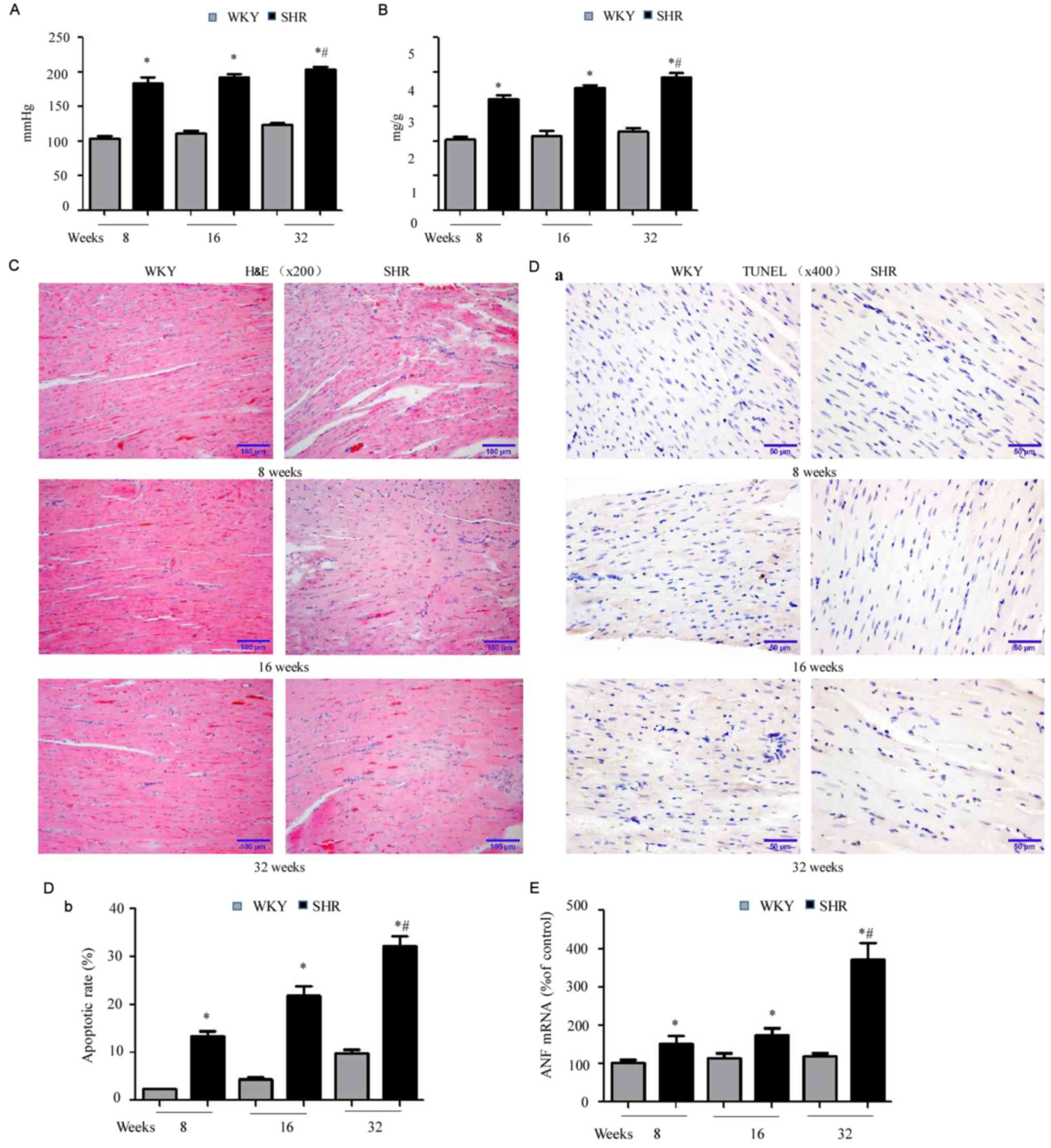
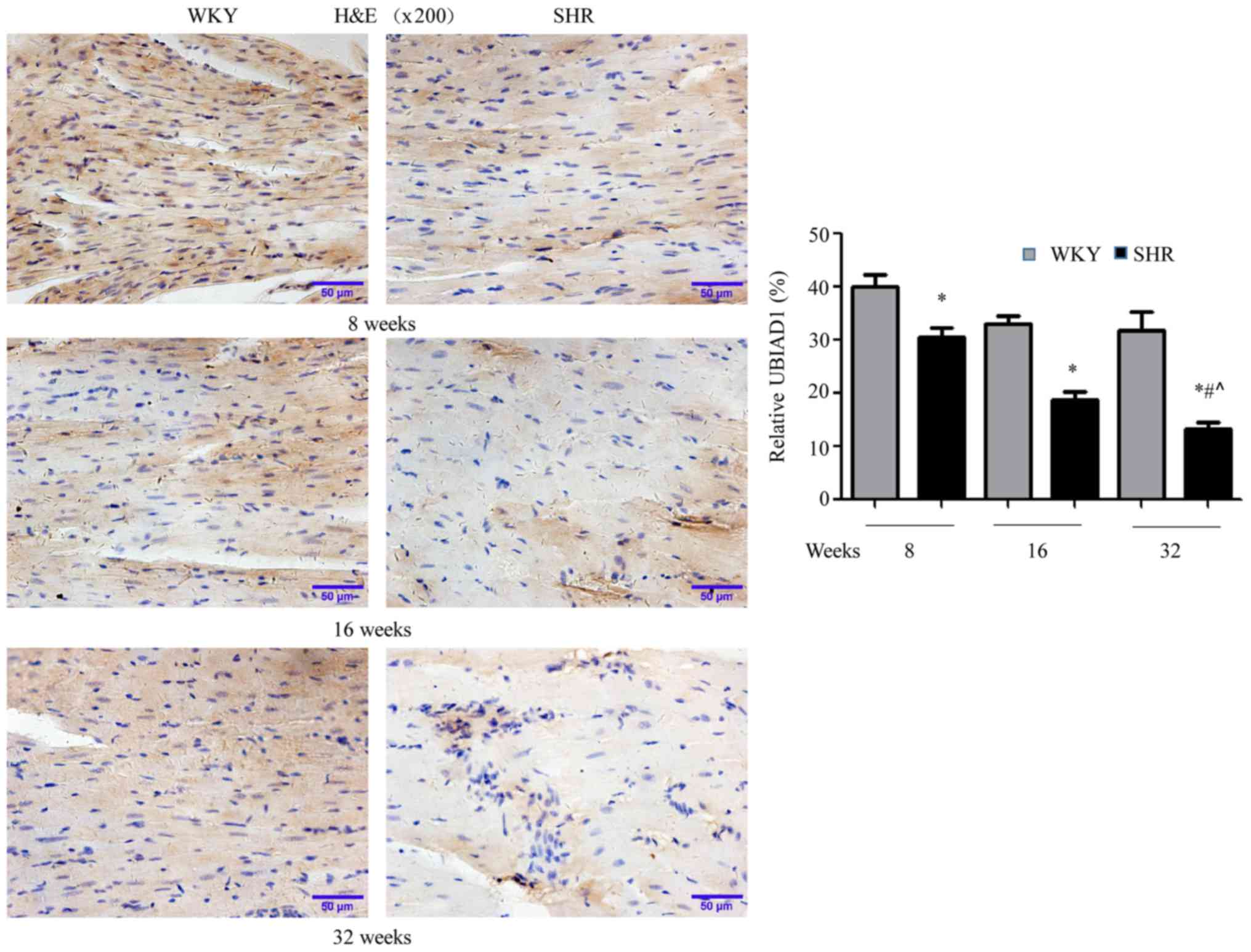
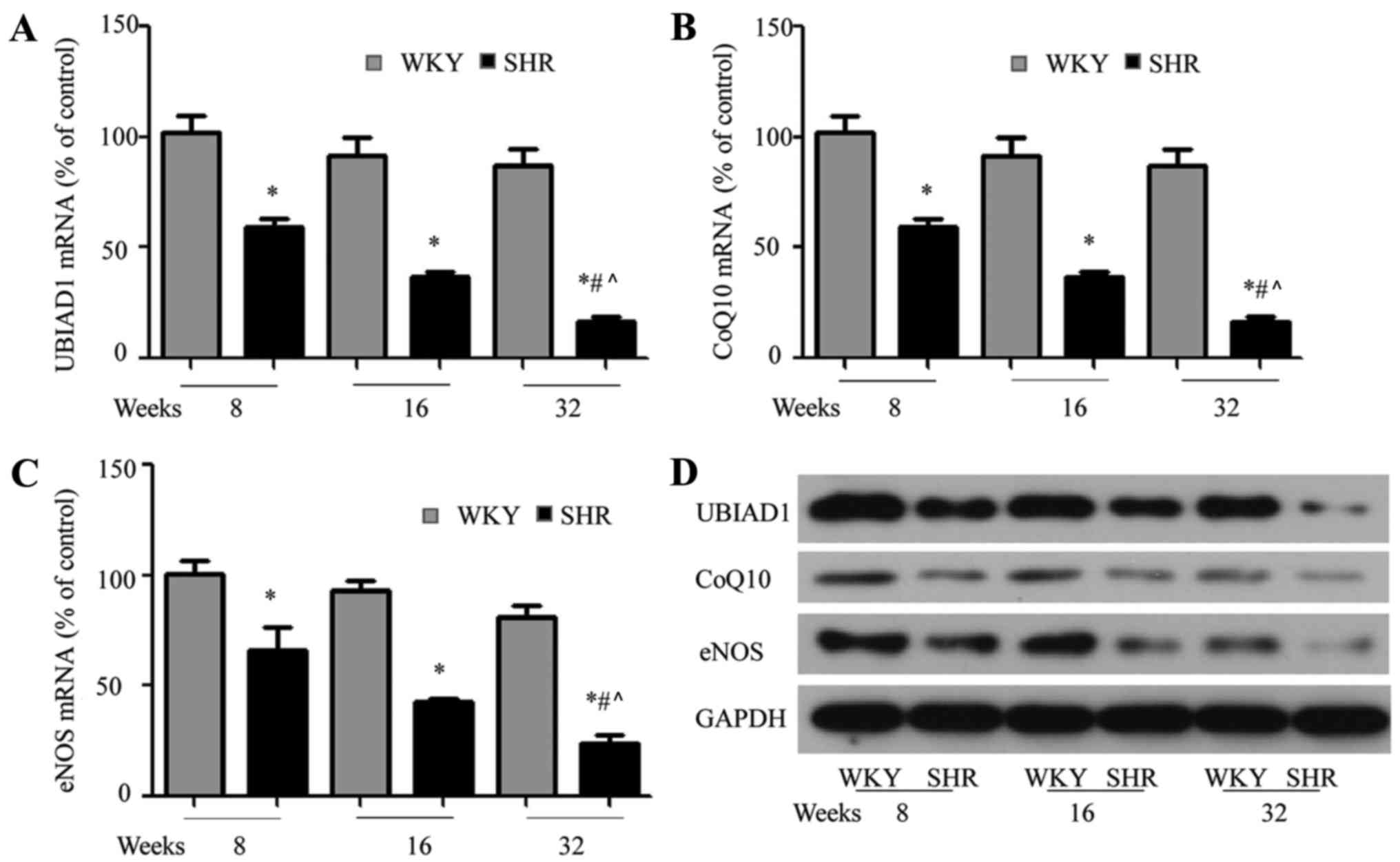
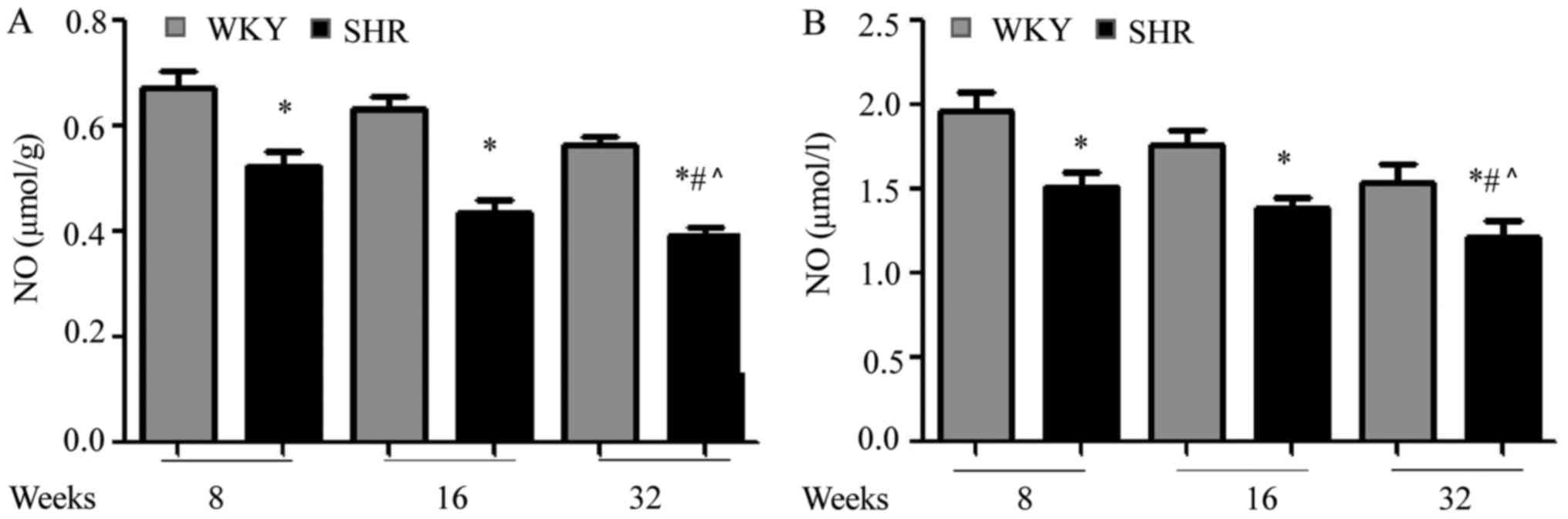
|
1
|
McGarvey TW, Nguyen T, Puthiyaveettil R,
Tomaszewski JE and Malkowicz SB: TERE1, a novel gene
affecting growth regulation in prostate carcinoma. Prostate.
54:144–155. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Orr A, Dubé MP, Marcadier J, Jiang H,
Federico A, George S, Seamone C, Andrews D, Dubord P, Holland S, et
