|
1
|
Ostrom QT, Gittleman H, Fulop J, Liu M,
Blanda R, Kromer C, Wolinsky Y, Kruchko C and Barnholtz-Sloan JS:
CBTRUS statistical report: Primary brain and central nervous system
tumors diagnosed in the united states in 2008-2012. Neuro Oncol. 4
Suppl 17:iv1–iv62. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Ho VK, Reijneveld JC, Enting RH, Bienfait
HP, Robe P, Baumert BG and Visser O; Dutch Society for
Neuro-Oncology (LWNO), : Changing incidence and improved survival
of gliomas. Eur J Cancer. 50:2309–2318. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Brabletz T, Kalluri R, Nieto MA and
Weinberg RA: EMT in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 18:128–134. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lamouille S, Xu J and Derynck R: Molecular
mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 15:178–196. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY and Nieto
MA: Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease.
Cell. 139:871–890. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Myatt SS and Lam EW: The emerging roles of
forkhead box (Fox) proteins in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 7:847–859.
2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Han B, Bhowmick N, Qu Y, Chung S, Giuliano
AE and Cui X: FOXC1: An emerging marker and therapeutic target for
cancer. Oncogene. 36:3957–3963. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Seo S, Fujita H, Nakano A, Kang M, Duarte
A and Kume T: The forkhead transcription factors, foxc1 and foxc2,
are required for arterial specification and lymphatic sprouting
during vascular development. Dev Biol. 294:458–470. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sun J, Ishii M, Ting MC and Maxson R:
Foxc1 controls the growth of the murine frontal bone rudiment by
direct regulation of a Bmp response threshold of Msx2. Development.
140:1034–1044. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bin L, Deng L, Yang H, Zhu L, Wang X,
Edwards MG, Richers B and Leung DY: Forkhead box C1 regulates human
primary keratinocyte terminal differentiation. PLoS One.
11:e01673922016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mirzayans F, Lavy R, Penner-Chea J and
Berry FB: Initiation of early osteoblast differentiation events
through the direct transcriptional regulation of Msx2 by FOXC1.
PLoS One. 7:e490952012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang J, Xu Y, Li L, Wang L, Yao R, Sun Q
and Du G: FOXC1 is associated with estrogen receptor alpha and
affects sensitivity of tamoxifen treatment in breast cancer. Cancer
Med. 6:275–287. 2017. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sizemore ST and Keri RA: The forkhead box
transcription factor FOXC1 promotes breast cancer invasion by
inducing matrix metalloprotease 7 (MMP7) expression. J Biol Chem.
287:24631–24640. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wei LX, Zhou RS, Xu HF, Wang JY and Yuan
MH: High expression of FOXC1 is associated with poor clinical
outcome in non-small cell lung cancer patients. Tumour Biol.
34:941–946. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen S, Jiao S, Jia Y and Li Y: Effects of
targeted silencing of FOXC1 gene on proliferation and in vitro
migration of human non-small-cell lung carcinoma cells. Am J Transl
Res. 8:3309–3318. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang J, Ray PS, Sim MS, Zhou XZ, Lu KP,
Lee AV, Lin X, Bagaria SP, Giuliano AE and Cui X: FOXC1 regulates
the functions of human basal-like breast cancer cells by activating
NF-kB signaling. Oncogene. 31:4798–4802. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Xia L, Huang W, Tian D, Zhu H, Qi X, Chen
Z, Zhang Y, Hu H, Fan D, Nie Y and Wu K: Overexpression of forkhead
box C1 promotes tumor metastasis and indicates poor prognosis in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 57:610–624. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ou-Yang L, Xiao SJ, Liu P, Yi SJ, Zhang
XL, Ou-Yang S, Tan SK and Lei X: Forkhead box C1 induces
epithelialmesenchymal transition and is a potential therapeutic
target in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Mol Med Rep. 12:8003–8009.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang J, Li L, Liu S, Zhao Y, Wang L and Du
G: FOXC1 promotes melanoma by activating MST1R/PI3K/AKT.
