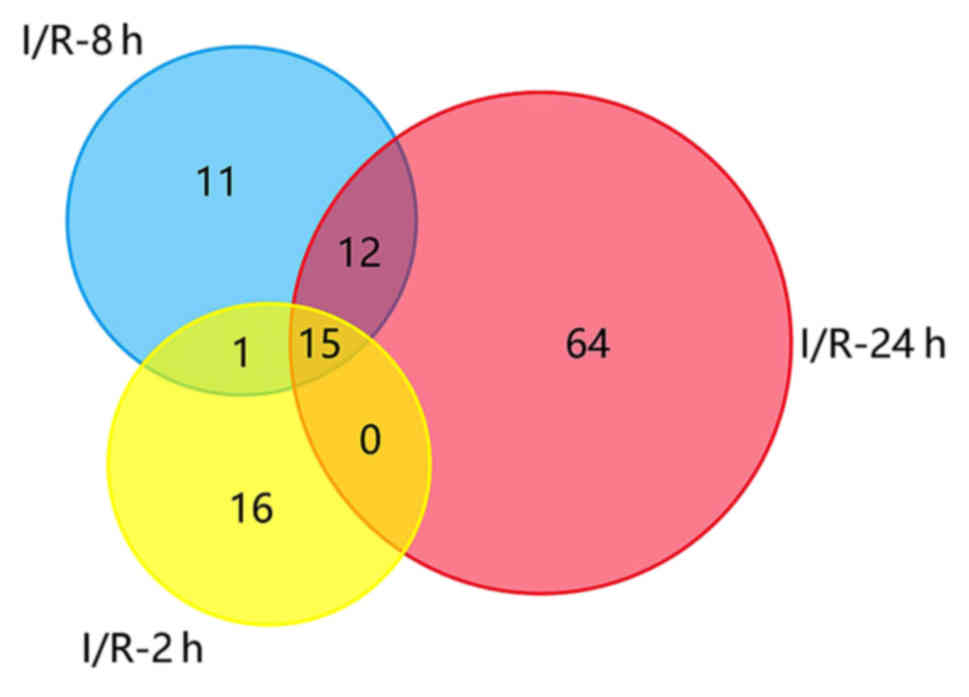
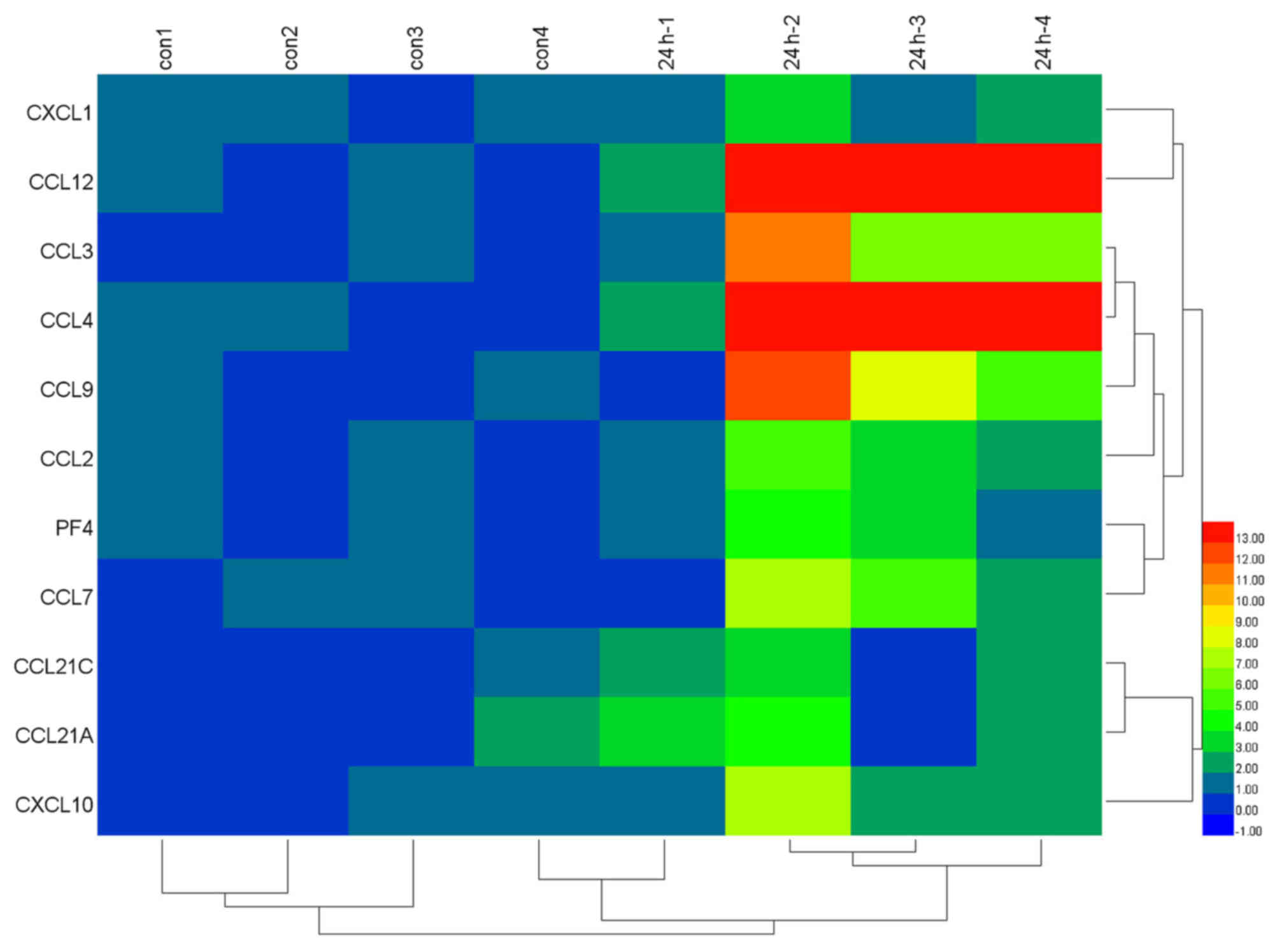
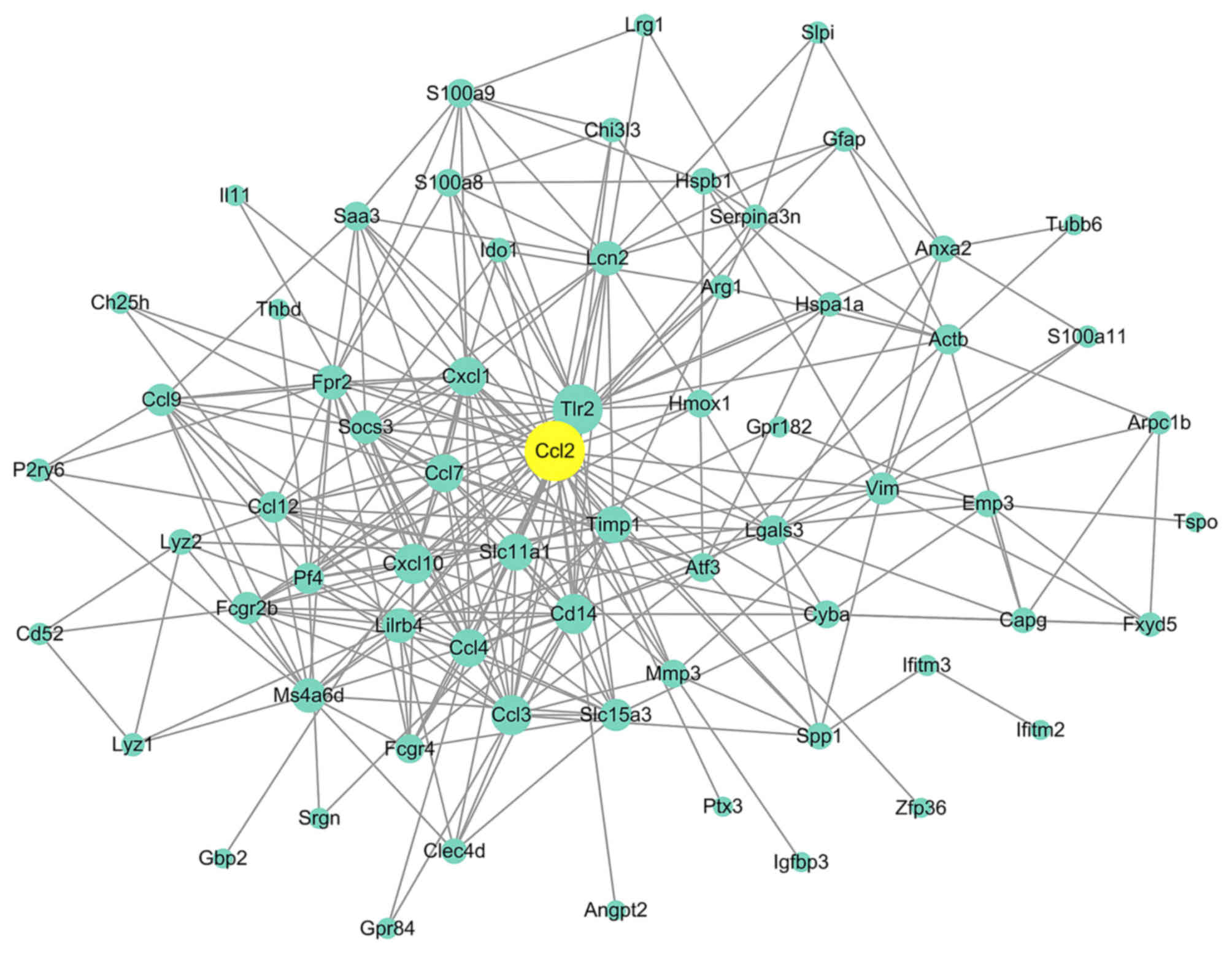
|
1
|
Donnan GA, Fisher M, Macleod M and Davis
SM: Stroke. Lancet. 371:1612–1623. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Go AS, Mozaffarian D, Roger VL, Benjamin
EJ, Berry JD, Blaha MJ, Dai S, Ford ES, Fox CS, Franco S, et al:
Heart disease and stroke statistics-2014 update: A report from the
American Heart Association. Circulation. 129:e28–e292. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Moskowitz MA, Lo EH and Iadecola C: The
science of stroke: Mechanisms in search of treatments. Neuron.
