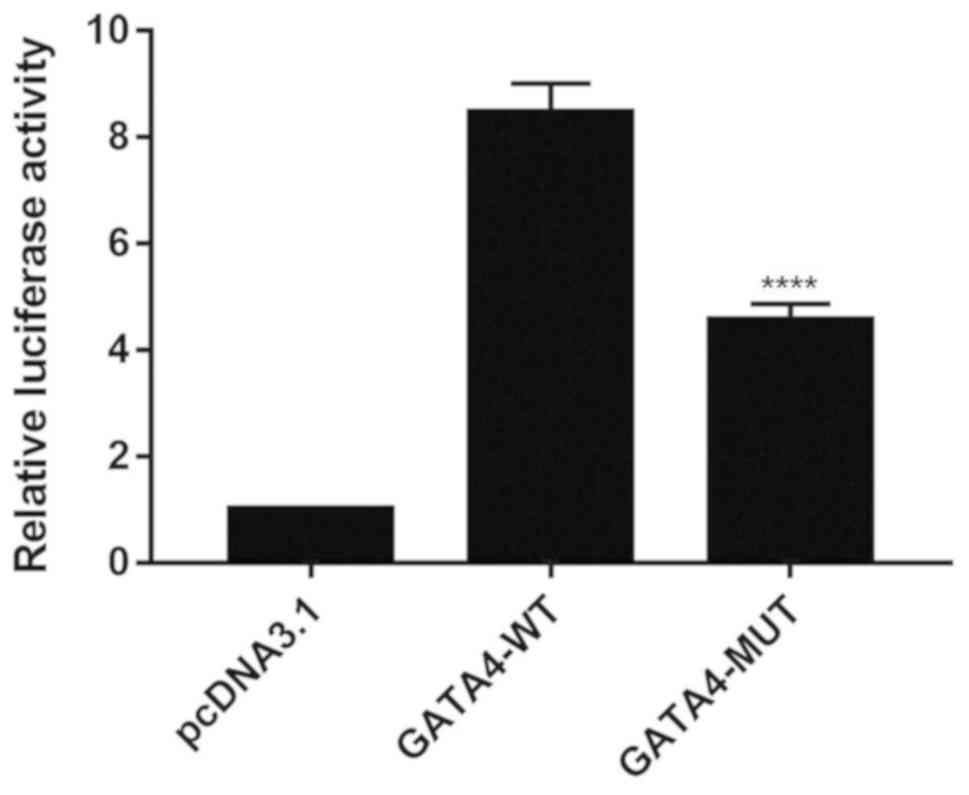
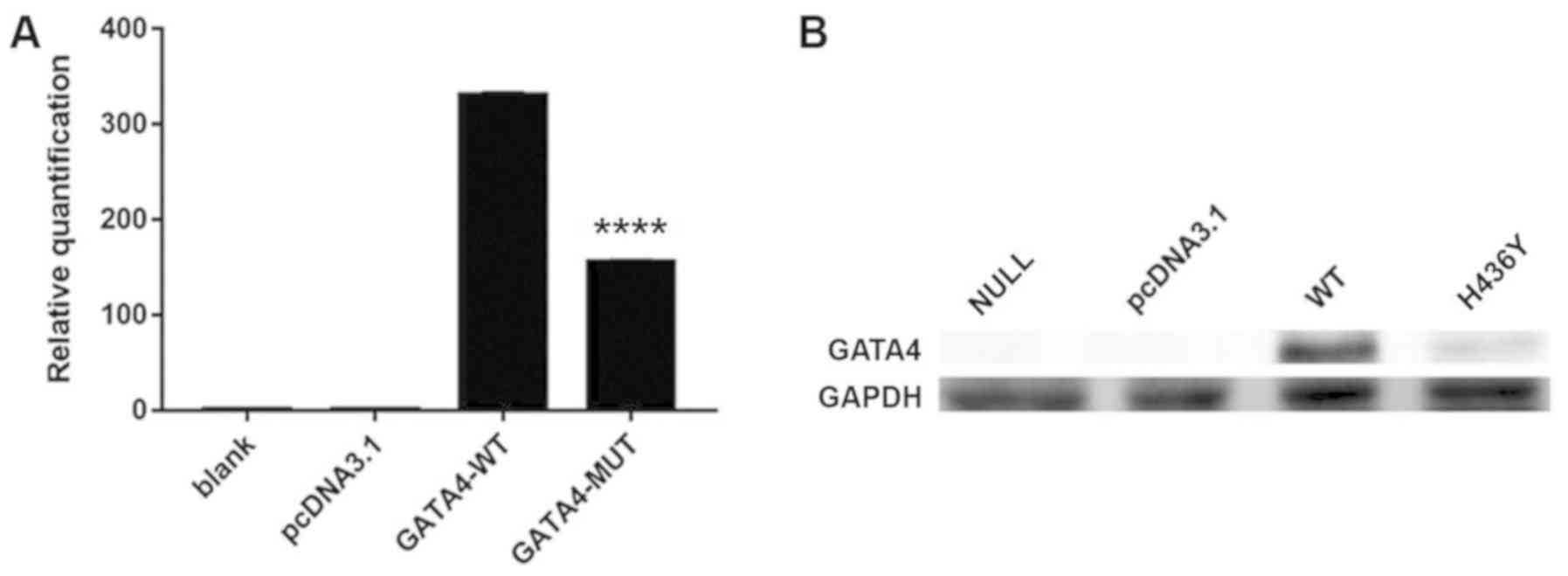
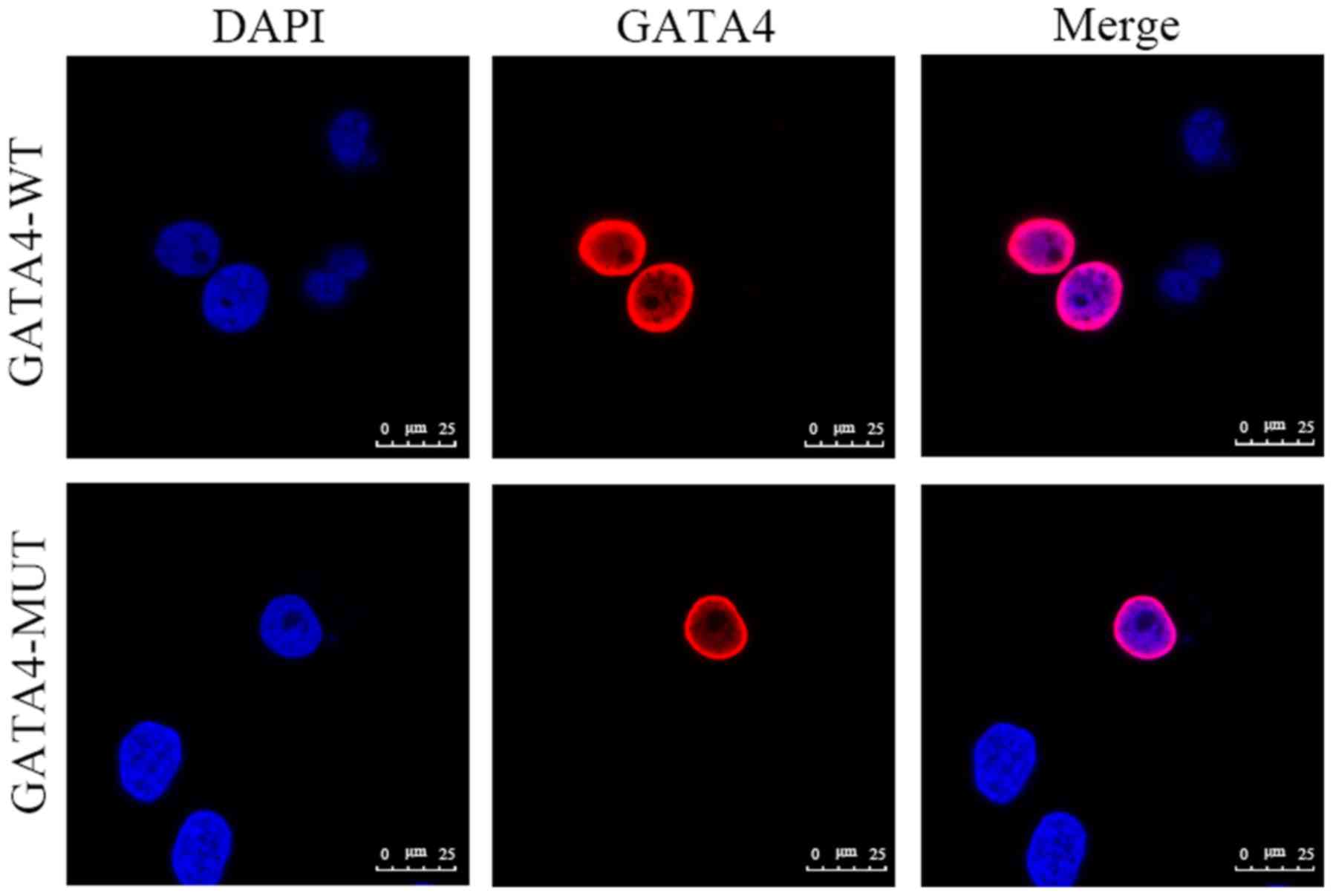
|
1
|
Zhao QM, Liu F, Wu L, Ma XJ, Niu C and
Huang GY: Prevalence of congenital heart disease at live birth in
China. J Pediatr. 204:53–58. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
van der Linde D, Konings EE, Slager MA,
Witsenburg M, Helbing WA, Takkenberg JJ and Roos-Hesselink JW:
Birth prevalence of congenital heart disease worldwide a systematic
review and meta-analysis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 58:2241–2247. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yu Z, Xi Y, Ding W, Han S, Cao L, Zhu C,
Wang X and Guo X: Congenital heart disease in a Chinese hospital:
Pre- and postnatal detection, incidence, clinical characteristics
and outcomes. Pediatr Int. 53:1059–1065. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Miranović V: The incidence of congenital
heart disease: Previous findings and perspectives. Srp Arh Celok
