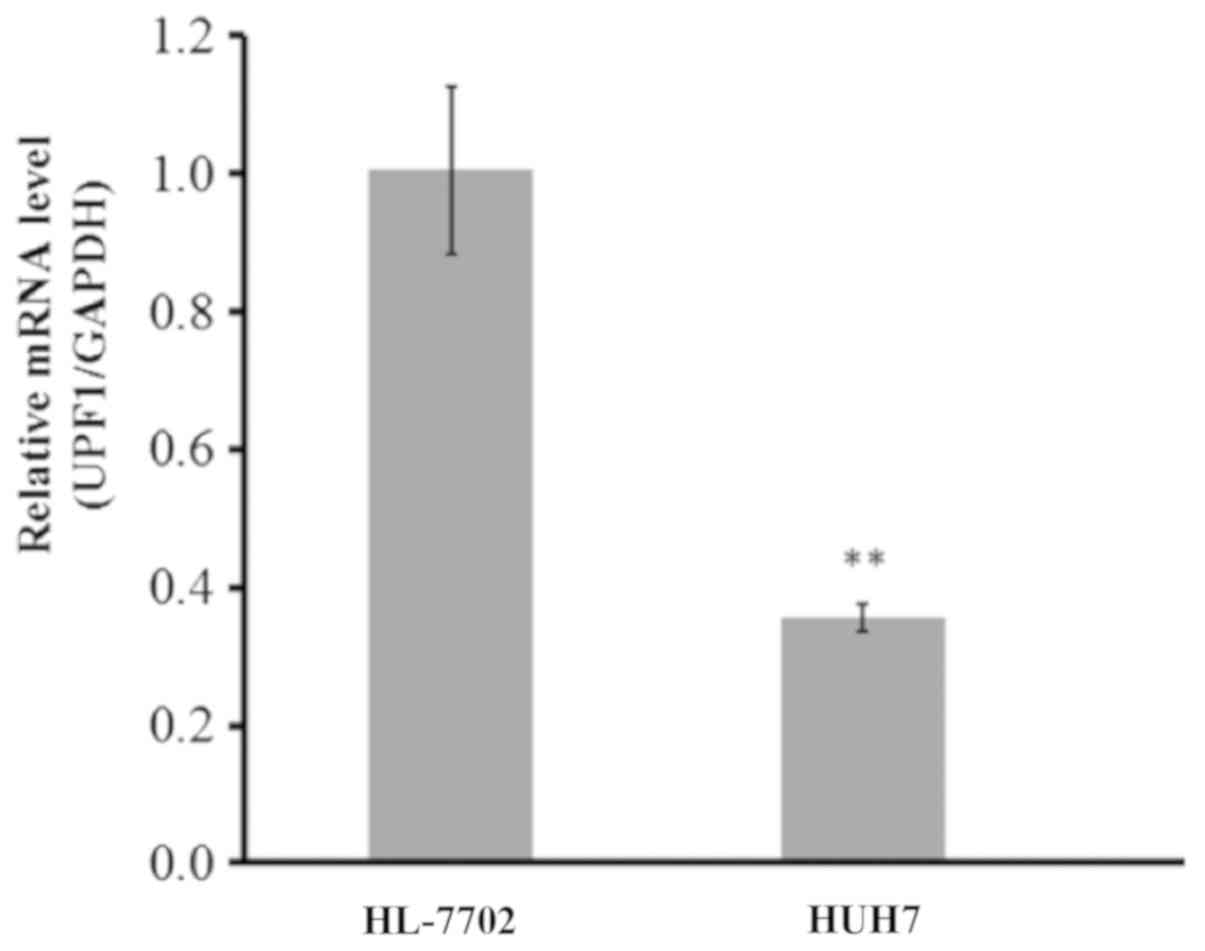
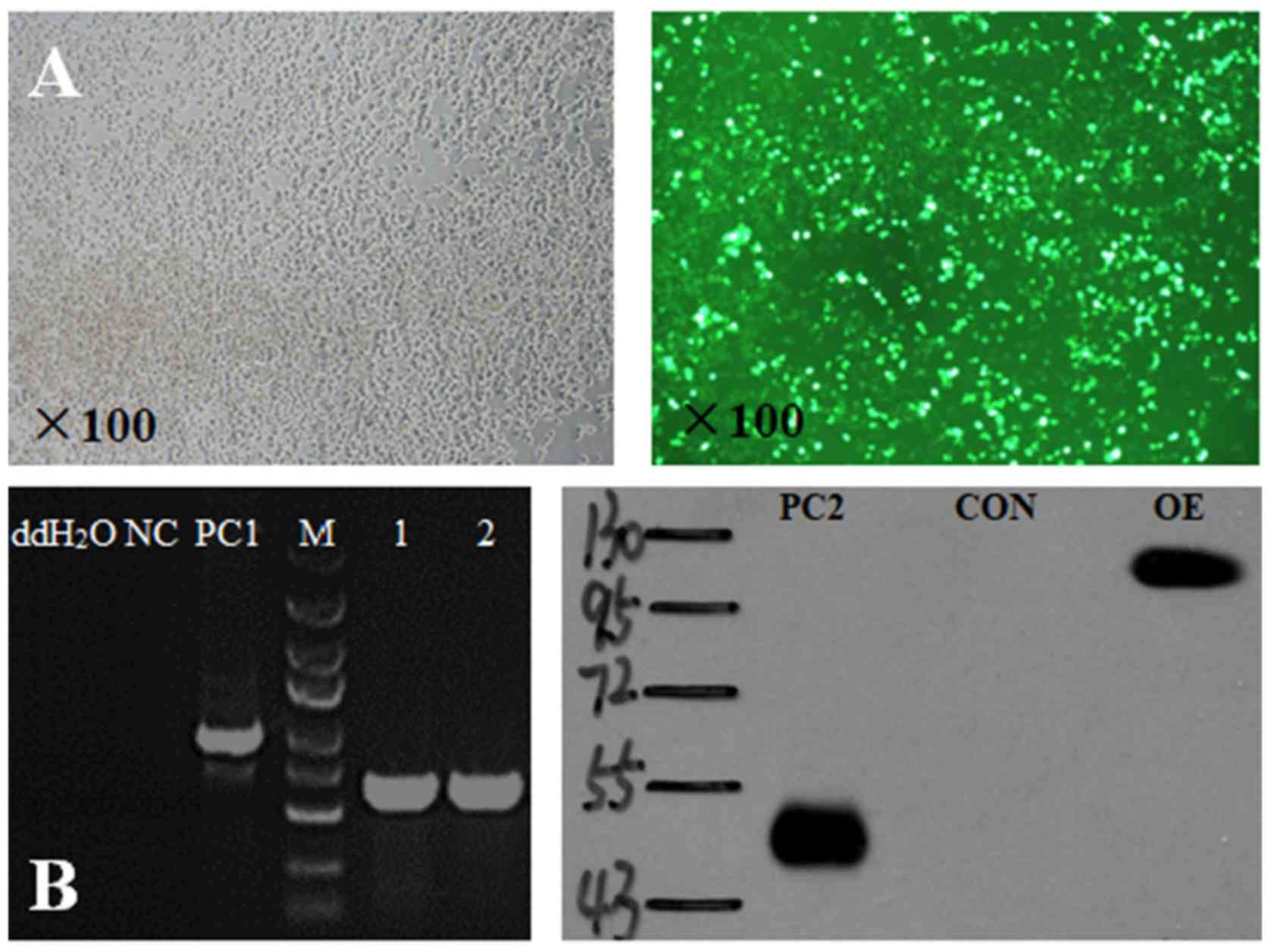
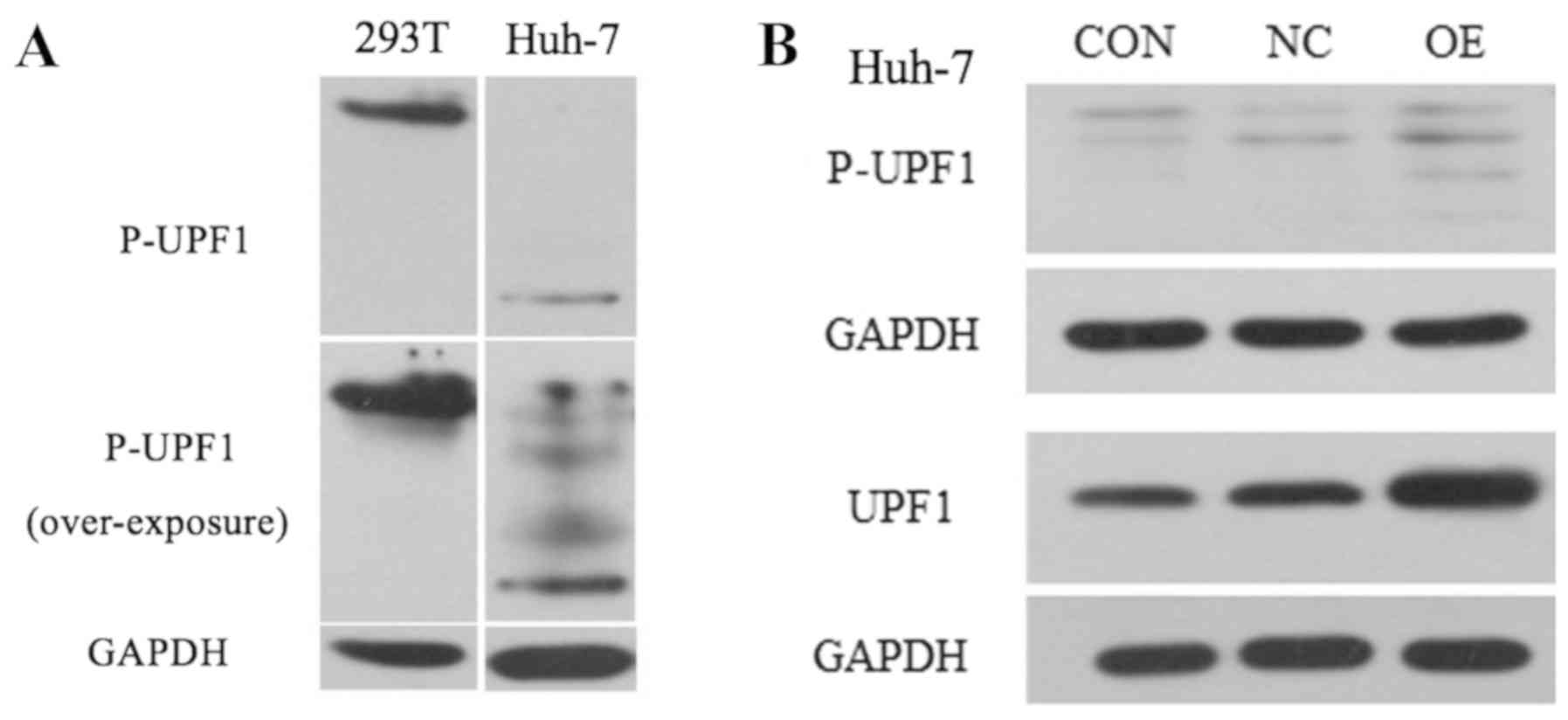
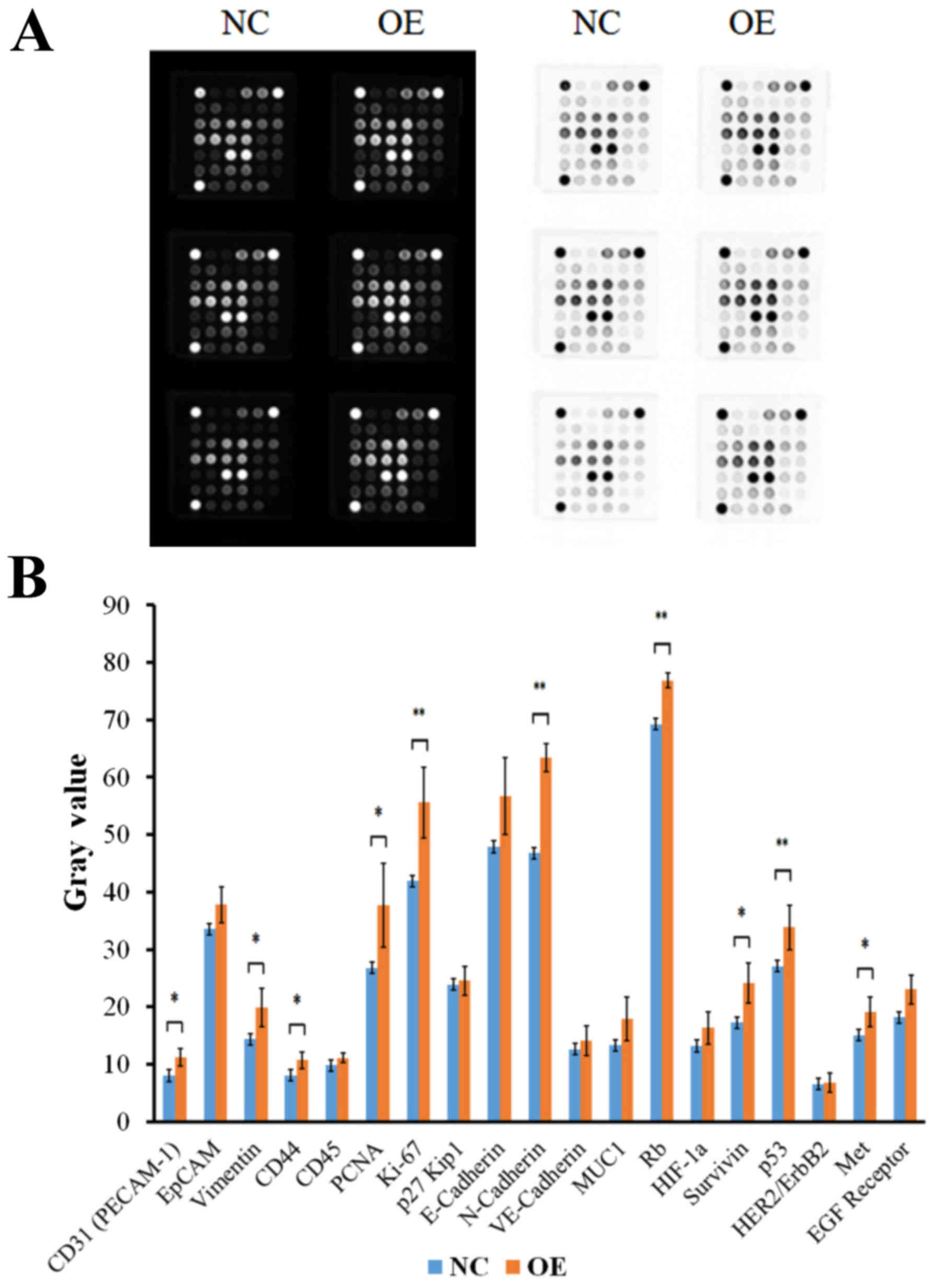
|
1
|
Klingenberg M, Matsuda A, Diederichs S and
Patel T: Non-coding RNA in hepatocellular carcinoma: Mechanisms,
biomarkers and therapeutic targets. J Hepatol. 67:603–618. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gong C, Fang J, Li G, Liu HH and Liu ZS:
Effects of microRNA-126 on cell proliferation, apoptosis and tumor
angiogenesis via the down-regulating ERK signaling pathway by
targeting EGFL7 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget.
