetmann A and Ødum N:
Constitutive STAT3 activation in intestinal T cells from patients
with Crohn's disease. J Biol Chem. 278:16777–16781. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Suzuki A, Hanada T, Mitsuyama K, Yoshida
T, Kamizono S, Hoshino T, Kubo M, Yamashita A, Okabe M, Takeda K,
et al: CIS3/SOCS3/SSI3 plays a negative regulatory role in STAT3
activation and intestinal inflammation. J Exp Med. 193:471–481.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission, .
Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China. 1. China Medical
Science and Technology Press; Beijing: pp. 573–575. 2010
|
|
33
|
Lin JM, Wei LH, Chen YQ, Liu XX, Hong ZF,
Sferra TJ and Peng J: Pien Tze Huang-induced apoptosis in human
colon cancer HT-29 cells is associated with regulation of the Bcl-2
family and activation of caspase 3. Chin J Integr Med. 17:685–690.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhuang QC, Hong F, Shen AL, Zheng LP, Zeng
JW, Lin W, Chen YQ, Sferra TJ, Hong ZF and Peng J: Pien Tze Huang
inhibits tumor cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis via
suppressing the STAT3 pathway in colorectal cancer mouse. Int J
Oncol. 40:1569–1574. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Shen AL, Hong F, Liu LY, Lin JM, Zhuang
QC, Hong ZF and Peng J: Effects of Pien Tze Huang on angiogenesis
in vivo and in vitro. Chin J Integr Med. 18:431–436. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Shen A, Hong F, Liu L, Lin J, Wei L, Cai
Q, Hong Z and Peng J: Pien Tze Huang inhibits the proliferation of
human colon carcinoma cells by arresting G1/S cell cycle
progression. Oncol Lett. 4:767–770. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Shen A, Chen Y, Hong F, Lin J, Wei L, Hong
Z, Sferra TJ and Peng J: Pien Tze Huang suppresses IL-6-inducible
STAT3 activation in human colon carcinoma cells through induction
of SOCS3. Oncol Rep. 28:2125–2130. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Shen A, Lin J, Chen Y, Lin W, Liu L, Hong
Z, Sferra TJ and Peng J: Pien Tze Huang inhibits tumor angiogenesis
in a mouse model of colorectal cancer via suppression of multiple
cellular pathways. Oncol Rep. 3:1701–1706. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Lin W, Zhuang QC, Zheng LP, Cao ZY, Shen
AL, Li QY, Fu CX, Feng JY and Peng J: Pien Tze Huang inhibits liver
metastasis by targeting TGF-β signaling in an orthotopic model of
colorectal cancer. Oncol Rep. 33:1922–1028. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wei L, Chen P, Chen Y, Shen A, Chen H, Lin
W, Hong Z, Sferra TJ and Peng J: Pien Tze Huang suppresses the
stem-like side population in colorectal cancer cells. Mol Med Rep.
9:261–266. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chen HW, Shen AL, Zhang YC, Chen YQ, Lin
JM, Lin W, Sferra TJ and Peng J: Pien Tze Huang inhibits
hypoxia-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human colon
carcinoma cells through suppression of the HIF-1 pathway. Exp Ther
Med. 7:1237–1242. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Shen AL, Lin W, Chen YQ, Liu LL, Chen HW,
Zhuang QF, Lin JM, Sferra TJ and Peng J: Pien Tze Huang inhibits
metastasis of human colorectal carcinoma cells via modulation of
TGF-β1/ZEB/miR-200 signaling network. Int J Oncol. 46:685–690.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Chen H, Feng J, Zhang Y, Shen A, Chen Y,
Lin J, Lin W, Sferra TJ and Peng J: Pien Tze Huang inhibits
hypoxia-induced angiogenesis via HIF-1α/VEGF-A pathway in
colorectal cancer. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2015:4542792015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Shen A, Chen H, Chen Y, Lin J, Lin W, Liu
L, Sferra TJ and Peng J: Pien Tze Huang overcomes multidrug
resistance and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human
colorectal carcinoma cells via suppression of TGF-β pathway. Evid
Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014:6794362014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Qi F, Wei L, Shen A, Chen Y, Lin J, Chu J,
Cai Q, Pan J and Peng J: Pien Tze Huang inhibits the proliferation,
and induces the apoptosis and differentiation of colorectal cancer
stem cells via suppression of the Notch1 pathway. Oncol Rep.
35:511–517. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Lin J, Feng J, Jin Y, Yan Z, Lai Z and
Peng J: Pien Tze Huang suppresses VEGF-C-mediated lymphangiogenesis
in colorectal cancer. Oncol Rep. 36:3568–3576. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Fu C, Chu J, Shen A, Liu L, Chen H, Lin J,
Sferra TJ, Chen Y and Peng J: Pien Tze Huang alleviates
5-fluorouracil-induced intestinal mucositis in CT-26 tumor-bearing
mice. Exp Ther Med. 14:2291–2297. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Chen Z, Shen A, Liu L, Chen Y, Chu J, Cai
Q, Qi F, Sferra TJ and Peng J: Pien Tze Huang induces apoptosis and
inhibits proliferation of 5-fluorouracil-resistant colorectal
carcinoma via increasing miR-22 expression. Exp Ther Med.
14:3533–3540. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Wan Y, Shen A, Qi F, Chu J, Cai Q, Sferra
TJ, Peng J and Chen Y: Pien Tze Huang inhibits the proliferation of
colorectal cancer cells by increasing the expression of miR-34c-5p.
Exp Ther Med. 14:3901–3907. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Qi F, Zhou S, Li L, Wei L, Shen A, Liu L,
Wang Y and Peng J: Pien Tze Huang inhibits the growth of
hepatocellular carcinoma cells by upregulating miR-16 expression.
Oncol Lett. 14:8132–8137. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Ke X, Zhou F, Gao Y, Xie B, Hu G, Fang W,
Peng J, Chen Y and Sferra T: Qing Hua Chang Yin exerts therapeutic
effects against ulcerative colitis through the inhibition of the
TLR4/TNF-κB pathway. Int J Mol Med. 32:926–930. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|