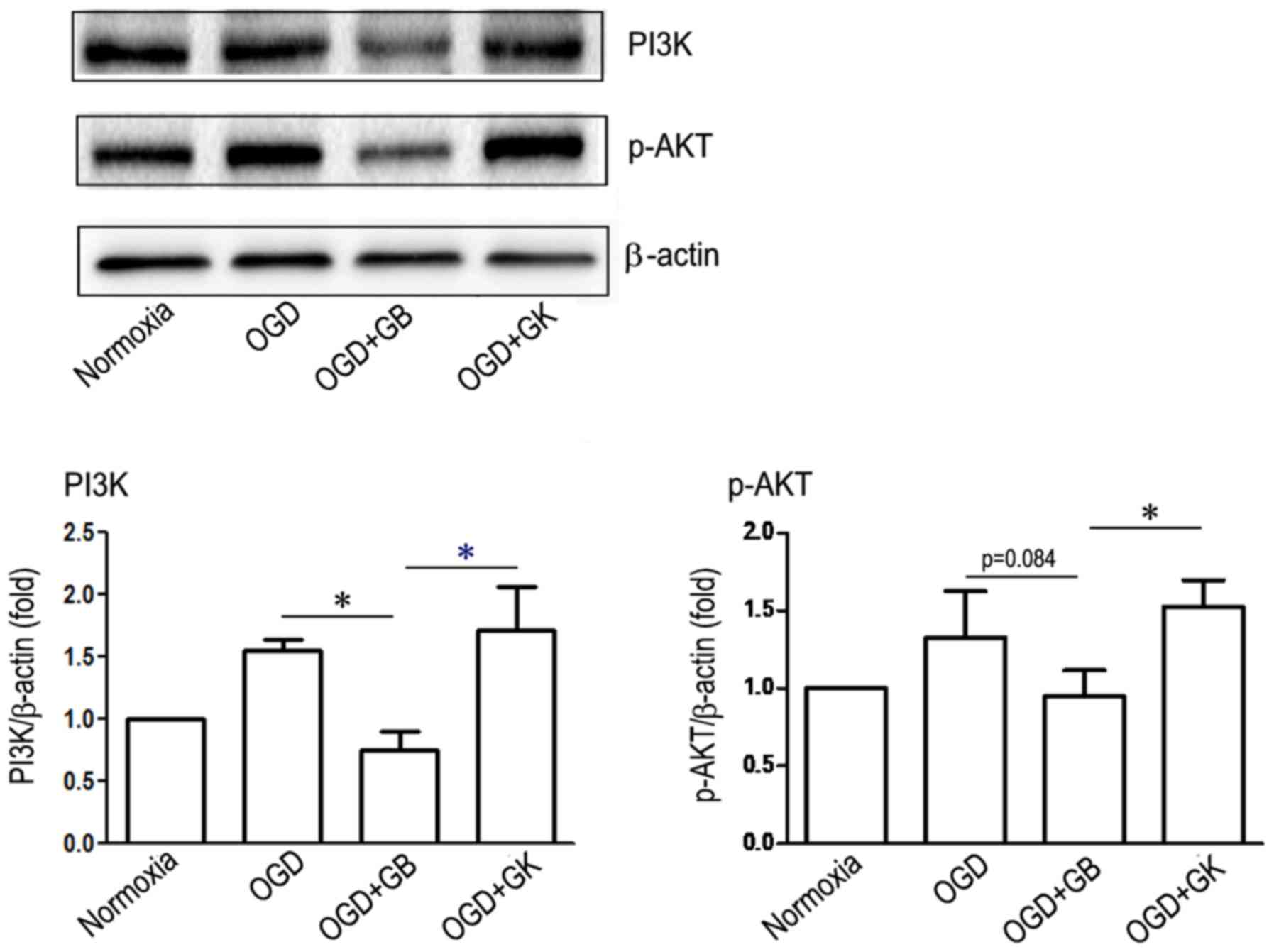
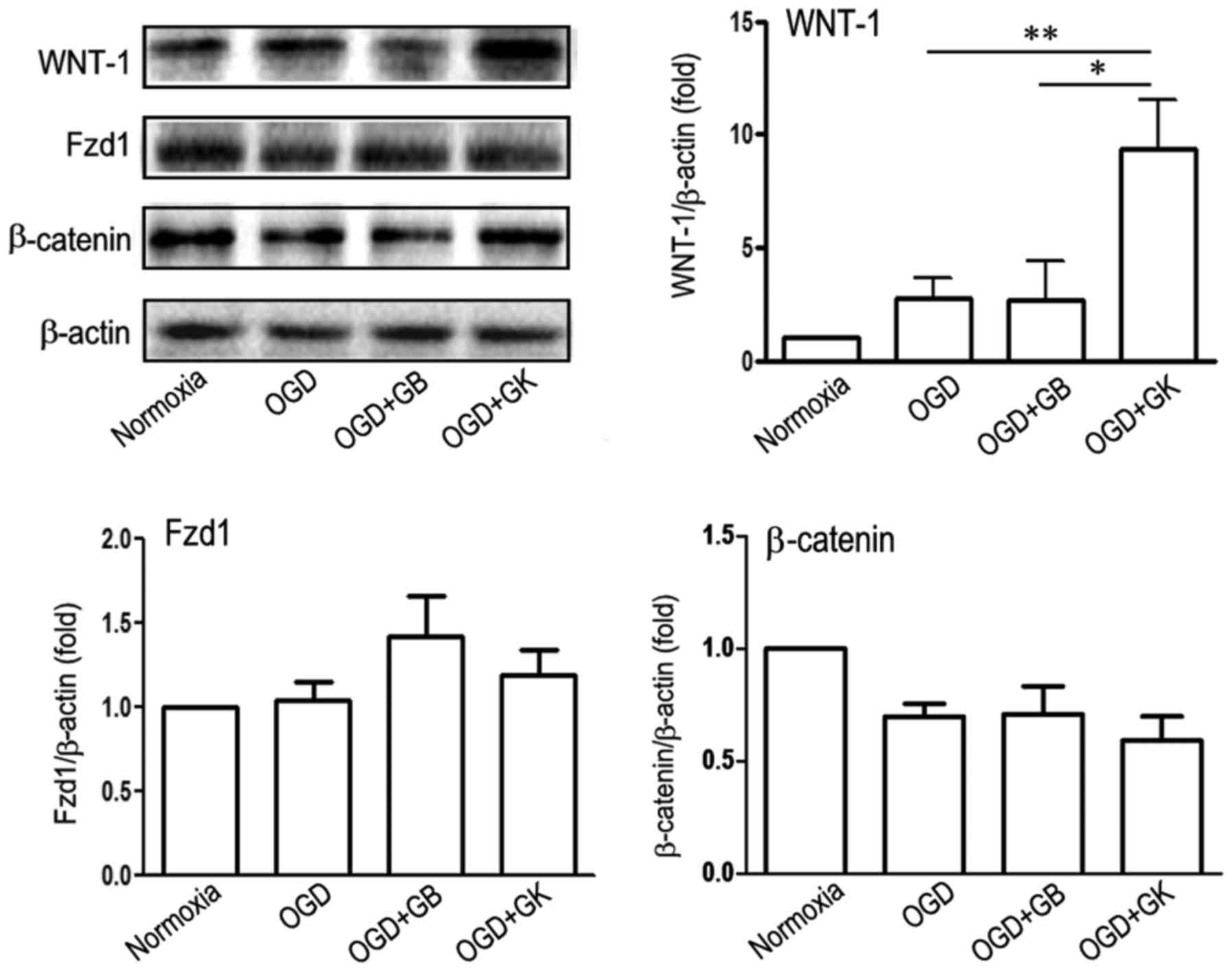
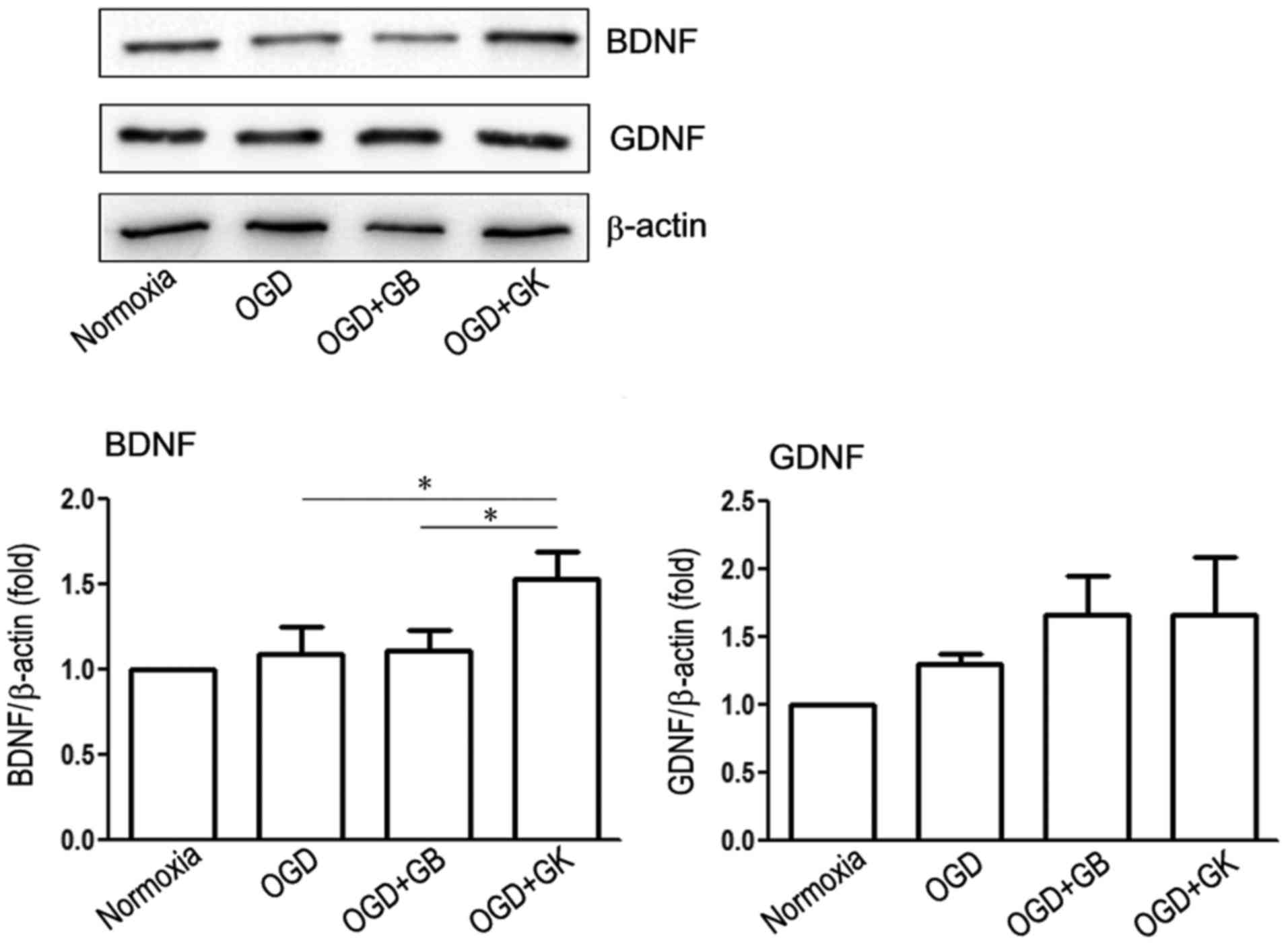
|
1
|
Seth P and Koul N: Astrocyte, the star
avatar: Redefined. J Biosci. 33:405–421. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Travis J: Glia: The brain's other cells.
Science. 266:970–972. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hahn J, Wang X and Margeta M: Astrocytes
increase the activity of synaptic GluN2B NMDA receptors. Front Cell
Neurosci. 9:1172015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Singh SK, Stogsdill JA, Pulimood NS,
Dingsdale H, Kim YH, Pilaz LJ, Kim IH, Manhaes AC, Rodrigues WS Jr,
Pamukcu A, et al: Astrocytes assemble thalamocortical synapses by
bridging NRX1α and NL1 via hevin. Cell. 164:183–196. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Filosa JA, Morrison HW, Iddings JA, Du W
