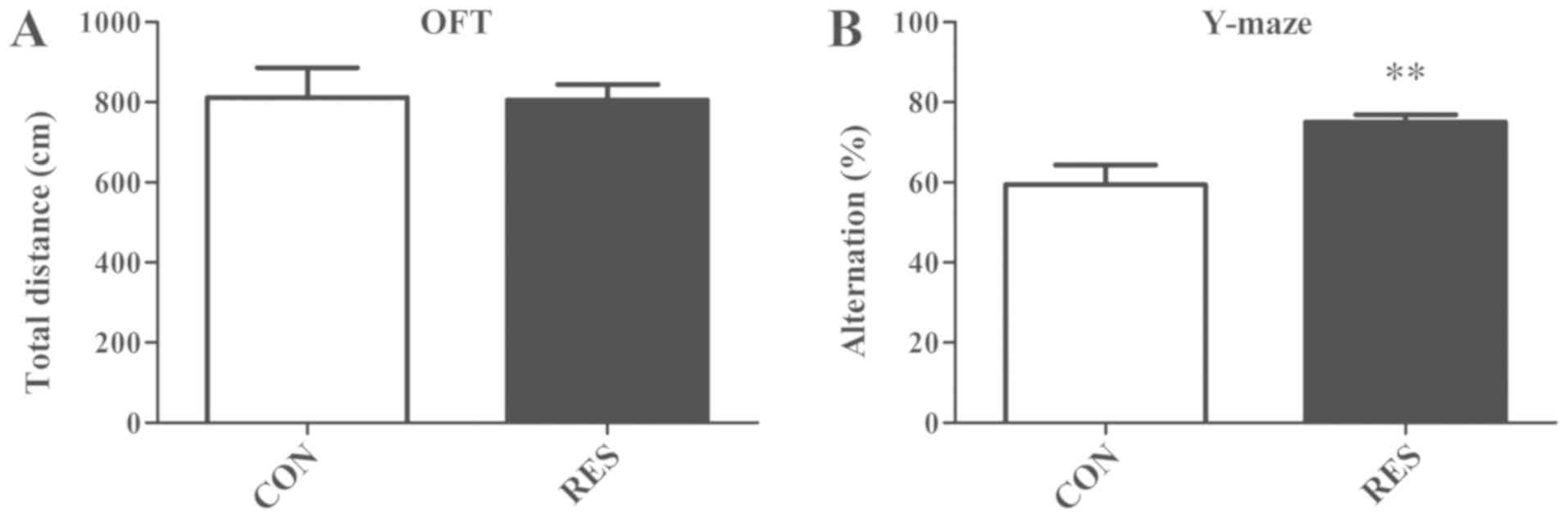
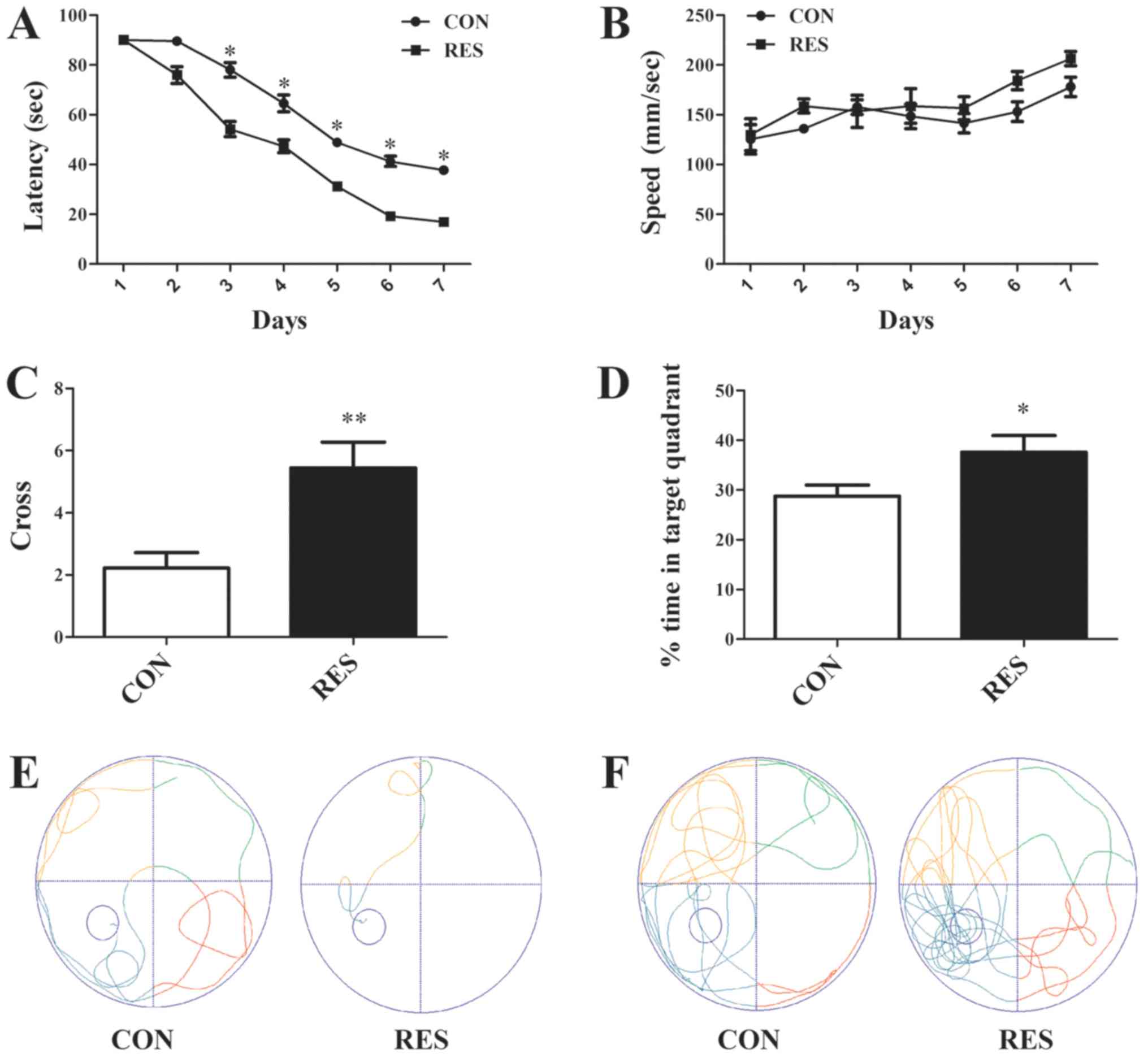
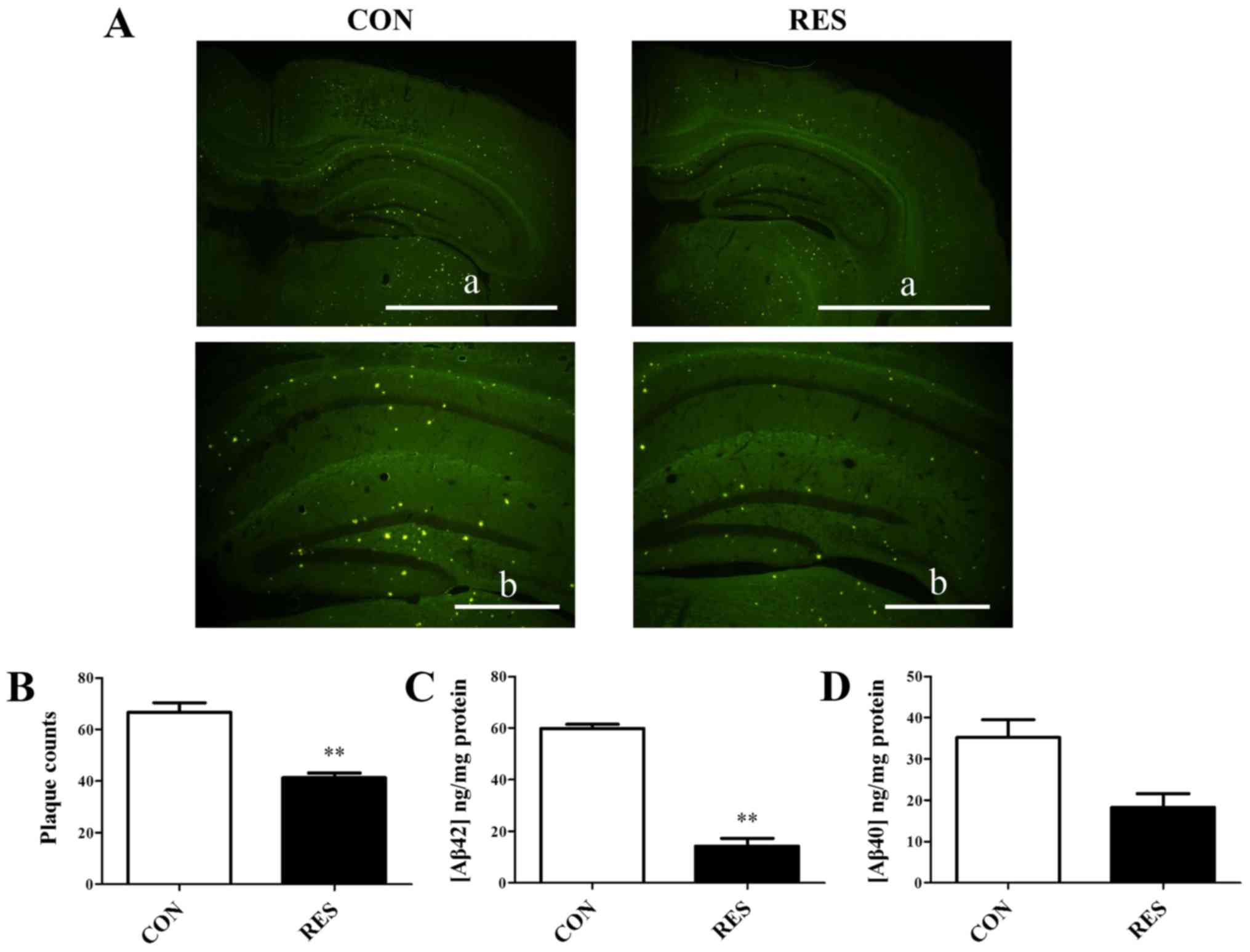
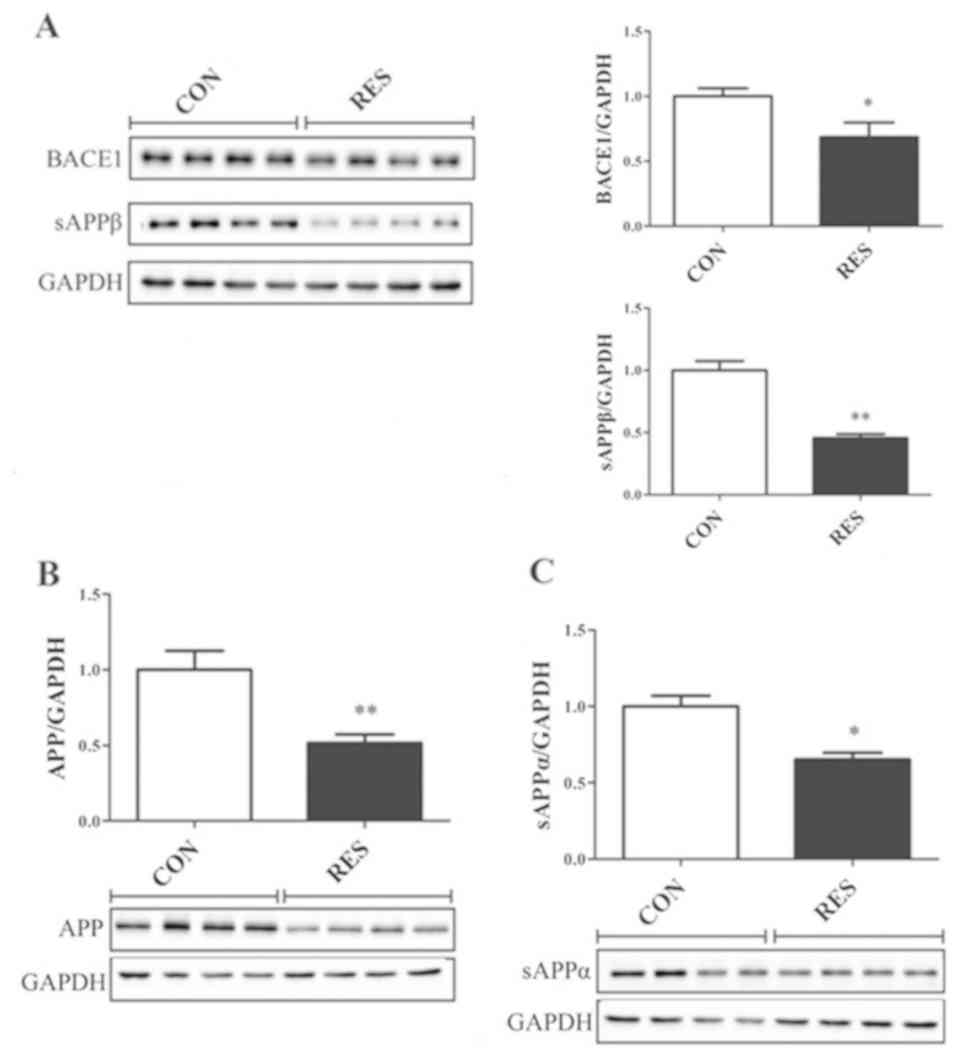
|
1
|
McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M, Katzman
R, Price D and Stadlan EM: Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's
disease: Report of the NINCDS-ADRDA work group under the auspices
of department of health and human services task force on
Alzheimer's disease. Neurology. 34:939–944. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Alzheimer's Association: 2011 Alzheimer's
disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 7:208–244. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Selkoe DJ and Schenk D: Schenk,
Alzheimer's disease: Molecular understanding predicts amyloid-based
therapeutics. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 43:545–584. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hardy J and Selkoe DJ: The amyloid
hypothesis of Alzheimer's disease: Progress and problems on the
road to therapeutics. Science. 297:353–356. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K, Tung YC, Quinlan
M, Wisniewski HM and Binder LI: Abnormal phosphorylation of the
microtubule-associated protein tau (tau) in Alzheimer cytoskeletal
pathology. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 83:4913–4917. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cole SL and Vassar R: BACE1 structure and
function in health and Alzheimer's disease. Curr Alzheimer Res.
