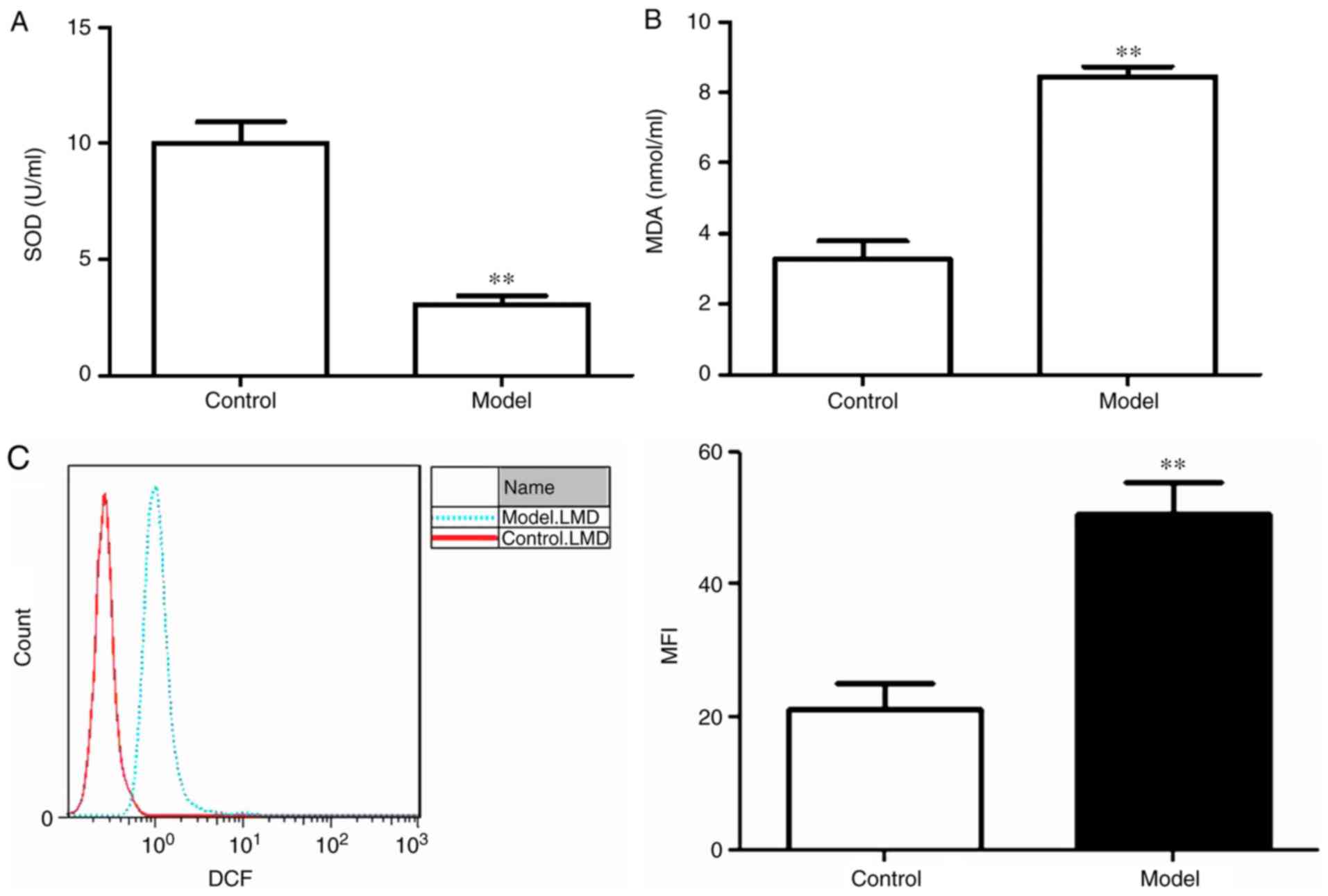
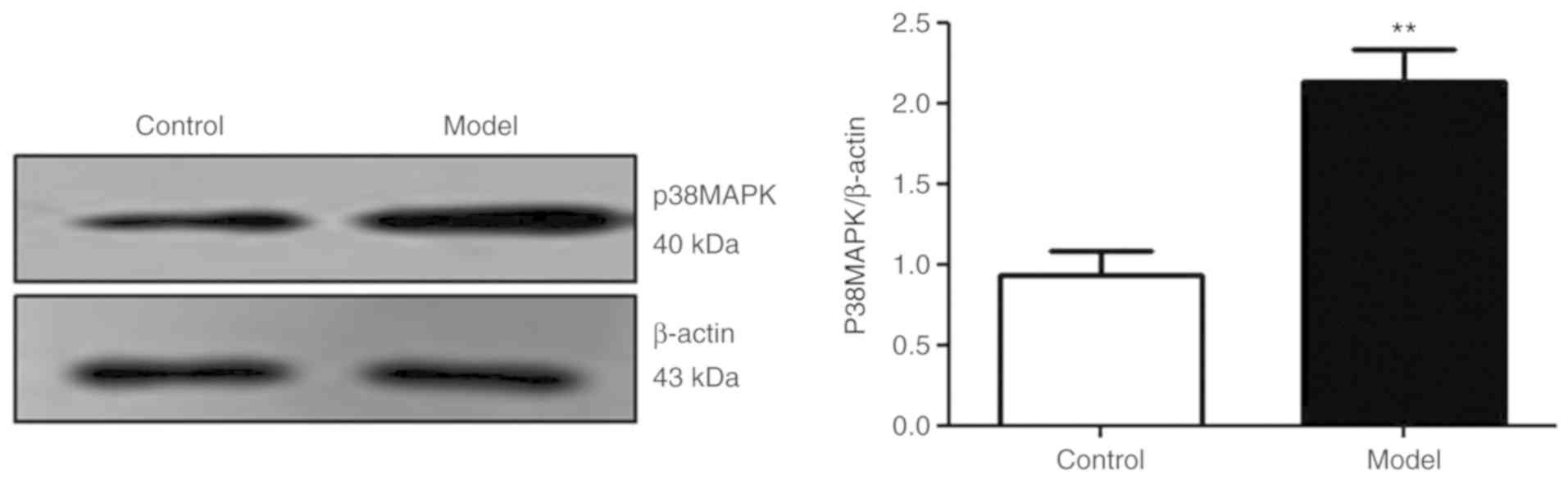
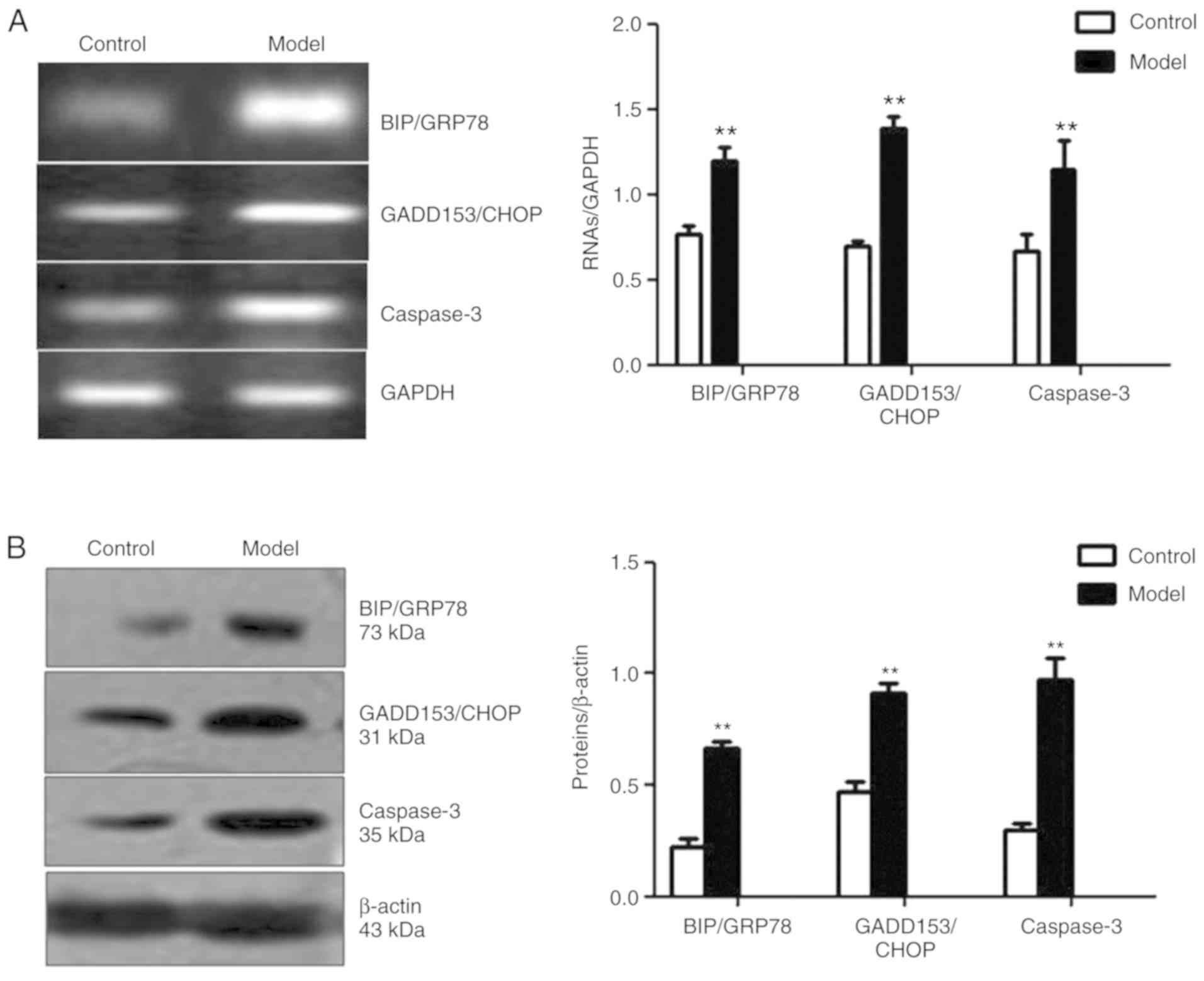
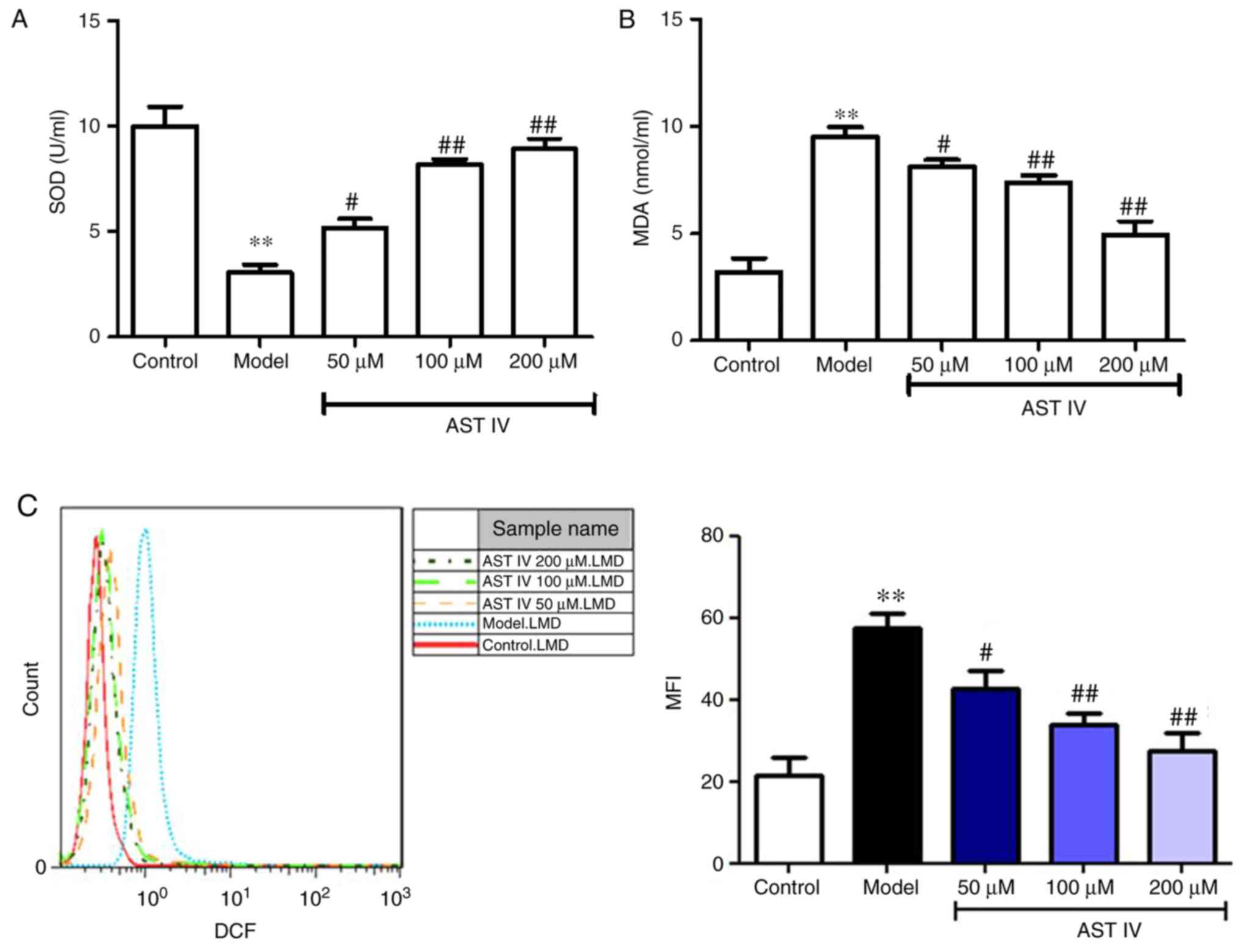
|
1
|
Ide K, Matsuoka N and Kawakami K: Is the
use of proton-pump inhibitors a risk factor for Alzheimer's
disease? Molecular mechanisms and clinical implications. Curr Med
Chem. 25:2166–2174. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lista S, Khachaturian ZS, Rujescu D,
Garaci F, Dubois B and Hampel H: Application of systems theory in
longitudinal studies on the origin and progression of Alzheimer's
disease. Methods Mol Biol 1303. 49–67. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Ellis B, Hye A and Snowden SG: Metabolic
modifications in human biofluids suggest the involvement of
sphingolipid, antioxidant, and glutamate metabolism in Alzheimer's
disease pathogenesis. J Alzheimers Dis. 46:313–327. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Liu H, Zhang X, Zhang S, Huang H, Wu J,
Wang Y, Yuan L, Liu C, Zeng X, Cheng X, et al: Oxidative stress
