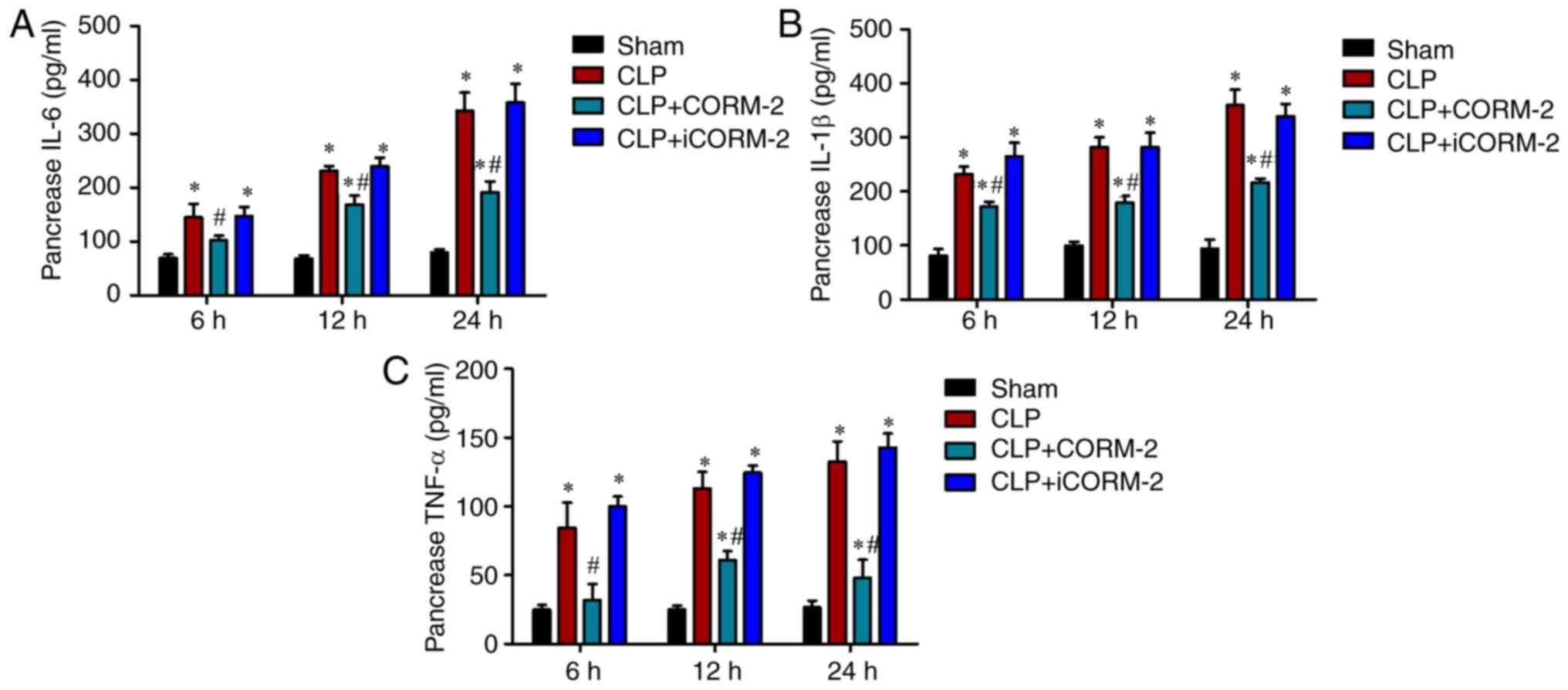
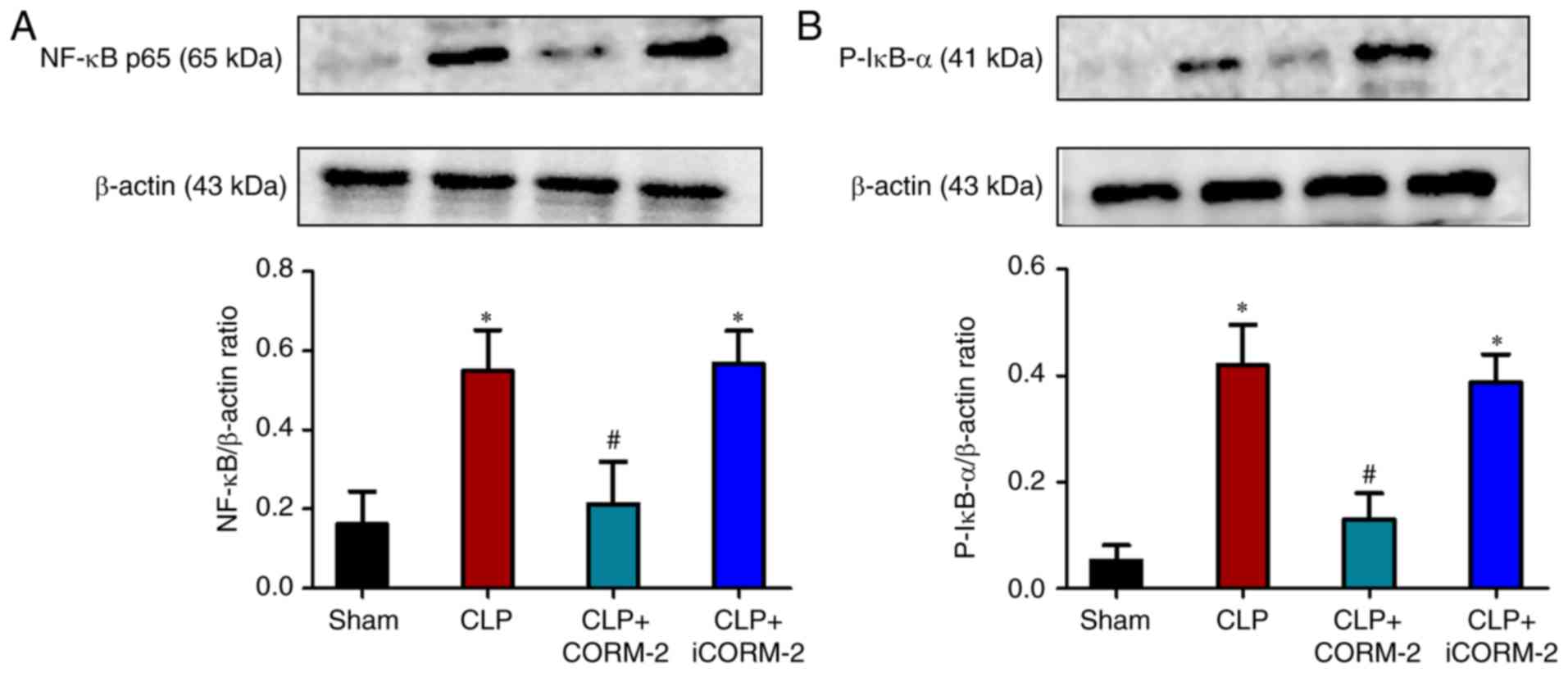
|
1
|
Abou Dagher G, Harmouche E, Jabbour E,
Bachir R, Zebian D and Bou Chebl R: Sepsis in hemodialysis
patients. BMC Emerg Med. 15:302015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Aikawa N: Revised Surviving Sepsis
Campaign Guidelines and therapy for severe sepsis. Jpn J Antibiot.
64:37–44. 2011.(In Japanese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Liu Z, Shi Q, Liu J, Abdel-Razek O, Xu Y,
Cooney RN and Wang G: Innate immune molecule surfactant protein D
attenuates sepsis-induced acute pancreatic injury through
modulating apoptosis and NF-κB-mediated inflammation. Sci Rep.
5:177982015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Levy MM, Fink MP, Marshall JC, Abraham E,
Angus D, Cook D, Cohen J, Opal SM, Vincent JL and Ramsay G;
SCCM/ESICM/ACCP/ATS/SIS, . 2001 SCCM/ESICM/ACCP/ATS/SIS
International Sepsis Definitions Conference. Crit Care Med.
31:1250–1256. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Marshall JC, Cook DJ, Christou NV, Bernard
GR, Sprung CL and Sibbald WJ: Multiple organ dysfunction score: A
reliable descriptor of a complex clinical outcome. Crit Care Med.