5:100–120. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lin X, Koelsch G, Wu S, Downs D, Dashti A
and Tang J: Human aspartic protease memapsin 2 cleaves the
beta-secretase site of beta-amyloid precursor protein. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 97:1456–1460. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhao J, Fu Y, Yasvoina M, Shao P, Hitt B,
O'Connor T, Logan S, Maus E, Citron M, Berry R, et al: Beta-site
amyloid precursor protein cleaving enzyme 1 levels become elevated
in neurons around amyloid plaques: Implications for Alzheimer's
disease pathogenesis. J Neurosci. 27:3639–3649. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kandalepas PC, Sadleir KR, Eimer WA, Zhao
J, Nicholson DA and Vassar R: The Alzheimer's β-secretase BACE1
localizes to normal presynaptic terminals and to dystrophic
presynaptic terminals surrounding amyloid plaques. Acta
Neuropathol. 126:329–352. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
De Strooper B: Proteases and proteolysis
in Alzheimer disease: A multifactorial view on the disease process.
Physiol Rev. 90:465–494. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Robb EL, Page MM, Wiens BE and Stuart JA:
Molecular mechanisms of oxidative stress resistance induced by
resveratrol: Specific and progressive induction of MnSOD. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 367:406–412. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Baltaci AK, Arslangil D, Mogulkoc R and
Patlar S: Effect of resveratrol administration on the element
metabolism in the blood and brain tissues of rats subjected to
acute swimming exercise. Biol Trace Elem Res. 175:421–427. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Baltaci SB, Mogulkoc R and Baltaci AK:
Resveratrol and Exercise. Biomed Rep. 5:525–530. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ladiwala AR, Lin JC, Bale SS,
Marcelino-Cruz AM, Bhattacharya M, Dordick JS and Tessier PM:
Resveratrol selectively remodels soluble oligomers and fibrils of
amyloid Abeta into off-pathway conformers. J Biol Chem.
285:24228–24237. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang J, Ho L, Zhao Z, Seror I, Humala N,
Dickstein DL, Thiyagarajan M, Percival SS, Talcott ST and Pasinetti
GM: Moderate consumption of Cabernet Sauvignon attenuates Abeta
neuropathology in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. FASEB J.
20:2313–2320. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Capiralla H, Vingtdeux V, Zhao H,
Sankowski R, Al-Abed Y, Davies P and Marambaud P: Resveratrol
mitigates lipopolysaccharide- and Aβ-mediated microglial
inflammation by inhibiting the TLR4/NF-κB/STAT signaling cascade. J
Neurochem. 120:461–472. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Crandall JP and Barzilai N: Exploring the
promise of resveratrol: Where do we go from here? Diabetes.
62:1022–1023. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Oakley H, Cole SL, Logan S, Maus E, Shao
P, Craft J, Guillozet-Bongaarts A, Ohno M, Disterhoft J, Van Eldik
L, et al: Intraneuronal beta-amyloid aggregates, neurodegeneration,
and neuron loss in transgenic mice with five familial Alzheimer's
disease mutations: Potential factors in amyloid plaque formation. J
Neurosci. 26:10129–10140. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
The NIH guidelines for the care and use of
laboratory animals, . NIH Publication. 85–23, 1985. 1985.
|
|
20
|
Menet MC, Baron S, Taghi M, Diestra R,
Dargère D, Laprévote O, Nivet-Antoine V, Beaudeux JL, Bédarida T
and Cottart CH: Distribution of trans-resveratrol and its
metabolites after acute or sustained administration in mouse heart,
brain, and liver. Mol Nutr Food Res. 61:2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ohno M, Tseng W, Silva AJ and Disterhoft
JF: Trace eyeblink conditioning requires the hippocampus but not
autophosphorylation of alphaCaMKII in mice. Learn Mem. 12:211–215.