mediates microcystin-LR-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress and
autophagy in KK-1 cells and C57BL/6 mice ovaries. Front Physiol.
9:10582018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Adzic M, Mitic M and Radojcic M:
Mitochondrial estrogen receptors as a vulnerability factor of
chronic stress and mediator of fluoxetine treatment in female and
male rat hippocampus. Brain Res 1671. 77–84. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Chen W, Chan Y, Wan W, Li Y and Zhang C:
Aβ1-42 induces cell damage via RAGE-dependent
endoplasmic reticulum stress in bEnd.3 cells. Exp Cell Res.
362:83–89. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fraga FJ, Mamani GQ, Johns E, Tavares G,
Falk TH and Phillips NA: Early diagnosis of mild cognitive
impairment and Alzheimer's with event-related potentials and
event-related desynchronization in N-back working memory tasks.
Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 164:1–13. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Song X, Liu B, Cui L, Zhou B, Liu L, Liu
W, Yao G, Xia M, Hayashi T, Hattori S, et al: Estrogen receptors
are involved in the neuroprotective effect of silibinin in
Aβ1-42-treated rats. Neurochem Res. 43:796–805. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kheiri G, Dolatshahi M, Rahmani F and
Rezaei N: Role of p38/MAPKs in Alzheimer's disease: Implications
for amyloid beta toxicity targeted therapy. Rev Neurosci. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li J, Ma X, Wang Y, Chen C, Hu M, Wang L,
Fu J, Shi G, Zhang D and Zhang T: Methyl salicylate lactoside
protects neurons ameliorating cognitive disorder through inhibiting
amyloid beta-induced neuroinflammatory response in Alzheimer's
disease. Front Aging Neurosci. 10:852018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Melone MAB, Dato C, Paladino S, Coppola C,
Trebini C, Giordana MT and Perrone L: Verapamil inhibits
Ser202/Thr205 phosphorylation of Tau by blocking TXNIP/ROS/p38 MAPK
pathway. Pharm Res. 35:442018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wong BL, Rybalsky I, Shellenbarger KC,
Tian C, McMahon MA, Rutter MM, Sawnani H and Jefferies JL:
Long-term outcome of interdisciplinary management of patients with
duchenne muscular dystrophy receiving daily glucocorticoid
treatment. J Pediatr. 182:296–303.e1. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Shen H, Pan XD, Zhang J, Zeng YQ, Zhou M,
Yang LM, Ye B, Dai XM, Zhu YG and Chen XC: Endoplasmic reticulum
stress induces the early appearance of pro-apoptotic and
anti-apoptotic proteins in neurons of five familial Alzheimer's
disease mice. Chin Med J (Engl). 129:2845–2852. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kobylewski SE, Henderson KA, Yamada KE and
Eckhert CD: Activation of the EIF2α/ATF4 and ATF6 pathways in
DU-145 cells by boric acid at the concentration reported in men at
the US mean boron intake. Biol Trace Elem Res. 176:278–293. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu XJ, Wei J, Shang YH, Huang HC and Lao
FX: Modulation of AβPP and GSK3β by endoplasmic reticulum stress
and involvement in Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers Dis.