67:181–198. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hacke W, Kaste M, Bluhmki E, Brozman M,
Dávalos A, Guidetti D, Larrue V, Lees KR, Medeghri Z, Machnig T, et
al: Thrombolysis with alteplase 3 to 4.5 h after acute ischemic
stroke. N Engl J Med. 359:1317–1329. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lansberg MG, Bluhmki E and Thijs VN:
Efficacy and safety of tissue plasminogen activator 3 to 4.5 h
after acute ischemic stroke: A metaanalysis. Stroke. 40:2438–2441.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jung JE, Kim GS, Chen H, Maier CM,
Narasimhan P, Song YS, Niizuma K, Katsu M, Okami N, Yoshioka H, et
al: Reperfusion and neurovascular dysfunction in stroke: From basic
mechanisms to potential strategies for neuroprotection. Mol
Neurobiol. 41:172–179. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ding G, Jiang Q, Li L, Zhang L, Zhang ZG,
Ledbetter KA, Gollapalli L, Panda S, Li Q, Ewing JR and Chopp M:
Angiogenesis detected after embolic stroke in rat brain using
magnetic resonance T2*WI. Stroke. 39:1563–1568. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
McColl BW, Allan SM and Rothwell NJ:
Systemic infection, inflammation and acute ischemic stroke.
Neuroscience. 158:1049–1061. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chamorro Á, Dirnagl U, Urra X and Planas
AM: Neuroprotection in acute stroke: Targeting excitotoxicity,
oxidative and nitrosative stress, and inflammation. Lancet Neurol.
15:869–881. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chen C, Chu SF, Liu DD, Zhang Z, Kong LL,
Zhou X and Chen NH: Chemokines play complex roles in cerebral
ischemia. Neurochem Int. 112:146–158. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu C, Zhao L, Han S, Li J and Li D:
Identification and functional analysis of MicroRNAs in mice
following focal cerebral ischemia injury. Int J Mol Sci.
16:24302–24318. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen MJ, Wong CH, Peng ZF, Manikandan J,
Melendez AJ, Tan TM, Crack PJ and Cheung NS: A global
transcriptomic view of the multifaceted role of glutathione
peroxidase-1 in cerebral ischemic-reperfusion injury. Free Radic
Biol Med. 50:736–748. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Barrett T, Wilhite SE, Ledoux P,
Evangelista C, Kim IF, Tomashevsky M, Marshall KA, Phillippy KH,
Sherman PM, Holko M, et al: NCBI GEO: Archive for functional
genomics data sets-update. Nucleic Acids Res. 41:(Database Issue).
D991–D995. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pathan M, Keerthikumar S, Ang CS, Gangoda
L, Quek CY, Williamson NA, Mouradov D, Sieber OM, Simpson RJ, Salim
A, et al: FunRich: An open access standalone functional enrichment
and interaction network analysis tool. Proteomics. 15:2597–2601.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein
D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT,
et al: Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. The Gene
Ontology Consortium. Nat Genet. 25:25–29. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Altermann E and Klaenhammer TR:
PathwayVoyager: Pathway mapping using the kyoto encyclopedia of
genes and genomes (KEGG) database. BMC Genomics. 6:602005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Deng W, Wang Y, Liu Z, Cheng H and Xue Y:
HemI: A toolkit for illustrating heatmaps. PLoS One. 9:e1119882014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Franceschini A, Szklarczyk D, Frankild S,
Kuhn M, Simonovic M, Roth A, Lin J, Minguez P, Bork P, von Mering C
and Jensen LJ: STRING v9.1: Protein-protein interaction networks,
with increased coverage and integration. Nucleic Acids Res.