al: Mutations in the UBIAD1 gene, encoding a potential
prenyltransferase, are causal for Schnyder crystalline corneal
dystrophy. PLoS One. 2:e6852007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
McGarvey TW, Nguyen T, Tomaszewski JE,
Monson FC and Malkowicz SB: Isolation and characterization of the
TERE1 gene, a gene down-regulated in transitional cell carcinoma of
the bladder. Oncogene. 20:1042–1051. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Nickerson ML, Kostiha BN, Brandt W,
Fredericks W, Xu KP, Yu FS, Gold B, Chodosh J, Goldberg M, Lu DW,
et al: UBIAD1 mutation alters a mitochondrial
prenyltransferase to cause Schnyder corneal dystrophy. PLoS One.
5:e107602010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mugoni V, Postel R, Catanzaro V, De Luca
E, Turco E, Digilio G, Silengo L, Murphy MP, Medana C, Stainier DY,
et al: Ubiad1 is an antioxidant enzyme that regulates eNOS activity
by CoQ10 synthesis. Cell. 152:504–518. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nakagawa K, Hirota Y, Sawada N, Yuge N,
Watanabe M, Uchino Y, Okuda N, Shimomura Y, Suhara Y and Okano T:
Identification of UBIAD1 as a novel human menaquinone-4
biosynthetic enzyme. Nature. 468:117–121. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hegarty JM, Yang H and Chi NC:
UBIAD1-mediated vitamin K2 synthesis is required for vascular
endothelial cell survival and development. Development.