57:1157–1170. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lan YL, Zhao J and Li S: Update on the
neuroprotective effect of estrogen receptor alpha against
Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 43:1137–1148. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wei H, Gao Z, Zheng L, Zhang C, Liu Z,
Yang Y, Teng H, Hou L, Yin Y and Zou X: Protective effects of
fucoidan on Aβ25-35 and d-Gal-induced neurotoxicity in PC12 cells
and d-Gal-induced cognitive dysfunction in mice. Mar Drugs.
15:E772017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Xu P, Wang H, Li Z and Yang Z: Triptolide
attenuated injury via inhibiting oxidative stress in
Amyloid-Beta25-35-treated differentiated PC12 cells. Life Sci.
145:19–26. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang J, Wu J, Zeng W, Zhao Y and Zu H:
Exendin-4, a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist, inhibits
Aβ25-35-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells by suppressing the
expression of endoplasmic reticulum stress-related proteins. Int J
Clin Exp Pathol. 8:12784–12792. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Basseri S and Austin RC: Endoplasmic
reticulum stress and lipid metabolism: Mechanisms and therapeutic
potential. Biochem Res Int 2012. 8413622012.
|
|
21
|
E L, Cheng Y and Zhao X: Protective
effects of high-density lipoprotein on mice cardiomyocytes induced
by oxygen and glucose deprivation through Akt signaling pathway.
Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 30:795–799. 2018.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen M, Liu Q, Chen L, Zhang L and Gu E:
Remifentanil postconditioning ameliorates histone H3 acetylation
modification in H9c2 cardiomyoblasts after hypoxia/reoxygenation
via attenuating endoplasmic reticulum stress. Apoptosis.
22:662–671. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yang Q, Gao H, Dong R and Wu YQ:
Sequential changes of endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis in
myocardial fibrosis of diabetes mellitus-induced rats. Mol Med Rep.
13:5037–5044. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sánchez-Rodríguez C, Cuadrado E,
Riestra-Ayora J and Sanz-Fernández R: Polyphenols protect against
age-associated apoptosis in female rat cochleae. Biogerontology.
19:159–169. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jian CY, Ouyang HB, Xiang XH, Chen JL, Li
YX, Zhou X, Wang JY, Yang Y, Zhong EY, Huang WH and Zhang HW:
Naringin protects myocardial cells from doxorubicininduced
apoptosis partially by inhibiting the p38MAPK pathway. Mol Med Rep.
16:9457–9463. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhou Y, Wang ZF, Li W, Hong H, Chen J,
Tian Y and Liu ZY: Protective effects of microRNA-330 on amyloid
β-protein production, oxidative stress, and mitochondrial
dysfunction in Alzheimer's disease by targeting VAV1 via the MAPK
signaling pathway. J Cell Biochem. 119:5437–5448. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Guo J, Chang L, Li C, Li M, Yan P, Guo Z,
Wang C, Zha Q and Wang Q: SB203580 reverses memory deficits and
depression-like behavior induced by microinjection of
Aβ1-42 into hippocampus of mice. Metab Brain Dis.
32:57–68. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Werner E, Wang H and Doetsch PW: Opposite
roles for p38MAPK-driven responses and reactive oxygen species in
the persistence and resolution of radiation-induced genomic
instability. PLoS One. 9:e1082342014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yang G, Yang W, Wu L and Wang R: H2S,
endoplasmic reticulum stress, and apoptosis of insulin-secreting
beta cells. J Biol Chem. 282:16567–16576. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Park JY, Kim EJ, Kwon KJ, Jung YS, Moon
CH, Lee SH and Baik EJ: Neuroprotection by
fructose-1,6-bisphosphate involves ROS alterations via p38
MAPK/ERK. Brain Res 1026. 295–301. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Sun Y, Xun L, Jin G and Shi L: Salidroside
protects renal tubular epithelial cells from hypoxia/reoxygenation
injury in vitro. J Pharmacol Sci. 137:170–176. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Pinceti E, Shults CL, Rao YS and Pak TR:
Differential effects of E2 on MAPK activity in the brain and heart
of aged female rats. PLoS One. 11:e01602762016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|