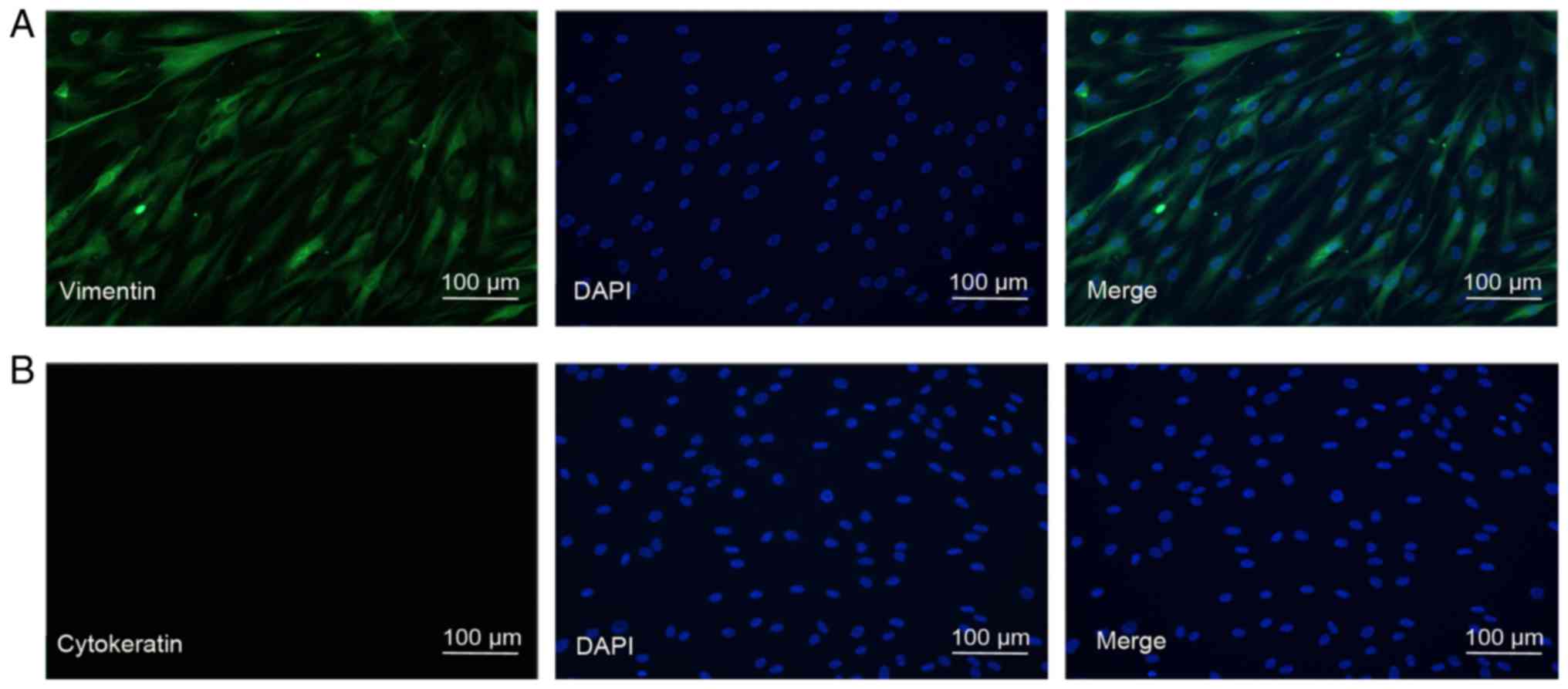
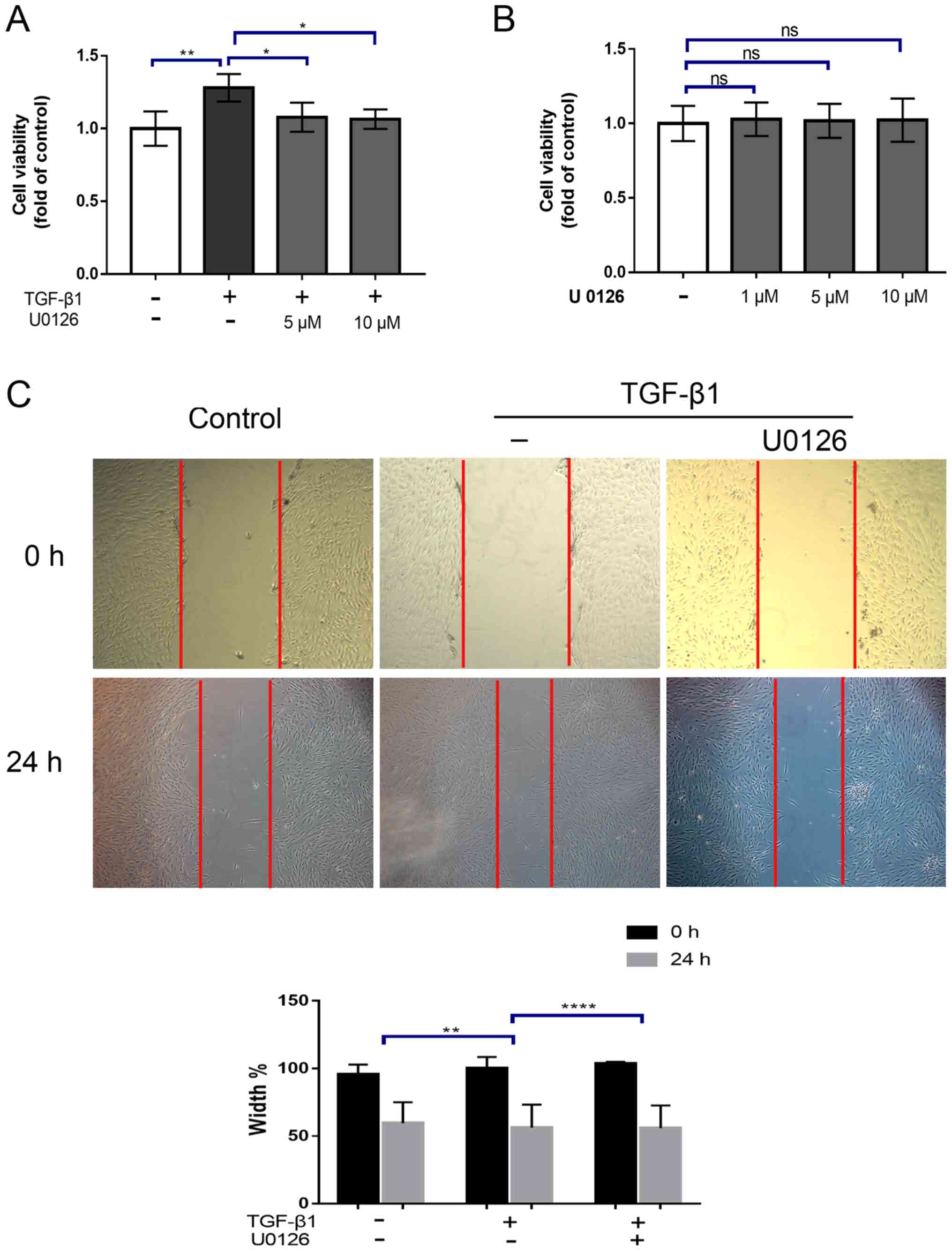
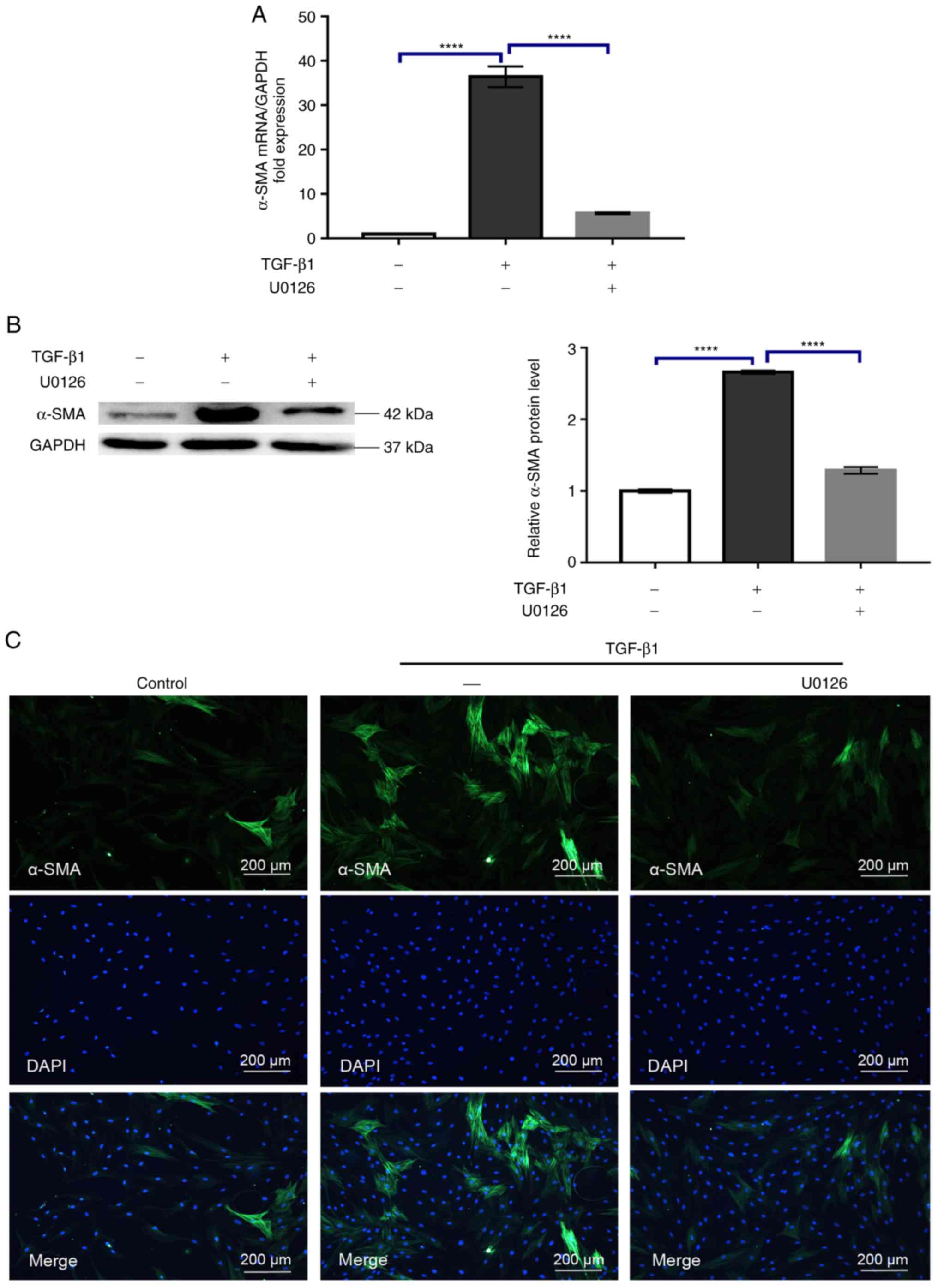
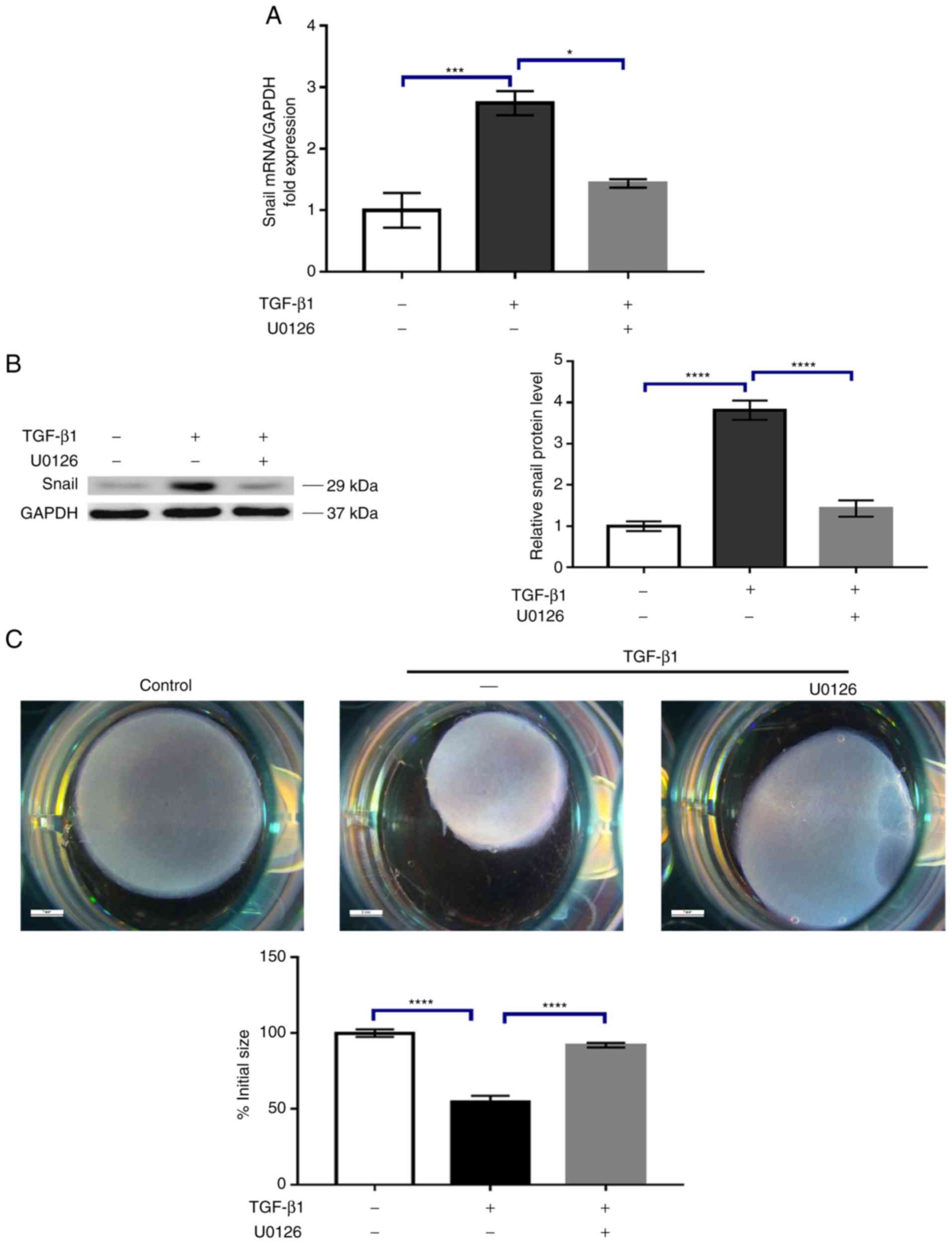
|
1
|
Fan Gaskin JC, Nguyen DQ, Soon Ang G,
O'Connor J and Crowston JG: Wound healing modulation in glaucoma
filtration surgery-conventional practices and new perspectives: The
role of antifibrotic agents (Part I). J Curr Glaucoma Pract.
8:37–45. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pimentel E and Schmidt J: Is mytomicyn
better than 5-fluorouracil as antimetabolite in trabeculectomy for
glaucoma? Medwave. 18:e71372018.(In English, Spanish). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kitazawa Y, Kawase K, Matsushita H and
Minobe M: Trabeculectomy with mitomycin. A comparative study with
fluorouracil. Arch Ophthalmol. 109:1693–1698. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Shi H, Wang H, Fu S, Xu K, Zhang X, Xiao Y
and Ye W: Losartan attenuates scar formation in filtering bleb
after trabeculectomy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 58:1478–1486.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chang L, Crowston JG, Cordeiro MF, Akbar
AN and Khaw PT: The role of the immune system in conjunctival wound
healing after glaucoma surgery. Surv Ophthalmol. 45:49–68. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hinz B, Phan SH, Thannickal VJ, Prunotto
M, Desmoulière A, Varga J, De Wever O, Mareel M and Gabbiani G:
Recent developments in myofibroblast biology: Paradigms for
connective tissue remodeling. Am J Pathol. 180:1340–1355. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hartupee J and Mann DL: Role of
inflammatory cells in fibroblast activation. J Mol Cell Cardiol.