Oncotarget. 7:84375–84387. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhu X, Wei L, Bai Y, Wu S and Han S: FoxC1
promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition through PBX1 dependent
transactivation of ZEB2 in esophageal cancer. Am J Cancer Res.
7:1642–1653. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Huang L, Huang Z, Fan Y, He L, Ye M, Shi
K, Ji B, Huang J, Wang Y and Li Q: FOXC1 promotes proliferation and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cervical carcinoma through the
PI3K-AKT signal pathway. Am J Transl Res. 9:1297–1306.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu Y, Han L, Bai Y, Du W and Yang B:
Down-regulation of MicroRNA-133 predicts poor overall survival and
regulates the growth and invasive abilities in glioma. Artif Cells
Nanomed Biotechnol. 46:206–210. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yu H, Xue Y, Wang P, Liu X, Ma J, Zheng J,
Li Z, Cai H and Liu Y: Knockdown of long non-coding RNA XIST
increases blood-tumor barrier permeability and inhibits glioma
angiogenesis by targeting miR-137. Oncogenesis. 6:e3032017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang L, Chai L, Ji Q, Cheng R, Wang J and
Han S: Forkhead box protein C1 promotes cell proliferation and
invasion in human cervical cancer. Mol Med Rep. 17:4392–4398.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xu YY, Tian J, Hao Q and Yin LR:
MicroRNA-495 downregulates FOXC1 expression to suppress cell growth
and migration in endometrial cancer. Tumour Biol. 37:239–251. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Deng L, Liu T, Zhang B, Wu H, Zhao J and
Chen J: Forkhead box C1 is targeted by microRNA-133b and promotes
cell proliferation and migration in osteosarcoma. Exp Ther Med.
14:2823–2830. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kalluri R and Weinberg RA: The basics of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Invest. 119:1420–1428.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yilmaz M and Christofori G: EMT, the
cytoskeleton, and cancer cell invasion. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
