|
1
|
Ogurtsova K, da Rocha Fernandes JD, Huang
Y, Linnenkamp U, Guariguata L, Cho NH, Cavan D, Shaw JE and
Makaroff LE: IDF diabetes atlas: Global estimates for the
prevalence of diabetes for 2015 and 2040. Diabetes Res Clin Pract.
128:40–50. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
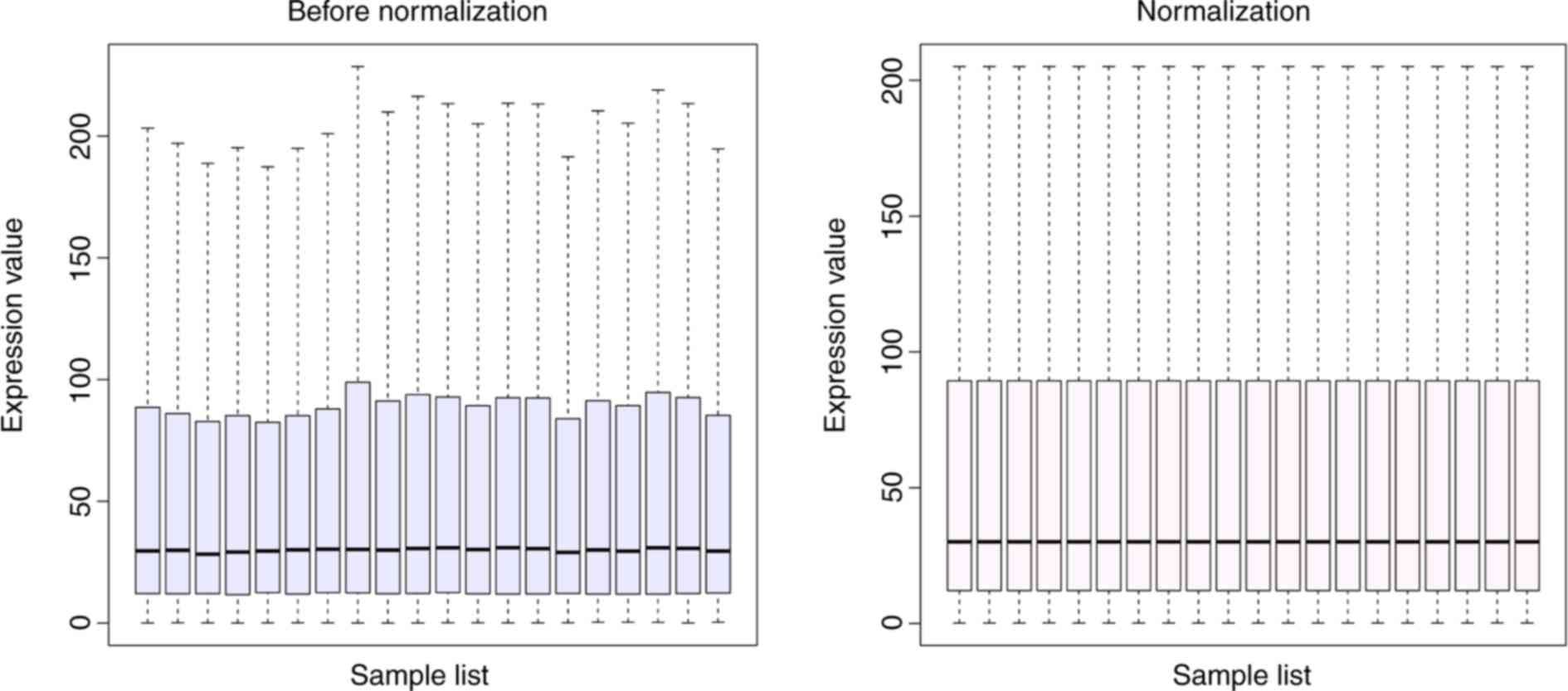
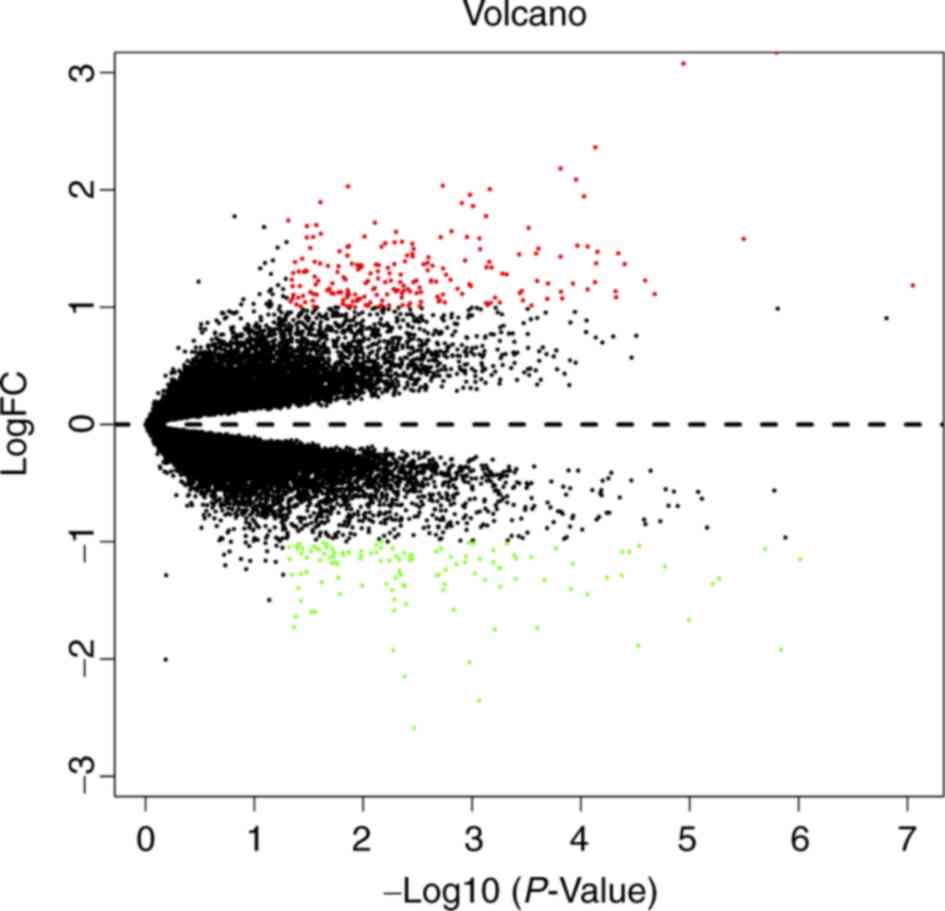
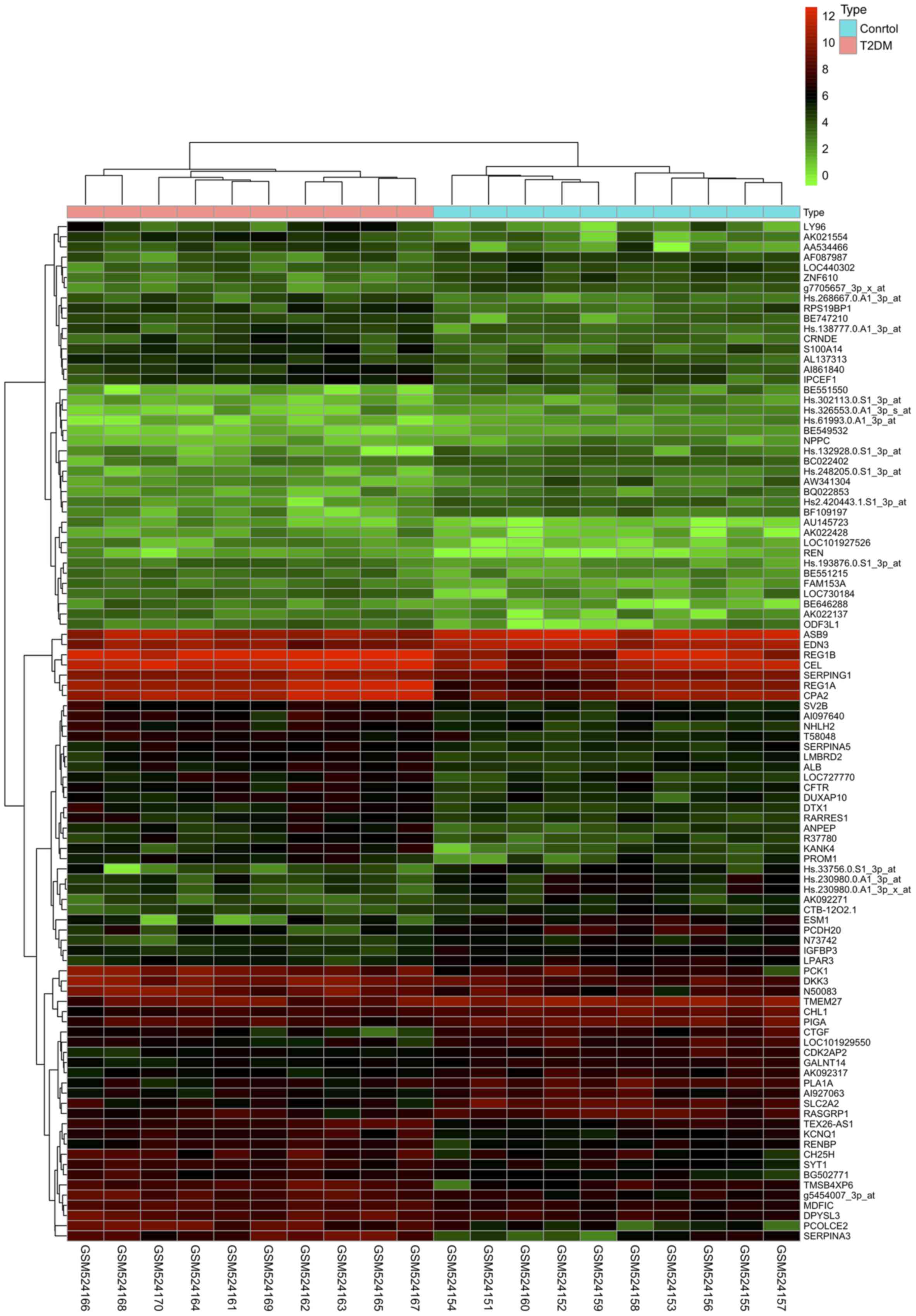
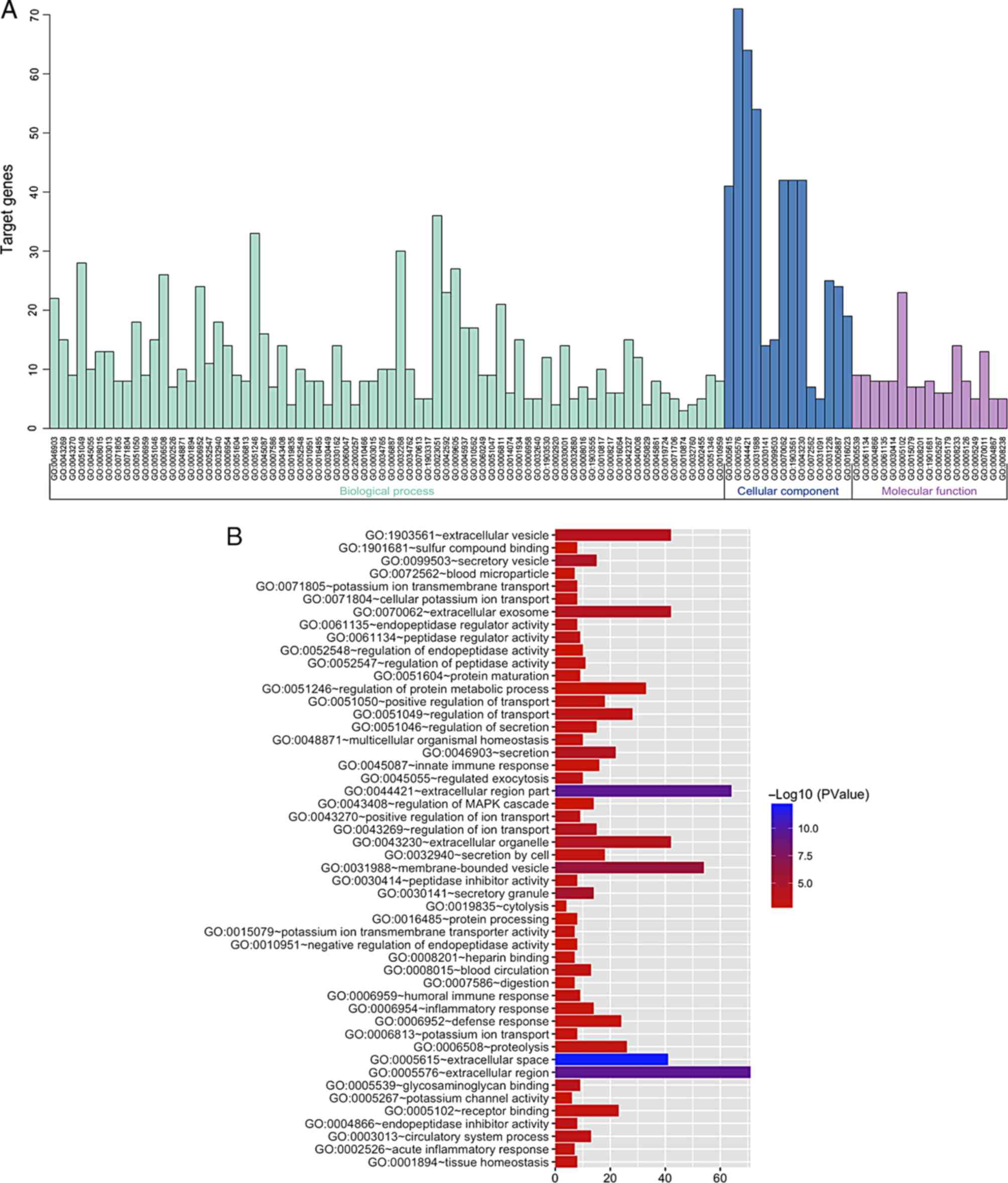
|
2
|
Zhao Q, Zhang A, Zong W, An N, Zhang H,