Lek. 142:243–248. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Marian AJ: Congenital heart disease the
remarkable journey from the ‘post-mortem room’ to adult clinics.
Circ Res. 120:895–897. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Srivastava D and Olson EN: A genetic
blueprint for cardiac development. Nature. 407:221–226. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yang YQ, Gharibeh L, Li RG, Xin YF, Wang
J, Liu ZM, Qiu XB, Xu YJ, Xu L, Qu XK, et al: GATA4
loss-of-function mutations underlie familial tetralogy of fallot.
Hum Mutat. 34:1662–1671. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Andersen TA, Troelsen Kde L and Larsen LA:
Of mice and men: Molecular genetics of congenital heart disease.
Cell Mol Life Sci. 71:1327–1352. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang X, Li P, Chen S, Xi L, Guo Y, Guo A
and Sun K: Influence of genes and the environment in familial
congenital heart defects. Mol Med Rep. 9:695–700. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Qu XK, Qiu XB, Yuan F, Wang J, Zhao CM,
Liu XY, Zhang XL, Li RG, Xu YJ, Hou XM, et al: A novel NKX2.5
loss-of-function mutation associated with congenital bicuspid
aortic valve. Am J Cardiol. 114:1891–1895. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
McCulley DJ and Black BL: Transcription
factor pathways and congenital heart disease. Curr Top Dev Biol.
100:253–277. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dai YS, Cserjesi P, Markham BE and
Molkentin JD: The transcription factors GATA4 and dHAND physically
interact to synergistically activate cardiac gene expression
through a p300-dependent mechanism. J Biol Chem. 277:24390–24398.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Molkentin JD, Kalvakolanu DV and Markham
BE: Transcription factor GATA-4 regulates cardiac muscle-specific
expression of the alpha-myosin heavy-chain gene. Mol Cell Biol.
