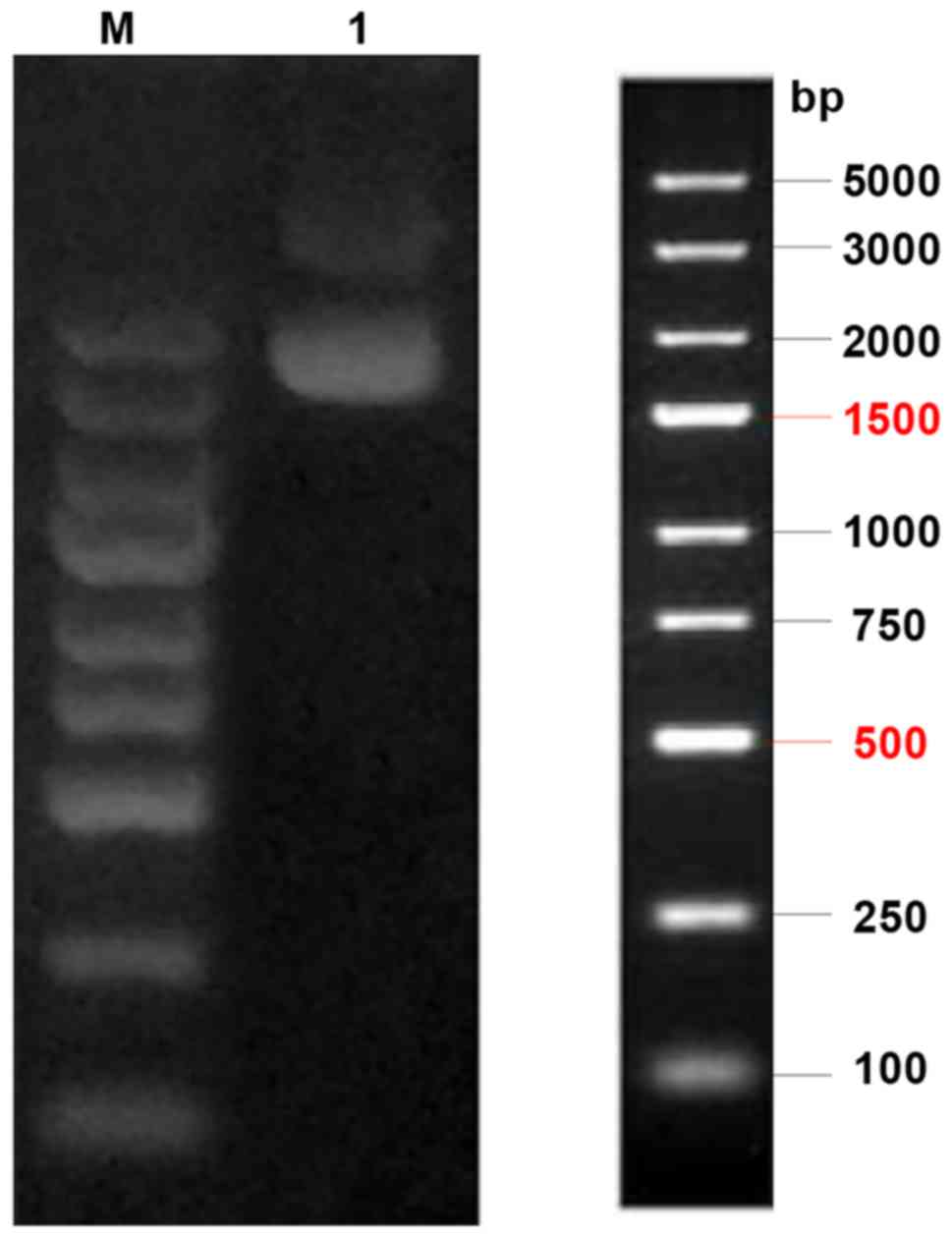
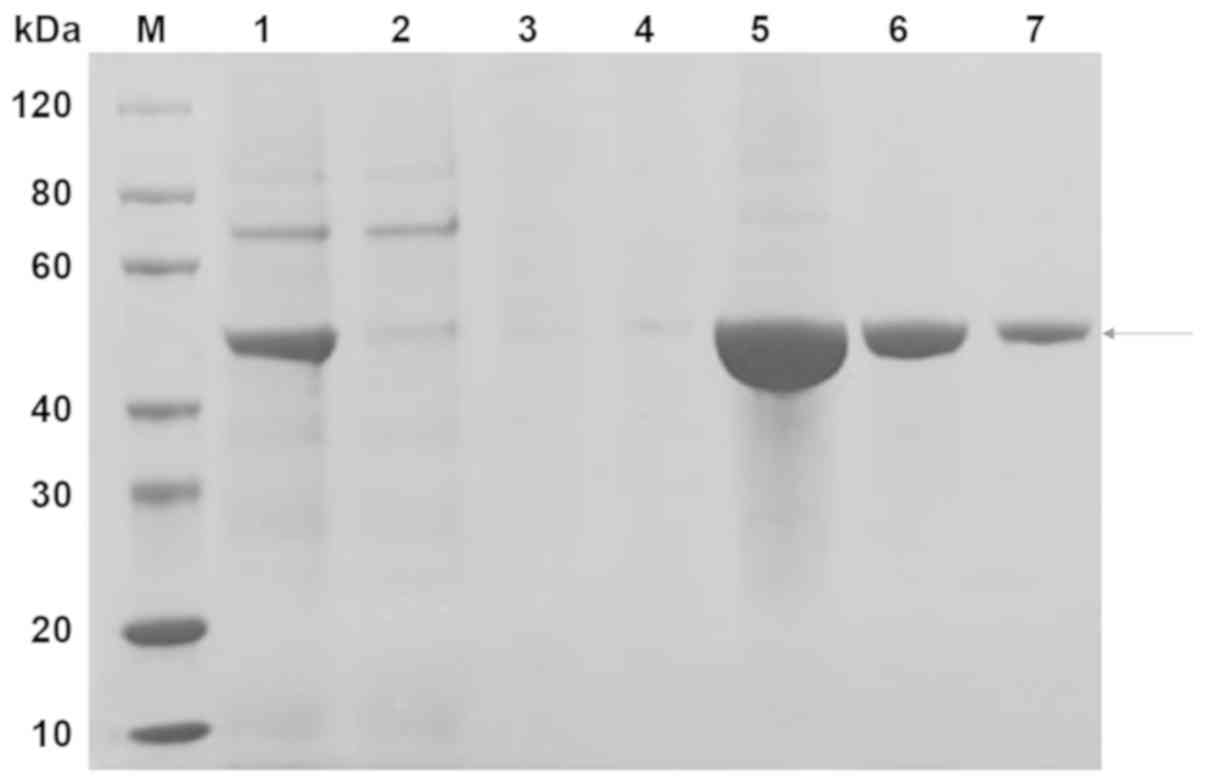
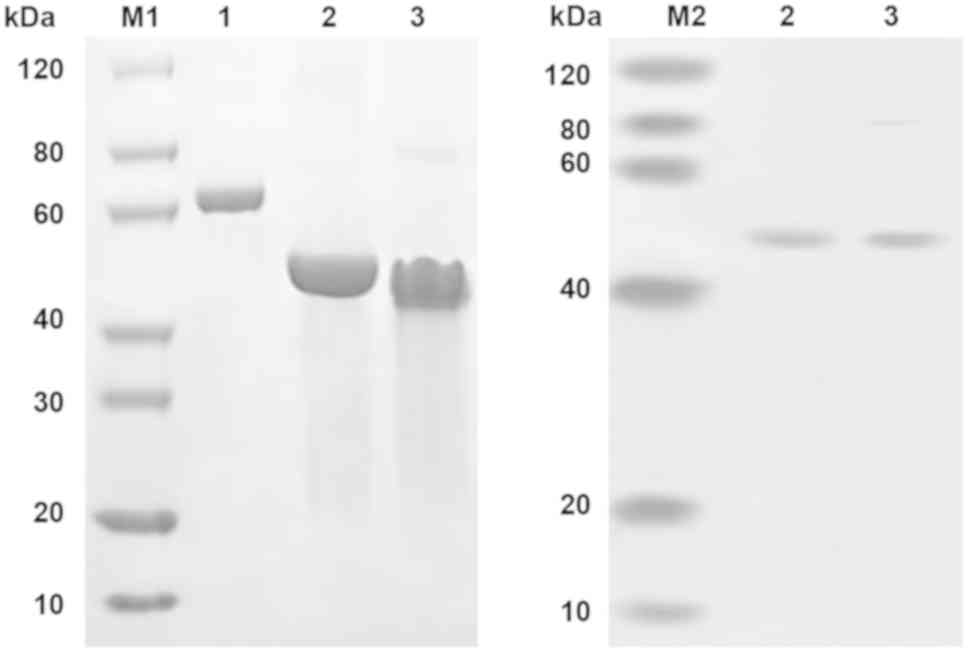
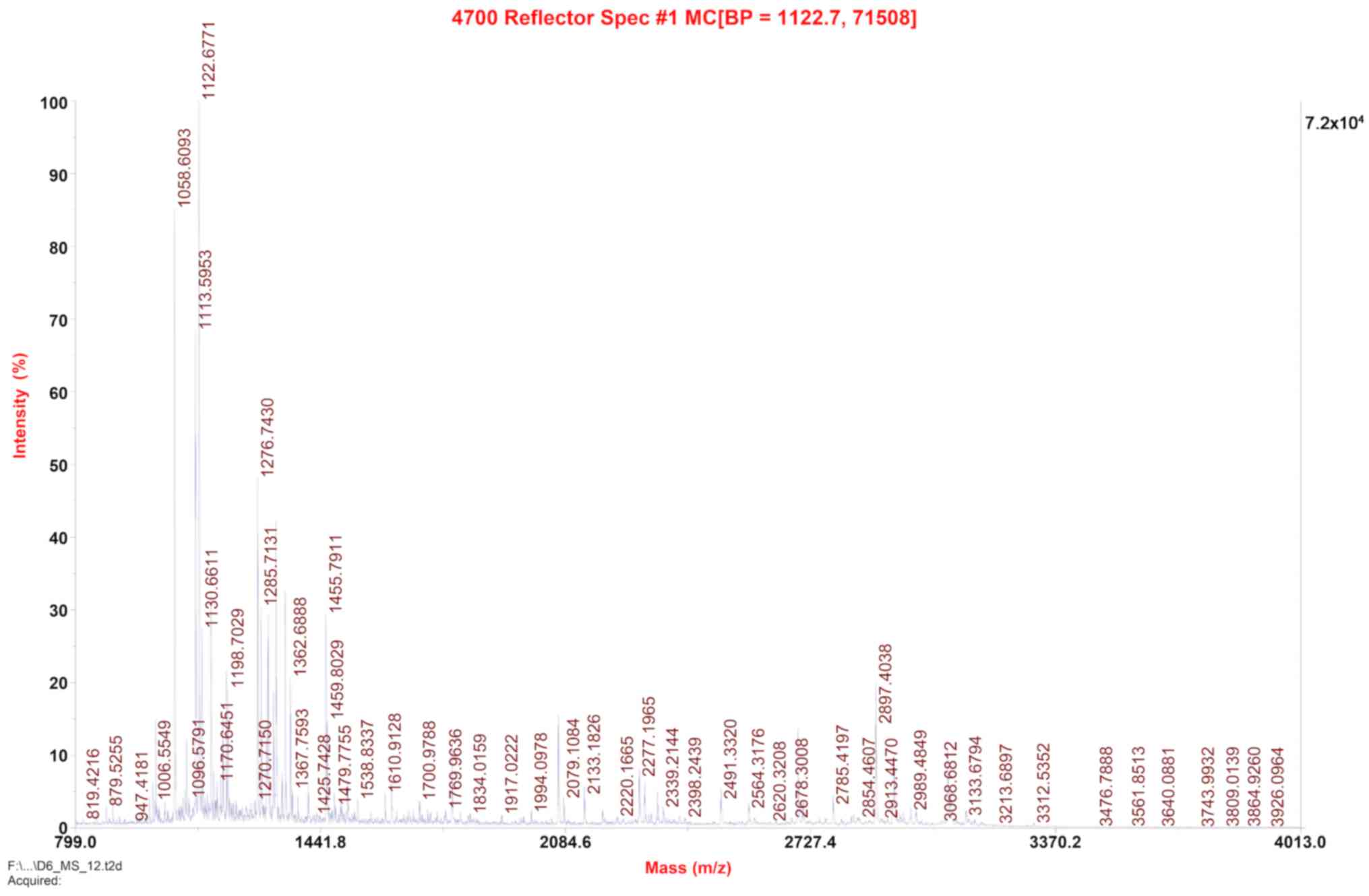
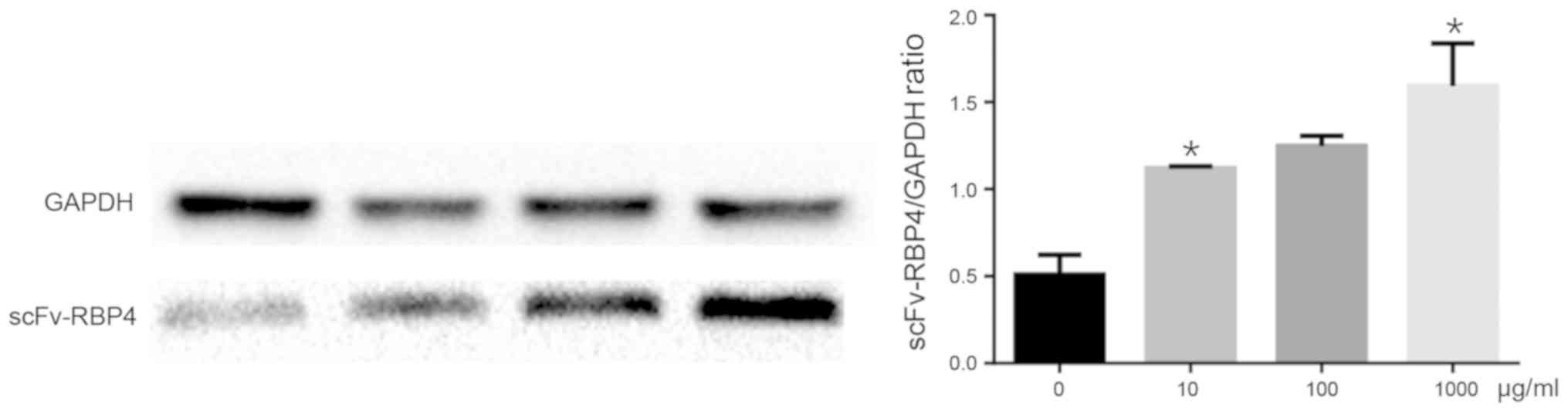
