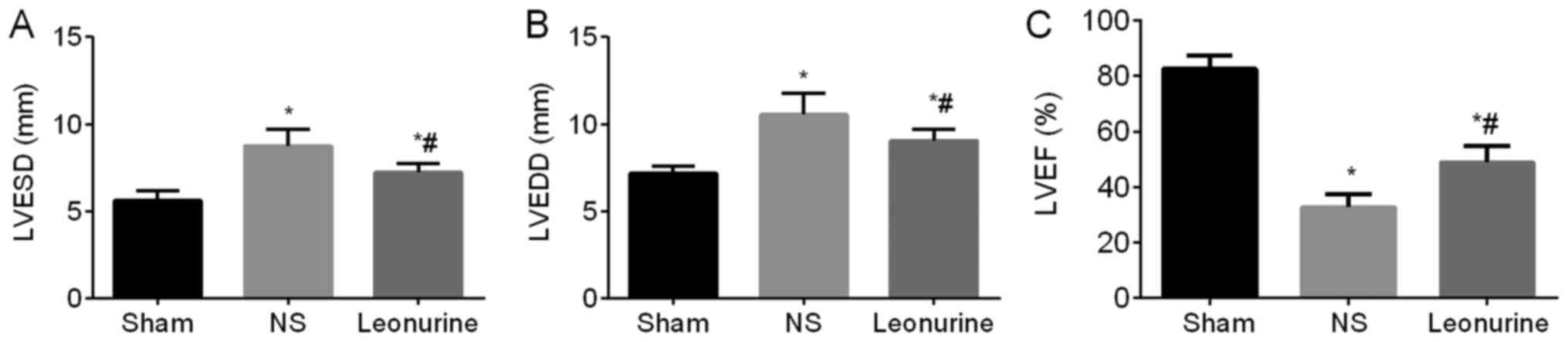
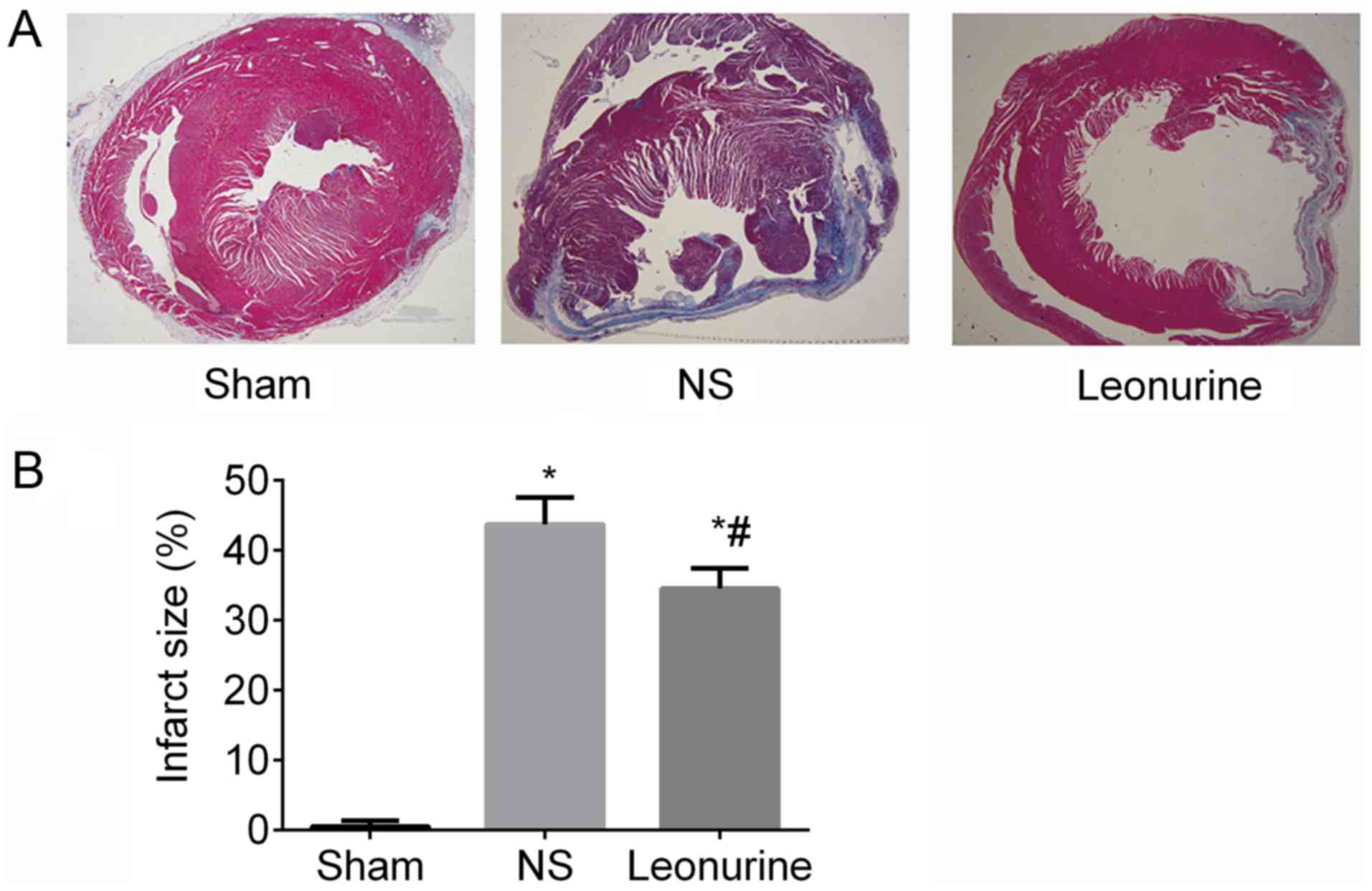
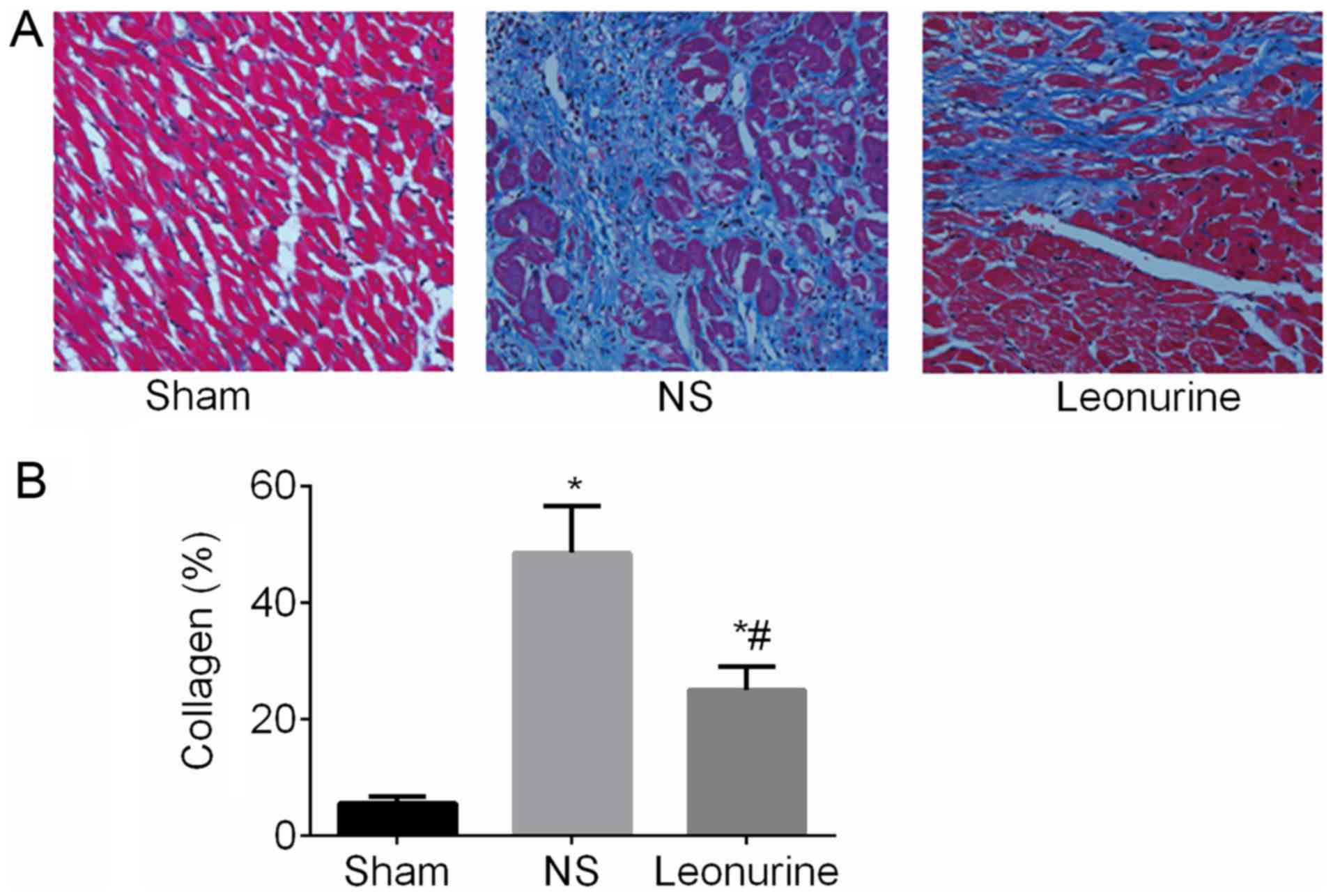
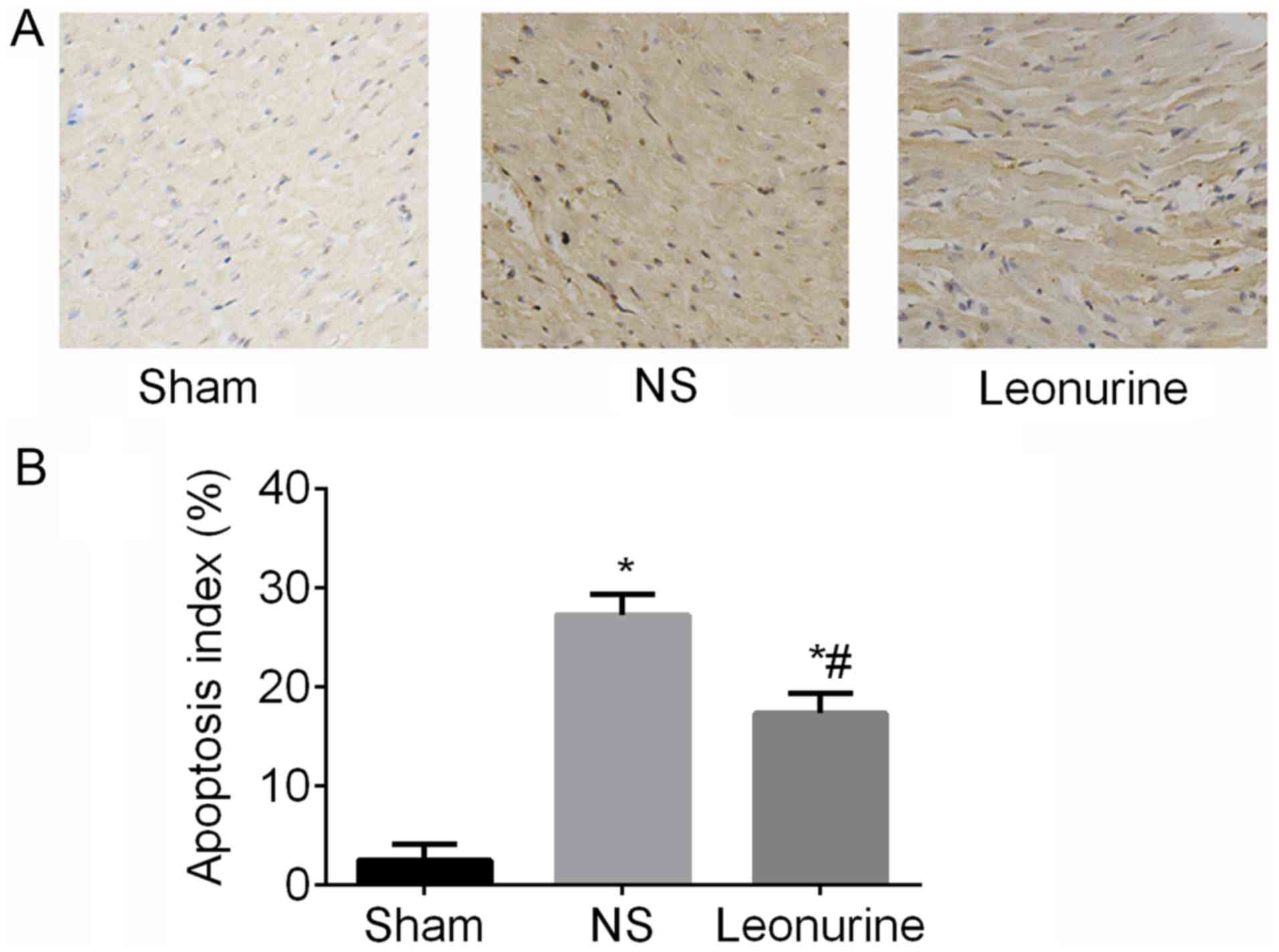
|
1
|
Zhu YZ, Chong CL, Chuah SC, Huang SH, Nai
HS, Tong HT, Whiteman M and Moore PK: Cardioprotective effects of
nitroparacetamol and paracetamol in acute phase of myocardial
infarction in experimental rats. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
290:H517–H524. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Liu C, Guo W, Maerz S, Gu X and Zhu Y:
3,5-Dimethoxy-4-(3-(2-carbonyl-ethyldisulfanyl)-propionyl)-benzoic
acid 4-guanidino-butyl ester: A novel twin drug that prevents
primary cardiac myocytes from hypoxia-induced apoptosis. Eur J
Pharmacol. 700:118–126. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gallogly MM, Shelton MD, Qanungo S, Pai
HV, Starke DW, Hoppel CL, Lesnefsky EJ and Mieyal JJ: Glutaredoxin
