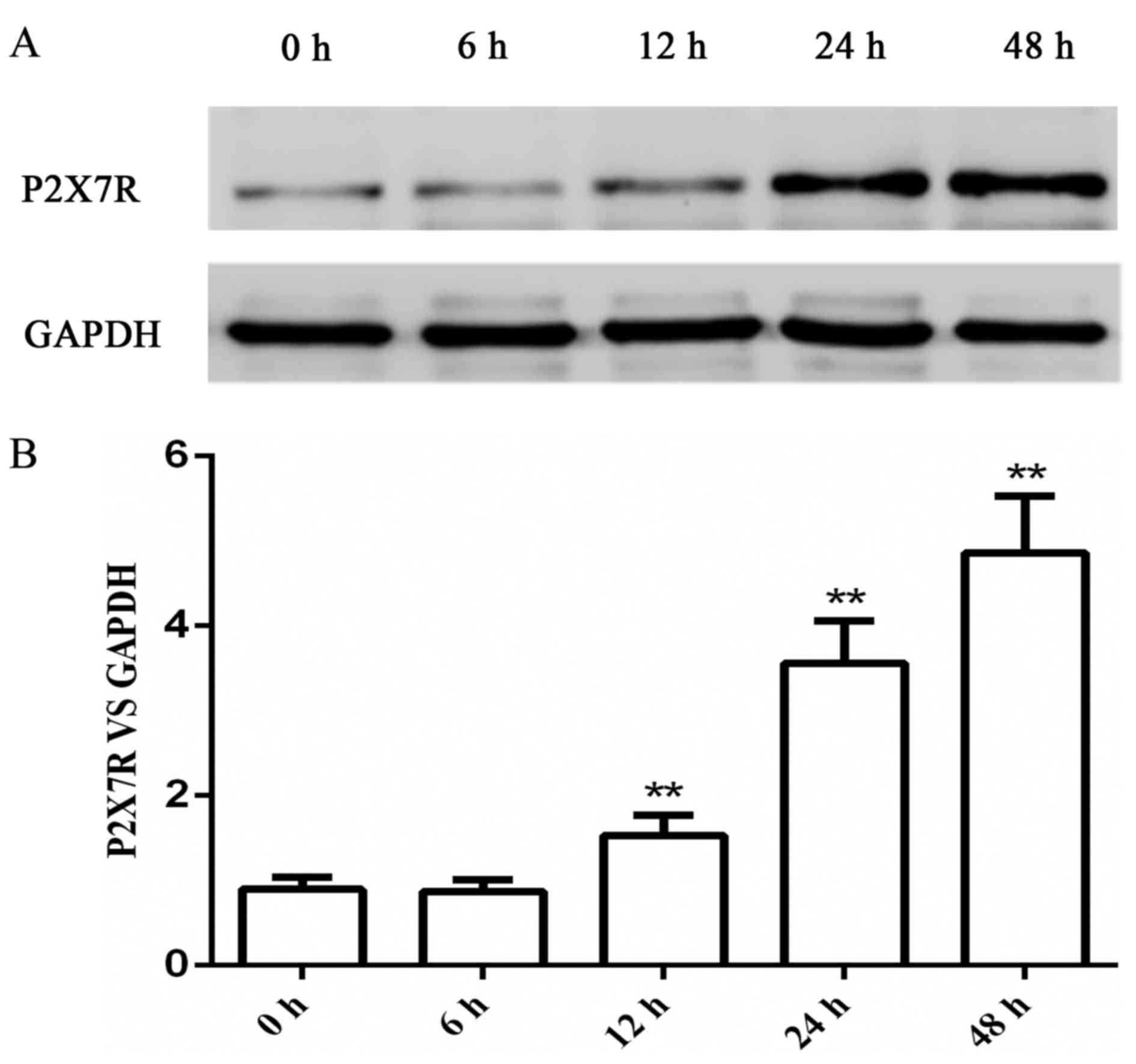
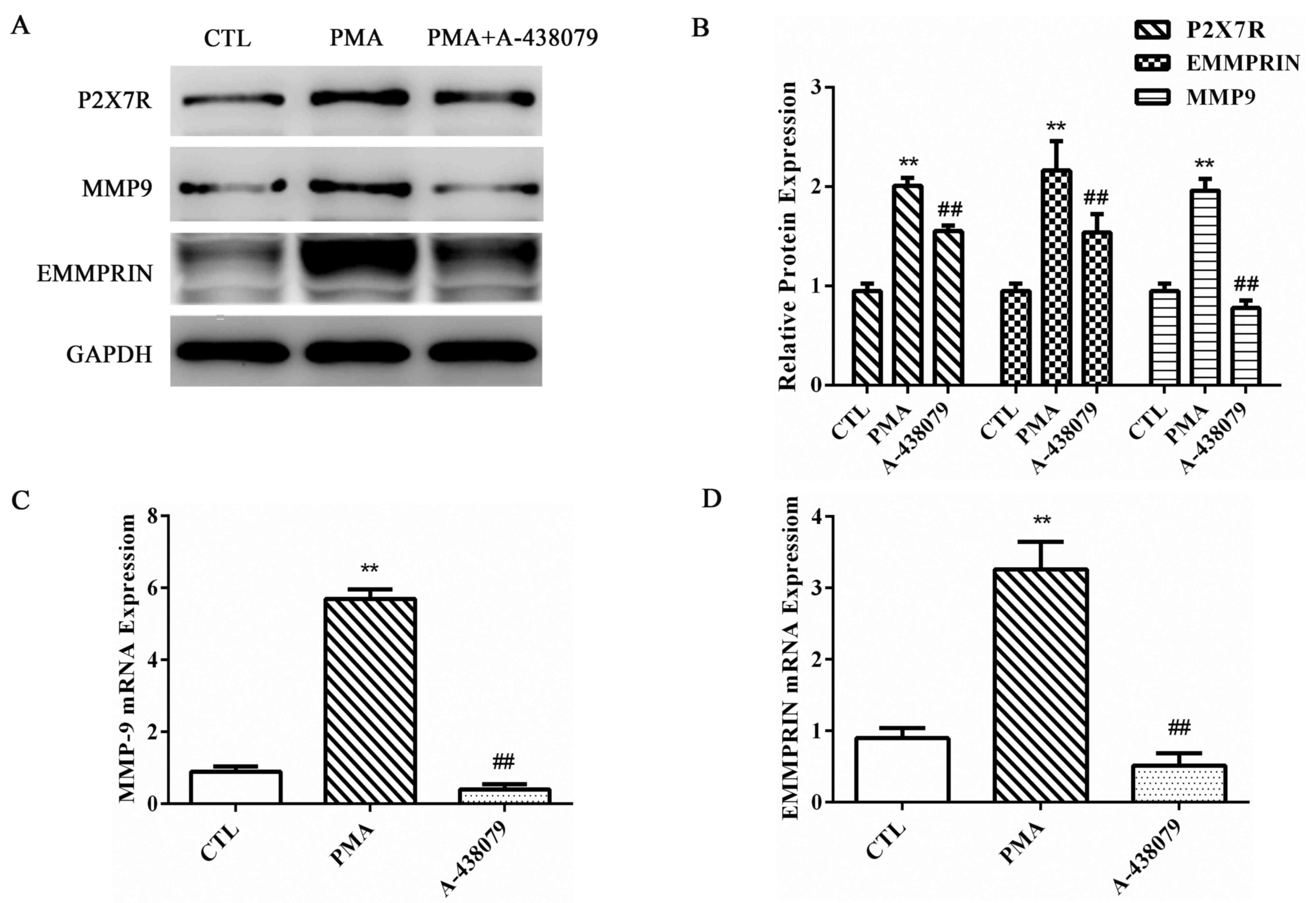
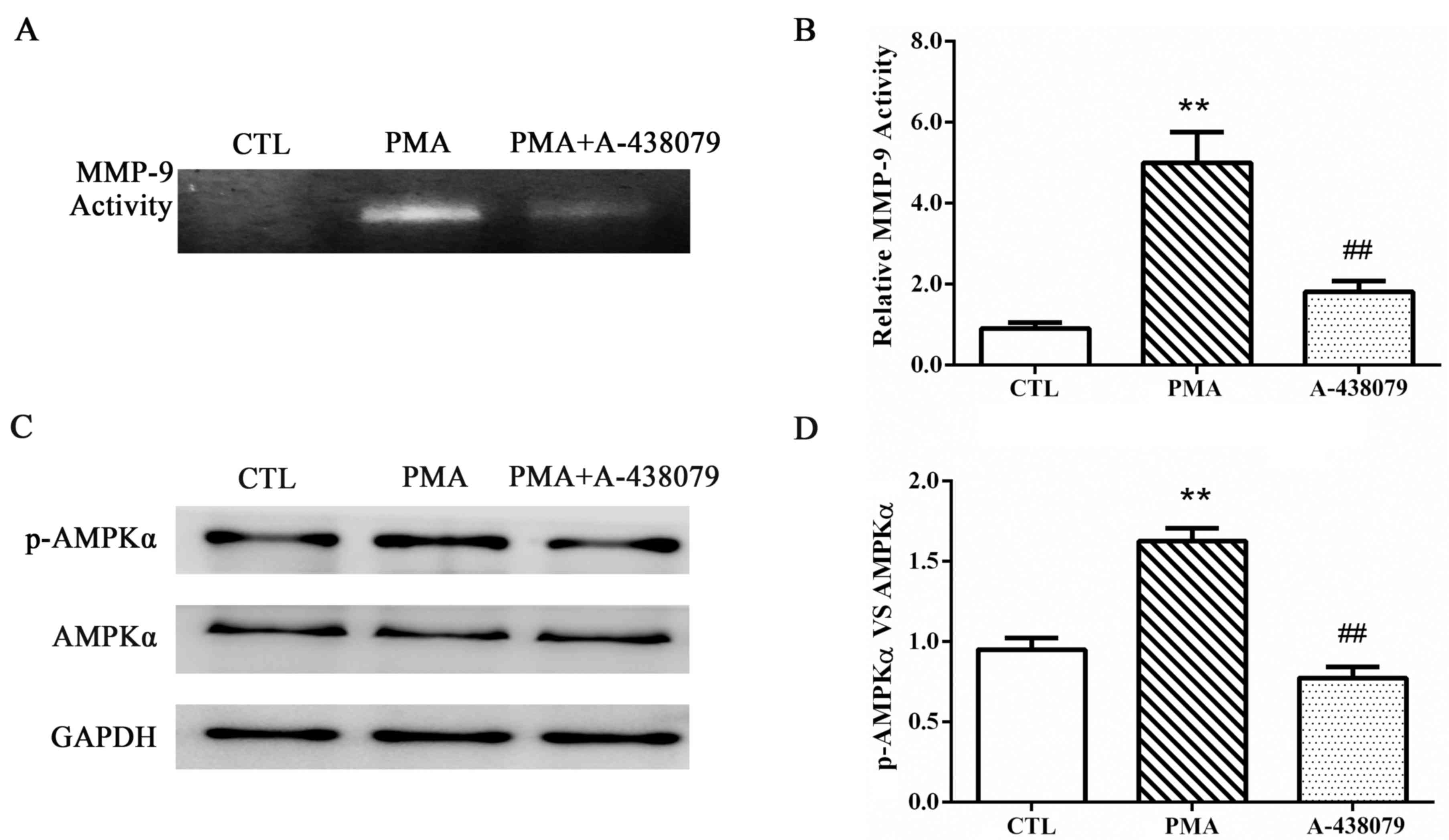
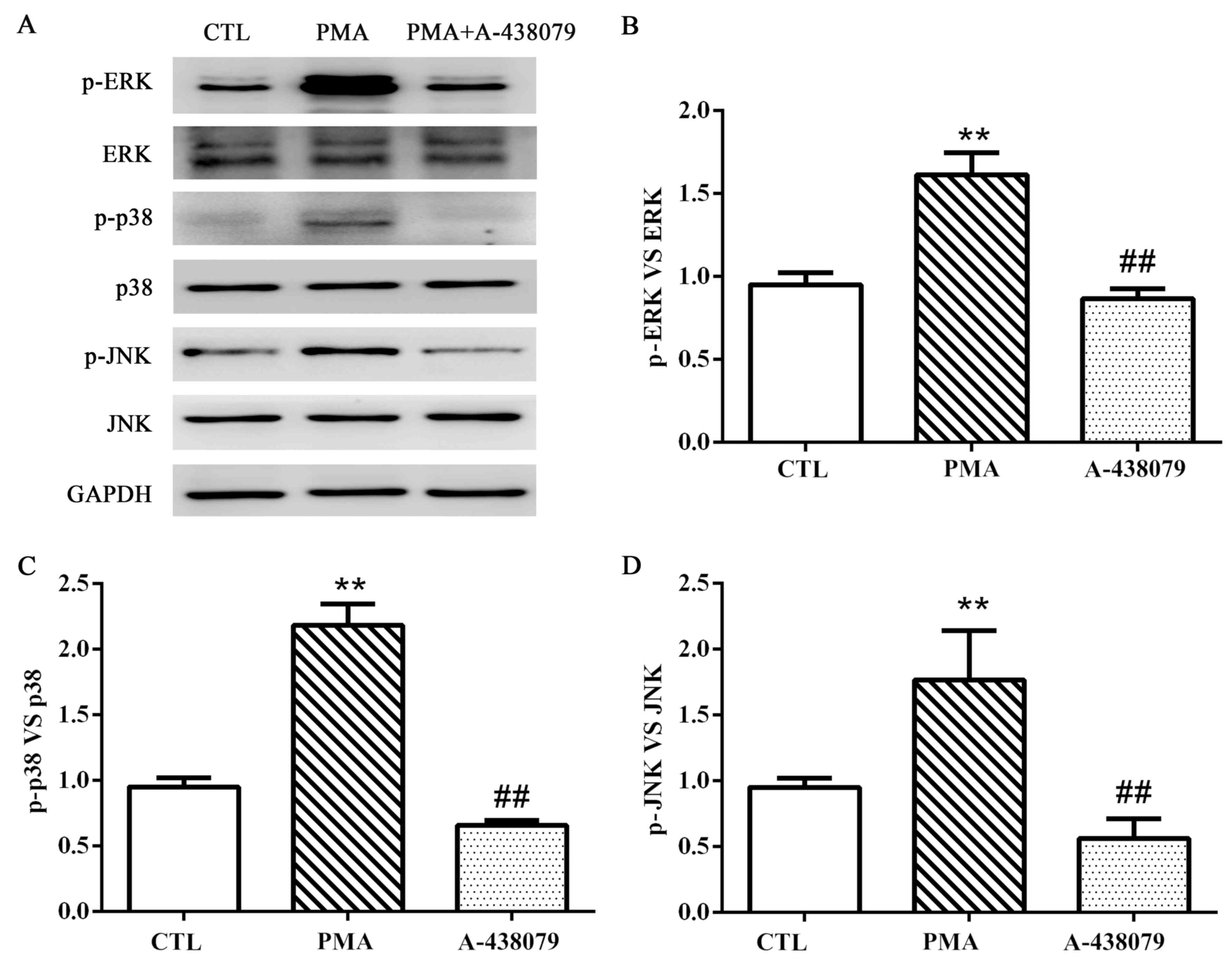
|
1
|
Ross R: ATHEROSCLEROSIS-An inflammatory
disease. N Engl J Med. 340:115–126. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bartlett R, Stokes L and Sluyter R: The
P2X7 receptor channel: Recent developments and the use of P2X7
antagonists in models of disease. Pharmacol Rev. 66:638–675. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Baroja-Mazo A and Pelegrin P: Modulating
P2X7 receptor signaling during rheumatoid arthritis: New
therapeutic approaches for bisphosphonates. J Osteoporo.
2012:4082422012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Piscopiello M, Sessa M, Anzalone N,
Castellano R, Maisano F, Ferrero E, Chiesa R, Alfieri O, Comi G,
Ferrero ME and Foglieni C: P2X7 receptor is expressed in human
vessels and might play a role in atherosclerosis. Int J Cardiol.
