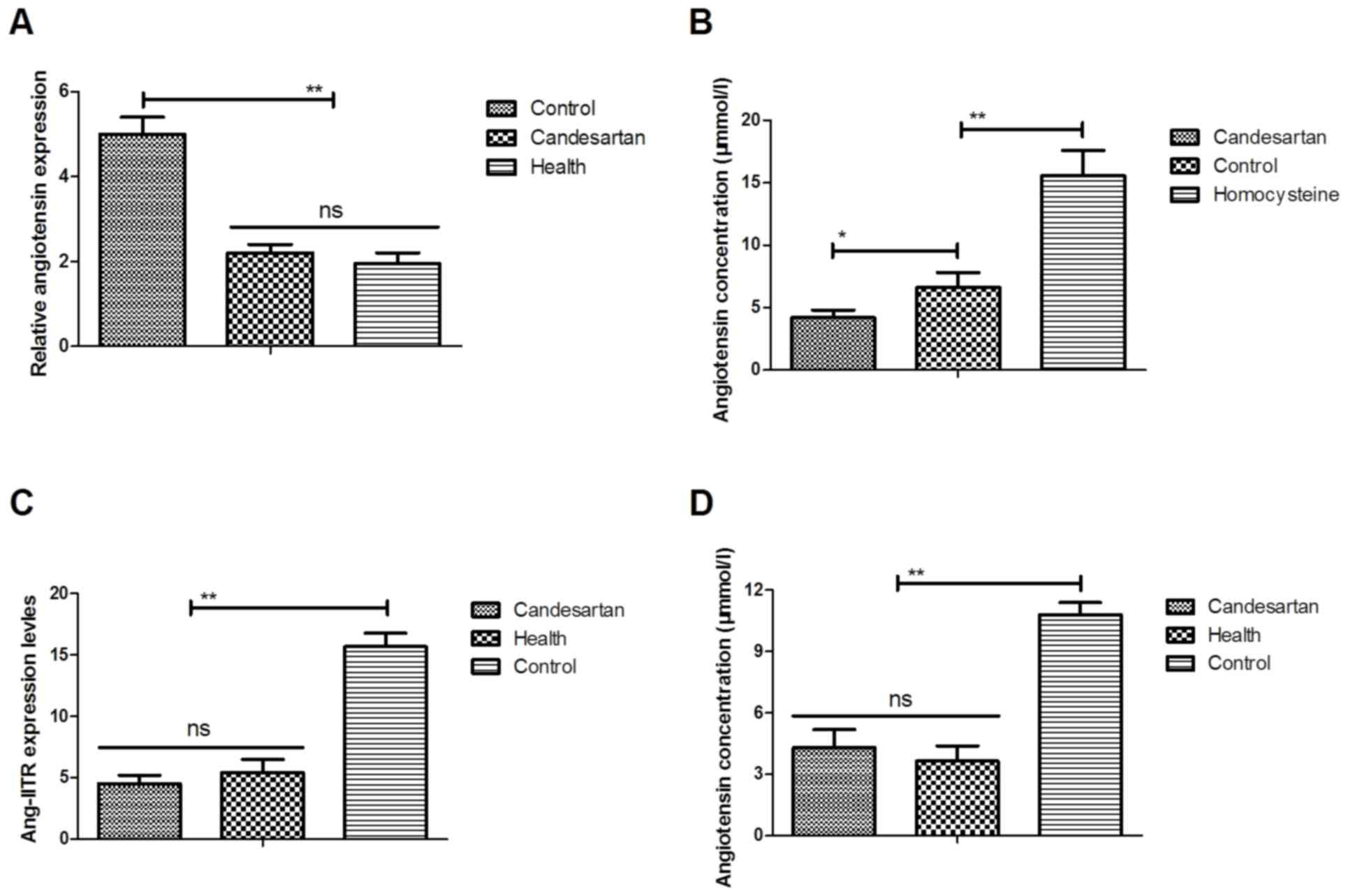
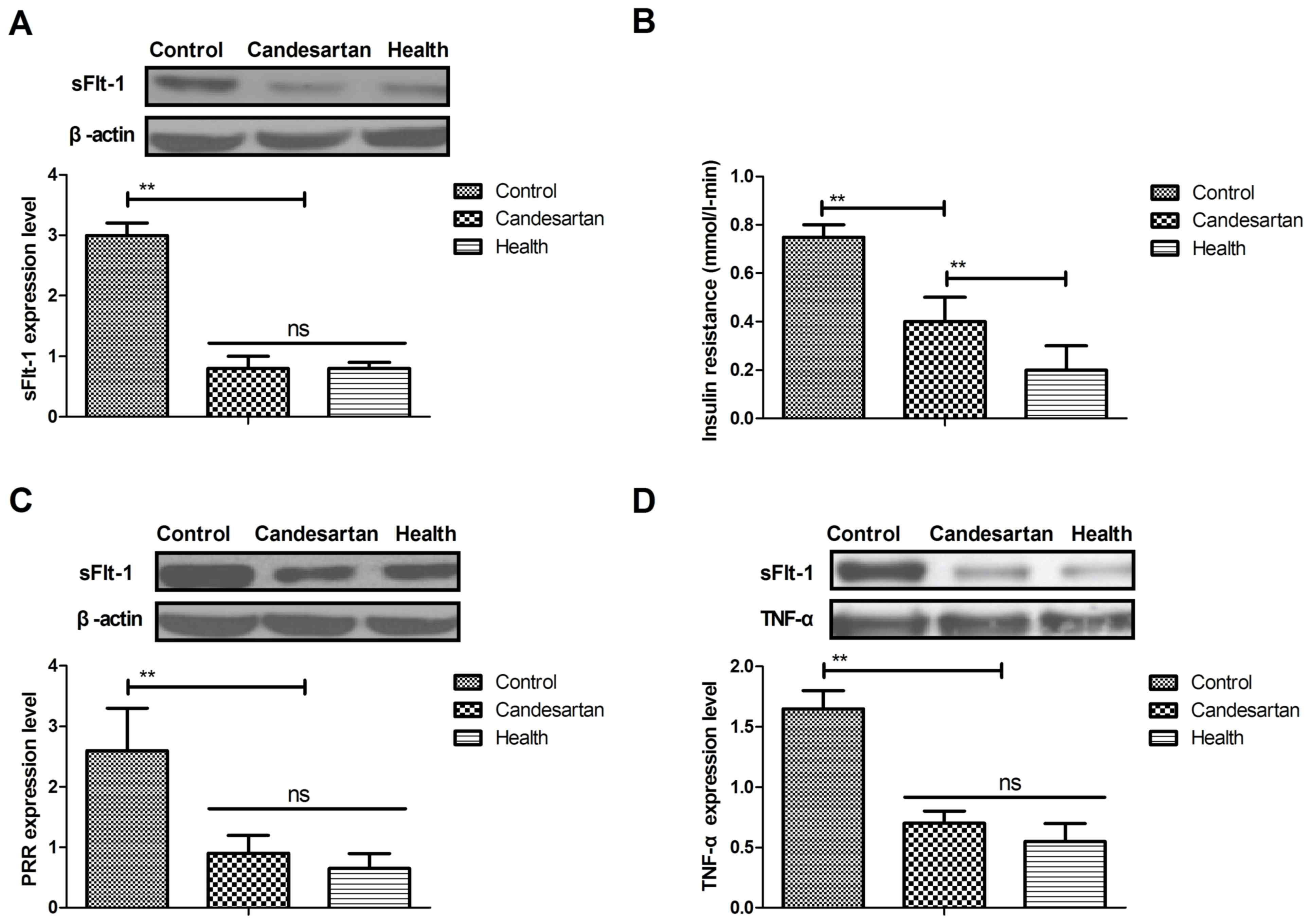
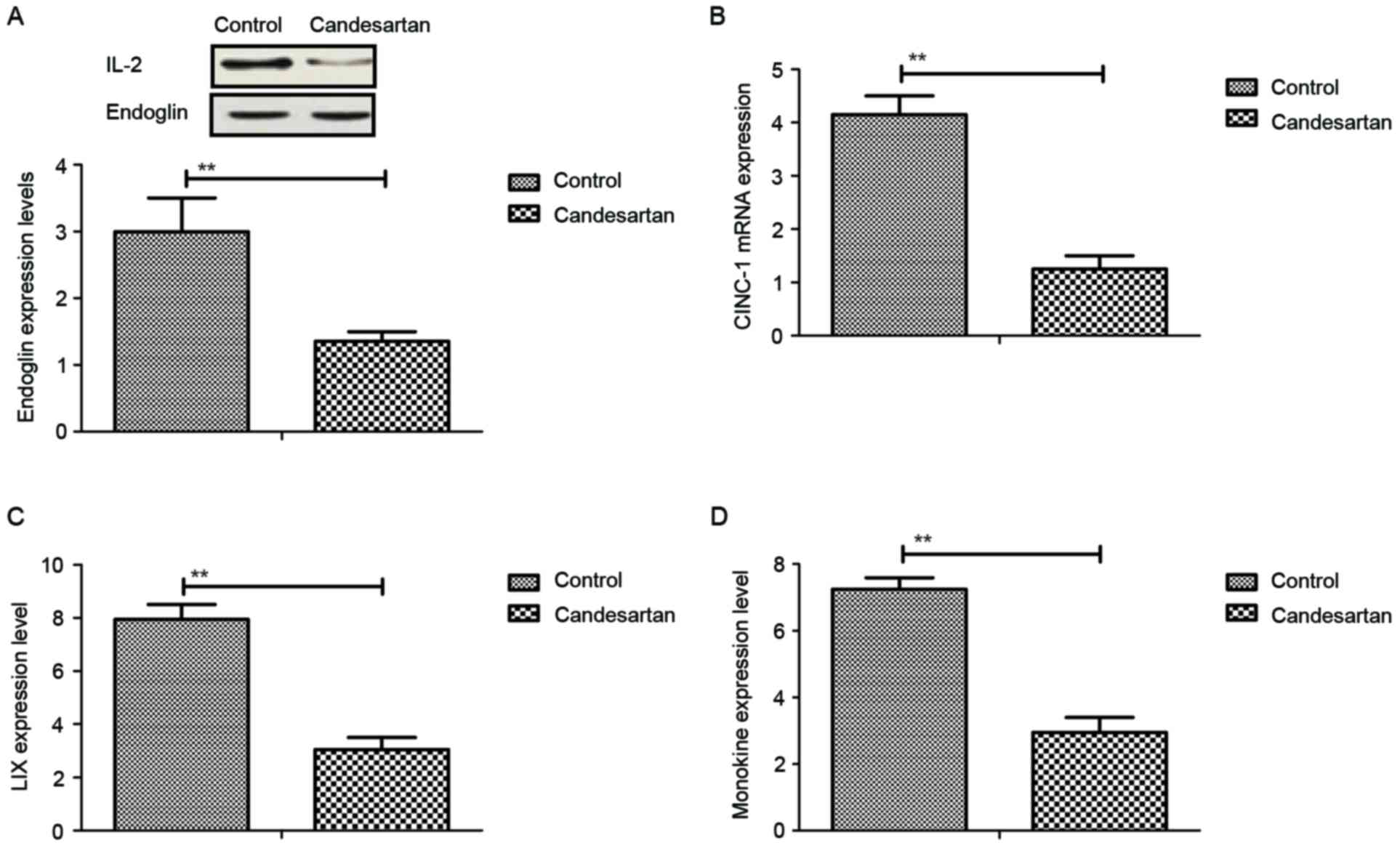
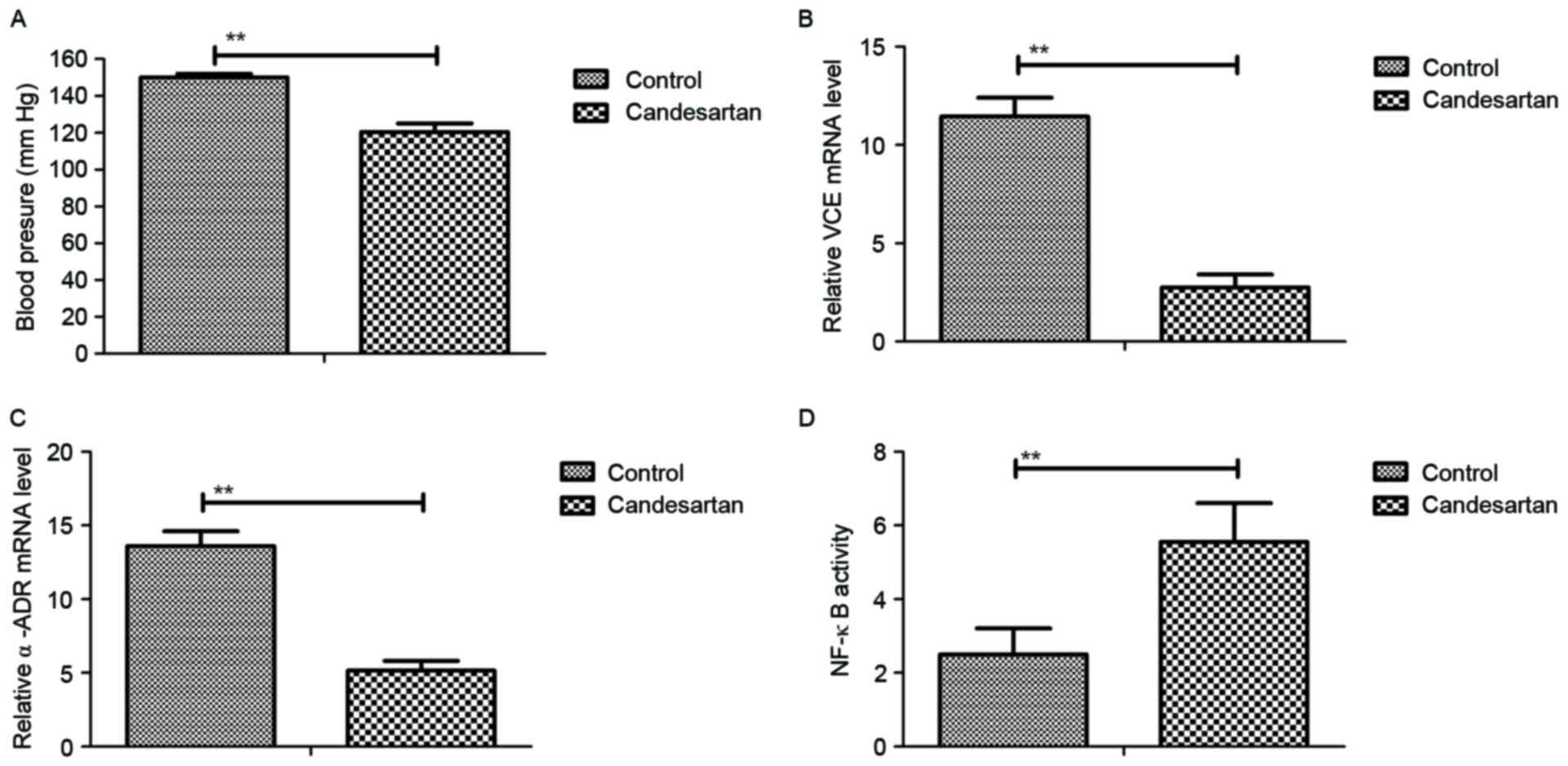
|
1
|
Kennedy DA, Woodland C and Koren G: Lead
exposure, gestational hypertension and pre-eclampsia: A systematic
review of cause and effect. J Obstet Gynaecol. 32:512–517. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Huang YH, Chen YP, Liang CC, Chang YL and
Hsieh CC: Impetigo herpetiformis with gestational hypertension: A
case report and literature review. Dermatology. 222:221–224. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Razi Mohamad ZR and Schindler AE: Review
on role of progestogen (dydrogesterone) in the prevention of
gestational hypertension. Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig. 27:73–76.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pengo MF, Rossi GP and Steier J:
Obstructive sleep apnea, gestational hypertension and preeclampsia:
A review of the literature. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 20:588–594. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhu YC, Sun Y and Yang HX: Chronic
hypertension superimposed on preeclampsia at 13 gestational weeks:
A case report with review. Chin Med J(Engl). 125:2067–2069.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Grandone E, Margaglione M, Colaizzo D,
Cappucci G, Sciannamé N, Montanaro S, Paladini D, Martinelli P and
Di Minno G: Prothrombotic genetic risk factors and the occurrence
of gestational hypertension with or without proteinuria. Thromb
Haemost. 81:349–352. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Vasapollo B, Novelli GP, Gagliardi G,
Tiralongo GM, Pisani I, Manfellotto D, Giannini L and Valensise H:
Medical treatment of early-onset mild gestational hypertension
reduces total peripheral vascular resistance and influences
maternal and fetal complications. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol.