41:(Database Issue). D808–D815. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kohl M, Wiese S and Warscheid B:
Cytoscape: Software for visualization and analysis of biological
networks. Methods Mol Biol. 696:291–303. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang C, Liu M, Pan Y, Bai B and Chen J:
Global gene expression profile of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion
injury in rat MCAO model. Oncotarget. 8:74607–74622. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang L, Yu Y, Yang J, Zhao X and Li Z:
Dissecting Xuesaitong's mechanisms on preventing stroke based on
the microarray and connectivity map. Mol Biosyst. 11:3033–3039.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
White RE, Palm C, Xu L, Ling E, Ginsburg
M, Daigle BJ, Han R, Patterson A, Altman RB and Giffard RG: Mice
lacking the β2 adrenergic receptor have a unique genetic profile
before and after focal brain ischaemia. ASN Neuro. 4:pii: e00096.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wu L, Jiang Y, Zhu J, Wen Z, Xu X, Xu X,
Xie Y, Yang L, Xu L, Lan W, et al: Orosomucoid1: Involved in
vascular endothelial growth factor-induced blood-brain barrier
leakage after ischemic stroke in mouse. Brain Res Bull. 109:88–98.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chen C, Chu SF, Liu DD, Zhang Z, Kong LL,
Zhou X and Chen NH: Chemokines play complex roles in cerebral
ischemia. Neurochem Int. 112:146–158. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Goazigo Réaux-Le A, Van Steenwinckel J,
Rostène W and Parsadaniantz Mélik S: Current status of chemokines
in the adult CNS. Prog Neurobiol. 104:67–92. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang X, Yue TL, Barone FC and Feuerstein
GZ: Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 messenger RNA expression in
rat ischemic cortex. Stroke. 26:661–666. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yamagami S, Tamura M, Hayashi M, Endo N,
Tanabe H, Katsuura Y and Komoriya K: Differential production of
MCP-1 and cytokine-induced neutrophil chemoattractant in the
ischemic brain after transient focal ischemia in rats. J Leukoc
Biol. 65:744–749. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mirabelli-Badenier M, Braunersreuther V,
Viviani GL, Dallegri F, Quercioli A, Veneselli E, Mach F and
Montecucco F: CC and CXC chemokines are pivotal mediators of
cerebral injury in ischaemic stroke. Thromb Haemost. 105:409–420.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Cowell RM, Xu H, Galasso JM and
Silverstein FS: Hypoxic-ischemic injury induces macrophage
inflammatory protein-1alpha expression in immature rat brain.
Stroke. 33:795–801. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Boddeke EW, Meigel I, Frentzel S, Gourmala
NG, Harrison JK, Buttini M, Spleiss O and Gebicke-Härter P:
Cultured rat microglia express functional beta-chemokine receptors.
J Neuroimmunol. 98:176–184. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang X, Li X, Yaish-Ohad S, Sarau HM,
Barone FC and Feuerstein GZ: Molecular cloning and expression of
the rat monocyte chemotactic protein-3 gene: A possible role in
stroke. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 71:304–312. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Arac A, Grimbaldeston MA, Nepomuceno AR,
Olayiwola O, Pereira MP, Nishiyama Y, Tsykin A, Goodall GJ,
Schlecht U, Vogel H, et al: Evidence that meningeal mast cells can
worsen stroke pathology in mice. Am J Pathol. 184:2493–2504. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Losy J, Zaremba J and Skrobanski P: CXCL1
(GRO-alpha) chemokine in acute ischaemic stroke patients. Folia
Neuropathol. 43:97–102. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Iadecola C and Anrather J: The immunology
of stroke: From mechanisms to translation. Nat Med. 17:796–808.
2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Schilling M, Besselmann M, Leonhard C,
Mueller M, Ringelstein EB and Kiefer R: Microglial activation
precedes and predominates over macrophage infiltration in transient
focal cerebral ischemia: A study in green fluorescent protein
transgenic bone marrow chimeric mice. Exp Neurol. 183:25–33. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Jin R, Yang G and Li G: Inflammatory
mechanisms in ischemic stroke: Role of inflammatory cells. J Leukoc
Biol. 87:779–789. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Abe T, Shimamura M, Jackman K, Kurinami H,
Anrather J, Zhou P and Iadecola C: Key role of CD36 in Toll-like
receptor 2 signaling in cerebral ischemia. Stroke. 41:898–904.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Marsh BJ, Williams-Karnesky RL and
Stenzel-Poore MP: Toll-like receptor signaling in endogenous
neuroprotection and stroke. Neuroscience. 158:1007–1020. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ziegler G, Freyer D, Harhausen D,
Khojasteh U, Nietfeld W and Trendelenburg G: Blocking TLR2 in vivo
protects against accumulation of inflammatory cells and neuronal
injury in experimental stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab.
31:757–766. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|