and Kim KJ: Beyond neurovascular coupling, role of astrocytes in
the regulation of vascular tone. Neuroscience. 323:96–109. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Xu L, Dan M, Shao A, Cheng X, Zhang C,
Yokel RA, Takemura T, Hanagata N, Niwa M and Watanabe D: Silver
nanoparticles induce tight junction disruption and astrocyte
neurotoxicity in a rat blood-brain barrier primary triple coculture
model. Int J Nanomedicine. 10:6105–6118. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Giaume C and Oliet S: Introduction to the
special issue: Dynamic and metabolic interactions between
astrocytes and neurons. Neuroscience. 323:1–2. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tewari SG, Gottipati MK and Parpura V:
Mathematical modeling in neuroscience: Neuronal activity and its
modulation by astrocytes. Front Integr Neurosci. 10:32016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Capani F, Quarracino C, Caccuri R and Sica
RE: Astrocytes as the main players in primary degenerative
disorders of the human central nervous system. Front Aging
Neurosci. 8:452016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liu Z and Chopp M: Astrocytes, therapeutic
targets for neuroprotection and neurorestoration in ischemic
stroke. Prog Neurobiol. 144:103–120. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Verkhratsky A, Steardo L, Parpura V and
Montana V: Translational potential of astrocytes in brain
disorders. Prog Neurobiol. 144:188–205. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ahlemeyer B and Krieglstein J:
Pharmacological studies supporting the therapeutic use of ginkgo
biloba extract for Alzheimer's disease. Pharmacopsychiatry. 1(Suppl
36): S8–S14. 2003.
