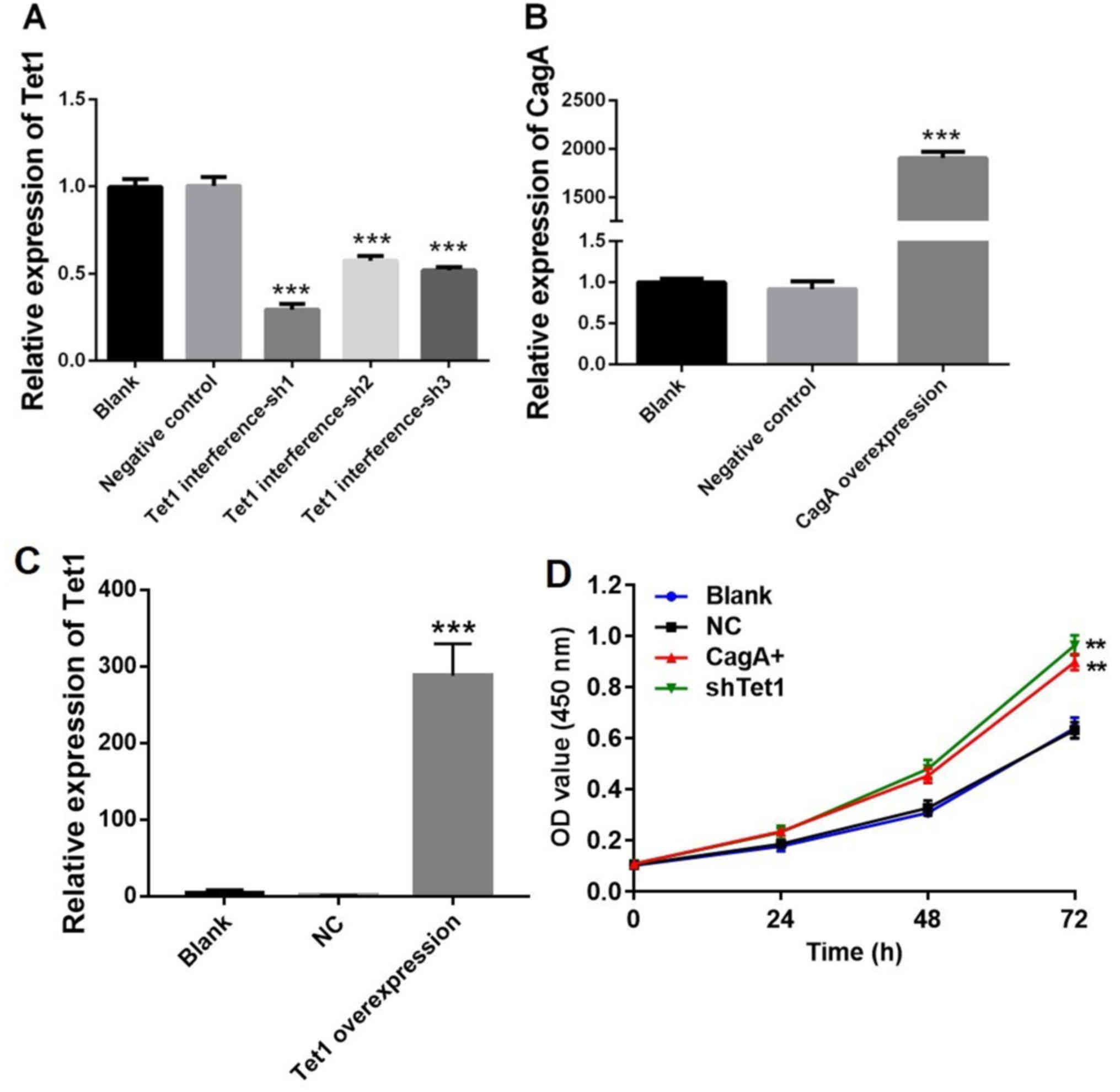
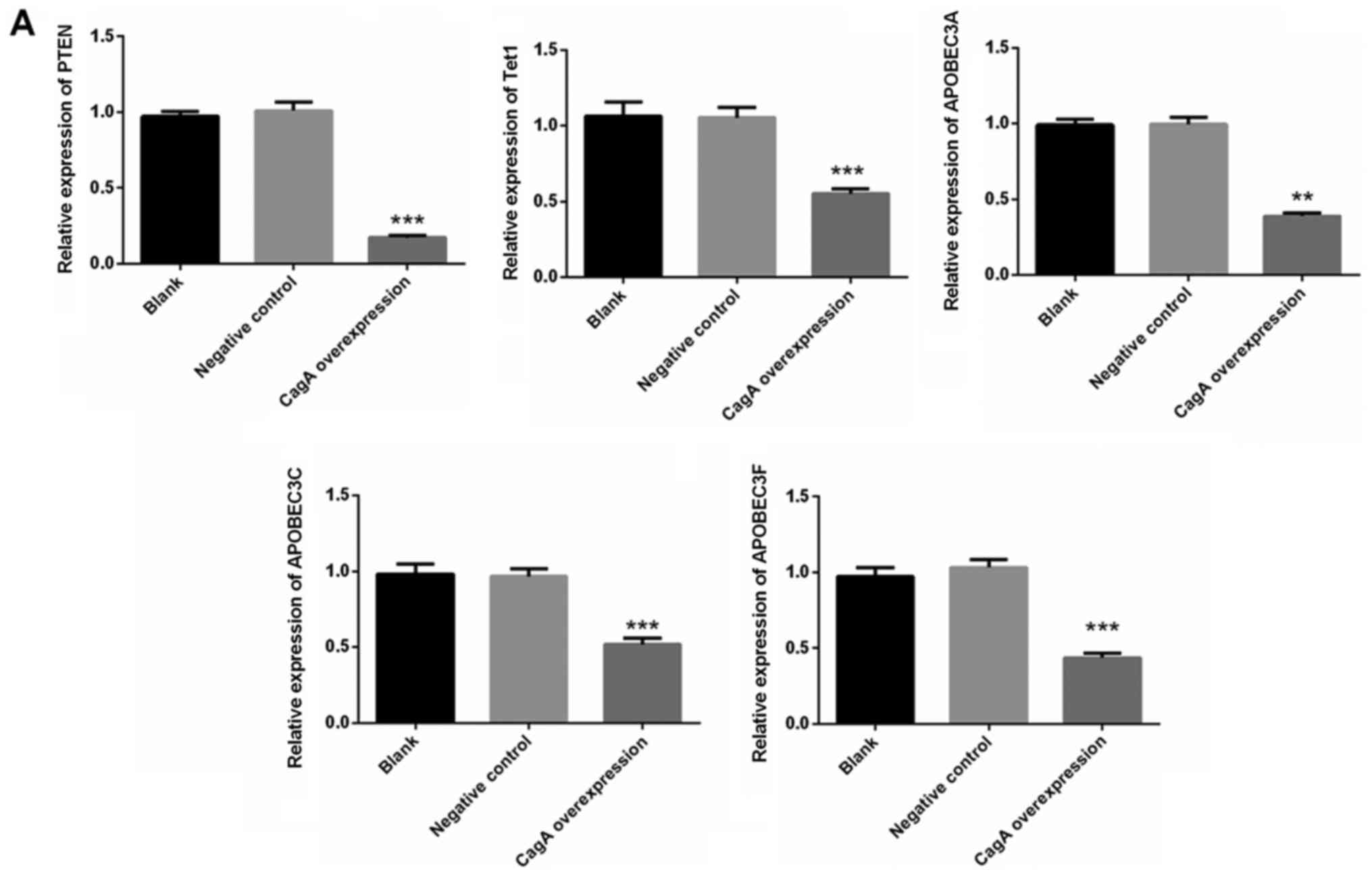
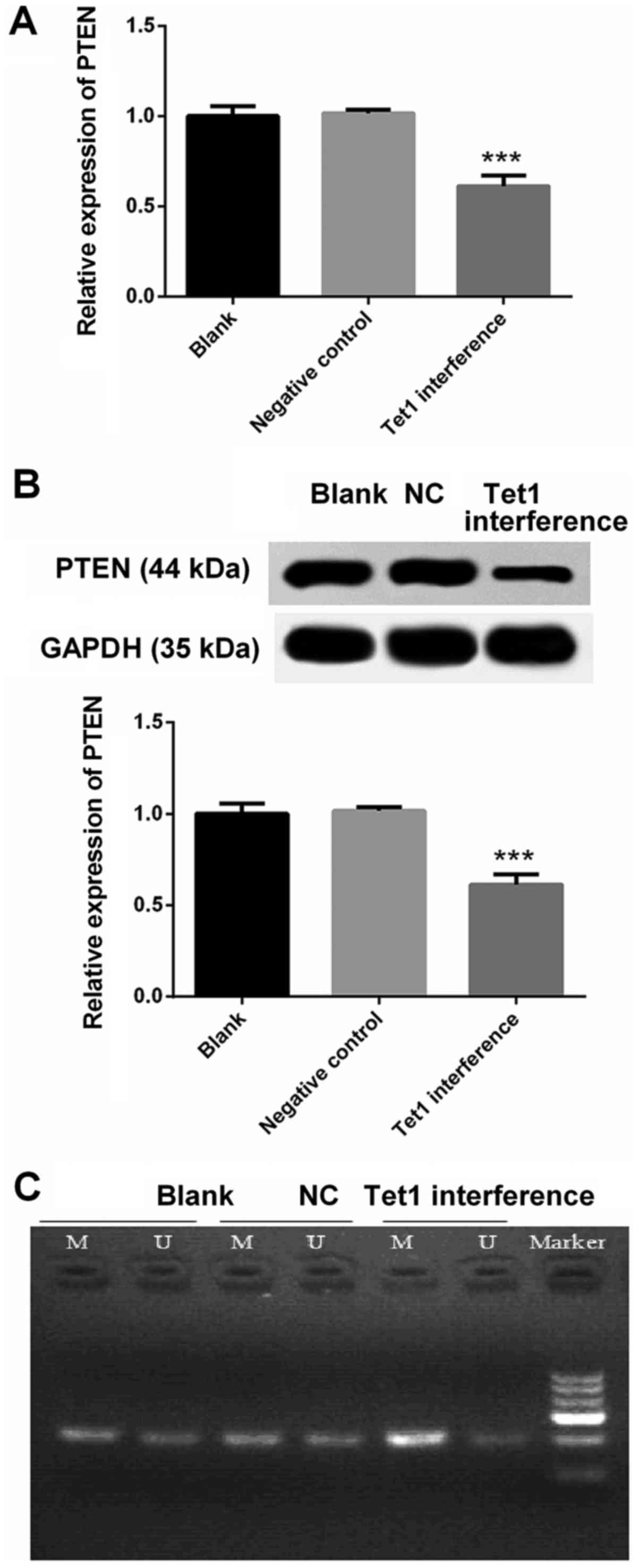
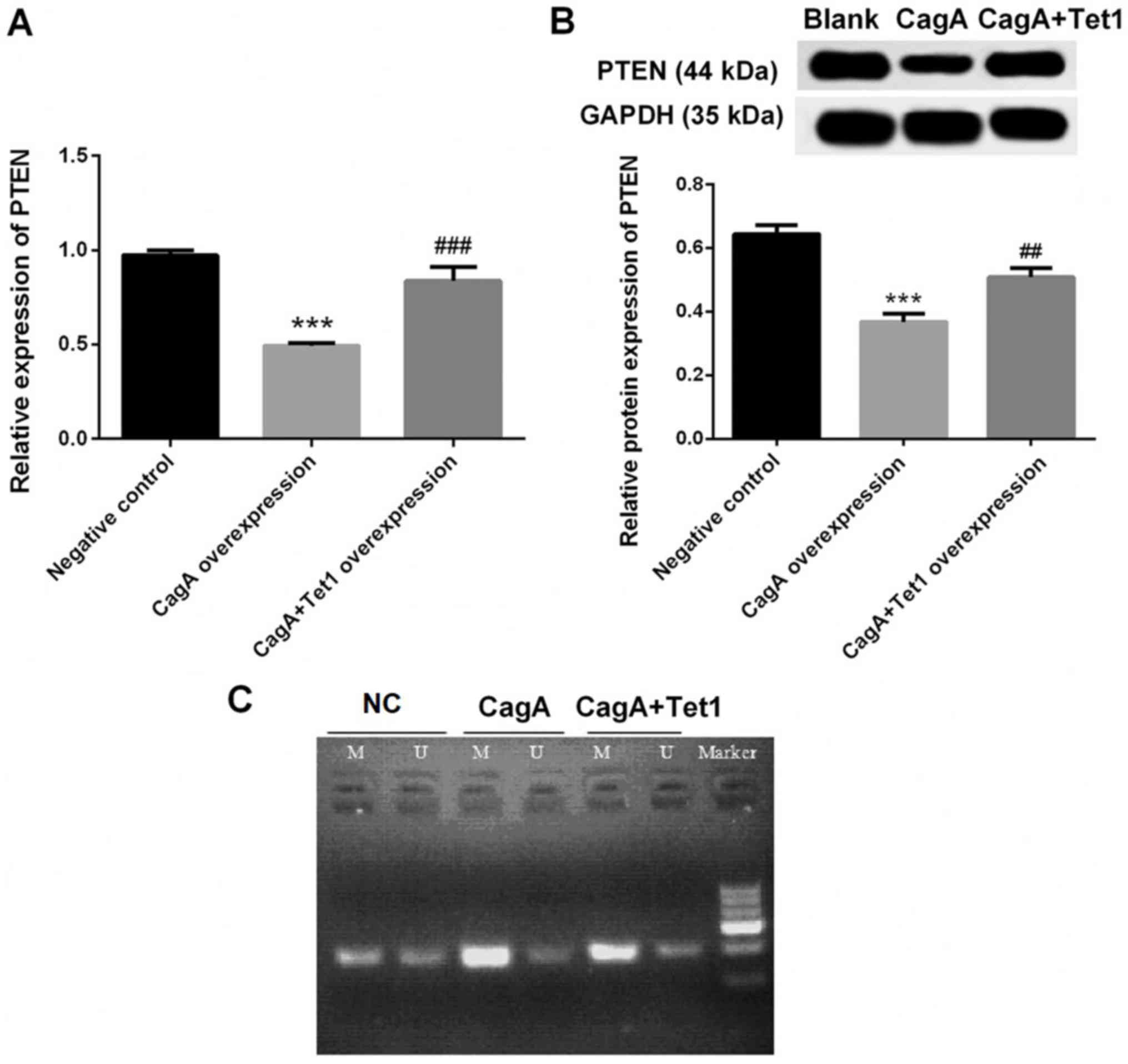
|
1
|
Zhu AL and Sonnenberg A: Is gastric cancer
again rising? J Clin Gastroenterol. 46:804–806. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Correa P: Gastric cancer: Two epidemics?
Dig Dis Sci. 56:1585–1586; author reply, 1586. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jeyamani L, Jayarajan J, Leelakrishnan V
