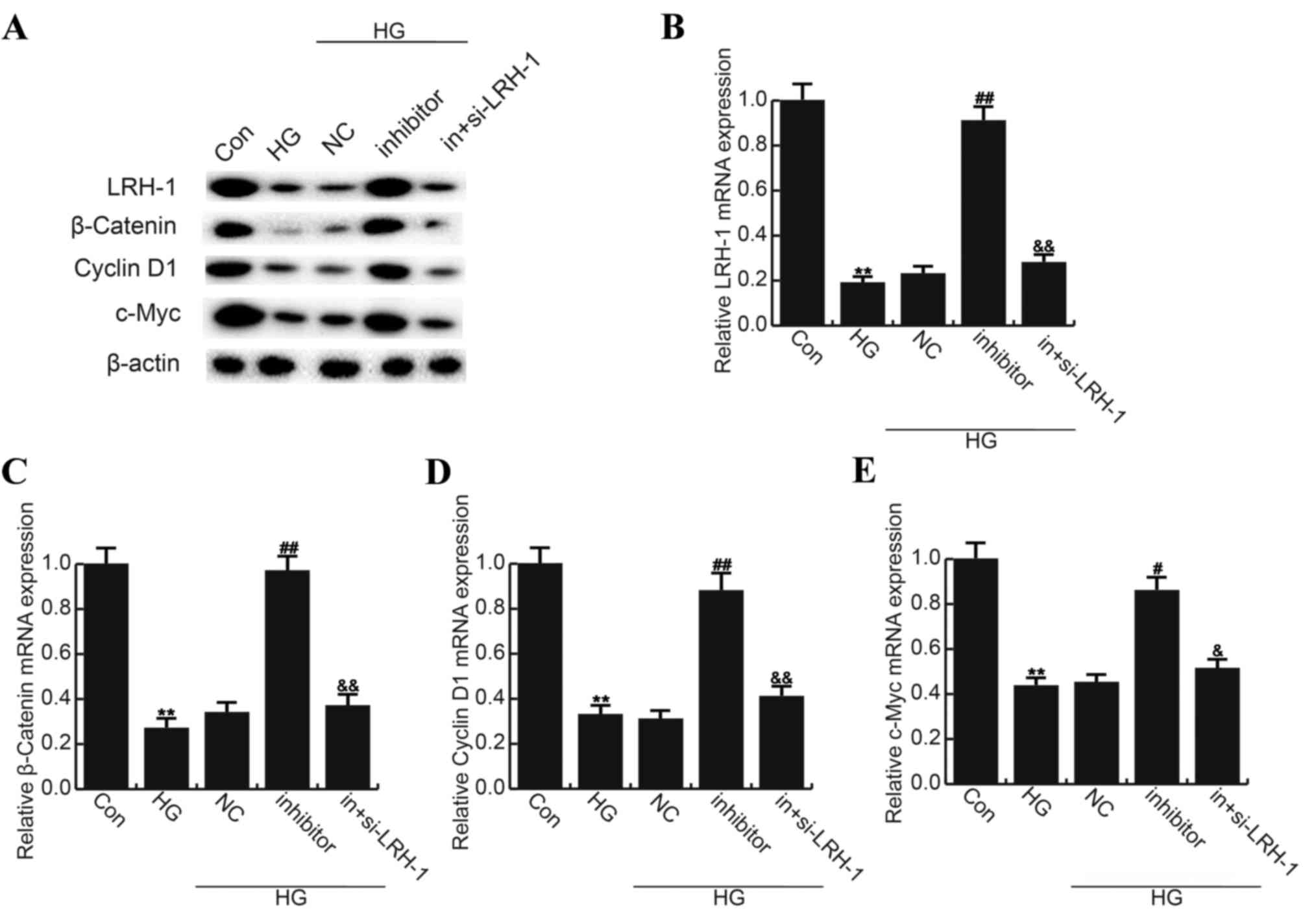
|
1
|
Ding J and Wong TY: Current epidemiology
of diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular edema. Curr Diab Rep.
12:346–354. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yau JW, Rogers SL, Kawasaki R, Lamoureux
EL, Kowalski JW, Bek T, Chen SJ, Dekker JM, Fletcher A, Grauslund
J, et al: Global prevalence and major risk facers of diabetic
retinopathy. Diabetes Care. 35:556–564. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kim VN, Han J and Siomi MC: Biogenesis of
small RNAs in animals. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 10:126–139. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Valencia-Sanchez MA, Liu J, Hannon GJ and
Parker R: Control of translation and mRNA degradation by miRNAs and
siRNAs. Genes Dev. 20:515–524. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kovacs B, Lumayag S, Cowan C and Xu S:
MicroRNAs in early diabetic retinopathy in streptozotocin-induced
diabetic rats. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 52:4402–4409. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lin X, Zhou X, Liu D, Yun L, Zhang L, Chen
X, Chai Q and Li L: MicroRNA-29 regulates high-glucose-induced
apoptosis in human retinal pigment epithelial cells through PTEN.