Luan Y, Sun H, Wang X and Cao H: Exploring potential biomarkers and
determining the metabolic mechanism of type 2 diabetes mellitus
using liquid chromatography coupled to high-resolution mass
spectrometry. RSC Adv. 7:441862017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Leibowitz G, Kaiser N and Cerasi E:
Balancing needs and means: The dilemma of the beta-cell in the
modern world. Diabetes Obes Metab. 11 (Suppl 4):S1–S9. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Hoshino A, Ariyoshi M, Okawa Y, Kaimoto S,
Uchihashi M, Fukai K, Iwai-Kanai E, Ikeda K, Ueyama T, Ogata T and
Matoba S: Inhibition of p53 preserves Parkin-mediated mitophagy and
pancreatic β-cell function in diabetes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
111:3116–3121. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chaurasia B and Summers SA:
Ceramides-lipotoxic inducers of metabolic disorders. Trends
Endocrinol Metab. 26:538–550. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Park YJ, Lee S, Kieffer TJ, Warnock GL,
Safikhan N, Speck M, Hao Z, Woo M and Marzban L: Deletion of Fas
protects islet beta cells from cytotoxic effects of human islet
amyloid polypeptide. Diabetologia. 1–Feb;2012.(Epub ahead of
print). View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
7
|
Marselli L, Thorne J, Dahiya S, Sgroi DC,
Sharma A, Bonner-Weir S, Marchetti P and Weir GC: Gene expression
profiles of beta-cell enriched tissue obtained by laser capture
microdissection from subjects with type 2 diabetes. PLoS One.