23:1638–1652. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tribl B, Sibbald WJ, Vogelsang H,
Spitzauer S, Gangl A and Madl C: Exocrine pancreatic dysfunction in
sepsis. Eur J Clin Invest. 33:239–243. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tribl B, Madl C, Mazal PR, Schneider B,
Spitzauer S, Vogelsang H and Gangl A: Exocrine pancreatic function
in critically ill patients: Septic shock versus non-septic
patients. Crit Care Med. 28:1393–1398. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sun BW and Chen X: Carbon monoxide
releasing molecules: New insights for anticoagulation strategy in
sepsis. Cell Mol Life Sci. 66:365–369. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Soni H, Pandya G, Patel P, Acharya A, Jain
M and Mehta AA: Beneficial effects of carbon monoxide-releasing
molecule-2 (CORM-2) on acute doxorubicin cardiotoxicity in mice:
Role of oxidative stress and apoptosis. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
253:70–80. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chung SW, Liu X, Macias AA, Baron RM and
Perrella MA: Heme oxygenase-1-derived carbon monoxide enhances the
host defense response to microbial sepsis in mice. J Clin Invest.
118:239–247. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sun B, Sun Z, Jin Q and Chen X:
CO-releasing molecules (CORM-2)-liberated CO attenuates leukocytes
infiltration in the renal tissue of thermally injured mice. Int J
Biol Sci. 4:176–183. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lee S, Lee SJ, Coronata AA, Fredenburgh
LE, Chung SW, Perrella MA, Nakahira K, Ryter SW and Choi AM: Carbon
monoxide confers protection in sepsis by enhancing beclin
1-dependent autophagy and phagocytosis. Antioxid Redox Signal.
20:432–442. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Coburn RF: The measurement of endogenous
carbon monoxide production. J Appl Physiol (1985). 112:1949–1955.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ryter SW and Choi AM: Carbon monoxide:
Present and future indications for a medical gas. Korean J Intern
Med. 28:123–140. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ozaki KS, Yoshida J, Ueki S, Pettigrew GL,
Ghonem N, Sico RM, Lee LY, Shapiro R, Lakkis FG, Pacheco-Silva A
and Murase N: Carbon monoxide inhibits apoptosis during cold
storage and protects kidney grafts donated after cardiac death.
Transpl Int. 25:107–117. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu DM, Sun BW, Sun ZW, Jin Q, Sun Y and
Chen X: Suppression of inflammatory cytokine production and
oxidative stress by CO-releasing molecules-liberated CO in the
small intestine of thermally-injured mice. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
29:838–846. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Katada K, Bihari A, Mizuguchi S, Yoshida
N, Yoshikawa T, Fraser DD, Potter RF and Cepinskas G: Carbon
monoxide liberated from CO-releasing molecule (CORM-2) attenuates
ischemia/reperfusion (I/R)-induced inflammation in the small
intestine. Inflammation. 33:92–100. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sun BW, Jin Q, Sun Y, Sun ZW, Chen X, Chen
ZY and Cepinskas G: Carbon liberated from CO-releasing molecules
attenuates leukocyte infiltration in the small intestine of
thermally injured mice. World J Gastroenterol. 13:6183–6190. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sun B, Sun H, Liu C, Shen J, Chen Z and
Chen X: Role of CO-releasing molecules liberated CO in attenuating
leukocytes sequestration and inflammatory responses in the lung of
thermally injured mice. J Surg Res. 139:128–135. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen P, Sun B, Chen H, Wang G, Pan S, Kong
R, Bai X and Wang S: Effects of carbon monoxide releasing
molecule-liberated CO on severe acute pancreatitis in rats.