and Swaminathan M: CagA and VacA genes of Helicobacter
pylori and their clinical relevance. Indian J Pathol Microbiol.
61:66–69. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Weel JF, van der Hulst RW, Gerrits Y,
Roorda P, Feller M, Dankert J, Tytgat GN and van der Ende A: The
interrelationship between cytotoxin-associated gene A, vacuolating
cytotoxin, and Helicobacter pylori-related diseases. J
Infect Dis. 173:1171–1175. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Huang JQ, Zheng GF, Sumanac K, Irvine EJ
and Hunt RH: Meta-analysis of the relationship between cagA
seropositivity and gastric cancer. Gastroenterology. 125:1636–1644.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Franco AT, Israel DA, Washington MK,
Krishna U, Fox JG, Rogers AB, Neish AS, Collier-Hyams L,
Perez-Perez GI, Hatakeyama M, et al: Activation of beta-catenin by
carcinogenic Helicobacter pylori. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
102:10646–10651. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Basso D, Zambon CF, Letley DP, Stranges A,
Marchet A, Rhead JL, Schiavon S, Guariso G, Ceroti M, Nitti D, et
al: Clinical relevance of Helicobacter pylori cagA and vacA
gene polymorphisms. Gastroenterology. 135:91–99. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Keniry M and Parsons R: The role of PTEN
signaling perturbations in cancer and in targeted therapy.