40:325–331. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Banhidy F, Acs N, Puho EH and Czeizel AE:
The efficacy of antihypertensive treatment in pregnant women with
chronic and gestational hypertension: A population-based study.
Hypertens Res. 33:460–466. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Schoenaker DA, Soedamah-Muthu SS and
Mishra GD: The association between dietary factors and gestational
hypertension and pre-eclampsia: A systematic review and
meta-analysis of observational studies. BMC Med. 12:1572014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Rashid Zainul MR, Lim JF, Nawawi NH,
Luqman M, Zolkeplai MF, Rangkuty HS, Nor Mohamad NA, Tamil A, Shah
SA, Tham SW and Schindler AE: A pilot study to determine whether
progestogen supplementation using dydrogesterone during the first
trimester will reduce the incidence of gestational hypertension in
primigravidae. Gynecol Endocrinol. 30:217–220. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang YA, Chughtai AA, Farquhar CM, Pollock
W, Lui K and Sullivan EA: Increased incidence of gestational
hypertension and preeclampsia after assisted reproductive
technology treatment. Fertil Steril. 105:920–926, e922. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hua X, Zhang J, Guo Y, Shen M, Gaudet L,
Janoudi G, Walker M and Wen SW: Effect of folic acid
supplementation during pregnancy on gestational
hypertension/preeclampsia: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Hypertens Pregnancy. 35:447–460. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Basaran A, Basaran M, Topatan B and Martin
JN Jr: Effect of chorionic villus sampling on the occurrence of
preeclampsia and gestational hypertension: An updated systematic
review and meta-analysis. J Turk Ger Gynecol Assoc. 17:65–72. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chinnathambi V, More AS, Hankins GD,
Yallampalli C and Sathishkumar K: Gestational exposure to elevated
testosterone levels induces hypertension via heightened vascular
angiotensin II type 1 receptor signaling in rats. Biol Reprod.
91:62014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Seremak-Mrozikiewicz A, Drews K, Chmara E,
Mrozikiewicz PM and Slomko Z: Gestational hypertension (GH) and
a1166c polymorphism of angiotensin II type 1 receptor. Ginekol Pol.
71:783–788. 2000.(In Polish). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen PM, Lai TS, Chen PY, Lai CF, Wu V,
Chiang WC, Chen YM, Wu KD and Tsai TJ: Renoprotective effect of
combining pentoxifylline with angiotensin-converting enzyme
inhibitor or angiotensin II receptor blocker in advanced chronic
kidney disease. J Formos Med Assoc. 113:219–226. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mavrakanas TA, Gariani K and Martin PY:
Mineralocorticoid receptor blockade in addition to angiotensin
converting enzyme inhibitor or angiotensin II receptor blocker
treatment: An emerging paradigm in diabetic nephropathy: A
systematic review. Eur J Intern Med. 25:173–176. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tsutamoto T, Nishiyama K, Yamaji M,
Kawahara C, Fujii M, Yamamoto T and Horie M: Comparison of the
long-term effects of candesartan and olmesartan on plasma
angiotensin II and left ventricular mass index in patients with
hypertension. Hypertens Res. 33:118–122. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kjeldsen SE, Stålhammar J, Hasvold P,
Bodegard J, Olsson U and Russell D: Effects of losartan vs
candesartan in reducing cardiovascular events in the primary
treatment of hypertension. J Hum Hypertens. 24:263–273. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fogari R, Zoppi A, Salvadeo SA, Mugellini
A, Lazzari P, Santoro T and Derosa G: Fibrinolysis and insulin
sensitivity in imidapril and candesartan (FISIC study) recipients
with hypertension. Hypertens Res. 34:509–515. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Nishida Y, Takahashi Y, Nakayama T, Soma
M, Kitamura N and Asai S: Effect of candesartan monotherapy on
lipid metabolism in patients with hypertension: A retrospective
longitudinal survey using data from electronic medical records.
