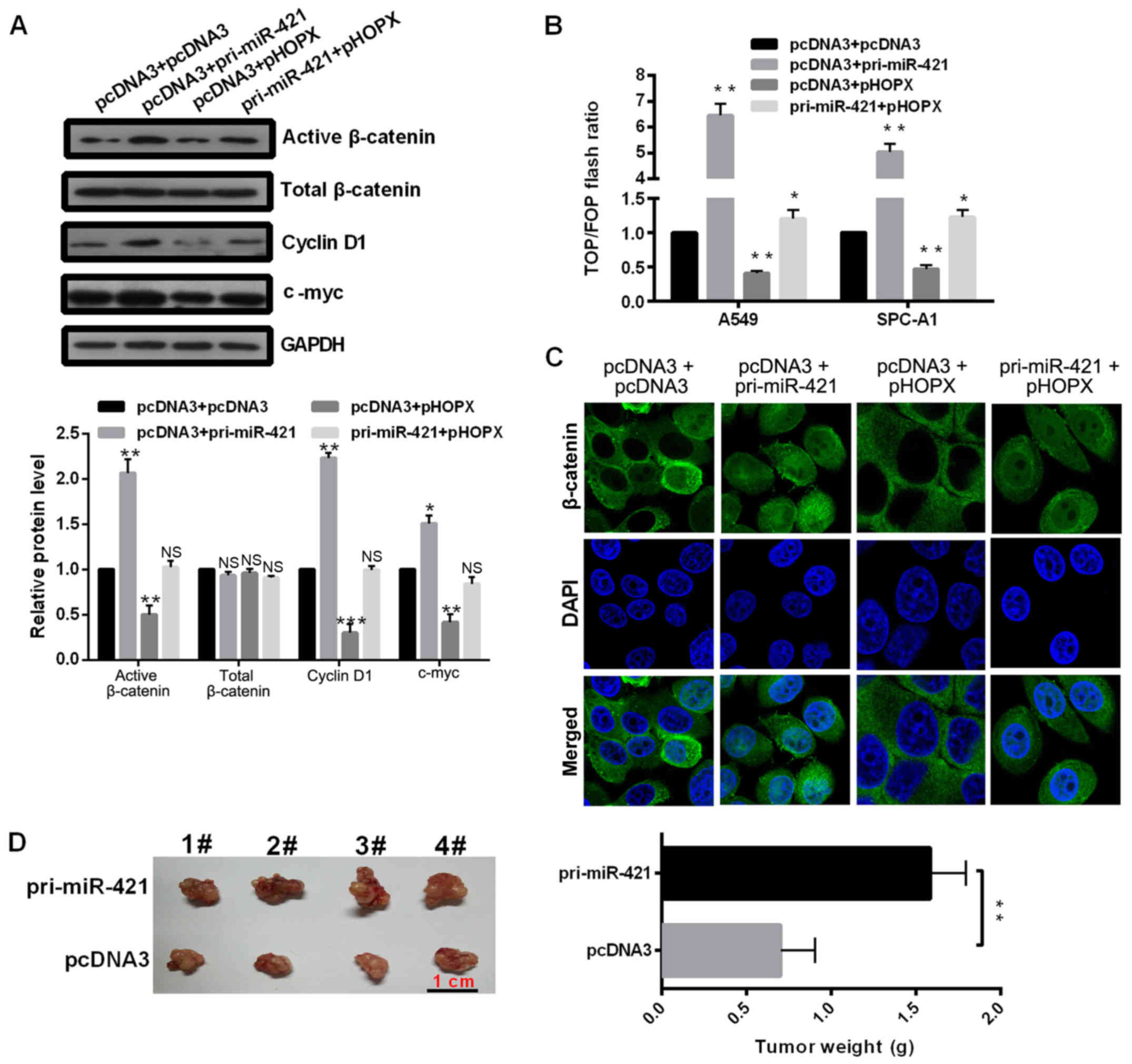
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:7–30. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Holdenrieder S and Stieber P: New
challenges for laboratory diagnostics in non-small cell lung
cancer. Cancer Biomark. 6:119–121. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wood SL, Pernemalm M, Crosbie PA and
Whetton AD: Molecular histology of lung cancer: From targets to
treatments. Cancer Treat Rev. 41:361–375. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Marmarelis M, Thompson JC, Aggarwal C,
Evans TL, Carpenter E, Cohen RB, Langer CJ and Bauml J: Emerging
uses of circulating tumor DNA in advanced stage non-small cell lung
cancer. Ann Transl Med. 5:3802017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Laskin JJ and Sandler AB: State of the art
in therapy for non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Invest.