93:143–148. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Carthy JM: TGFβ signaling and the control
of myofibroblast differentiation: Implications for chronic
inflammatory disorders. J Cell Physiol. 233:98–106. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nickel J, Ten Dijke P and Mueller TD:
TGF-β family co-receptor function and signaling. Acta Biochim
Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 50:12–36. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lin X, Yu M, Wu K, Yuan H and Zhong H:
Effects of pirfenidone on proliferation, migration, and collagen
contraction of human Tenon's fibroblasts in vitro. Invest
Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 50:3763–3770. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li DQ, Lee SB and Tseng SC: Differential
expression and regulation of TGF-beta1, TGF-beta2, TGF-beta3,
TGF-betaRI, TGF-betaRII and TGF-betaRIII in cultured human corneal,
limbal, and conjunctival fibroblasts. Curr Eye Res. 19:154–161.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fu S, Sun L, Zhang X, Shi H, Xu K, Xiao Y
and Ye W: 5-Aza-2′-deoxycytidine induces human Tenon's capsule
fibroblasts differentiation and fibrosis by up-regulating TGF-β
type I receptor. Exp Eye Res. 165:47–58. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Stahnke T, Kowtharapu BS, Stachs O,
Schmitz KP, Wurm J, Wree A, Guthoff RF and Hovakimyan M:
Suppression of TGF-β pathway by pirfenidone decreases extracellular
matrix deposition in ocular fibroblasts in vitro. PLoS One.
12:e01725922017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Meyer-Ter-Vehn T, Gebhardt S, Sebald W,
Buttmann M, Grehn F, Schlunck G and Knaus P: p38 inhibitors prevent
TGF-beta-induced myofibroblast transdifferentiation in human tenon
fibroblasts. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 47:1500–1509. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shu DY and Lovicu FJ: Myofibroblast
transdifferentiation: The dark force in ocular wound healing and
fibrosis. Prog Retin Eye Res. 60:44–65. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hsu CK, Lin HH, Harn HI, Hughes MW, Tang
MJ and Yang CC: Mechanical forces in skin disorders. J Dermatol
Sci. 90:232–240. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu Y, Kimura K, Orita T, Teranishi S,
Suzuki K and Sonoda KH: Inhibition by all-trans-retinoic acid of
transforming growth factor-β-induced collagen gel contraction
mediated by human tenon fibroblasts. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
55:4199–4205. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Meyer-ter-Vehn T, Sieprath S, Katzenberger
B, Gebhardt S, Grehn F and Schlunck G: Contractility as a
prerequisite for TGF-beta-induced myofibroblast
transdifferentiation in human tenon fibroblasts. Invest Ophthalmol
Vis Sci. 47:4895–4904. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wallace HA and Bhimji SS: Wound, Healing,
Phases, in StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing StatPearls Publishing
LLC; Treasure Island (FL): 2017
|
|
21
|
Reiter C, Wimmer S, Schultheiss A, Klink
T, Grehn F and Geerling G: Corneal epitheliopathy following
trabeculectomy with postoperative adjunctive 5-fluorouracil. Klin
Monbl Augenheilkd. 227:887–891. 2010.(In German). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Fan Gaskin JC, Nguyen DQ, Soon Ang G,
O'Connor J and Crowston JG: Wound healing modulation in glaucoma
filtration surgery-conventional practices and new perspectives:
Antivascular endothelial growth factor and novel agents (Part II).
J Curr Glaucoma Pract. 8:46–53. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bindlish R, Condon GP, Schlosser JD,
D'Antonio J, Lauer KB and Lehrer R: Efficacy and safety of
mitomycin-C in primary trabeculectomy: Five-year follow-up.
Ophthalmology. 109:1336–1342. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Khaw PT, Sherwood MB, Doyle JW, Smith MF,
Grierson I, McGorray S and Schultz GS: Intraoperative and post
operative treatment with 5-fluorouracil and mitomycin-c: Long term
effects in vivo on subconjunctival and scleral fibroblasts. Int
Ophthalmol. 16:381–385. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chang HH, Chang MC, Wu IH, Huang GF, Huang
WL, Wang YL, Lee SY, Yeh CY, Guo MK, Chan CP, et al: Role of
ALK5/Smad2/3 and MEK1/ERK signaling in transforming growth factor
beta 1-modulated growth, collagen turnover and differentiation of
stem cells from apical papilla of human tooth. J Endod.