regulates apoptosis in cardiomyocytes via NFkappaB targets Bcl-2
and Bcl-xL: Implications for cardiac aging. Antioxid Redox Signal.
12:1339–1353. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lee Y and Gustafsson AB: Role of apoptosis
in cardiovascular disease. Apoptosis. 14:536–548. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Haunstetter A and Izumo S: Toward
antiapoptosis as a new treatment modality. Circ Res. 86:371–376.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liu XH, Xin H and Zhu YZ: More than a
‘mother-benefiting’ herb: Cardioprotective effect of Herba leonuri.
Sheng Li Xue Bao. 59:578–584. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kuang PG, Zhou XF, Zhang FY and Lang SY:
Motherwort and cerebral ischemia. J Tradit Chin Med. 8:37–40.
1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang ZS, Li DW, Xia WJ, Qiu HQ and Zhu LY:
The therapeutic effect of herba leonuri in the treatment of
coronary myocardial ischemia. J Tradit Chin Med. 8:103–106.
1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu XH, Xin H, Hou AJ and Zhu YZ:
Protective effects of leonurine in neonatal rat hypoxic
cardiomyocytes and rat infarcted heart. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol.
36:696–703. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liu XH, Chen PF, Pan LL, Silva RD and Zhu
YZ: 4-Guanidino-n-butyl syringate (Leonurine, SCM 198) protects
H9c2 rat ventricular cells from hypoxia-induced apoptosis. J
Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 54:437–444. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu X, Pan L, Gong Q and Zhu Y: Leonurine
(SCM-198) improves cardiac recovery in rat during chronic
infarction. Eur J Pharmacol. 649:236–241. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu XH, Pan LL, Deng HY, Xiong QH, Wu D,
Huang GY, Gong QH and Zhu YZ: Leonurine (SCM-198) attenuates
myocardial fibrotic response via inhibition of NADPH oxidase 4.
Free Radic Biol Med. 54:93–1042. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu H, Zhang X, Du Y, Ji H, Li S, Li L,
Xing Y, Zhang X, Dong L, Wang C, et al: Leonurine protects brain
injury by increased activities of UCP4, SOD, CAT and Bcl-2,
decreased levels of MDA and Bax, and ameliorated ultrastructure of
mitochondria in experimental stroke. Brain Res. 1474:73–81. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yu-Shengyou and LI Y: Dexamethasone
inhibits podocyte apoptosis by stabilizing the PI3K/Akt signal
pathway. Biomed Res Int. 2013:3269862013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Franke TF, Hornik CP, Segev L, Shostak GA
and Sugimoto C: PI3K/Akt and apoptosis: size matters. Oncogene.
