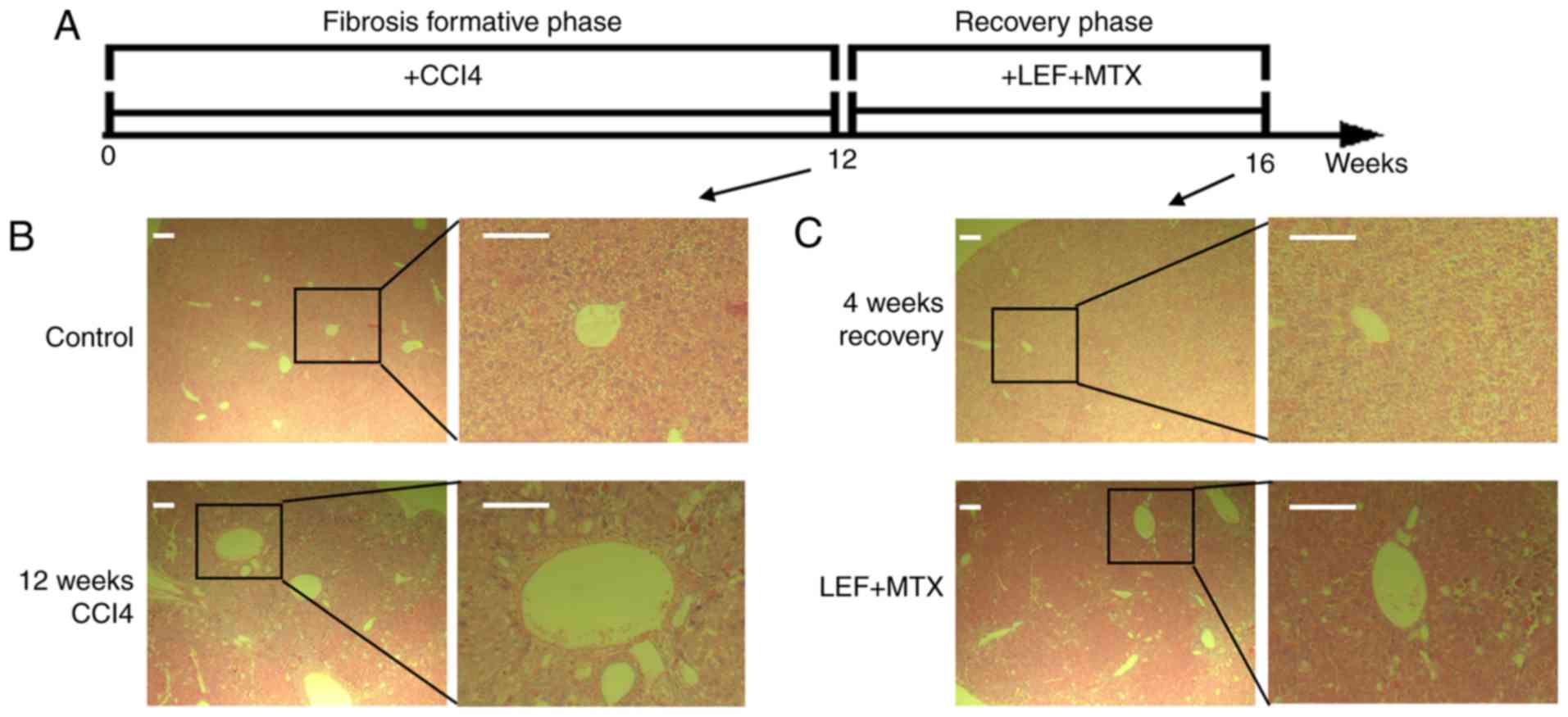
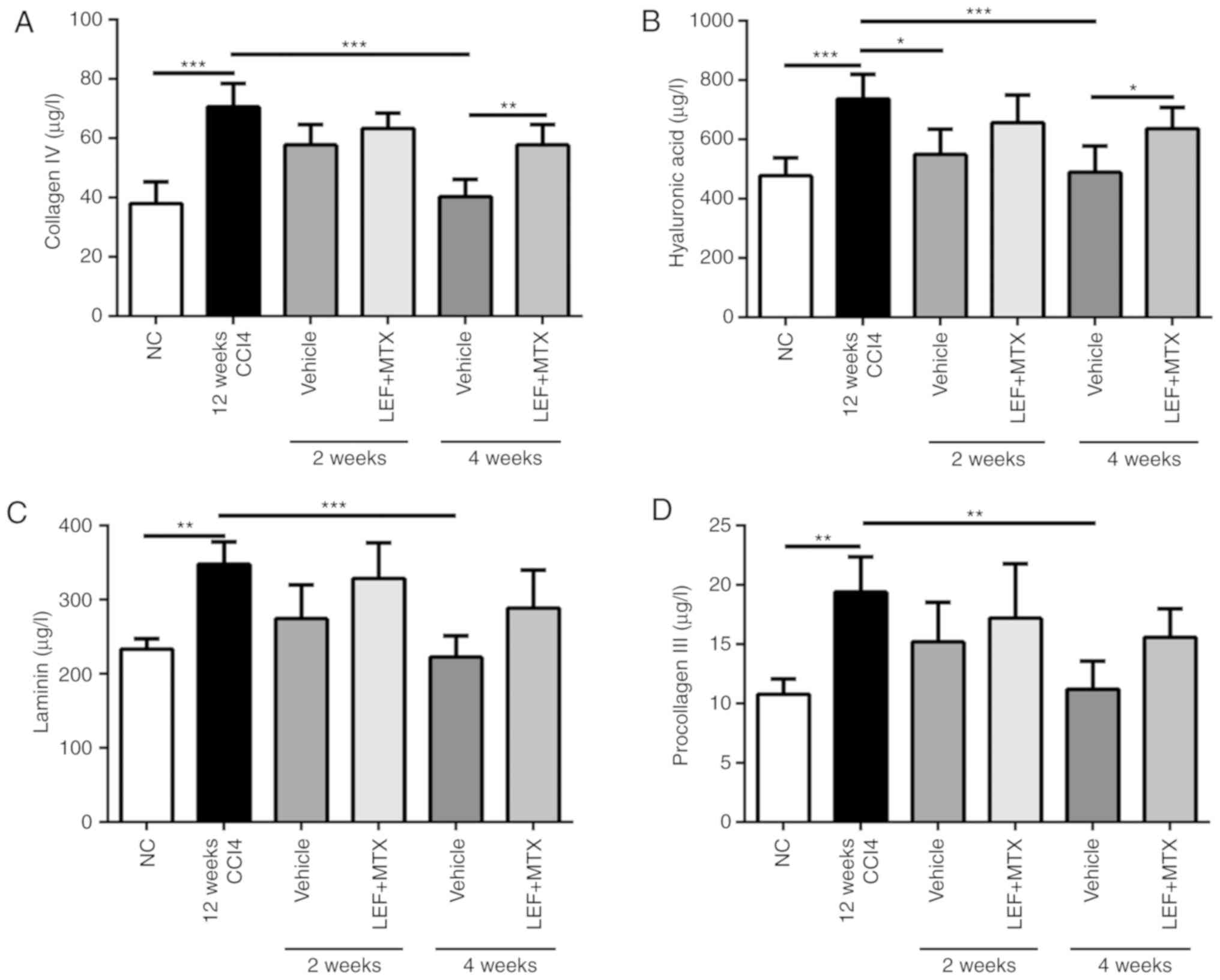
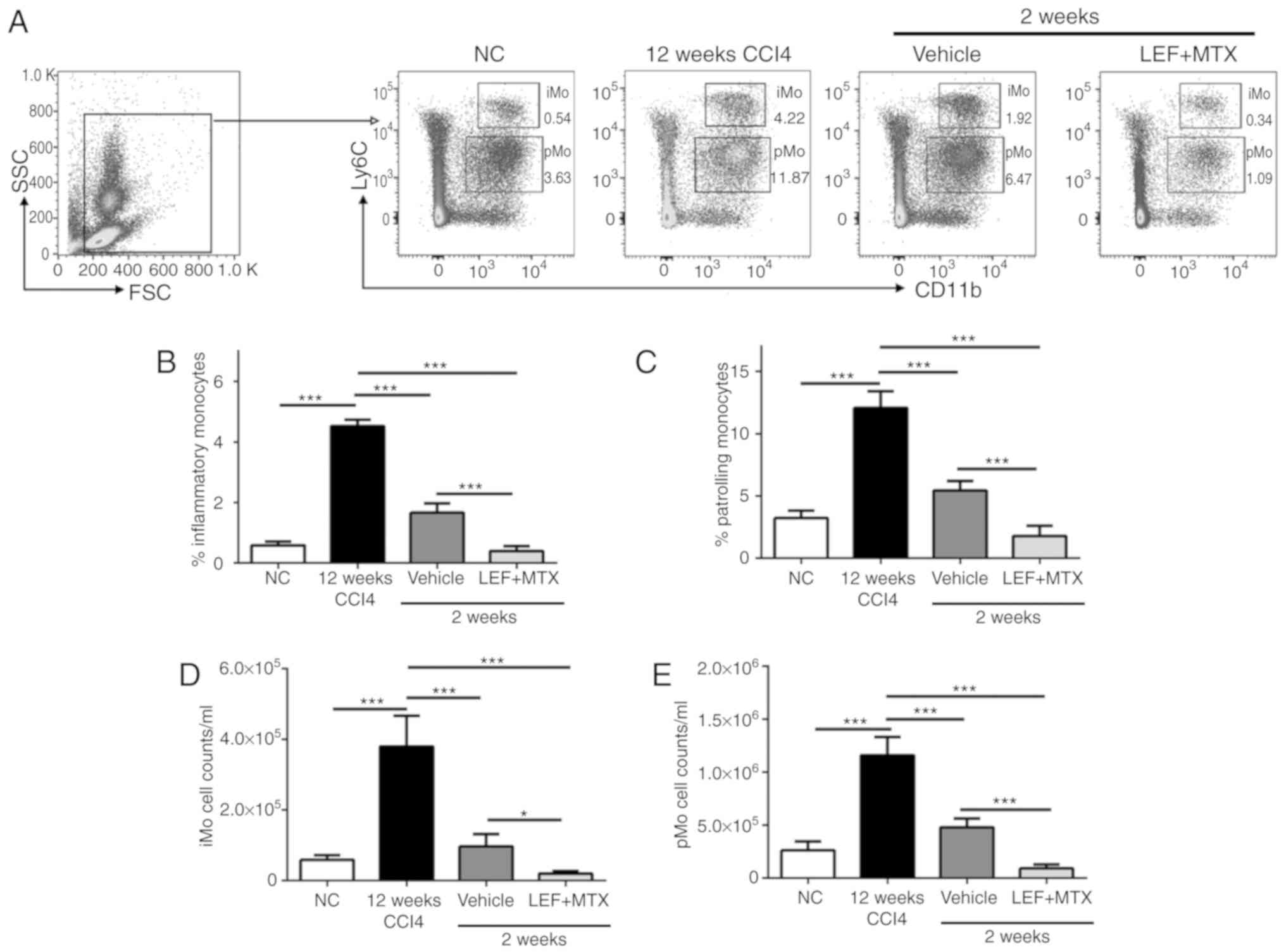