14:4947–4957. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pikkarainen S, Tokola H, Kerkelä R and
Ruskoaho H: GATA transcription factors in the developing and adult
heart. Cardiovasc Res. 63:196–207. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Misra C, Sachan N, McNally CR, Koenig SN,
Nichols HA, Guggilam A, Lucchesi PA, Pu WT, Srivastava D and Garg
V: Congenital heart disease-causing Gata4 mutation displays
functional deficits in vivo. PLoS Genet. 8:e10026902012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Epstein JA and Parmacek MS: Recent
advances in cardiac development with therapeutic implications for
adult cardiovascular disease. Circulation. 112:592–597. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang H, Chen M, Fang T, Zhang T and Ni W:
Establishment and verification of a mouse model of Gata4 gene H435Y
mutation. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 38:1245–1249. 2018.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen MW, Pang YS, Guo Y, Pan JH, Liu BL,
Shen J and Liu TW: GATA4 mutations in Chinese patients with
congenital cardiac septal defects. Pediatr Cardiol. 31:85–89. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kaetzke A and Eschrich K: Simultaneous
determination of different DNA sequences by mass spectrometric
evaluation of Sanger sequencing reactions. Nucleic Acids Res.
30:e1172002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Seidman CE, Wong DW, Jarcho JA, Bloch KD
and Seidman JG: Cis-acting sequences that modulate atrial
natriuretic factor gene-expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
85:4104–4108. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sprenkle AB, Murray SF and Glembotski CC:
Involvement of multiple cis-elements in basal-inducible and
alpha-adrenergic agonist-inducible atrial-natriuretic-factor
transcription-roles for serum response elements and an sp-1-like
element. Circ Res. 77:1060–1069. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
McFadden DG, Charite J, Richardson JA,
Srivastava D, Firulli AB and Olson EN: A GATA-dependent right
ventricular enhancer controls dHAND transcription in the developing
heart. Development. 127:5331–5341. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Garg V, Kathiriya IS, Barnes R,
Schluterman MK, King IN, Butler CA, Rothrock CR, Eapen RS,
Hirayama-Yamada K, Joo K, et al: GATA4 mutations cause human
congenital heart defects and reveal an interaction with TBX5.
Nature. 424:443–447. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang E, Sun S, Qiao B, Duan W, Huang G, An
Y, Xu S, Zheng Y, Su Z, Gu X, et al: Identification of functional
mutations in GATA4 in patients with congenital heart disease. PLoS
One. 8:e621382013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
White RA, Dowler LL, Pasztor LM, Gatson
LL, Adkison LR, Angeloni SV and Wilson DB: Assignment of the
transcription factor gata4 gene to human-chromosome-8 and mouse
chromosome-14-GATA4 is a candidate gene for ds (disorganization).
Genomics. 27:20–26. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang X, Wang J, Wang B, Chen S, Fu Q and
Sun K: A novel missense mutation of GATA4 in a chinese family with
congenital heart disease. PLoS One. 11:e01589042016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chen J, Qi B, Zhao J, Liu W, Duan R and
Zhang M: A novel mutation of GATA4 (K300T) associated with familial
atrial septal defect. Gene. 575:473–477. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Heineke J, Auger-Messier M, Xu J, Oka T,
Sargent MA, York A, Klevitsky R, Vaikunth S, Duncan SA, Aronow BJ,
et al: Cardiomyocyte GATA4 functions as a stress-responsive
regulator of angiogenesis in the murine heart. J Clin Invest.
117:3198–3210. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Morrisey EE, Ip HS, Tang Z and Parmacek
MS: GATA-4 activates transcription via two novel domains that are
conserved within the GATA-4/5/6 subfamily. J Biol Chem.
272:8515–8524. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Nemer G, Fadlalah F, Usta J, Nemer M,
Dbaibo G, Obeid M and Bitar F: A novel mutation in the GATA4 gene
in patients with tetralogy of fallot. Hum Mutat. 27:293–294. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chen Y, Mao J, Sun Y, Zhang Q, Cheng HB,
Yan WH, Choy KW and Li H: A novel mutation of GATA4 in a familial
atrial septal defect. Clin Chim Acta. 411:1741–1745. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Moreau JLM, Kesteven S, Martin EMMA, Lau
KS, Yam MX, O'Reilly VC, Del Monte-Nieto G, Baldini A, Feneley MP,
Moon AM, et al: Gene-environment interaction impacts on heart
development and embryo survival. Development. 146:dev1729572019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Thomford NE, Dzobo K, Yao NA, Chimusa E,
Evans J, Okai E, Kruszka P, Muenke M, Awandare G, Wonkam A and
Dandara C: Genomics and epigenomics of congenital heart defects:
Expert review and lessons learned in Africa. OMICS. 22:301–321.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|