168:2863–2866. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Peng K, Liu L, Wei D, Lv Y, Wang G, Xiong
W, Wang X, Altaf A, Wang L, He D, et al: P2X7R is involved in the
progression of atherosclerosis by promoting NLRP3 inflammasome
activation. Int J Mol Med. 35:1179–1188. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Vandooren J, Van den Steen PE and
Opdenakker G: Biochemistry and molecular biology of gelatinase B or
matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9): The next decade. Crit Rev
Biochem Mol Biol. 48:222–272. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hsu S, Koren E, Chan Y, Koscec M, Sheehy
A, Kolodgie F, Virmani R and Feder D: Effects of everolimus on
macrophage-derived foam cell behavior. Cardiovasc Revasc Med.
15:269–277. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Moustardas P, Kadoglou NP, Katsimpoulas M,
Kapelouzou A, Kostomitsopoulos N, Karayannacos PE, Kostakis A and
Liapis CD: The complementary effects of atorvastatin and exercise
treatment on the composition and stability of the atherosclerotic
plaques in ApoE knockout mice. PloS One. 9:e1082402014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Biswas C, Zhang Y, DeCastro R, Guo H,
Nakamura T, Kataoka H and Nabeshima K: The human tumor cell-derived
collagenase stimulatory factor (renamed EMMPRIN) is a member of the
immunoglobulin superfamily. Cancer Res. 55:434–439. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yoon YW, Kwon HM, Hwang KC, Choi EY, Hong
BK, Kim D, Kim HS, Cho SH, Song KS and Sangiorgi G: Upstream
regulation of matrix metalloproteinase by EMMPRIN; extracellular
matrix metalloproteinase inducer in advanced atherosclerotic
plaque. Atherosclerosis. 180:37–44. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang C, Jin R, Zhu X, Yan J and Li G:
Function of CD147 in atherosclerosis and atherothrombosis. J
Cardiovasc Transl Res. 8:59–66. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Major TC, Liang L, Lu X, Rosebury W and
Bocan TM: Extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer (EMMPRIN)
is induced upon monocyte differentiation and is expressed in human
atheroma. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 22:1200–1207. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Joghetaei N, Stein A, Byrne RA, Schulz C,
King L, May AE and Schmidt R: The extracellular matrix
metalloproteinase inducer (EMMPRIN, CD147)-a potential novel target
in atherothrombosis prevention? Thromb Res. 131:474–480. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Riteau N, Gasse P, Fauconnier L, Gombault
A, Couegnat M, Fick L, Kanellopoulos J, Quesniaux VFJ,
Marchand-Adam S, Crestani B, et al: Extracellular ATP Is a danger
signal activating P2X7receptor in lung inflammation and fibrosis.
Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 182:774–783. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Huang C, Yu W, Cui H, Wang Y, Zhang L, Han
F and Huang T: P2X7 blockade attenuates mouse liver fibrosis. Mol
Med Rep. 9:57–62. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gu BJ and Wiley JS: Rapid ATP-induced
release of matrix metalloproteinase 9 is mediated by the P2X7
receptor. Blood. 107:4946–4953. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Habets DD, Coumans WA, Voshol PJ, den Boer
MA, Febbraio M, Bonen A, Glatz JF and Luiken JJ: AMPK-mediated
increase in myocardial long-chain fatty acid uptake critically
depends on sarcolemmal CD36. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
355:204–210. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang X, Jia Q, Xiao J, Jiao H and Lin H:
Glucocorticoids retard skeletal muscle development and myoblast
protein synthesis through a mechanistic target of rapamycin
(mTOR)-signaling pathway in broilers (gallus gallus domesticus).