Cardiovasc Diabetol. 9:382010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wai-Hoe L, Wing-Seng L, Ismail Z and
Lay-Harn G: SDS-PAGE-Based quantitative assay for screening of
kidney stone disease. Biol Proced Online. 11:145–160. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Armstrong DW, Tse MY, O'Tierney-Ginn PF,
Wong PG, Ventura NM, Janzen-Pang JJ, Matangi MF, Johri AM, Croy BA,
Adams MA and Pang SC: Gestational hypertension in atrial
natriuretic peptide knockout mice and the developmental origins of
salt-sensitivity and cardiac hypertrophy. Regul Pept. 186:108–115.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Partyka R, Chmiel B, Sikora J, Grabowska
T, Wróbel B, Praisner A, Pióro A, Jałowieicki P and Kokocinska D:
Lipofuscin, homocysteine and tissue polypeptide specific antigen in
gestational hypertension. Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 28:311–314.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xiao S, Wang J and Xiao N: MicroRNAs as
noninvasive biomarkers in bladder cancer detection: A diagnostic
meta-analysis based on qRT-PCR data. Int J Biol Markers.
31:e276–e285. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yang L, Zhang W, Zhang L, Zhang S, Yang Y,
Wang Q, Shao J, Chen G and Wang Y: Gestational hypertension risk
evaluation based on epidemiological, biochemical, and hemodynamic
factors. Clin Exp Obstet Gynecol. 40:61–65. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Van Guilder GP, Pretorius M, Luther JM,
Byrd JB, Hill K, Gainer JV and Brown NJ: Bradykinin type 2 receptor
BE1 genotype influences bradykinin-dependent vasodilation during
angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition. Hypertension. 51:454–459.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Iwatsubo K and Umemura S: Alpha adrenergic
receptor blockers for patients with hypertension. Nihon Rinsho. 64
Suppl 6:S294–S299. 2006.(In Japanese).
|
|
30
|
Mancia G: Introduction to a compendium on
hypertension. Circ Res. 116:923–924. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Davidovich IM, Bloshchinskaia IA and
Petrichko TA: Gestational arterial hypertension. Mechanisms of
formation. Treatment with normodipin. Ter Arkh. 75:50–54. 2003.(In
Russian). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kong J and Li YC: Effect of ANG II type I
receptor antagonist and ACE inhibitor on vitamin D receptor-null
mice. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 285:R255–R261. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hagiwara S, Iwasaka H, Hidaka S, Hasegawa
A, Koga H and Noguchi T: Antagonist of the type-1 ANG II receptor
prevents against LPS-induced septic shock in rats. Intensive Care
Med. 35:1471–1478. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Rakusan K, Chvojkova Z, Oliviero P,
Ostadalova I, Kolar F, Chassagne C, Samuel JL and Ostadal B: ANG II
type 1 receptor antagonist irbesartan inhibits coronary
angiogenesis stimulated by chronic intermittent hypoxia in neonatal
rats. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 292:H1237–H1244. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yasuno S, Fujimoto A, Nakagawa Y, Kuwahara
K and Ueshima K: Fixed-dose combination therapy of candesartan
cilexetil and amlodipine besilate for the treatment of hypertension
in Japan. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 10:577–583. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Barrios V and Escobar C: Candesartan in
the treatment of hypertension: What have we learnt in the last
decade? Expert Opin Drug Saf. 10:957–968. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kwon BJ, Jang SW, Choi KY, Kim DB, Cho EJ,
Ihm SH, Youn HJ and Kim JH: Comparison of the efficacy between
hydrochlorothiazide and chlorthalidone on central aortic pressure
when added on to candesartan in treatment-naive patients of
hypertension. Hypertens Res. 36:79–84. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Henriksson M, Russell D, Bodegard J,
Kjeldsen S, Hasvold P, Stålhammar J and Levin LÅ: Health-care costs
of losartan and candesartan in the primary treatment of
hypertension. J Hum Hypertens. 25:130–136. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Moltzer E, Raso Mattace FU, Karamermer Y,
Boersma E, Webb GD, Simoons ML, Danser AH, van den Meiracker AH and
Roos-Hesselink JW: Comparison of candesartan versus metoprolol for
treatment of systemic hypertension after repaired aortic
coarctation. Am J Cardiol. 105:217–222. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Meredith PA, Murray LS and McInnes GT:
Comparison of the efficacy of candesartan and losartan: A
meta-analysis of trials in the treatment of hypertension. J Hum
Hypertens. 24:525–531. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ogihara T, Nakao K, Fukui T, Fukiyama K,
Fujimoto A, Ueshima K, Oba K, Shimamoto K, Matsuoka H and Saruta T:
CASE-J Trial Group: The optimal target blood pressure for
antihypertensive treatment in Japanese elderly patients with
high-risk hypertension: A subanalysis of the candesartan
antihypertensive survival evaluation in Japan (CASE-J) trial.