Oncogene. 27:5477–5485. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Krymskaya VP and Goncharova EA:
PI3K/mTORC1 activation in hamartoma syndromes: Therapeutic
prospects. Cell Cycle. 8:403–413. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sansal I and Sellers WR: The biology and
clinical relevance of the PTEN tumor suppressor pathway. J Clin
Oncol. 22:2954–2963. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Stambolic V, Suzuki A, de la Pompa JL,
Brothers GM, Mirtsos C, Sasaki T, Ruland J, Penninger JM,
Siderovski DP and Mak TW: Negative regulation of PKB/Akt-dependent
cell survival by the tumor suppressor PTEN. Cell. 95:29–39. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fu HL, Ma Y, Lu LG, Hou P, Li BJ, Jin WL
and Cui DX: TET1 exerts its tumor suppressor function by
interacting with p53-EZH2 pathway in gastric cancer. J Biomed
Nanotechnol. 10:1217–1230. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Pastor WA, Aravind L and Rao A: TETonic
shift: Biological roles of TET proteins in DNA demethylation and
transcription. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 14:341–356. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Blaser MJ, Perez-Perez GI, Kleanthous H,
Cover TL, Peek RM, Chyou PH, Stemmermann GN and Nomura A: Infection
with Helicobacter pylori strains possessing cagA is
associated with an increased risk of developing adenocarcinoma of
the stomach. Cancer Res. 55:2111–2115. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Miehlke S, Kirsch C, Agha-Amiri K, Günther
T, Lehn N, Malfertheiner P, Stolte M, Ehninger G and Bayerdörffer
E: The Helicobacter pylori vacA s1, m1 genotype and cagA is
associated with gastric carcinoma in Germany. Int J Cancer.
87:322–327. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Plummer M, van Doorn LJ, Franceschi S,
Kleter B, Canzian F, Vivas J, Lopez G, Colin D, Muñoz N and Kato I:
Helicobacter pylori cytotoxin-associated genotype and
gastric precancerous lesions. J Natl Cancer Inst. 99:1328–1334.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Loh JT, Shaffer CL, Piazuelo MB, Bravo LE,
McClain MS, Correa P and Cover TL: Analysis of cagA in
Helicobacter pylori strains from Colombian populations with
contrasting gastric cancer risk reveals a biomarker for disease
severity. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 20:2237–2249. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Churin Y, Al-Ghoul L, Kepp O, Meyer TF,
Birchmeier W and Naumann M: Helicobacter pylori CagA protein
targets the c-Met receptor and enhances the motogenic response. J
Cell Biol. 161:249–255. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Faller G and Kirchner T: Immunological and
morphogenic basis of gastric mucosa atrophy and metaplasia.
Virchows Arch. 446:1–9. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hlubek F, Spaderna S, Schmalhofer O, Jung
A, Kirchner T and Brabletz T: Wnt/FZD signaling and colorectal
cancer morphogenesis. Front Biosci. 12:458–470. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bagnoli F, Buti L, Tompkins L, Covacci A
and Amieva MR: Helicobacter pylori CagA induces a transition
from polarized to invasive phenotypes in MDCK cells. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 102:16339–16344. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Weydig C, Starzinski-Powitz A, Carra G,
Löwer J and Wessler S: CagA-independent disruption of adherence
junction complexes involves E-cadherin shedding and implies
multiple steps in Helicobacter pylori pathogenicity. Exp
Cell Res. 313:3459–3471. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Murata-Kamiya N, Kurashima Y, Teishikata
Y, Yamahashi Y, Saito Y, Higashi H, Aburatani H, Akiyama T, Peek RM
Jr, Azuma T and Hatakeyama M: Helicobacter pylori CagA
interacts with E-cadherin and deregulates the beta-catenin signal
that promotes intestinal transdifferentiation in gastric epithelial
cells. Oncogene. 26:4617–4626. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Pei YF, Tao R, Li JF, Su LP, Yu BQ, Wu XY,
Yan M, Gu QL, Zhu ZG and Liu BY: TET1 inhibits gastric cancer
growth and metastasis by PTEN demethylation and re-expression.
Oncotarget. 7:31322–31335. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen S, Li X, Qin J, Chen Y, Liu L and
Zhang D, Wang M, Wang M and Zhang D: APOBEC3A possesses anticancer
and antiviral effects by differential inhibition of HPV E6 and E7
expression on cervical cancer. Int J Clin Exp Med. 8:10548–10557.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gansmo LB, Romundstad P, Hveem K, Vatten
L, Nik-Zainal S, Lønning PE and Knappskog S: APOBEC3A/B deletion
polymorphism and cancer risk. Carcinogenesis. 39:118–124. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
28
|
Yu Q, Chen D, König R, Mariani R, Unutmaz
D and Landau NR: APOBEC3B and APOBEC3C are potent inhibitors of
simian immunodeficiency virus replication. J Biol Chem.
279:53379–53386. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ara A, Love RP, Follack TB, Ahmed KA,
Adolph MB and Chelico L: Mechanism of enhanced HIV restriction by
virion coencapsidated cytidine deaminases APOBEC3F and APOBEC3G. J
Virol. 91:e02230–16. 2016.
|