Stress. 18:686–698. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Iwanaka N, Egawa T, Satoubu N, Karaike K,
Ma X, Masuda S and Hayashi T: Leucine modulates contraction- and
insulin-stimulated glucose transport and upstream signaling events
in rat skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol. 108:274–282. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cao J, Han Z, Tian L, Chen K, Fan Y, Ye B,
Huang W, Wang C and Huang Z: Curcumin inhibits EMMPRIN and MMP-9
expression through AMPK-MAPK and PKC signaling in PMA induced
macrophages. J Transl Mad. 12:2662014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Byun HJ, Hong IK, Kim E, Jin YJ, Jeoung
DI, Hahn JH, Kim YM, Park SH and Lee H: A splice variant of CD99
increases motility and MMP-9 expression of human breast cancer
cells through the AKT-, ERK-, and JNK-dependent AP-1 activation
signaling pathways. J Biol Chem. 281:34833–34847. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lee SJ, Kim CE, Yun MR, Seo KW, Park HM,
Yun JW, Shin HK, Bae SS and Kim CD: 4-Hydroxynonenal enhances MMP-9
production in murine macrophages via 5-lipoxygenase-mediated
activation of ERK and p38 MAPK. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
242:191–198. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Luo J, Lee S, Wu D, Yeh J, Ellamushi H,
Wheeler AP, Warnes G, Zhang Y and Bo X: P2X7 purinoceptors
contribute to the death of Schwann cells transplanted into the
spinal cord. Cell Death Dis. 4:e8292013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Auwerx J: The human leukemia cell line,
THP-1: A multifacetted model for the study of monocyte-macrophage
differentiation. Experientia. 47:22–31. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Qin Z: The use of THP-1 cells as a model
for mimicking the function and regulation of monocytes and
macrophages in the vasculature. Atherosclerosis. 221:2–11. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang QM, Wang H, Li YF, Xie ZY, Ma Y, Yan
JJ, Gao YF, Wang ZM and Wang LS: Inhibition of EMMPRIN and MMP-9
expression by epigallocatechin-3-gallate through 67-kda laminin
receptor in PMA-induced macrophages. Cell Physiol Biochem.
39:2308–2319. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Erlinge D and Burnstock G: P2 receptors in
cardiovascular regulation and disease. Purinergic Signal. 4:1–20.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Newby AC: Metalloproteinase expression in
monocytes and macrophages and its relationship to atherosclerotic
plaque instability. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 28:2108–2114.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lenertz LY, Gavala ML, Zhu Y and Bertics
PJ: Transcriptional control mechanisms associated with the
nucleotide receptor P2X7, a critical regulator of immunologic,
osteogenic, and neurologic functions. Immunol Res. 50:22–38. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kong F, Ye B, Cao J, Cai X, Lin L, Huang
S, Huang W and Huang Z: Curcumin represses NLRP3 inflammasome
activation via TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB and P2X7R signaling in PMA-induced
macrophages. Front Pharmacol. 7:3692016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yang F, Zhao K, Zhang X, Zhang J and Xu B:
ATP induces disruption of tight junction proteins via il-1
Beta-dependent MMP-9 activation of human blood-brain barrier in
vitro. Neural Plast. 2016:89285302016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Rubio-Araiz A, Perez-Hernandez M, Urrutia
A, Porcu F, Borcel E, Gutierrez-Lopez MD, O'Shea E and Colado MI:
3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA, ecstasy) disrupts
blood-brain barrier integrity through a mechanism involving P2X7
receptors. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 17:1243–1255. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Rekha RS, Muvva Rao SS, Wan M, Raqib R,
Bergman P, Brighenti S, Gudmundsson GH and Agerberth B:
Phenylbutyrate induces ll-37-dependent autophagy and intracellular
killing of mycobacterium tuberculosis in human macrophages.
Autophagy. 11:1688–1699. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wu Q, Xu H, Hao L, Ma G, Sun J, Song X,
Ding F and Wang N: P2X7 receptor regulates sympathoexcitatory
response in myocardial infarction rats via NF-kappaB and MAPK
pathways. Am J Transl Res. 9:4954–4962. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Okumura H, Shiba D, Kubo T and Yokoyama T:
P2X7 receptor as sensitive flow sensor for ERK activation in
osteoblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 372:486–490. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li W, Li G, Zhang Y, Wei S, Song M, Wang
W, Yuan X, Wu H and Yang Y: Role of P2 × 7 receptor in the
differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells into osteoblasts and
adipocytes. Exp Cell Res. 339:367–379. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sathanoori R, Sward K, Olde B and Erlinge
D: The ATP receptors P2X7 and P2X4 modulate high glucose and
palmitate-induced inflammatory responses in endothelial cells. PLoS
One. 10:e01251112015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|