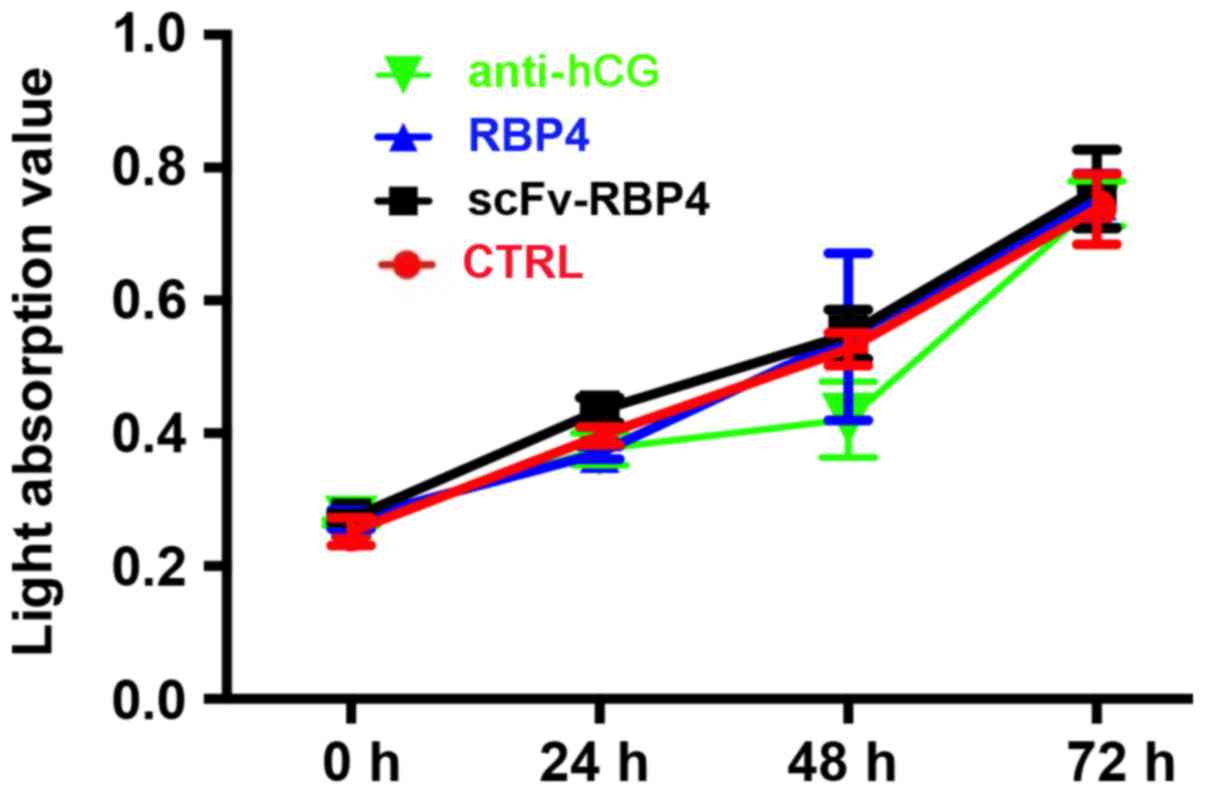
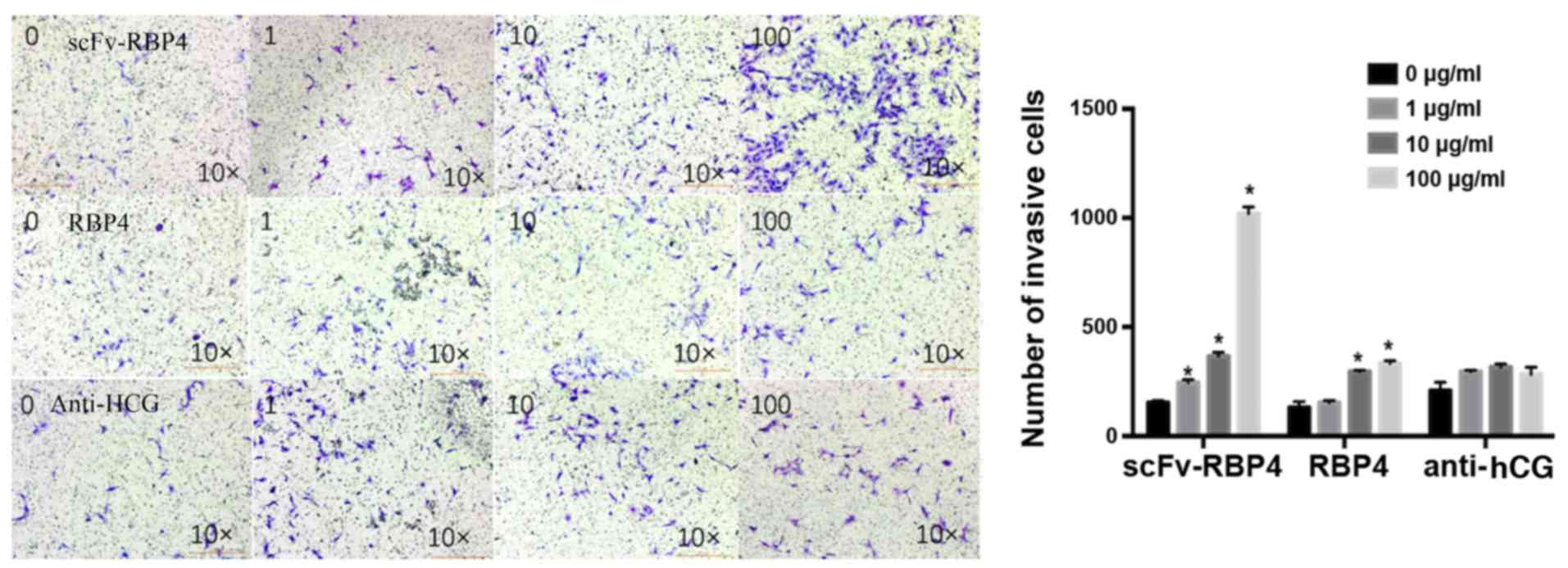
|
1
|
Poon LC and Nicolaides KH: Early
prediction of preeclampsia. Obstet Gynecol Int. 2014:2973972014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Redman CW and Sargent IL: Latest advances
in understanding preeclampsia. Science. 308:1592–1594. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rana S, Lemoine E, Granger J and
Karumanchi SA: Preeclampsia. Circ Res. 124:1094–1112. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ball E, Bulmer JN, Ayis S, Lyall F and
Robson SC: Late sporadic miscarriage is associated with
abnormalities in spiral artery transformation and trophoblast
invasion. J Pathol. 208:535–542. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Goldman-Wohl D and Yagel S: Regulation of
trophoblast invasion: From normal implantation to pre-eclampsia.