Cytokine. 49:15–23. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xue J and Habtezion A: Carbon
monoxide-based therapy ameliorates acute pancreatitis via TLR4
inhibition. J Clin Invest. 124:437–447. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu D, Liang F, Wang X, Cao J, Qin W and
Sun B: Suppressive effect of CORM-2 on LPS-induced platelet
activation by glycoprotein mediated HS1 phosphorylation
interference. PLoS One. 8:e831122013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu J, Abdel-Razek O, Liu Z, Hu F, Zhou Q,
Cooney RN and Wang G: Role of surfactant proteins A and D in
sepsis-induced acute kidney injury. Shock. 43:31–38. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tang Z, Ni L, Javidiparsijani S, Hu F,
Gatto LA, Cooney R and Wang G: Enhanced liver autophagic activity
improves survival of septic mice lacking surfactant proteins A and
D. Tohoku J Exp Med. 231:127–138. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Deng W, Hui Y, Yu J, Wang W, Xu S, Chen C
and Xiong X: A new pathological scoring method for adrenal injury
in rats with severe acute pancreatitis. Pathol Res Pract.
210:1011–1017. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Shen WC, Wang X, Qin WT, Qiu XF and Sun
BW: Exogenous carbon monoxide suppresses Escherichia coli vitality
and improves survival in an Escherichia coli-induced murine sepsis
model. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 35:1566–1576. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hillegass LM, Griswold DE, Brickson B and
Albrightson-Winslow C: Assessment of myeloperoxidase activity in
whole rat kidney. J Pharmacol Methods. 24:285–295. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhou X, Liu Z, Jang F, Xiang C, Li Y and
He Y: Autocrine sonic hedgehog attenuates inflammation in
cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis in mice via upregulation of
IL-10. PLoS One. 7:e441212012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tribl B, Bateman RM, Milkovich S, Sibbald
WJ and Ellis CG: Effect of nitric oxide on capillary hemodynamics
and cell injury in the pancreas during Pseudomonas
pneumonia-induced sepsis. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
286:H340–H345. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Pieracci FM and Barie PS: Management of
severe sepsis of abdominal origin. Scand J Surg. 96:184–196. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kong XY, Du YQ, Li L, Liu JQ, Wang GK, Zhu
JQ, Man XH, Gong YF, Xiao LN, Zheng YZ, et al: Plasma miR-216a as a
potential marker of pancreatic injury in a rat model of acute
pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol. 16:4599–4604. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Choudhury S, Kandasamy K, Maruti BS,
Addison MP, Kasa JK, Darzi SA, Singh TU, Parida S, Dash JR, Singh V
and Mishra SK: Atorvastatin along with imipenem attenuates acute
lung injury in sepsis through decrease in inflammatory mediators
and bacterial load. Eur J Pharmacol. 765:447–456. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Queiroga CS, Vercelli A and Vieira HL:
Carbon monoxide and the CNS: Challenges and achievements. Br J
Pharmacol. 172:1533–1545. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Song M, Wang X, Qin W, Zhuang M, Xu X,
Zhang Y and Sun B: Effects of exogenous carbon monoxide-releasing
molecule 2 intervention in vitro on formation of human neutrophil
extracellular traps stimulated by endotoxin/lipopolysaccharide and
its mechanism. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 32:82–88. 2016.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liu D, Wang X, Qin W, Chen J, Wang Y,
Zhuang M and Sun B: Suppressive effect of exogenous carbon monoxide
on endotoxin-stimulated platelet over-activation via the
glycoprotein-mediated PI3K-Akt-GSK3β pathway. Sci Rep. 6:236532016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Qin W, Zhang J, Lv W, Wang X and Sun B:
Effect of carbon monoxide-releasing molecules II-liberated CO on
suppressing inflammatory response in sepsis by interfering with
nuclear factor kappa B activation. PLoS One. 8:e758402013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Motterlini R, Clark JE, Foresti R,
Sarathchandra P, Mann BE and Green CJ: Carbon monoxide-releasing
molecules: Characterization of biochemical and vascular activities.
Circ Res. 90:E17–E24. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Motterlini R, Sawle P, Hammad J, Bains S,
Alberto R, Foresti R and Green CJ: CORM-A1: A new pharmacologically
active carbon monoxide-releasing molecule. FASEB J. 19:284–286.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Johnson TR, Mann BE, Clark JE, Foresti R,
Green CJ and Motterlini R: Metal carbonyls: A new class of
pharmaceuticals? Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 42:3722–3729. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Clark JE, Naughton P, Shurey S, Green CJ,
Johnson TR, Mann BE, Foresti R and Motterlini R: Cardioprotective
actions by a water-soluble carbon monoxide-releasing molecule. Circ
Res. 93:e2–e8. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Cioffi WG, Burleson DG and Pruitt BA Jr:
Leukocyte responses to injury. Arch Surg. 128:1260–1267. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Bradley PP, Priebat DA, Christensen RD and
Rothstein G: Measurement of cutaneous inflammation: Estimation of
neutrophil content with an enzyme marker. J Invest Dermatol.