|
|
13
|
Luo Y, Smith JV, Paramasivam V, Burdick A,
Curry KJ, Buford JP, Khan I, Netzer WJ, Xu H and Butko P:
Inhibition of amyloid-beta aggregation and caspase-3 activation by
the ginkgo biloba extract EGb761. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
99:12197–12202. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Curtis-Prior P, Vere D and Fray P:
Therapeutic value of ginkgo biloba in reducing symptoms of decline
in mental function. J Pharm Pharmacol. 51:535–541. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chung KF, Dent G, McCusker M, Guinot P,
Page CP and Barnes PJ: Effect of a ginkgolide mixture (BN 52063) in
antagonising skin and platelet responses to platelet activating
factor in man. Lancet. 1:248–251. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Pei HX, Hua R, Guan CX and Fang X:
Ginkgolide B reduces the degradation of membrane phospholipids to
prevent ischemia/reperfusion myocardial injury in rats.
Pharmacology. 96:233–239. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shu ZM, Shu XD, Li HQ, Sun Y, Shan H, Sun
XY, Du RH, Lu M, Xiao M, Ding JH and Hu G: Ginkgolide B protects
against ischemic stroke via modulating microglia polarization in
mice. CNS Neurosci Ther. 22:729–739. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zheng JL, Li BS, Cao XC, Zhuo WK and Zhang
G: Alleviation of spinal cord injury by ginkgolide B via the
inhibition of STAT1 expression. Genet Mol Res. 15:42482016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Zhou T, You WT, Ma ZC, Liang QD, Tan HL,
Xiao CR, Tang XL, Zhang BL, Wang YG and Gao Y: Ginkgolide B
protects human umbilical vein endothelial cells against xenobiotic
injuries via PXR activation. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 37:177–186. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chi CL, Shen DF, Wang PJ, Li HL and Zhang
L: Effect of ginkgolide B on brain metabolism and tissue
oxygenation in severe haemorrhagic stroke. Int J Clin Exp Med.
8:3522–3529. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ma S, Liu H, Jiao H, Wang L, Chen L, Liang
J, Zhao M and Zhang X: Neuroprotective effect of ginkgolide K on
glutamate-induced cytotoxicity in PC 12 cells via inhibition of ROS
generation and Ca(2+) influx. Neurotoxicology. 33:59–69. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ma S, Liu X, Xun Q and Zhang X:
Neuroprotective effect of Ginkgolide K against H2O2-induced PC12
cell cytotoxicity by ameliorating mitochondrial dysfunction and
oxidative stress. Biol Pharm Bull. 37:217–225. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang S, Wang Z, Fan Q, Guo J, Galli G, Du
G, Wang X and Xiao W: Ginkgolide K protects the heart against
endoplasmic reticulum stress injury by activating the
inositol-requiring enzyme 1α/X box-binding protein-1 pathway. Br J
Pharmacol. 173:2402–2418. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ma S, Yin H, Chen L, Liu H, Zhao M and
Zhang X: Neuroprotective effect of ginkgolide K against acute
ischemic stroke on middle cerebral ischemia occlusion in rats. J
Nat Med. 66:25–31. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Maclennan KM, Darlington CL and Smith PF:
The CNS effects of ginkgo biloba extracts and ginkgolide B. Prog
Neurobiol. 67:235–257. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rao CY, Fu LY, Hu CL, Chen DX, Gan T, Wang
YC and Zhao XY: H2S mitigates severe acute pancreatitis through the
PI3K/AKT-NF-κB pathway in vivo. World J Gastroenterol.