23:427–442. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kim VN, Han J and Siomi MC: Biogenesis of
small RNAs in animals. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 10:126–139. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Djuranovic S, Nahvi A and Green R: A
parsimonious model for gene regulation by miRNAs. Science.
331:550–553. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Huntzinger E and Izaurralde E: Gene
silencing by microRNAs: Contributions of translational repression
and mRNA decay. Nat Rev Genet. 12:99–110. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Stahlhut C and Slack FJ: Combinatorial
action of MicroRNAs let-7 and miR-34 effectively synergizes with
erlotinib to suppress non-small cell lung cancer cell
proliferation. Cell Cycle. 14:2171–2180. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu L, Cui S, Zhang R, Shi Y and Luo L:
MiR-421 inhibits the malignant phenotype in glioma by directly
targeting MEF2D. Am J Cancer Res. 7:857–868. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ge X, Liu X, Lin F, Li P, Liu K, Geng R,
Dai C, Lin Y, Tang W, Wu Z, et al: MicroRNA-421 regulated by HIF-1α
promotes metastasis, inhibits apoptosis, and induces cisplatin
resistance by targeting E-cadherin and caspase-3 in gastric cancer.
Oncotarget. 7:24466–24482. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Long MJ, Wu FX, Li P, Liu M, Li X and Tang
H: MicroRNA-10a targets CHL1 and promotes cell growth, migration
and invasion in human cervical cancer cells. Cancer Lett.
324:186–196. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Weidenfeld K and Barkan D: EMT and
stemness in tumor dormancy and outgrowth: Are they intertwined
processes? Front Oncol. 8:3812018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Polyak K and Weinberg RA: Transitions
between epithelial and mesenchymal states: Acquisition of malignant
and stem cell traits. Nat Rev Cancer. 9:265–273. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jain R, Li D, Gupta M, Manderfield LJ,
Ifkovits JL, Wang Q, Liu F, Liu Y, Poleshko A, Padmanabhan A, et
al: HEART DEVELOPMENT. Integration of Bmp and Wnt signaling by Hopx
specifies commitment of cardiomyoblasts. Science. 348:aaa60712015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang Q, Jiang S, Song A, Hou S, Wu Q, Qi L
and Gao X: HOXD-AS1 functions as an oncogenic ceRNA to promote
NSCLC cell progression by sequestering miR-147a. Onco Targets Ther.
10:4753–4763. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Pan JY, Zhang F, Sun CC, Li SJ, Li G, Gong
FY, Bo T, He J, Hua RX, Hu WD, et al: miR-134: A human cancer
suppressor? Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 6:140–149. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu X, Xu Y, Pang Z, Guo F, Qin Q, Yin T,
Sang Y, Feng C, Li X, Jiang L, et al: Knockdown of SUMO-activating
enzyme subunit 2 (SAE2) suppresses cancer malignancy and enhances
chemotherapy sensitivity in small cell lung cancer. J Hematol
Oncol. 8:672015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang Z, Yang Y and Zhang X: MiR-770
inhibits tumorigenesis and EMT by targeting JMJD6 and regulating
WNT/β-catenin pathway in non-small cell lung cancer. Life Sci.