140:1713–1719. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tousoulis D, Kampoli AM, Tentolouris C,
Papageorgiou N and Stefanadis C: The role of nitric oxide on
endothelial function. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 10:4–18. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Vos M, Esposito G, Edirisinghe JN, Vilain
S, Haddad DM, Slabbaert JR, Van Meensel S, Schaap O, De Strooper B,
Meganathan R, et al: Vitamin K2 is a mitochondrial
electron carrier that rescues pink1 deficiency. Science.
336:1306–1310. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xia Y, Wei X, Wu S, Wang B, Wang X and
Hong L: Down-regulation of TERE1/UBIAD1 activated Ras-MAPK
signalling and induced cell proliferation. Cell Biol Int Rep.
17:e000052010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Zhan CD: The role of nitric oxide in the
prevention of myocardial hypertrophic response and its mechanisms.
Sheng Li Ke Xue Jin Zhan. 31:322–324. 2000.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wollert KC and Drexler H: Regulation of
cardiac remodeling by nitric oxide: Focus on cardiac myocyte
hypertrophy and apoptosis. Heart Fail Rev. 7:317–325. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ozaki M, Kawashima S, Yamashita T, Hirase
T, Ohashi Y, Inoue N, Hirata K and Yokoyama M: Overexpression of
endothelial nitric oxide synthase attenuates cardiac hypertrophy
induced by chronic isoproterenol infusion. Circ J. 66:851–856.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Flaherty MP, Brown M, Grupp IL, Schultz
JE, Murphree SS and Jones WK: eNOS deficient mice develop
progressive cardiac hypertrophy with altered cytokine and calcium
handling protein expression. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 7:165–177. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Brede M, Roell W, Ritter O, Wiesmann F,
Jahns R, Haase A, Fleischmann BK and Hein L: Cardiac hypertrophy is
associated with decreased eNOS expression in angiotensin AT2
receptor-deficient mice. Hypertension. 42:1177–1182. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yan B, Sun Y and Wang J: Depletion of ubiA
prenyltransferase domain containing 1 expression promotes
angiotensin II-induced hypertrophic response in AC16 human
myocardial cells via modulating the expression levels of coenzyme
Q10 and endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Mol Med Rep.
16:6910–6915. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2ΔΔCT method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ridnour LA, Sim JE, Hayward MA, Wink DA,
Martin SM, Buettner GR and Spitz DR: A spectrophotometric method
for the direct detection and quantitation of nitric oxide, nitrite,
and nitrate in cell culture media. Anal Biochem. 281:223–229. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nordborg C and Johansson BB: Morphometric
study on cerebral vessels in spontaneously hypertensive rats.
Stroke. 11:266–270. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Diez J, Panizo A, Hernández M, Vega F,
Sola I, Fortuño MA and Pardo J: Cardiomyocyte apoptosis and cardiac
angiotensin-converting enzyme in spontaneously hypertensive rats.
Hypertension. 30:1029–1034. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Förstermann U and Sessa WC: Nitric oxide
synthases: Regulation and function. Eur Heart J. 33:829–837,
837a-837d. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Nakagawa K, Sawada N, Hirota Y, Uchino Y,
Suhara Y, Hasegawa T, Amizuka N, Okamoto T, Tsugawa N, Kamao M, et
al: Vitamin K2 biosynthetic enzyme, UBIAD1 is essential
for embryonic development of mice. PLoS One. 9:e1040782014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Funahashi N, Hirota Y, Nakagawa K, Sawada
N, Watanabe M, Suhara Y and Okano T: YY1 positively regulates human
UBIAD1 expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 460:238–244. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Beketaev I, Zhang Y, Kim EY, Yu W, Qian L
and Wang J: Critical role of YY1 in cardiac morphogenesis. Dev Dyn.
