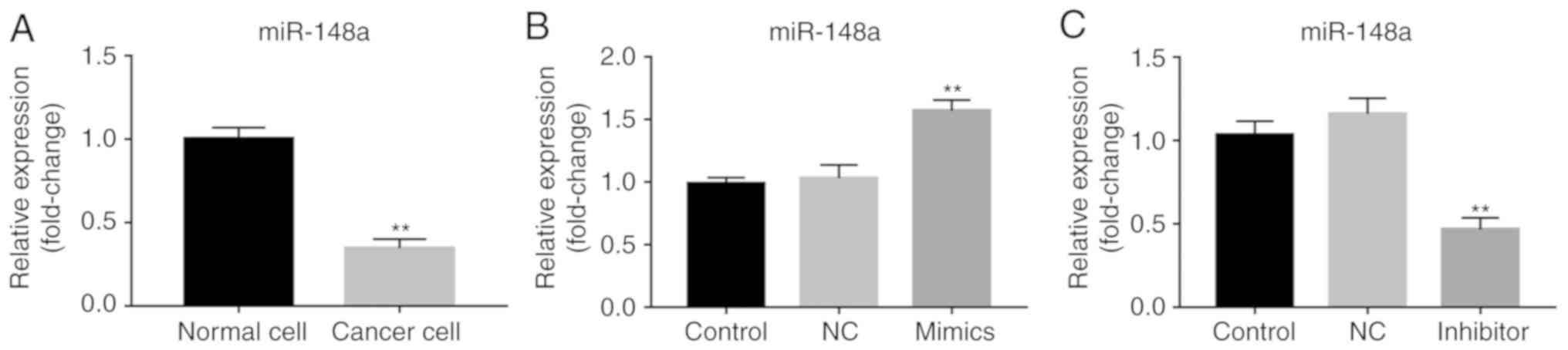
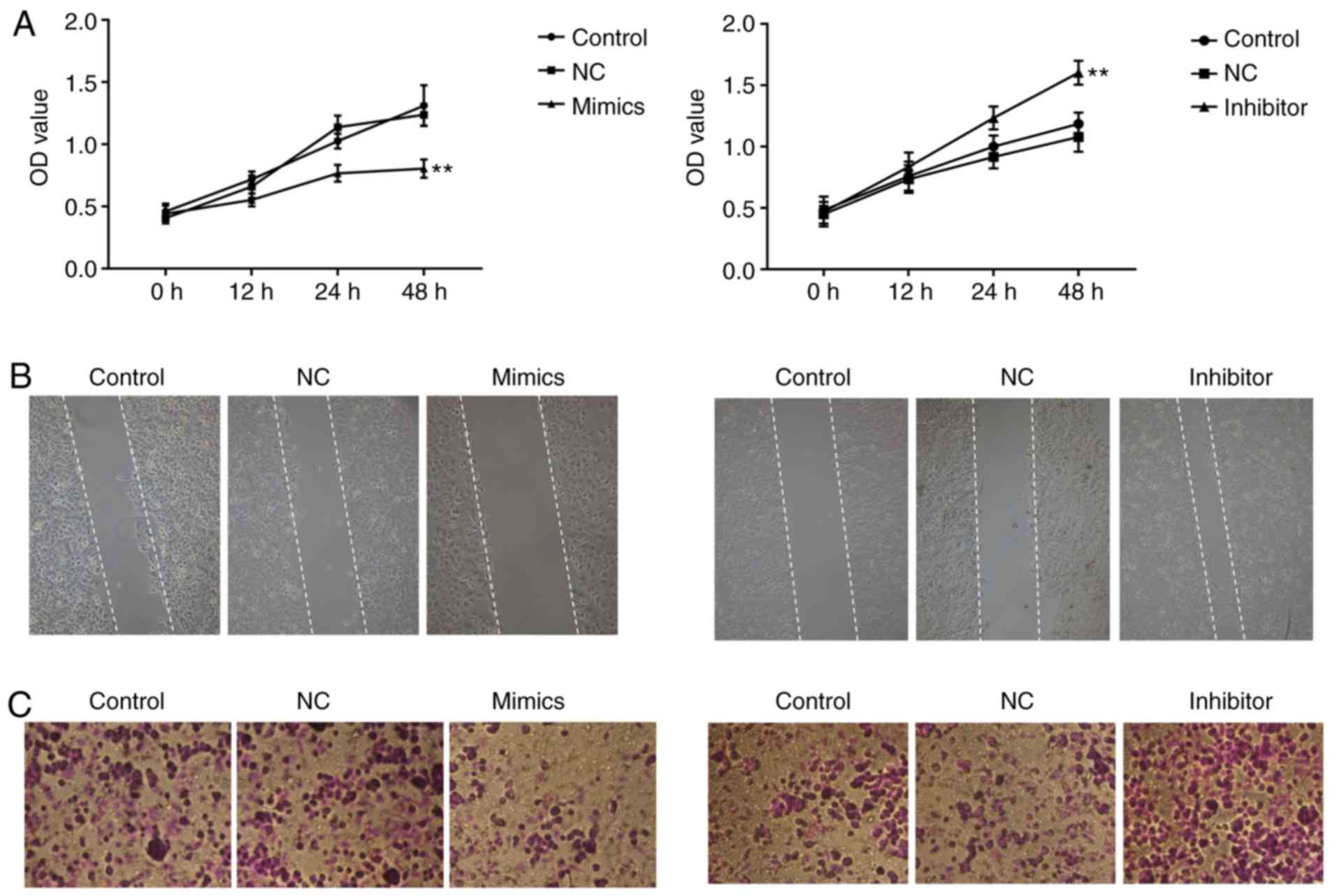
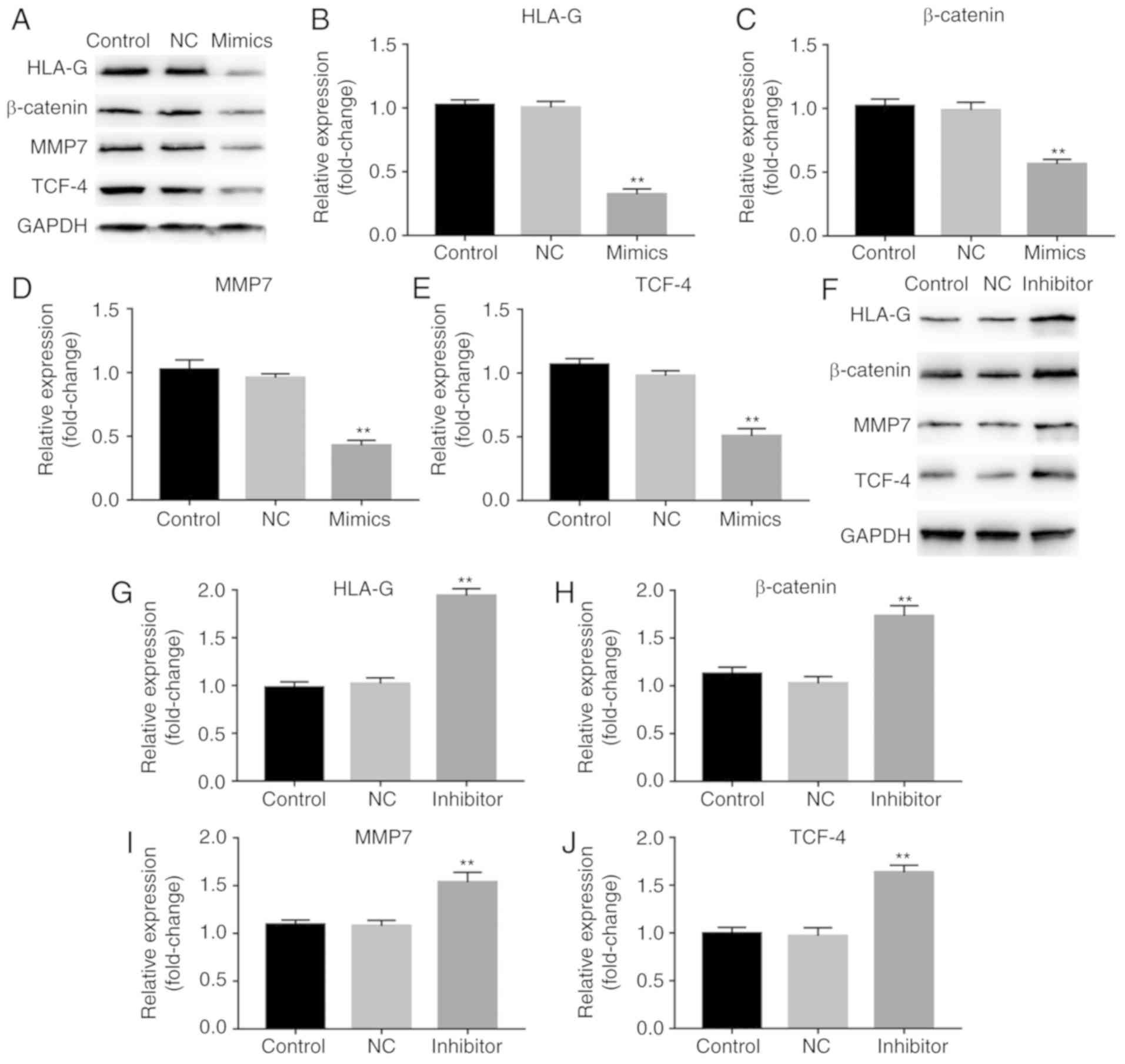
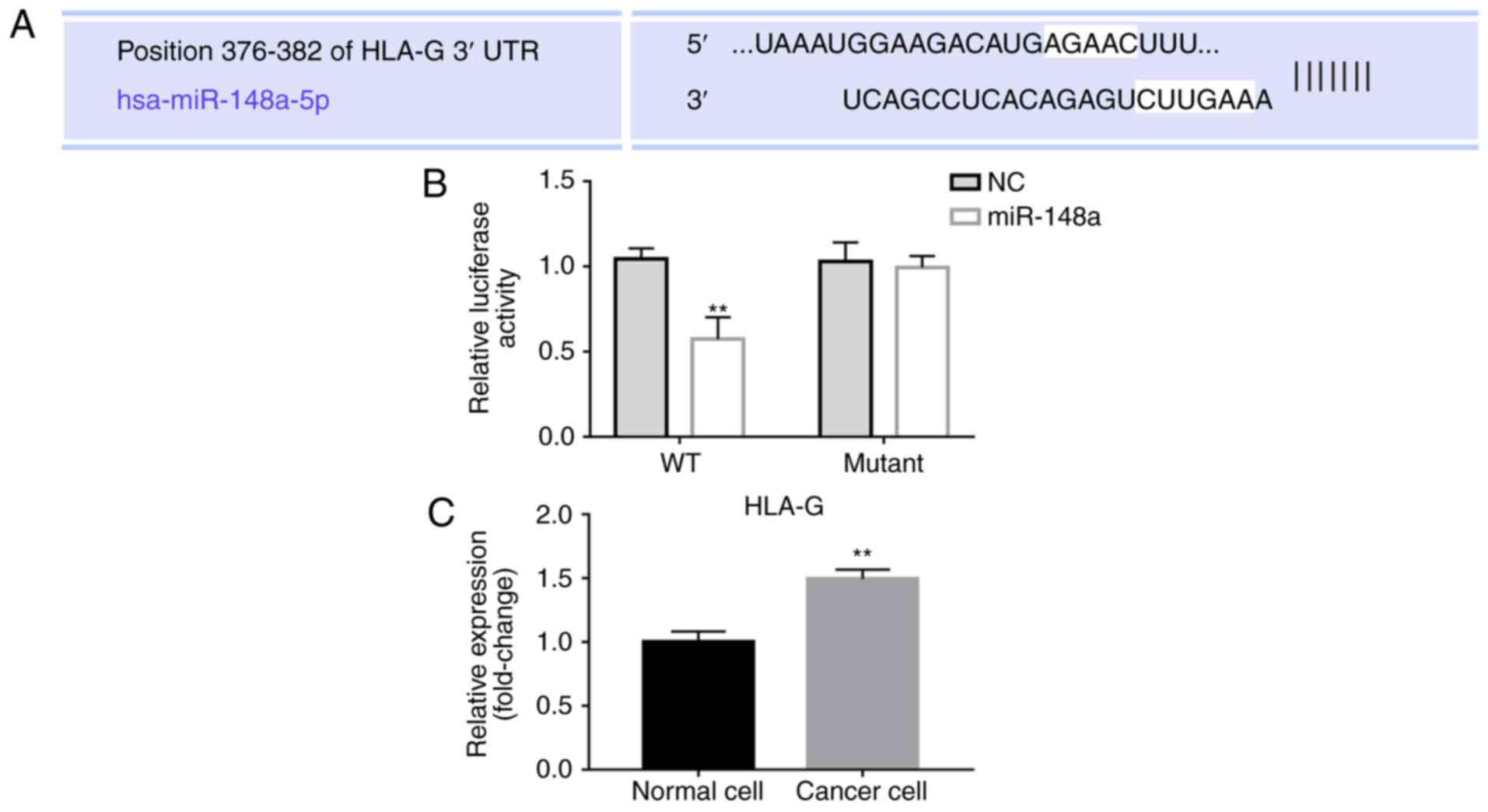
|
1
|
Tang H, Wu Z, Zhang J and Su B: Salivary
lncRNA as a potential marker for oral squamous cell carcinoma
diagnosis. Mol Med Rep. 7:761–766. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhao E, Xu J, Yin X, Sun Y, Shi J and Li
X: Detection of deregulated pathways to lymphatic metastasis in
oral squamous cell carcinoma. Pathol Oncol Res. 15:217–223. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Singh P, Barpande SR, Bhavthankar JD,