Mol Cell Endocrinol. 187:233–238. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zanotti G and Berni R: Plasma
retinol-binding protein: Structure and interactions with retinol,
retinoids, and transthyretin. Vitam Horm. 69:271–295. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Christou GA, Tselepis AD and Kiortsis DN:
The metabolic role of retinol binding protein 4: An update. Horm
Metab Res. 44:6–14. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kotnik P, Fischer-Posovszky P and Wabitsch
M: RBP4: A controversial adipokine. Eur J Endocrinol. 165:703–711.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Grönwall C and Ståhl S: Engineered
affinity proteins-generation and applications. J Biotechnol.
140:254–269. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Uzan J, Carbonnel M, Piconne O, Asmar R
and Ayoubi JM: Pre-eclampsia: Pathophysiology, diagnosis, and
management. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 7:467–474. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
North RA, Ferrier C, Long D, Townend K and
Kincaid-Smith P: Uterine artery Doppler flow velocity waveforms in
the second trimester for the prediction of preeclampsia and fetal
growth retardation. Obstet Gynecol. 83:378–386. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Meekins JW, Pijnenborg R, Hanssens M,
McFadyen IR and van Asshe A: A study of placental bed spiral
arteries and trophoblast invasion in normal and severe
pre-eclamptic pregnancies. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 101:669–674. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sibai B, Dekker G and Kupferminc M:
Pre-eclampsia. Lancet. 365:785–799. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang A, Rana S and Karumanchi SA:
Preeclampsia: The role of angiogenic factors in its pathogenesis.
Physiology (Bethesda). 24:147–158. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Meads CA, Cnossen JS, Meher S,
Juarez-Garcia A, ter Riet G, Duley L, Roberts TE, Mol BW van der
Post JA, Leeflang MM, et al: Methods of prediction and prevention
of pre-eclampsia: Systematic reviews of accuracy and effectiveness
literature with economic modelling. Health Technol Assess.
12:iii–iv, 1-270. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Schroeder BM; American College of
Obstetricians Gynecologists, : ACOG practice bulletin on diagnosing
and managing preeclampsia and eclampsia. American College of
Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Am Fam Physician. 66:330–331.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Laginha KM, Moase EH, Yu N, Huang A and
Allen TM: Bioavailability and therapeutic efficacy of HER2
scFv-targeted liposomal doxorubicin in a murine model of
HER2-overexpressing breast cancer. J Drug Target. 16:605–610. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yang Q, Graham TE, Mody N, Preitner F,
Peroni OD, Zabolotny JM, Kotani K, Quadro L and Kahn BB: Serum
retinol binding protein 4 contributes to insulin resistance in
obesity and type 2 diabetes. Nature. 436:356–362. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen CH, Hsieh TJ, Lin KD, Lin HY, Lee MY,
Hung WW, Hsiao PJ and Shin SJ: Increased unbound retinol-binding
protein 4 concentration induces apoptosis through receptor-mediated
signaling. J Biol Chem. 287:9694–9707. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lu Q, Liu C, Liu Y, Zhang N, Deng H and
Zhang Z: Serum markers of pre-eclampsia identified on proteomics. J
Obstet Gynaecol Res. 42:1111–1118. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|