8:52527–52542. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer Statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kuo TC, Chen CK, Hua KT, Yu P, Lee WJ,
Chen MW, Jeng YM, Chien MH, Kuo KT, Hsiao M and Kuo ML: Glutaminase
2 stabilizes Dicer to repress Snail and metastasis in
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett. 383:282–294. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Luo W, Zhu X, Liu W, Ren Y, Bei C, Qin L,
Miao X, Tang F, Tang G and Tan S: MYC associated zinc finger
protein promotes the invasion and metastasis of hepatocellular
carcinoma by inducing epithelial mesenchymal transition.
Oncotarget. 7:86420–86432. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yoshinaga T, Uwabe K, Naito S, Higashino
K, Nakano T, Numata Y and Kihara A: AM251 suppresses
epithelial-mesenchymal transition of renal tubular epithelial
cells. PLoS One. 11:e01678482016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kim CW, Hwang KA and Choi KC:
Anti-metastatic potential of resveratrol and its metabolites by the
inhibition of epithelial-mesenchymal transition, migration, and
invasion of malignant cancer cells. Phytomedicine. 23:1787–1796.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Azzalin CM and Lingner J: The human RNA
surveillance factor UPF1 is required for S phase progression and
genome stability. Curr Biol. 16:433–439. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lou CH, Shao A, Shum EY, Espinoza JL,
Huang L, Karam R and Wilkinson MF: Posttranscriptional control of
the stem cell and neurogenic programs by the nonsense-mediated RNA
decay pathway. Cell Rep. 6:748–764. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liu C, Karam R, Zhou Y, Su F, Ji Y, Li G,
Xu G, Lu L, Wang C, Song M, et al: The UPF1 RNA surveillance gene
is commonly mutated in pancreatic adenosquamous carcinoma. Nat Med.
20:596–598. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Carr MI, Roderick JE, Gannon HS, Kelliher
MA and Jones SN: Mdm2 phosphorylation regulates its stability and
has contrasting effects on oncogene and radiation-induced
tumorigenesis. Cell Rep. 16:2618–2629. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Takada M, Zhang W, Suzuki A, Kuroda TS, Yu
Z, Inuzuka H, Gao D, Wan L, Zhuang M, Hu L, et al: FBW7 loss
promotes chromosomal instability and tumorigenesis via cyclin
E1/CDK2-mediated phosphorylation of CENP-A. Cancer Res.
77:4881–4893. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ma F, Li W, Liu C, Li W, Yu H, Lei B, Ren
Y, Li Z, Pang D and Qian C: MiR-23a promotes TGF-β1-induced EMT and
tumor metastasis in breast cancer cells by directly targeting CDH1
and activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Oncotarget. 8:69538–69550.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Natsuizaka M, Whelan KA, Kagawa S, Tanaka
K, Giroux V, Chandramouleeswaran PM, Long A, Sahu V, Darling DS,
Que J, et al: Interplay between Notch1 and Notch3 promotes EMT and
tumor initiation in squamous cell carcinoma. Nat Commun.
8:17582017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Solomon H, Brosh R, Buganim Y and Rotter
V: Inactivation of the p53 tumor suppressor gene and activation of
the Ras oncogene: Cooperative events in tumorigenesis. Discov Med.