Mandale MS and Bhagwat AU: Serum Cyfra 21-1 levels in oral squamous
cell carcinoma patients and its clinicopathologic correlation.
Indian J Dent Res. 28:162–168. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jerjes W, Upile T, Petrie A, Riskalla A,
Hamdoon Z, Vourvachis M, Karavidas K, Jay A, Sandison A, Thomas GJ,
et al: Clinicopathological parameters, recurrence, locoregional and
distant metastasis in 115 T1-T2 oral squamous cell carcinoma
patients. Head Neck Oncol. 2:92010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rich A, Hussaini H, Parachuru P and
Seymour G: The tumour microenvironment in oral squamous cell
carcinoma. Pathology. 46 (Suppl 1):S92014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Kato K, Hara A, Kuno T, Kitaori N, Huilan
Z, Mori H, Toida M and Shibata T: Matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9
in oral squamous cell carcinomas: Manifestation and localization of
their activity. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 131:340–346. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shahrabi S, Hadad EH, Asnafi AA, Behzad
MM, Ehsanpour A and Saki N: Human leukocyte antigens in cancer
metastasis: Prognostic approach and therapeutic susceptibility.
Histol Histopathol. 34:111–124. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Alizadeh N, Mosaferi E, Farzadi L, Majidi
J, Monfaredan A, Yousefi B and Baradaran B: Frequency of null
allele of human leukocyte antigen-G (HLA-G) locus in subjects to
recurrent miscarriage. Int J Reprod Biomed (Yazd). 14:459–464.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yie SM, Li LH, Xiao R and Librach CL: A
single base-pair mutation in the 3′-untranslated region of HLA-G
mRNA is associated with pre-eclampsia. Mol Hum Reprod. 14:649–653.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ferreira LM, Meissner TB, Tilburgs T and
Strominger JL: HLA-G: At the interface of maternal-fetal tolerance.