21:4555–4563. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
de Oliveira MR, Ferreira GC and Schuck PF:
Protective effect of carnosic acid against paraquat-induced redox
impairment and mitochondrial dysfunction in SH-SY5Y cells: Role for
PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 pathway. Toxicol In Vitro. 32:41–54. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tang K, Yang J, Gao X, Wang C, Liu L,
Kitani H, Atsumi T and Jing N: Wnt-1 promotes neuronal
differentiation and inhibits gliogenesis in P19 cells. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 293:167–173. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Masckauchan TN, Shawbe CJ, Funahashi Y, Li
CM and Kitajewski J: Wnt/beta-catenin signaling induces
proliferation, survival and interleukin-8 in human endothelial
cells. Angiogenesis. 8:43–51. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liu M, Kay JC, Shen S and Qiao LY:
Endogenous BDNF augments NMDA receptor phosphorylation in the
spinal cord via PLCgamma, PKC, and PI3K/Akt pathways during
colitis. J Neuroinflammation. 12:1512015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yang JW, Ru J, Ma W, Gao Y, Liang Z, Liu
J, Guo JH and Li LY: BDNF promotes the growth of human neurons
through crosstalk with the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway via
GSK-3β. Neuropeptides. 54:35–46. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Magnusson JP, Goritz C, Tatarishvili J,
Dias DO, Smith EM, Lindvall O, Kokaia Z and Frisén J: A latent
neurogenic program in astrocytes regulated by Notch signaling in
the mouse. Science. 346:237–241. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Rossi DJ, Brady JD and Mohr C: Astrocyte
metabolism and signaling during brain ischemia. Nat Neurosci.
10:1377–1386. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Choudhury GR and Ding S: Reactive
astrocytes and therapeutic potential in focal ischemic stroke.
Neurobiol Dis. 85:234–244. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Amantea D, Micieli G, Tassorelli C,
Cuartero MI, Ballesteros I, Certo M, Moro MA, Lizasoain I and
Bagetta G: Rational modulation of the innate immune system for
neuroprotection in ischemic stroke. Front Neurosci. 9:1472015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Vargas MR and Johnson JA: The Nrf2-ARE
cytoprotective pathway in astrocytes. Expert Rev Mol Med.
11:e172009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Cao X, Xiao H, Zhang Y, Zou L, Chu Y and
Chu X: 1, 5-Dicaffeoylquinic acid-mediated glutathione synthesis
through activation of Nrf2 protects against OGD/reperfusion-induced
oxidative stress in astrocytes. Brain Res. 1347:142–148. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Pan H, Wang H, Zhu L, Mao L, Qiao L and Su
X: Depletion of Nrf2 enhances inflammation induced by oxyhemoglobin
in cultured mice astrocytes. Neurochem Res. 36:2434–2441. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Jeong WS, Kim IW, Hu R and Kong AN:
Modulatory properties of various natural chemopreventive agents on
the activation of NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Pharm Res.
21:661–670. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Jin W, Wang H, Yan W, Zhu L, Hu Z, Ding Y
and Tang K: Role of Nrf2 in protection against traumatic brain
injury in mice. J Neurotrauma. 26:131–139. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Sondergaard JN, Poghosyan S, Hontelez S,
Louche P, Looman MW, Ansems M and Adema GJ: DC-SCRIPT regulates
IL-10 production in human dendritic cells by modulating NF-κBp65
activation. J Immunol. 195:1498–1505. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hovsepian E, Penas F, Siffo S, Mirkin GA
and Goren NB: IL-10 inhibits the NF-κB and ERK/MAPK-mediated
production of pro-inflammatory mediators by up-regulation of SOCS-3
in Trypanosoma cruzi-infected cardiomyocytes. PLoS One.
8:e794452013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wang Y, Fan L, Meng X, Jiang F, Chen Q,
Zhang Z and Yan H: Transplantation of IL-10-transfected endothelial
progenitor cells improves retinal vascular repair via suppressing
inflammation in diabetic rats. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol.
254:1957–1965. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Jang HJ, Hong EM, Kim M, Kim JH, Jang J,
Park SW, Byun HW, Koh DH, Choi MH, Kae SH and Lee J: Simvastatin
induces heme oxygenase-1 via NF-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2)
activation through ERK and PI3K/Akt pathway in colon cancer.