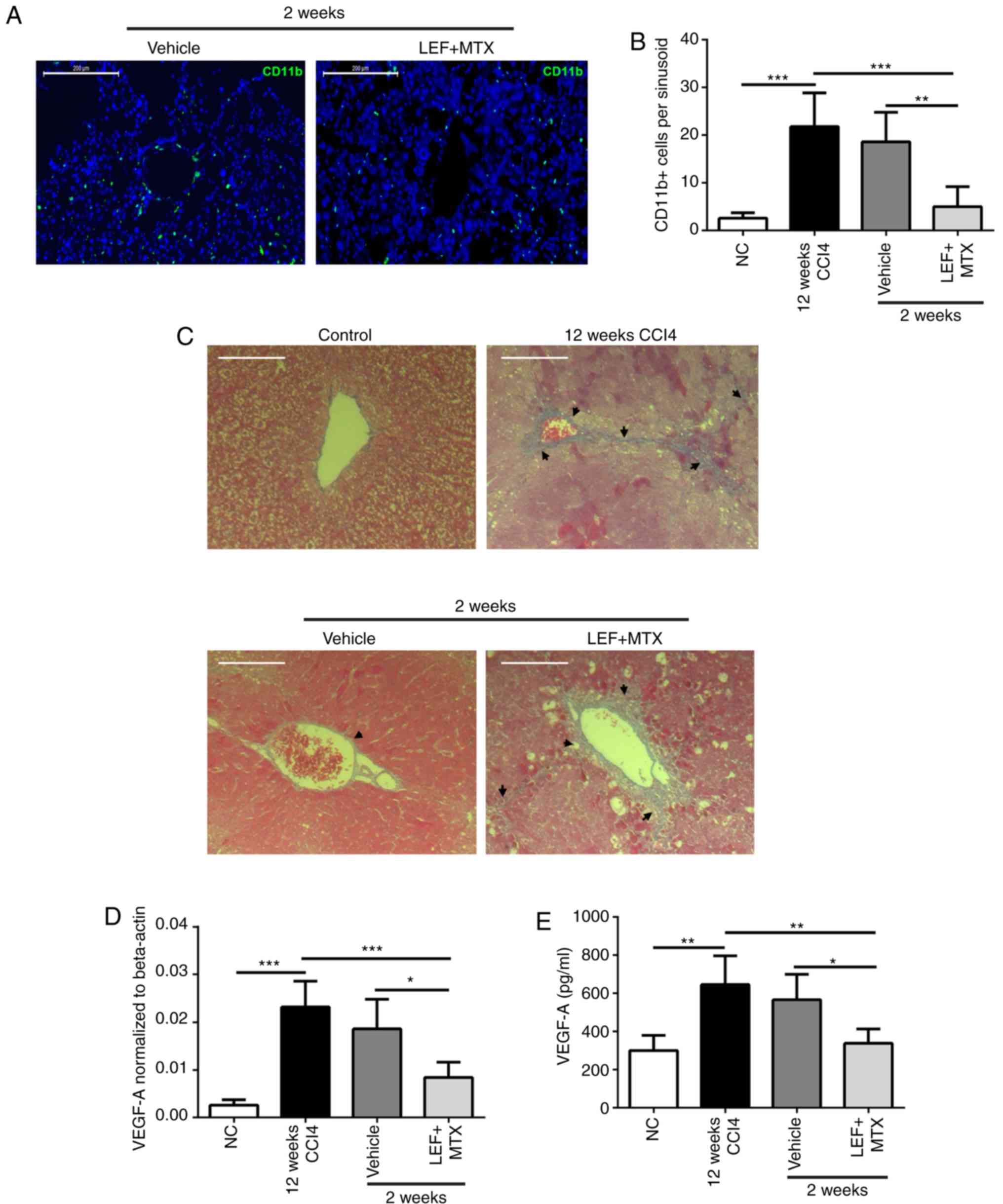
|
1
|
Patten DA and Shetty S: Chronic liver
disease: Scavenger hunt for novel therapies. Lancet. 391:104–105.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tsuchida T and Friedman SL: Mechanisms of
hepatic stellate cell activation. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol.