28:15–33. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Xu ZY, Ding SM, Zhou L, Xie HY, Chen KJ,
Zhang W, Xing CY, Guo HJ and Zheng SS: FOXC1 contributes to
microvascular invasion in primary hepatocellular carcinoma via
regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Int J Biol Sci.
8:1130–1141. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
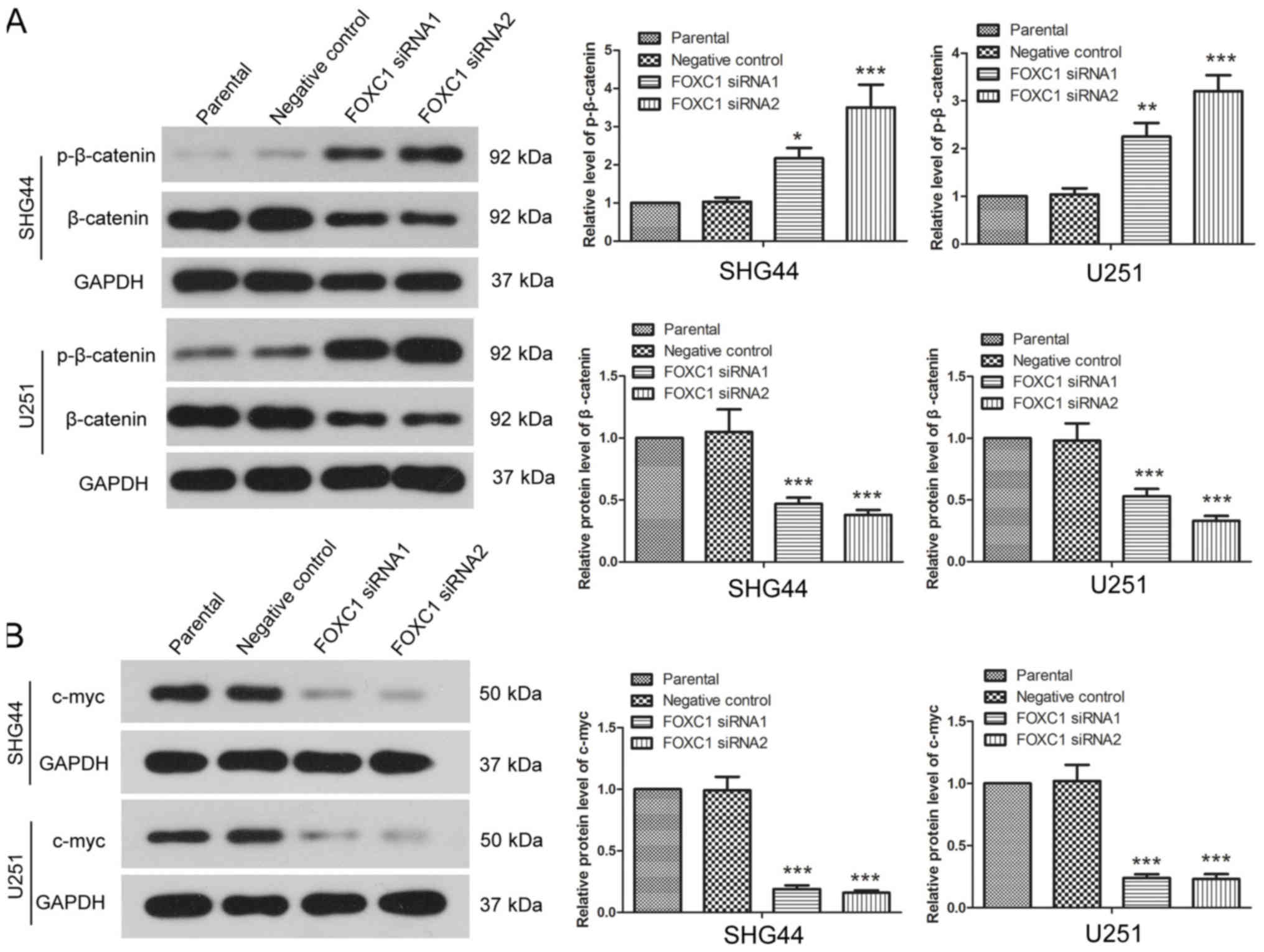
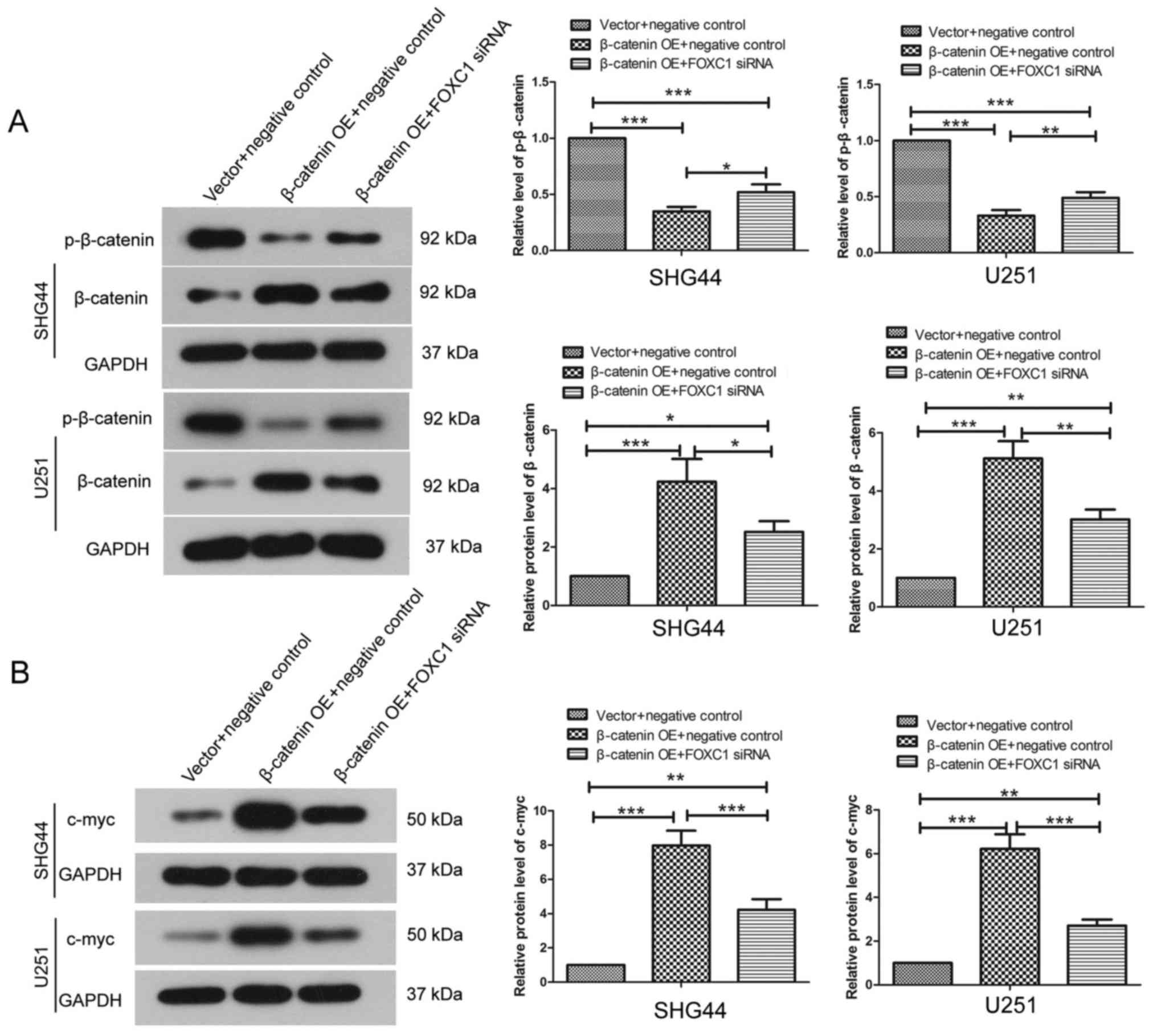
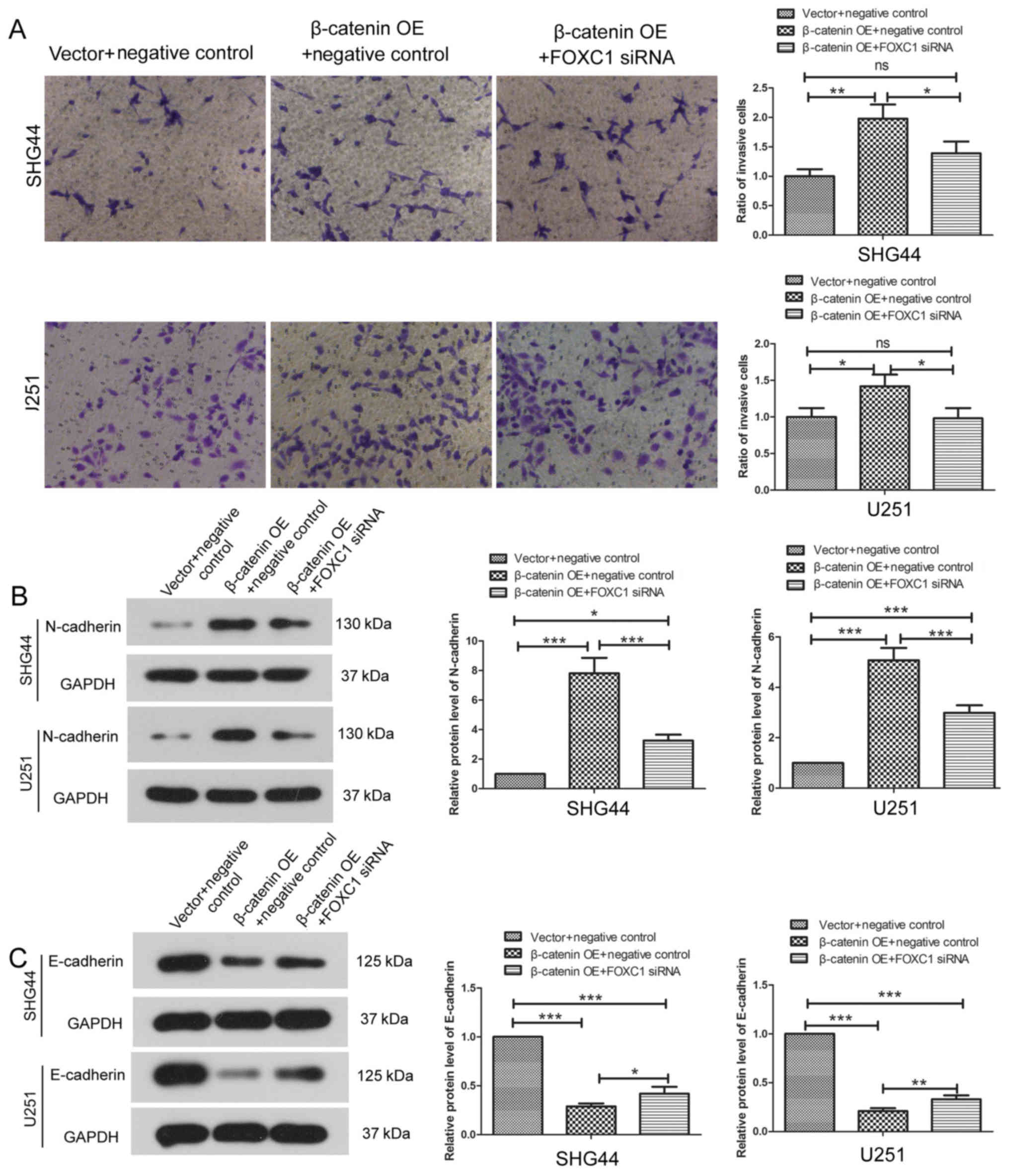
Clevers H and Nusse R: Wnt/β-catenin
signaling and disease. Cell. 149:1192–1205. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Saito-Diaz K, Chen TW, Wang X, Thorne CA,
Wallace HA, Page-McCaw A and Lee E: The way Wnt works: Components
and mechanism. Growth Factors. 31:1–31. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Anastas JN and Moon RT: WNT signalling
pathways as therapeutic targets in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
13:11–26. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li Y, Zhu G, Zeng W, Wang J, Li Z, Wang B,
Tian B, Lu D, Zhang X, Gao G and Li L: Long noncoding RNA AB073614
promotes the malignance of glioma by activating Wnt/β-catenin
signaling through downregulating SOX7. Oncotarget. 8:65577–65587.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liu X, Wang L, Zhao S, Ji X, Luo Y and
Ling F: β-catenin overexpression in malignant glioma and its role
in proliferation and apoptosis in glioblastma cells. Med Oncol.
28:608–614. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang K, Zhang J, Han L, Pu P and Kang C:
Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in glioma. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol.
7:740–749. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Mishra S, Choe Y, Pleasure SJ and
Siegenthaler JA: Cerebrovascular defects in Foxc1 mutants correlate
with aberrant WNT and VEGF-A pathways downstream of retinoic acid
from the meninges. Dev Biol. 420:148–165. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Savage J, Voronova A, Mehta V,
Sendi-Mukasa F and Skerjanc IS: Canonical Wnt signaling regulates
Foxc1/2 expression in P19 cells. Differentiation. 79:31–40. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|