2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hong YA, Bae SY, Ahn SY, Kim J, Kwon YJ,
Jung WY and Ko GJ: Resveratrol ameliorates contrast induced
nephropathy through the activation of SIRT1-PGC-1α-Foxo1 signaling
in mice. Kidney Blood Press Res. 42:641–653. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Area-Gomez E and Schon EA: Alzheimer
disease. Adv Exp Med Biol. 997:149–156. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Barage SH and Sonawane KD: Amyloid cascade
hypothesis: Pathogenesis andtherapeutic strategies in Alzheimer's
disease. Neuropeptides. 52:1–18. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Andreeva TV, Lukiw WJ and Rogaev EI:
Biological basis for amyloidogenesis in Alzheimer's disease.
Biochemistry (Mosc). 82:122–139. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Billings LM, Oddo S, Green KN, McGaugh JL
and LaFerla FM: Intraneuronal Abeta causes the onset of early
Alzheimer's disease-related cognitive deficits in transgenic mice.
Neuron. 45:675–688. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Selkoe DJ and Schenk D: Alzheimer's
disease: Molecular understanding predicts amyloid-based
therapeutics. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 43:545–584. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fukumoto H, Takahashi H, Tarui N, Matsui
J, Tomita T, Hirode M, Sagayama M, Maeda R, Kawamoto M, Hirai K, et
al: A noncompetitive BACE1 inhibitor TAK-070 ameliorates Abeta
pathology and behavioral deficits in a mouse model of Alzheimer's
disease. J Neurosci. 30:11157–11166. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Han YS, Bastianetto S, Dumont Y and
Quirion R: Specific plasma membrane binding sites for polyphenols,
including resveratrol, in the rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther.
318:238–245. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gilgun-Sherki Y, Melamed E and Offen D:
Oxidative stress induced-neurodegenerative diseases: The need for
antioxidants that penetrate the blood brain barrier.
Neuropharmcology. 40:959–975. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Marambaud P, Zhao H and Davies P:
Resveratrol promotes clearance of Alzheimer's disease amyloid-beta
peptides. J Biol Chem. 280:37377–37382. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ho L, Chen LH, Wang J, Zhao W, Talcott ST,
Ono K, Teplow D, Humala N, Cheng A, Percival SS, et al:
Heterogeneity in red wine polyphenolic contents differentially
influences Alzheimer's disease-type neuropathology and cognitive
deterioration. J Alzheimers Dis. 16:59–72. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Jia Y, Wang N and Liu X: Resveratrol and
amyloid-beta: Mechanistic insights. Nutrients. 9(pii): E11222017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Deng H and Mi MT: Resveratrol attenuates
Aβ25–35 caused neurotoxicity by inducing autophagy through the
TyrRS-PARP1-SIRT1 signaling pathway. Neurochem Res. 41:2367–2379.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chen CJ, Yu W, Fu YC, Wang X, Li JL and
Wang W: Resveratrol protects cardiomyocytes from hypoxia-induced
apoptosis through the SIRT1-FoxO1 pathway. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 378:389–393. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Jang JH and Surh YJ: Protective effect of
resveratrol on beta-amyloid-induced oxidative PC12 cell death. Free
RadicBiol Med. 34:1100–1110. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Kim D, Nguyen MD, Dobbin MM, Fischer A,
Sananbenesi F, Rodgers JT, Delalle I, Baur JA, Sui G, Armour SM, et
al: SIRT1 deacetylase protects against neurodegeneration in models
for Alzheimer's disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. EMBO J.
26:3169–3179. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lagouge M, Argmann C, Gerhart-Hines Z,
Meziane H, Lerin C, Daussin F, Messadeq N, Milne J, Lambert P,
Elliott P, et al: Resveratrol improves mitochondrial function and
protects against metabolic disease by activating SIRT1 and
PGC-1alpha. Cell. 127:1109–1122. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Porquet D, Griñán-Ferré C, Ferrer I,
Camins A, Sanfeliu C, Del Valle J and Pallàs M: Neuroprotective
role of trans-resveratrol in a murine model of familial Alzheimer's
disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 42:1209–1220. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Bastianetto S, Ménard C and Quirion R:
Neuroprotective action of resveratrol. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1852:1195–1201. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hou Y, Wang K, Wan W, Cheng Y, Pu X and Ye
X: Resveratrol provides neuroprotection by regulating the
JAK2/STAT3/PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway after stroke in rats. Genes Dis.
5:245–255. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|