Trends Immunol. 38:272–286. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bian X, Si Y, Zhang M, Wei R, Yang X, Ren
H, Zheng G, Wang C and Zhang Y: Down-expression of miR-152 lead to
impaired anti-tumor effect of NK via upregulation of HLA-G. Tumour
Biol. 37:3749–3756. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Costa CH, Gelmini GF, Nardi FS, Roxo VM,
Schuffner A and da Graça Bicalho M: HLA-G profile of infertile
couples who underwent assisted reproduction treatment. Hum Immunol.
77:1179–1186. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lazarte J, Adamson MB, Tumiati LC and
Delgado DH: 10-year experience with HLA-G in heart transplantation.
Hum Immunol. 79:587–593. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Beneventi F, Badulli C, Locatelli E,
Caporali R, Ramoni V, Cavagnoli C, Simonetta M, Garbin G, Tinelli
C, Alpini C, et al: Soluble HLA-G in pregnancies complicated by
autoimmune rheumatic diseases. J Reprod Immunol. 110:67–73. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Seliger B: Role of microRNAs on HLA-G
expression in human tumors. Hum Immunol. 77:760–763. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li X, Liu F, Lin B, Luo H, Liu M, Wu J, Li
C, Li R, Zhang X, Zhou K and Ren D: miR-150 inhibits proliferation
and tumorigenicity via retarding G1/S phase transition in
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 50:1097–1108. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
17
|
Ro S, Park C, Young D, Sanders KM and Yan
W: Tissue-dependent paired expression of miRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res.
35:5944–5953. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mallory AC and Vaucheret H: MicroRNAs:
Something important between the genes. Curr Opin Plant Biol.
7:120–125. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Garzon R, Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNAs
in cancer. Annu Rev Med. 60:167–179. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhou X, Zhao F, Wang ZN, Song YX, Chang H,
Chiang Y and Xu HM: Altered expression of miR-152 and miR-148a in
ovarian cancer is related to cell proliferation. Oncol Rep.
27:447–454. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yang JS, Li BJ, Lu HW, Chen Y, Lu C, Zhu
RX, Liu SH, Yi QT, Li J and Song CH: Serum miR-152, miR-148a,
miR-148b, and miR-21 as novel biomarkers in non-small cell lung
cancer screening. Tumour Biol. 36:3035–3042. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen Q, Luo G and Zhang X: MiR-148a
modulates HLA-G expression and influences tumor apoptosis in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Exp Ther Med. 14:4448–4452.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sun J, Chu H, Ji J, Huo G, Song Q and
Zhang X: Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR modulates HLA-G expression by
absorbing miR-148a in human cervical cancer. Int J Oncol.
49:943–952. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tao S, He H, Chen Q and Yeu W: GPER
mediated estradiol reduces miR-148a to promote HLA-G expression in
breast cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 451:74–78. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Imani R, Seyedmajidi M, Ghasemi N, Moslemi
D, Shafaee S and Bijani A: HLA-G expression is associated with an
unfavorable prognosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Asian Pac J
Cancer Prev. 19:2527–2533. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gonçalves AS, Wastowski IJ, Capeletti LR,
Sacono NT, Cortez AP, Valadares MC, Silva TA and Batista AC: The
clinicopathologic significance of the expression of HLA-G in oral
squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral
Radiol. 117:361–368. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cui Z, Liu G and Kong D: miRNA-27a
promotes the proliferation and inhibits apoptosis of human
pancreatic cancer cells by Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Oncol Rep.