9:448–454. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Rivlin N, Brosh R, Oren M and Rotter V:
Mutations in the p53 tumor suppressor gene: Important milestones at
the various steps of tumorigenesis. Gene Cancer. 2:466–474. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Venook AP, Papandreou C, Furuse J and de
Guevara LL: The incidence and epidemiology of hepatocellular
carcinoma: A global and regional perspective. Oncologist. 15 Suppl
4:5–13. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jin H, Li Q, Cao F, Wang SN, Wang RT, Wang
Y, Tan QY, Li CR, Zou H, Wang D and Xu CX: miR-124 inhibits lung
tumorigenesis induced by K-ras mutation and NNK. Mol Ther Nucleic
Acids. 9:145–154. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Furic L, Rong L, Larsson O, Koumakpayi IH,
Yoshida K, Brueschke A, Petroulakis E, Robichaud N, Pollak M,
Gaboury LA, et al: eIF4E phosphorylation promotes tumorigenesis and
is associated with prostate cancer progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 107:14134–14139. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang X, Qiao Y, Wu Q, Chen Y, Zou S, Liu
X, Zhu G, Zhao Y, Chen Y, Yu Y, et al: The essential role of YAP
O-GlcNAcylation in high-glucose-stimulated liver tumorigenesis. Nat
Commun. 8:152802017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chang L, Li C, Guo T, Wang H, Ma W, Yuan
Y, Liu Q, Ye Q and Liu Z: The human RNA surveillance factor UPF1
regulates tumorigenesis by targeting Smad7 in hepatocellular
carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 35:82016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Darini C, Wang S, Krishnamoorthy J and
Koromilas A: Translation initiation factor eIF2 serine 51
phosphorylation suppresses HER2-mediated tumorigenesis and
increases sensitivity of HER2+ breast cancer to
trastuzumab therapy. Mol Cancer Res. 16:82–83. 2018.
|
|
24
|
Zhang Y, Yu G, Chu H, Wang X, Xiong L, Cai
G, Liu R, Gao H, Tao B, Li W, et al: Macrophage-associated PGK1
phosphorylation promotes aerobic glycolysis and tumorigenesis. Mol
Cell. 71:201–215.e7. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Han T, Zhan W, Gan M, Liu F, Yu B, Chin YE
and Wang JB: Phosphorylation of glutaminase by PKCε is essential
for its enzymatic activity and critically contributes to
tumorigenesis. Cell Res. 28:655–669. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Dai X, Ahn KS, Wang LZ, Kim C,
Deivasigamni A, Arfuso F, Um JY, Kumar AP, Chang YC, Kumar D, et
al: Ascochlorin enhances the sensitivity of doxorubicin leading to
the reversal of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cancer Ther. 15:2966–2976. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang WN, Li W, Wang XL, Hu Z, Zhu D, Ding
WC, Liu D, Li KZ, Ma D and Wang H: CLDN1 expression in cervical
cancer cells is related to tumor invasion and metastasis.
Oncotarget. 7:87449–87461. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ross JS, Wang K, Sheehan CE, Boguniewicz
AB, Otto G, Downing SR, Sun J, He J, Curran JA, Ali S, et al:
Relapsed classic E-cadherin (CDH1)-mutated invasive lobular breast
cancer shows a high frequency of HER2 (ERBB2) gene mutations. Clin
Cancer Res. 19:2668–2676. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Balakrishnan S, Bhat FA, Raja Singh P,
Mukherjee S, Elumalai P, Das S, Patra CR and Arunakaran J: Gold
nanoparticle-conjugated quercetin inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal
transition, angiogenesis and invasiveness via EGFR/VEGFR-2-mediated
pathway in breast cancer. Cell Prolif. 49:678–697. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bokhari AA, Baker TM, Dorjbal B, Waheed S,
Zahn CM, Hamilton CA, Maxwell GL and Syed V: Nestin suppression
attenuates invasive potential of endometrial cancer cells by
downregulating TGF-β signaling pathway. Oncotarget. 7:69733–69748.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Du J, Wang Y, Chen D, Ji G, Ma Q, Liao S,
Zheng Y, Zhang J and Hou Y: BAY61-3606 potentiates the anti-tumor
effects of TRAIL against colon cancer through up-regulating DR4 and
down-regulating NF-κB. Cancer Lett. 383:145–153. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang H, You Y and Zhu Z: The human RNA
surveillance factor Up-frameshift 1 inhibits hepatic cancer
progression by targeting MRP2/ABCC2. Biomed Pharmacother.
92:365–372. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|