Hypertens Res. 31:1595–1601. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Gu JW, Tian N, Shparago M, Tan W, Bailey
AP and Manning RD Jr: Renal NF-kappaB activation and TNF-alpha
upregulation correlate with salt-sensitive hypertension in Dahl
salt-sensitive rats. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol.
291:R1817–R1824. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ortiz LA, Champion HC, Lasky JA, Gambelli
F, Gozal E, Hoyle GW, Beasley MB, Hyman AL, Friedman M and Kadowitz
PJ: Enalapril protects mice from pulmonary hypertension by
inhibiting TNF-mediated activation of NF-kappaB and AP-1. Am J
Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 282:L1209–L1221. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Henke N, Schmidt-Ullrich R, Dechend R,
Park JK, Qadri F, Wellner M, Obst M, Gross V, Dietz R, Luft FC, et
al: Vascular endothelial cell-specific NF-kappaB suppression
attenuates hypertension-induced renal damage. Circ Res.
101:268–276. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Alonso F, Krattinger N, Mazzolai L, Simon
A, Waeber G, Meda P and Haefliger JA: An angiotensin II- and
NF-kappaB-dependent mechanism increases connexin 43 in murine
arteries targeted by renin-dependent hypertension. Cardiovasc Res.
87:166–176. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Purkayastha S, Zhang G and Cai D:
Uncoupling the mechanisms of obesity and hypertension by targeting
hypothalamic IKK-β and NFκB. Nat Med. 17:883–887. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Li XW, Guo B, Shen YY and Yang JR: Effect
of chrysin on expression of NOX4 and NF-kappaB in right ventricle
of monocrotaline-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension of rats.
Yao Xue Xue Bao. 50:1128–1134. 2015.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Carney EF: Hypertension: sFlt-1 removal
seems to be beneficial in women with pre-eclampsia. Nat Rev
Nephrol. 11:6902015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Valbuena-Diez AC, Blanco FJ, Oujo B, Langa
C, Gonzalez-Nuñez M, Llano E, Pendas AM, Díaz M, Castrillo A,
Lopez-Novoa JM and Bernabeu C: Oxysterol-induced soluble endoglin
release and its involvement in hypertension. Circulation.
126:2612–2624. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Daly AL, Robertson A, Johnson P, Middleton
S, Bobek G, Sullivan C and Hennessy A: PP162. sFlt-1 controlled by
CPAP in a pregnant patient with chronic hypertension. Pregnancy
Hypertens. 2:3272012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Gluchowska M, Kowalska-Koprek U and
Karowicz-Bilińska A: Evaluation of the usefulness of endoglin level
as a predictor of preeclampsia in pregnant women with hypertension.
Ginekol Pol. 84:835–840. 2013.(In Polish). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Muda P, Kampus P, Teesalu R, Zilmer K,
Ristimäe T, Fischer K and Zilmer M: Effects of amlodipine and
candesartan on oxidized LDL level in patients with mild to moderate
essential hypertension. Blood Press. 15:313–318. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Ikeda H, Inoue T, Uemura S, Kaibara R,
Tanaka H and Node K: Effects of candesartan for middle-aged and
elderly women with hypertension and menopausal-like symptoms.
Hypertens Res. 29:1007–1012. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Nzelu D, Dumitrascu-Biris D, Hunt KF,
Cordina M and Kametas NA: Pregnancy outcomes in women with previous
gestational hypertension: A cohort study to guide counselling and
management. Pregnancy Hypertens. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Pauli JM, Lauring JR, Stetter CM, Repke
JT, Botti JJ, Ural SH and Ambrose A: Management of gestational
hypertension-the impact of HYPITATa. J Perinat Med. 41:415–420.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Sibai BM: Management of late preterm and
early-term pregnancies complicated by mild gestational
hypertension/pre-eclampsia. Semin Perinatol. 35:292–296. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|