In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 52:419–426. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Qin B, Liu J, Liu S, Li B and Ren J:
MiR-20b targets AKT3 and modulates vascular endothelial growth
factor-mediated changes in diabetic retinopathy. Acta Biochim
Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 48:732–740. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang LQ, Cui H, Wang L, Fang X and Su S:
Role of microRNA-29a in the development of diabetic retinopathy by
targeting AGT gene in a rat model. Exp Mol Pathol. 102:296–302.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li EH, Huang QZ, Li GC, Xiang ZY and Zhang
X: Effects of miRNA-200b on the development of diabetic retinopathy
by targeting VEGFA gene. Biosci Rep. 37:pii: BSR20160572. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Wang Q, Zhu L, Jiang Y, Xu J, Wang F and
He Z: miR-219-5p suppresses the proliferation and invasion of
colorectal cancer cells by targeting calcyphosin. Oncol Lett.
13:1319–1324. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li C, Dong J, Han Z and Zhang K:
MicroRNA-219-5p represses the proliferation, migration, and
invasion of gastric cancer cells by targeting the
LRH-1/Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Oncol Res. 25:617–627. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Huang C, Cai Z, Huang M, Mao C, Zhang Q,
Lin Y, Zhang X, Tang B, Chen Y, Wang X, et al: miR-219-5p modulates
cell growth of papillary thyroid carcinoma by targeting estrogen
receptor α. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 100:E204–E213. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Huang N, Lin J, Ruan J, Su N, Qing R, Liu
F, He B, Lv C, Zheng D and Luo R: MiR-219-5p inhibits
hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation by targeting
glypican-3. FEBS Lett. 586:884–891. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ruiz MA, Feng B and Chakrabarti S:
Polycomb repressive complex 2 regulates MiR-200b in retinal
endothelial cells: Potential relevance in diabetic retinopathy.
PLoS One. 10:e01239872015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhao S, Li T, Li J, Lu Q, Han C, Wang N,
Qiu Q, Cao H, Xu X, Chen H and Zheng Z: miR-23b 3p induces the
cellular metabolic memory of high glucose in diabetic retinopathy
through a SIRT1-dependent signalling pathway. Diabetologia.
59:644–654. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhai G, Song J, Shu T, Yan J, Jin X, He J
and Yin Z: LRH-1 senses signaling from phosphatidylcholine to
regulate the expansion growth of digestive organs via synergy with
Wnt/β-catenin signaling in zebrafish. J Genet Genomics. 44:307–317.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ahsan H: Diabetic retinopathy-biomolecules
and multiple pathophysiology. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 9:51–54. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Simó R, Villarroel M, Corraliza L,
Hernández C and Garcia-Ramírez M: The retinal pigment epithelium:
Something more than a constituent of the blood-retinal
barrier-implications for the pathogenesis of diabetic retinopathy.
J Biomed Biotechnol. 2010:1907242010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cheng J, Deng R, Zhang P, Wu C, Wu K, Shi
L, Liu X, Bai J, Deng M, Shuai X, et al: miR-219-5p plays a tumor
suppressive role in colon cancer by targeting oncogene Sall4. Oncol
Rep. 34:1923–1932. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sablin EP, Blind RD, Uthayaruban R, Chiu
HJ, Deacon AM, Das D, Ingraham HA and Fletterick RJ: Structure of
liver receptor homolog-1 (NR5A2) with PIP3 hormone bound in the
ligand binding pocket. J Struct Biol. 192:342–348. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Fayard E, Auwerx J and Schoonjans K:
LRH-1: An orphan nuclear receptor involved in development,
metabolism and steroidogenesis. Trends Cell Biol. 14:250–260. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Stein S and Schoonjans K: Molecular basis
for the regulation of the nuclear receptor LRH-1. Curr Opin Cell
Biol. 33:26–34. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang Q, Zhao S, Pang X and Chi B:
MicroRNA-381 suppresses cell growth and invasion by targeting the
liver receptor homolog-1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Rep.
35:1831–1840. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jiang W, Tian Y, Jiang S, Liu S, Zhao X
and Tian D: MicroRNA-376c suppresses non-small-cell lung cancer
cell growth and invasion by targeting LRH-1-mediated Wnt signaling
pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 473:980–986. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Baquié M, St-Onge L, Kerr-Conte J,
Cobo-Vuilleumier N, Lorenzo PI, Moreno Jimenez CM, Cederroth CR,
Nef S, Borot S, Bosco D, et al: The liver receptor homolog-1
(LRH-1) is expressed in human islets and protects {beta}-cells
against stress-induced apoptosis. Hum Mol Genet. 20:2823–2833.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang S, Lan F, Huang L, Dong L, Zhu Z, Li
Z, Xie Y and Fu J: Suppression of hLRH-1 mediated by a DNA
vector-based RNA interference results in cell cycle arrest and
induction of apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cell BEL-7402.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 333:917–924. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|