41:1272–1280. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen X, Ye S, Xiao W, Wang W, Luo L and
Liu Y: ERK1/2 pathway mediates epithelial-mesenchymal transition by
cross-interacting with TGFβ/Smad and Jagged/Notch signaling
pathways in lens epithelial cells. Int J Mol Med. 33:1664–1670.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nickells RW: The cell and molecular
biology of glaucoma: mechanisms of retinal ganglion cell death.
Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 53:2476–2481. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gupta VK, You Y, Li JC, Klistorner A and
Graham SL: Protective effects of 7,8-dihydroxyflavone on retinal
ganglion and RGC-5 cells against excitotoxic and oxidative stress.
J Mol Neurosci. 49:96–104. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wei J, Jiang H, Gao H and Wang G: Raf-1
kinase inhibitory protein (RKIP) promotes retinal ganglion cell
survival and axonal regeneration following optic nerve crush. J Mol
Neurosci. 57:243–248. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Luo JM, Cen LP, Zhang XM, Chiang SW, Huang
Y, Lin D, Fan YM, van Rooijen N, Lam DS, Pang CP and Cui Q:
PI3K/akt, JAK/STAT and MEK/ERK pathway inhibition protects retinal
ganglion cells via different mechanisms after optic nerve injury.
Eur J Neurosci. 26:28–42. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Hinz B, Mastrangelo D, Iselin CE,
Chaponnier C and Gabbiani G: Mechanical tension controls
granulation tissue contractile activity and myofibroblast
differentiation. Am J Pathol. 159:1009–1020. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Biswas H and Longmore GD: Action of SNAIL1
in cardiac myofibroblasts is important for cardiac fibrosis
following hypoxic injury. PLoS One. 11:e01626362016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Reichard JF and Petersen DR: Involvement
of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and extracellular-regulated kinase
in hepatic stellate cell antioxidant response and myofibroblastic
transdifferentiation. Arch Biochem Biophys. 446:111–118. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Makino T, Jinnin M, Muchemwa FC, Fukushima
S, Kogushi-Nishi H, Moriya C, Igata T, Fujisawa A, Johno T and Ihn
H: Basic fibroblast growth factor stimulates the proliferation of
human dermal fibroblasts via the ERK1/2 and JNK pathways. Br J
Dermatol. 162:717–723. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Derynck R and Zhang YE: Smad-dependent and
Smad-independent pathways in TGF-beta family signalling. Nature.
425:577–584. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Guo X and Wang XF: Signaling cross-talk
between TGF-beta/BMP and other pathways. Cell Res. 19:71–88. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Pardali E, Sanchez-Duffhues G,
Gomez-Puerto MC and Ten Dijke P: TGF-β-induced
endothelial-mesenchymal transition in fibrotic diseases. Int J Mol
Sci. 18(pii): E21572017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zeglinski MR, Roche P, Hnatowich M, Jassal
DS, Wigle JT, Czubryt MP and Dixon IM: TGFβ1 regulates Scleraxis
expression in primary cardiac myofibroblasts by a Smad-independent
mechanism. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 310:H239–H249. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Che X, Wang Q, Xie Y, Xu W, Shao X, Mou S
and Ni Z: Astragaloside IV suppresses transforming growth factor-β1
induced fibrosis of cultured mouse renal fibroblasts via inhibition
of the MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 464:1260–1266. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kamaraju AK and Roberts AB: Role of
Rho/ROCK and p38 MAP kinase pathways in transforming growth
factor-beta-mediated Smad-dependent growth inhibition of human
breast carcinoma cells in vivo. J Biol Chem. 280:1024–1036. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Iwayama H, Sakamoto T, Nawa A and Ueda N:
Crosstalk between Smad and mitogen-activated protein kinases for
the regulation of apoptosis in cyclosporine A- induced renal
tubular injury. Nephron Extra. 1:178–189. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhu Y, Gu J, Zhu T, Jin C, Hu X and Wang
X: Crosstalk between Smad2/3 and specific isoforms of ERK in
TGF-β1-induced TIMP-3 expression in rat chondrocytes. J Cell Mol
Med. 21:1781–1790. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Boye A, Kan H, Wu C, Jiang Y, Yang X, He S
and Yang Y: MAPK inhibitors differently modulate TGF-β/Smad
signaling in HepG2 cells. Tumour Biol. 36:3643–3651. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|