5:e114992010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Troyanskaya O, Cantor M, Sherlock G, Brown
P, Hastie T, Tibshirani R, Botstein D and Altman RB: Missing value
estimation methods for DNA microarrays. Bioinformatics. 17:520–525.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bolstad BM, Irizarry RA, Astrand M and
Speed TP: A comparison of normalization methods for high density
oligonucleotide array data based on variance and bias.
Bioinformatics. 19:185–193. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Espina V, Wulfkuhle JD, Calvert VS,
VanMeter A, Zhou W, Coukos G, Geho DH, Petricoin EF III and Liotta
LA: Laser-capture microdissection. Nat Protoc. 1:586–603. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lontchi-Yimagou E, Sobngwi E, Matsha TE
and Kengne AP: Diabetes mellitus and inflammation. Curr Diab Rep.
13:435–444. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Velloso LA, Eizirik DL and Cnop M: Type 2
diabetes mellitus-an autoimmune disease? Nat Rev Endocrinol.
9:750–755. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Arystarkhova E, Liu YB, Salazar C,
Stanojevic V, Clifford RJ, Kaplan JH, Kidder GM and Sweadner KJ:
Hyperplasia of pancreatic beta cells and improved glucose tolerance
in mice deficient in the FXYD2 subunit of Na,K-ATPase. J Biol Chem.
288:7077–7085. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Arystarkhova E: Beneficial renal and
pancreatic phenotypes in a mouse deficient in FXYD2 regulatory
subunit of Na,K-ATPase. Front Physiol. 7:882016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Markiewski MM and Lambris JD: The role of
complement in inflammatory diseases from behind the scenes into the
spotlight. Am J Pathol. 171:715–727. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Huang C, Fisher KP, Hammer SS, Navitskaya
S, Blanchard GJ and Busik JV: Plasma exosomes contribute to
microvascular damage in diabetic retinopathy by activating
classical complement pathway. Diabetes. 67:1639–1649. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Flyvbjerg A: The role of the complement
system in diabetic nephropathy. Nat Rev Nephrol. 13:311–318. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Uldry M and Thorens B: The SLC2 family of
facilitated hexose and polyol transporters. Pflugers Arch.
447:480–489. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Laukkanen O, Lindström J, Eriksson J,
Valle TT, Hämäläinen H, Ilanne-Parikka P, Keinänen-Kiukaanniemi S,
Tuomilehto J, Uusitupa M and Laakso M; Finnish Diabetes Prevention
Study, : Polymorphisms in the SLC2A2 (GLUT2) gene are associated
with the conversion from impaired glucose tolerance to type 2
diabetes: The finnish diabetes prevention study. Diabetes.