39:755–763. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mo D, Yang D, Xiao X, Sun R, Huang L and
Xu J: MiRNA-145 suppresses lung adenocarcinoma cell invasion and
migration by targeting N-cadherin. Biotechnol Lett. 39:701–710.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Liu F, Zhang G, Lv S, Wen X and Liu P:
miRNA-301b-3p accelerates migration and invasion of high-grade
ovarian serous tumor via targeting CPEB3/EGFR axis. J Cell Biochem.
Mar 4–2019.(Epub ahead of print). doi: 10.1002/jcb.28528.
|
|
31
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:857–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Esquela-Kerscher A and Slack FJ:
Oncomirs-microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
6:259–269. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kent OA and Mendell JT: A small piece in
the cancer puzzle: microRNAs as tumor suppressors and oncogenes.
Oncogene. 25:6188–6196. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chang KW, Kao SY, Wu YH, Tsai MM, Tu HF,
Liu CJ, Lui MT and Lin SC: Passenger strand miRNA miR-31* regulates
the phenotypes of oral cancer cells by targeting RhoA. Oral Oncol.
49:27–33. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chawla JP, Iyer N, Soodan KS, Sharma A,
Khurana SK and Priyadarshni P: Role of miRNA in cancer diagnosis,
prognosis, therapy and regulation of its expression by Epstein-Barr
virus and human papillomaviruses: With special reference to oral
cancer. Oral Oncol. 51:731–737. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ren Y, Zhu H, Chi C, Yang F and Xu X:
MiRNA-139 regulates oral cancer Tca8113 cells apoptosis through Akt
signaling pathway. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:4588–4594.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang F, Jiang C, Sun Q, Yan F, Wang L, Fu
Z, Liu T and Hu F: miR-195 is a key regulator of Raf1 in thyroid
cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 8:3021–3028. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wang M, Zhang J, Tong L, Ma X and Qiu X:
MiR-195 is a key negative regulator of hepatocellular carcinoma
metastasis by targeting FGF2 and VEGFA. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
8:14110–14120. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yilaz Susluer S, Biray Avci C, Dodurga Y,
Ozlem Dogan Sigva Z, Oktar N and Gunduz C: Downregulation of
miR-195 via cyclosporin A in human glioblastoma cells. J BUON.
20:1337–1340. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Li L, Li C, Wang S, Wang Z, Jiang J, Wang
W, Li X, Chen J, Liu K, Li C and Zhu G: Exosomes derived from
hypoxic oral squamous cell carcinoma cells deliver miR-21 to
normoxic cells to elicit a prometastatic phenotype. Cancer Res.
76:1770–1780. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
He S, Lai R, Chen D, Yan W, Zhang Z, Liu
Z, Ding X and Chen Y: Downregulation of miR-221 inhibits cell
migration and invasion through targeting methyl-CpG binding domain
protein 2 in human oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. Biomed Res
Int. 2015:7516722015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Cheng CM, Shiah SG, Huang CC, Hsiao JR and
Chang JY: Up-regulation of miR-455-5p by the TGF-β-SMAD signalling
axis promotes the proliferation of oral squamous cancer cells by
targeting UBE2B. J Pathol. 240:38–49. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhang H, Li Y, Huang Q, Ren X, Hu H, Sheng
H and Lai M: MiR-148a promotes apoptosis by targeting Bcl-2 in
colorectal cancer. Cell Death Differ. 18:1702–1710. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Lagos-Quintana M, Rauhut R, Lendeckel W
and Tuschl T: Identification of novel genes coding for small
expressed RNAs. Science. 294:853–858. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Liu H, Liu X, Jin H, Yang F, Gu W and Li
X: Proteomic analysis of knock-down HLA-G in invasion of human
trophoblast cell line JEG-3. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 6:2451–2459.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Rouas-Freiss N, Moreau P, Ferrone S and
Carosella ED: HLA-G proteins in cancer: Do they provide tumor cells
with an escape mechanism? Cancer Res. 65:10139–10144. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Tripathi P and Agrawal S: Non-classical
HLA-G antigen and its role in the cancer progression. Cancer
Invest. 24:178–186. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|