244:669–680. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Stauffer BL, Dockstader K, Russell G,
Hijmans J, Walker L, Cecil M, Demos-Davies K, Medway A, McKinsey TA
and Sucharov CC: Transgenic over-expression of YY1 induces
pathologic cardiac hypertrophy in a sex-specific manner. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 462:131–137. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sucharov CC, Dockstader K and McKinsey TA:
YY1 protects cardiac myocytes from pathologic hypertrophy by
interacting with HDAC5. Mol Biol Cell. 19:4141–4153. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sucharov CC, Mariner P, Long C, Bristow M
and Leinwand L: Yin Yang 1 is increased in human heart failure and
represses the activity of the human alpha-myosin heavy chain
promoter. J Biol Chem. 278:31233–31239. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kumar A, Kaur H, Devi P and Mohan V: Role
of coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) in cardiac disease, hypertension and
Meniere-like syndrome. Pharmacol Ther. 124:259–268. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Muraro PA, Vergelli M, Kalbus M, Banks DE,
Nagle JW, Tranquill LR, Nepom GT, Biddison WE, McFarland HF and
Martin R: Immunodominance of a low-affinity major
histocompatibility complex-binding myelin basic protein epitope
(residues 111-129) in HLA-DR4 (B1*0401) subjects is associated with
a restricted T cell receptor repertoire. J Clin Invest.
100:339–349. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ghule AE, Kulkarni CP, Bodhankar SL and
Pandit VA: Effect of pretreatment with coenzyme Q10 on
isoproterenol-induced cardiotoxicity and cardiac hypertrophy in
rats. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 70:460–471. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Fotino AD, Thompson-Paul AM and Bazzano
LA: Effect of coenzyme Q10 supplementation on heart
failure: A meta-analysis. Am J Clin Nutr. 97:268–275. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sharma A, Fonarow GC, Butler J, Ezekowitz
JA and Felker GM: Coenzyme Q10 and heart failure: A
state-of-the-art review. Circ Heart Fail. 9:e0026392016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chew GT and Watts GF: Coenzyme Q10 and
diabetic endotheliopathy: Oxidative stress and the ‘recoupling
hypothesis’. QJM. 97:537–548. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tsai KL, Huang YH, Kao CL, Yang DM, Lee
HC, Chou HY, Chen YC, Chiou GY, Chen LH, Yang YP, et al: A novel
mechanism of coenzyme Q10 protects against human endothelial cells
from oxidative stress-induced injury by modulating NO-related
pathways. J Nutr Biochem. 23:458–468. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Forstermann U and Münzel T: Endothelial
nitric oxide synthase in vascular disease: From marvel to menace.
Circulation. 113:1708–1714. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Bian K, Doursout MF and Murad F: Vascular
system: Role of nitric oxide in cardiovascular diseases. J Clin
Hypertens. 10:304–310. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Kang JH, Wiggs JL, Rosner BA, Haines J,
Abdrabou W and Pasquale LR: Endothelial nitric oxide synthase gene
variants and primary open-angle glaucoma: Interactions with
hypertension, alcohol intake and cigarette smoking. Arch
Ophthalmol. 129:773–780. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Li Q, Youn JY and Cai H: Mechanisms and
consequences of endothelial nitric oxide synthase dysfunction in
hypertension. J Hypertens. 33:1128–1136. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wang X, Wang D, Jing P, Wu Y, Xia Y, Chen
M and Hong L: A novel Golgi retention signal RPWS for tumor
suppressor UBIAD1. PLoS One. 8:e720152013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Fredericks WJ, McGarvey T, Wang H, Lal P,
Puthiyaveettil R, Tomaszewski J, Sepulveda J, Labelle E, Weiss JS,
Nickerson ML, et al: The bladder tumor suppressor protein TERE1
(UBIAD1) modulates cell cholesterol: Implications for tumor
progression. DNA Cell Biol. 30:851–864. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|