188:163–171. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang L, Liu W, Zhang YP and Huang XR: The
miR-224 promotes non-small cell lung cancer cell proliferation by
directly targeting RASSF8. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 21:3223–3231.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lu C, Xie Z and Peng Q: MiRNA-107 enhances
chemosensitivity to paclitaxel by targeting antiapoptotic factor
Bcl-w in non small cell lung cancer. Am J Cancer Res. 7:1863–1873.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li T, Ding ZL, Zheng YL and Wang W:
MiR-484 promotes non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) progression
through inhibiting Apaf-1 associated with the suppression of
apoptosis. Biomed Pharmacother. 96:153–164. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Fan N, Zhang J, Cheng C, Zhang X, Feng J
and Kong R: MicroRNA-384 represses the growth and invasion of
non-small-cell lung cancer by targeting astrocyte elevated
gene-1/Wnt signaling. Biomed Pharmacother. 95:1331–1337. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang L, Huang J, Yang N, Greshock J,
Megraw MS, Giannakakis A, Liang S, Naylor TL, Barchetti A, Ward MR,
et al: microRNAs exhibit high frequency genomic alterations in
human cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:9136–9141. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li Y, Cui X, Li Y, Zhang T and Li S:
Upregulated expression of miR-421 is associated with poor prognosis
in non-small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Manag Res. 10:2627–2633.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang W, Shi S, Jiang J, Li X, Lu H and
Ren F: LncRNA MEG3 inhibits cell epithelial-mesenchymal transition
by sponging miR-421 targeting E-cadherin in breast cancer. Biomed
Pharmacother. 91:312–319. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chen L, Tang Y, Wang J, Yan Z and Xu R:
miR-421 induces cell proliferation and apoptosis resistance in
human nasopharyngeal carcinoma via downregulation of FOXO4. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 435:745–750. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Rafael D, Doktorovová S, Florindo HF,
Gener P, Abasolo I, Schwartz S Jr and Videira MA: EMT blockage
strategies: Targeting Akt dependent mechanisms for breast cancer
metastatic behaviour modulation. Curr Gene Ther. 15:300–312. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Trivedi CM, Cappola TP, Margulies KB and
Epstein JA: Homeodomain only protein X is down-regulated in human
heart failure. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 50:1056–1058. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Trivedi CM, Zhu W, Wang Q, Jia C, Kee HJ,
Li L, Hannenhalli S and Epstein JA: Hopx and Hdac2 interact to
modulate Gata4 acetylation and embryonic cardiac myocyte
proliferation. Dev Cell. 19:450–459. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Palpant NJ, Wang Y, Hadland B, Zaunbrecher
RJ, Redd M, Jones D, Pabon L, Jain R, Epstein J, Ruzzo WL, et al:
Chromatin and transcriptional analysis of mesoderm progenitor cells
identifies HOPX as a regulator of primitive hematopoiesis. Cell
Rep. 20:1597–1608. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yamashita K, Kim MS, Park HL, Tokumaru Y,
Osada M, Inoue H, Mori M and Sidransky D: HOP/OB1/NECC1 promoter
DNA is frequently hypermethylated and involved in tumorigenic
ability in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Mol Cancer Res.
6:31–41. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yamaguchi S, Asanoma K, Takao T, Kato K
and Wake N: Homeobox gene HOPX is epigenetically silenced in
human uterine endometrial cancer and suppresses estrogen-stimulated
proliferation of cancer cells by inhibiting serum response factor.
Int J Cancer. 124:2577–2588. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ooki A, Yamashita K, Kikuchi S, Sakuramoto
S, Katada N, Kokubo K, Kobayashi H, Kim MS, Sidransky D and
Watanabe M: Potential utility of HOP homeobox gene promoter
methylation as a marker of tumor aggressiveness in gastric cancer.
Oncogene. 29:3263–3275. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|