54:2256–2260. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Leturque A, Brot-Laroche E and Le Gall M:
GLUT2 mutations, translocation, and receptor function in diet sugar
managing. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 296:E985–E992. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Takeda K, Kaisho T and Akira S: Toll-like
receptors. Annu Rev Immunol. 21:335–376. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Dasu MR, Devaraj S, Zhao L, Hwang DH and
Jialal I: High glucose induces toll-like receptor expression in
human monocytes: Mechanism of activation. Diabetes. 57:3090–3098.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Miyahara S, Kiryu J, Yamashiro K, Miyamoto
K, Hirose F, Tamura H, Katsuta H, Nishijima K, Tsujikawa A and
Honda Y: Simvastatin inhibits leukocyte accumulation and vascular
permeability in the retinas of rats with streptozotocin-induced
diabetes. Am J Pathol. 164:1697–1706. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Rajamani U and Jialal I: Hyperglycemia
induces Toll-like receptor-2 and −4 expression and activity in
human microvascular retinal endothelial cells: Implications for
diabetic retinopathy. J Diabetes Res. 2014:7909022014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chiu KC, Chuang LM, Chu A, Yoon C and Wang
M: Comparison of the impact of the I27L polymorphism of the
hepatocyte nuclear factor-1alpha on estimated and measured beta
cell indices. Eur J Endocrinol. 148:641–647. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Morita K, Saruwatari J, Tanaka T, Oniki K,
Kajiwara A, Otake K, Ogata Y and Nakagawa K: Associations between
the common HNF1A gene variant p.I27L (rs1169288) and risk of type 2
diabetes mellitus are influenced by weight. Diabetes Metab.
41:91–94. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gu N, Tsuda M, Matsunaga T, Adachi T,
Yasuda K, Ishihara A and Tsuda K: Glucose regulation of dipeptidyl
peptidase IV gene expression is mediated by hepatocyte nuclear
factor-1alpha in epithelial intestinal cells. Clin Exp Pharmacol
Physiol. 35:1433–1439. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Pedersen KB, Chhabra KH, Nguyen VK, Xia H
and Lazartigues E: The transcription factor HNF1α induces
expression of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in pancreatic
islets from evolutionarily conserved promoter motifs. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1829:1225–1235. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Banes-Berceli AK, Ketsawatsomkron P, Ogbi
S, Patel B, Pollock DM and Marrero MB: Angiotensin II and
endothelin-1 augment the vascular complications of diabetes via
JAK2 activation. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 293:H1291–H1299.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tiano JP, Delghingaro-Augusto V, Le May C,
Liu S, Kaw MK, Khuder SS, Latour MG, Bhatt SA, Korach KS, Najjar
SM, et al: Estrogen receptor activation reduces lipid synthesis in
pancreatic islets and prevents β cell failure in rodent models of
type 2 diabetes. J Clin Invest. 121:3331–3342. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ezzat S, Zheng L, Florez JC, Stefan N,
Mayr T, Hliang MM, Jablonski K, Harden M, Stančáková A, Laakso M,
et al: The cancer-associated FGFR4-G388R polymorphism enhances
pancreatic insulin secretion and modifies the risk of diabetes.
Cell Metab. 17:929–940. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Geelen CC, van Greevenbroek MM, van Rossum
EF, Schaper NC, Nijpels G, 't Hart LM, Schalkwijk CG, Ferreira I,
van der Kallen CJ and Sauerwein HP: BclI glucocorticoid receptor
polymorphism is associated with greater body fatness: The Hoorn and
CODAM studies. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 98:E595–E599. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Syed AA, Halpin CG, Irving JA, Unwin NC,
White M, Bhopal RS, Redfern CP and Weaver JU: A common intron 2
polymorphism of the glucocorticoid receptor gene is associated with
insulin resistance in men. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 68:879–884. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lu L, Pu LJ, Xu XW, Zhang Q, Zhang RY,
Zhang JS, Hu J, Yang ZK, Lu AK, Ding FH, et al: Association of
serum levels of glycated albumin, C-reactive protein and tumor
necrosis factor-alpha with the severity of coronary artery disease
and renal impairment in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Clin Biochem. 40:810–816. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Jin C, Lu L, Zhang RY, Zhang Q, Ding FH,
Chen QJ and Shen WF: Association of serum glycated albumin,
C-reactive protein and ICAM-1 levels with diffuse coronary artery
disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clin Chim Acta.
408:45–49. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Rodiño-Janeiro BK, González-Peteiro M,
Ucieda-Somoza R, González-Juanatey JR and Alvarez E: Glycated
albumin, a precursor of advanced glycation end-products,
up-regulates NADPH oxidase and enhances oxidative stress in human
endothelial cells: Molecular correlate of diabetic vasculopathy.
Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 26:550–558. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ichihara A, Sakoda M, Mito-Kurauchi A and
Itoh H: Activated prorenin as a therapeutic target for diabetic
nephropathy. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 82 (Suppl 1):S63–S66. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yokota H, Nagaoka T, Tani T, Takahashi A,
Sato E, Kato Y and Yoshida A: Higher levels of prorenin predict
development of diabetic retinopathy in patients with type 2
diabetes. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 12:290–294. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kamiyama M, Urushihara M, Morikawa T,
Konishi Y, Imanishi M, Nishiyama A and Kobori H: Oxidative
stress/angiotensinogen/renin-angiotensin system axis in patients
with diabetic nephropathy. Int J Mol Sci. 14:23045–23062. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Engström G, Hedblad B, Eriksson KF, Janzon
L and Lindgärde F: Complement C3 is a risk factor for the
development of diabetes: A population-based cohort study. Diabetes.
54:570–575. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yang S, Li Q, Song Y, Tian B, Cheng Q,
Qing H, Zhong L and Xia W: Serum complement C3 has a stronger
association with insulin resistance than high-sensitivity
C-reactive protein in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Fertil
Steril. 95:1749–1753. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wlazlo N, van Greevenbroek MM, Ferreira I,
Feskens EJ, van der Kallen CJ, Schalkwijk CG, Bravenboer B and
Stehouwer CD: Complement factor 3 is associated with insulin
resistance and with incident type 2 diabetes over a 7-year
follow-up period: The CODAM study. Diabetes Care. 37:1900–1909.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ribbing J, Hamrén B, Svensson MK and
Karlsson MO: A model for glucose, insulin, and beta-cell dynamics
in subjects with insulin resistance and patients with type 2
diabetes. J Clin Pharmacol. 50:861–872. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Atanes P, Ruz-Maldonado I, Pingitore A,
Hawkes R, Liu B, Zhao M, Huang GC, Persaud SJ and Amisten S: C3aR
and C5aR1 act as key regulators of human and mouse β-cell function.
Cell Mol Life Sci. 75:715–726. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Dos Santos RS, Marroqui L, Grieco FA,
Marselli L, Suleiman M, Henz SR, Marchetti P, Wernersson R and
Eizirik DL: Protective role of complement C3 against
cytokine-mediated β-cell apoptosis. Endocrinology. 158:2503–2521.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Nawaz MI, Van Raemdonck K, Mohammad G,
Kangave D, Van Damme J, Abu El-Asrar AM and Struyf S: Autocrine
CCL2, CXCL4, CXCL9 and CXCL10 signal in retinal endothelial cells
and are enhanced in diabetic retinopathy. Exp Eye Res. 109:67–76.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Liu ZH, Chen LL, Deng XL, Song HJ, Liao
YF, Zeng TS, Zheng J and Li HQ: Methylation status of CpG sites in
the MCP-1 promoter is correlated to serum MCP-1 in Type 2 diabetes.
J Endocrinol Invest. 35:585–589. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Ninomiya H, Katakami N, Osonoi T, Saitou
M, Yamamoto Y, Takahara M, Kawamori D, Matsuoka TA, Yamasaki Y and
Shimomura I: Association between new onset diabetic retinopathy and
monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) polymorphism in Japanese
type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 108:e35–e37. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Mina-Osorio P: The moonlighting enzyme
CD13: Old and new functions to target. Trends Mol Med. 14:361–371.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Pedersen HK, Gudmundsdottir V and Brunak
S: Pancreatic islet protein complexes and their dysregulation in
type 2 diabetes. Front Genet. 8:432017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Locke JM, Hysenaj G, Wood AR, Weedon MN
and Harries LW: Targeted allelic expression profiling in human
islets identifies cis-regulatory effects for multiple variants
identified by type 2 diabetes genome-wide association studies.
Diabetes. 64:1484–1491. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|