14:397–411. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Pellicoro A, Ramachandran P, Iredale JP
and Fallowfield JA: Liver fibrosis and repair: Immune regulation of
wound healing in a solid organ. Nat Rev Immunol. 14:181–194. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Janssen NM and Genta MS: The effects of
immunosuppressive and anti-inflammatory medications on fertility,
pregnancy, and lactation. Arch Intern Med. 160:610–619. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Dougados M, Emery P, Lemmel EM, Zerbini
CA, Brin S and van Riel P: When a DMARD fails, should patients
switch to sulfasalazine or add sulfasalazine to continuing
leflunomide? Ann Rheum Dis. 64:44–51. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wessels JA, Huizinga TW and Guchelaar HJ:
Recent insights in the pharmacological actions of methotrexate in
the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford).
47:249–255. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Rozman B: Clinical pharmacokinetics of
leflunomide. Clin Pharmacokinet. 41:421–430. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lee SW, Park HJ, Kim BK, Han KH, Lee SK,
Kim SU and Park YB: Leflunomide increases the risk of silent liver
fibrosis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis receiving
methotrexate. Arthritis Res Ther. 14:R2322012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ferri C, Sebastiani M, Antonelli A, Colaci
M, Manfredi A and Giuggioli D: Current treatment of hepatitis
C-associated rheumatic diseases. Arthritis Res Ther. 14:2152012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kantari-Mimoun C, Castells M, Klose R,
Meinecke AK, Lemberger UJ, Rautou PE, Pinot-Roussel H, Badoual C,
Schrödter K, Österreicher CH, et al: Resolution of liver fibrosis
requires myeloid cell-driven sinusoidal angiogenesis. Hepatology.
61:2042–2055. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Duffield JS, Forbes SJ, Constandinou CM,
Clay S, Partolina M, Vuthoori S, Wu S, Lang R and Iredale JP:
Selective depletion of macrophages reveals distinct, opposing roles
during liver injury and repair. J Clin Invest. 115:56–65. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kilkenny C, Browne W, Cuthill IC, Emerson
M and Altman DG; National Centre for the Replacement, Refinement
and Reduction of Amimals in Research, : Animal research: Reporting
in vivo experiments-the ARRIVE guidelines. J Cereb Blood Flow
Metab. 31:991–993. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fontana RJ, Dienstag JL, Bonkovsky HL,
Sterling RK, Naishadham D, Goodman ZD, Lok AS, Wright EC and Su GL;
HALT-C Trial Group, : Serum fibrosis markers are associated with
liver disease progression in non-responder patients with chronic
hepatitis C. Gut. 59:1401–1409. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yao HW, Li J, Chen JQ and Xu SY:
Inhibitory effect of leflunomide on hepatic fibrosis induced by
CCl4 in rats. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 25:915–920. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tang X, Yang J and Li J: Accelerative
effect of leflunomide on recovery from hepatic fibrosis involves
TRAIL-mediated hepatic stellate cell apoptosis. Life Sci.
84:552–557. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bjorkman DJ, Boschert M, Tolman KG, Clegg
DO and Ward JR: The effect of long-term methotrexate therapy on
hepatic fibrosis in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum.
36:1697–1701. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bilasy SE, Essawy SS, Mandour MF, Ali EA
and Zaitone SA: Myelosuppressive and hepatotoxic potential of
leflunomide and methotrexate combination in a rat model of
rheumatoid arthritis. Pharmacol Rep. 67:102–114. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Landsman L, Varol C and Jung S: Distinct
differentiation potential of blood monocyte subsets in the lung. J
Immunol. 178:2000–2007. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Nahrendorf M, Swirski FK, Aikawa E,
Stangenberg L, Wurdinger T, Figueiredo JL, Libby P, Weissleder R
and Pittet MJ: The healing myocardium sequentially mobilizes two
monocyte subsets with divergent and complementary functions. J Exp
Med. 204:3037–3047. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang L, Ma L, Lin Y, Liu X, Xiao L, Zhang
Y, Xu Y, Zhou H and Pan G: Leflunomide increases hepatic exposure
to methotrexate and its metabolite by differentially regulating
multidrug resistance-associated protein Mrp2/3/4 transporters via
peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α activation. Mol
Pharmacol. 93:563–574. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|