78:206–209. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Christofidou-Solomidou M, Nakada MT,
Williams J, Muller WA and DeLisser HM: Neutrophil platelet
endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 participates in neutrophil
recruitment at inflammatory sites and is down-regulated after
leukocyte extravasation. J Immunol. 158:4872–4878. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Imamoto E, Yoshida N, Uchiyama K, Kuroda
M, Kokura S, Ichikawa H, Naito Y, Tanigawa T and Yoshikawa T:
Inhibitory effect of pioglitazone on expression of adhesion
molecules on neutrophils and endothelial cells. Biofactors.
20:37–47. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Pereda J, Sabater L, Aparisi L, Escobar J,
Sandoval J, Viña J, López-Rodas G and Sastre J: Interaction between
cytokines and oxidative stress in acute pancreatitis. Curr Med
Chem. 13:2775–2787. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kim GY, Roh SI, Park SK, Ahn SC, Oh YH,
Lee JD and Park YM: Alleviation of experimental septic shock in
mice by acidic polysaccharide isolated from the medicinal mushroom
Phellinus linteus. Biol Pharm Bull. 26:1418–1423. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Xiang K, Cheng L, Luo Z, Ren J, Tian F,
Tang L, Chen T and Dai R: Glycyrrhizin suppresses the expressions
of HMGB1 and relieves the severity of traumatic pancreatitis in
rats. PLoS One. 9:e1159822014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Baeuerle PA and Henkel T: Function and
activation of NF-kappa B in the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol.
12:141–179. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Yin MJ, Yamamoto Y and Gaynor RB: The
anti-inflammatory agents aspirin and salicylate inhibit the
activity of I(kappa)B kinase-beta. Nature. 396:77–80. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Han B, Ji B and Logsdon CD: CCK
independently activates intracellular trypsinogen and NF-kappaB in
rat pancreatic acinar cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
280:C465–C472. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Kulms D and Schwarz T: NF-kappaB and
cytokines. Vitam Horm. 74:283–300. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Song YS, Lee YS, Narasimhan P and Chan PH:
Reduced oxidative stress promotes NF-kappaB-mediated
neuroprotective gene expression after transient focal cerebral
ischemia: Lymphocytotrophic cytokines and antiapoptotic factors. J
Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 27:764–775. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Dai B, Lei C, Lin R, Tao L, Bin Y, Peng H
and Lei B: Activation of liver X receptor α protects amyloid
β1-40 induced inflammatory and senescent responses in
human retinal pigment epithelial cells. Inflamm Res. 66:523–534.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Tao L, Qiu Y, Fu X, Lin R, Lei C, Wang J
and Lei B: Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 activator diminazene
aceturate prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation by
inhibiting MAPK and NF-κB pathways in human retinal pigment
epithelium. J Neuroinflammation. 13:352016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Lu Y, Li F, Xu T and Sun J: Tetrandrine
prevents multidrug resistance in the osteosarcoma cell line, U-2OS,
by preventing Pgp overexpression through the inhibition of NF-κB
signaling. Int J Mol Med. 39:993–1000. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Dolinay T, Szilasi M, Liu M and Choi AM:
Inhaled carbon monoxide confers antiinflammatory effects against
ventilator-induced lung injury. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
170:613–620. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
El-Mousleh T, Casalis PA, Wollenberg I,
Zenclussen ML, Volk HD, Langwisch S, Jensen F and Zenclussen AC:
Exploring the potential of low doses carbon monoxide as therapy in
pregnancy complications. Med Gas Res. 2:42012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Desmard M, Foresti R, Morin D, Dagouassat
M, Berdeaux A, Denamur E, Crook SH, Mann BE, Scapens D, Montravers
P, et al: Differential antibacterial activity against Pseudomonas
aeruginosa by carbon monoxide-releasing molecules. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 16:153–163. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|