22:8983–8998. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Vara Fresno JA, Casado E, De Castro J,
Cejas P, Belda-Iniesta C and González-Barón M: PI3K/Akt signalling
pathway and cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 30:193–204. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ohashi H, Takagi H, Oh H, Suzuma K, Suzuma
I, Miyamoto N, Uemura A, Watanabe D, Murakami T, Sugaya T, et al:
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt regulates angiotensin II-induced
inhibition of apoptosis in microvascular endothelial cells by
governing survivin expression and suppression of caspase-3
activity. Circ Res. 94:785–793. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tramontano AF, Muniyappar R, Black AD,
Blendea MC, Cohen I, Deng L, Sowers JR, Cutaia MV and El-Sherif N:
Erythropoietin protects cardiac myocytes from hypoxia-induced
apoptosis through an Akt-dependent pathway. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 308:990–994. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cai Z and Semenza GL:
Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase signaling is required for
erythropoietin-mediated acute protection against myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury. Circulation. 109:2050–2053. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Rayasam GV, Tulasi VK, Sodhi R, Davis JA
and Ray A: Glycogen synthase kinase 3: More than a namesake. Br J
Pharmacol. 156:885–98. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Maixner DW and Weng HR: The role of
glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta in neuroinflammation and pain. J
Pharm Pharmacol (Los Angel). 1:0012013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cross DA, Alessi DR, Cohen P, Andjelkovich
M and Hemmings BA: Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3 by
insulin mediated by protein kinase B. Nature. 378:785–789. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Descamps S, Pawlowski V, Révillion F,
Hornez L, Hebbar M, Boilly B, Hondermarck H and Peyrat JP:
Expression of nerve growth factor receptors and their prognostic
value in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 61:4337–4340.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Morisco C, Zebrowski D, Condorelli G,
Tsichlis P, Vatner SF and Sadoshima J: The Akt-glycogen synthase
kinase 3beta pathway regulates transcription of atrial natriuretic
factor induced by beta-adrenergic receptor stimulation in cardiac
myocytes. J Biol Chem. 275:14466–14475. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Badorff C, Ruetten H, Mueller S, Stahmer
M, Gehring D, Jung F, Ihling C, Zeiher AM and Dimmeler S: Fas
receptor signaling inhibits glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta and
induces cardiac hypertrophy following pressure overload. J Clin
Invest. 109:373–381. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gong R, Rifai A and Dworkin LD: Activation
of PI3K-Akt-GSK3beta pathway mediates hepatocyte growth factor
inhibition of RANTES expression in renal tubular epithelial cells.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 330:27–33. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wagner C, Tillack D, Simonis G, Strasser
RH and Weinbrenner C: Ischemic post-conditioning reduces infarct
size of the in vivo rat heart: Role of PI3-K, mTOR, GSK-3beta and
apoptosis. Mol Cell Biochem. 339:135–147. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Somervaille TC, Linch DC and Khwaja A:
Growth factor withdrawal from primary human erythroid progenitors
induces apoptosis through a pathway involving glycogen synthase
kinase-3 and Bax. Blood. 98:1374–1381. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sun J, Huang SH, Zhu YC, Whiteman M, Wang
MJ, Tan BK and Zhu YZ: Anti-oxidative stress effects of Herba
leonuri on ischemic rat hearts. Life Sci. 76:3043–3056. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liu X, Pan L, Wang X, Gong Q and Zhu YZ:
Leonurine protects against tumor necrosis factor-α-mediated
inflammation in human umbilical vein endothelial cells.
Atherosclerosis. 222:34–42. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Loh KP, Qi J, Tan BK, Liu XH, Wei BG and
Zhu YZ: Leonurine protects middle cerebral artery occluded rats
through antioxidant effect and regulation of mitochondrial
function. Stroke. 41:2661–2668. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|