Oncotarget. 7:46219–46229. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Xu L, He S, Yin P, Li D, Mei C, Yu X, Shi
Y, Jiang L and Liu F: Punicalagin induces Nrf2 translocation and
HO-1 expression via PI3K/Akt, protecting rat intestinal epithelial
cells from oxidative stress. Int J Hyperthermia. 32:465–473. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Palgan K and Bartuzi Z: Platelet
activating factor in allergies. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol.
28:584–589. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Aihara M, Ishii S, Kume K and Shimizu T:
Interaction between neurone and microglia mediated by
platelet-activating factor. Genes Cells. 5:397–406. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Montrucchio G, Alloatti G and Camussi G:
Role of platelet-activating factor in cardiovascular
pathophysiology. Physiol Rev. 80:1669–1699. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Li Z, Shu Q, Li L, Ge M and Zhang Y:
Sequential expression of cyclooxygenase-2, glutamate receptor-2,
and platelet activating factor receptor in rat hippocampal neurons
after fluid percussion injury. Neural Regen Res. 9:978–985. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Lu J, Caplan MS, Li D and Jilling T:
Polyunsaturated fatty acids block platelet-activating
factor-induced phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase/Akt-mediated apoptosis
in intestinal epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver
Physiol. 294:G1181–G1190. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Nakaso K, Yano H, Fukuhara Y, Takeshima T,
Wada-Isoe K and Nakashima K: PI3K is a key molecule in the
Nrf2-mediated regulation of antioxidative proteins by hemin in
human neuroblastoma cells. FEBS Lett. 546:181–184. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Hwang YP and Jeong HG: Ginsenoside Rb1
protects against 6-hydroxydopamine-induced oxidative stress by
increasing heme oxygenase-1 expression through an estrogen
receptor-related PI3K/Akt/Nrf2-dependent pathway in human
dopaminergic cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 242:18–28. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Xu X, Li H, Hou X, Li D, He S, Wan C, Yin
P, Liu M, Liu F and Xu J: Punicalagin induces Nrf2/HO-1 expression
via upregulation of PI3K/AKT pathway and inhibits LPS-induced
oxidative stress in RAW264.7 macrophages. Mediators Inflamm.
2015:3802182015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Pekny M and Pekna M: Astrocyte
intermediate filaments in CNS pathologies and regeneration. J
Pathol. 204:428–437. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Machon O, Backman M, Machonova O, Kozmik
Z, Vacik T, Andersen L and Krauss S: A dynamic gradient of Wnt
signaling controls initiation of neurogenesis in the mammalian
cortex and cellular specification in the hippocampus. Dev Biol.
311:223–237. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Zhou CJ, Borello U, Rubenstein JL and
Pleasure SJ: Neuronal production and precursor proliferation
defects in the neocortex of mice with loss of function in the
canonical Wnt signaling pathway. Neuroscience. 142:1119–1131. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
L'Episcopo F, Serapide MF, Tirolo C, Testa
N, Caniglia S, Morale MC, Pluchino S and Marchetti B: A Wnt1
regulated Frizzled-1/β-Catenin signaling pathway as a candidate
regulatory circuit controlling mesencephalic dopaminergic
neuron-astrocyte crosstalk: Therapeutical relevance for neuron
survival and neuroprotection. Mol Neurodegener. 6:492011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Chacon MA, Varela-Nallar L and Inestrosa
NC: Frizzled-1 is involved in the neuroprotective effect of Wnt3a
against Abeta oligomers. J Cell Physiol. 217:215–227. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Lie DC, Colamarino SA, Song HJ, Désiré L,
Mira H, Consiglio A, Lein ES, Jessberger S, Lansford H, Dearie AR
and Gage FH: Wnt signalling regulates adult hippocampal
neurogenesis. Nature. 437:1370–1375. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Kalani MY, Cheshier SH, Cord BJ, Bababeygy
SR, Vogel H, Weissman IL, Palmer TD and Nusse R: Wnt-mediated
self-renewal of neural stem/progenitor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 105:16970–16975. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Harada T, Harada C, Nakayama N, Okuyama S,
Yoshida K, Kohsaka S, Matsuda H and Wada K: Modification of
glial-neuronal cell interactions prevents photoreceptor apoptosis
during light-induced retinal degeneration. Neuron. 26:533–541.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Yi H, Hu J, Qian J and Hackam AS:
Expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor is regulated by the
wnt signaling pathway. Neuroreport. 23:189–194. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|