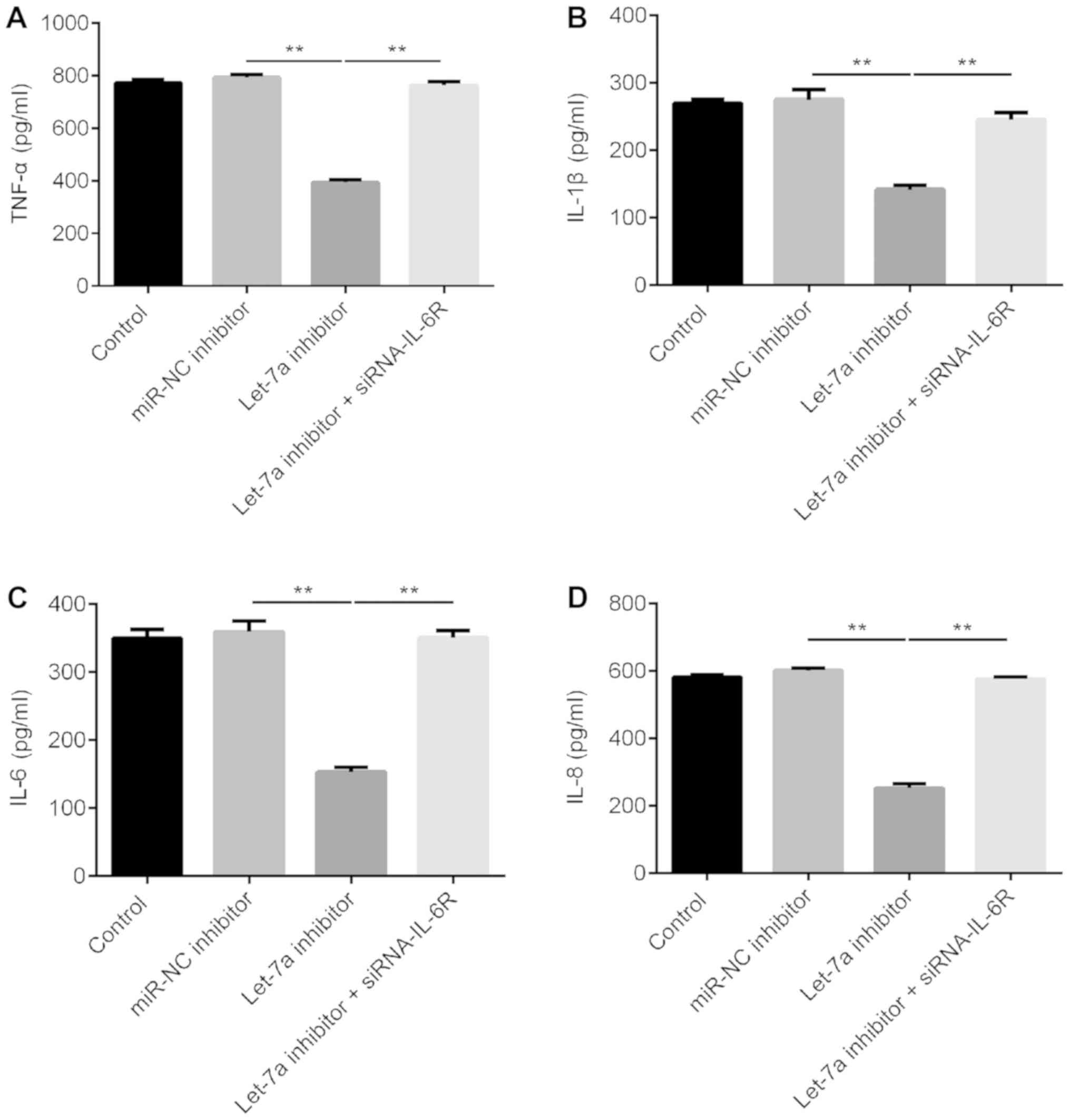
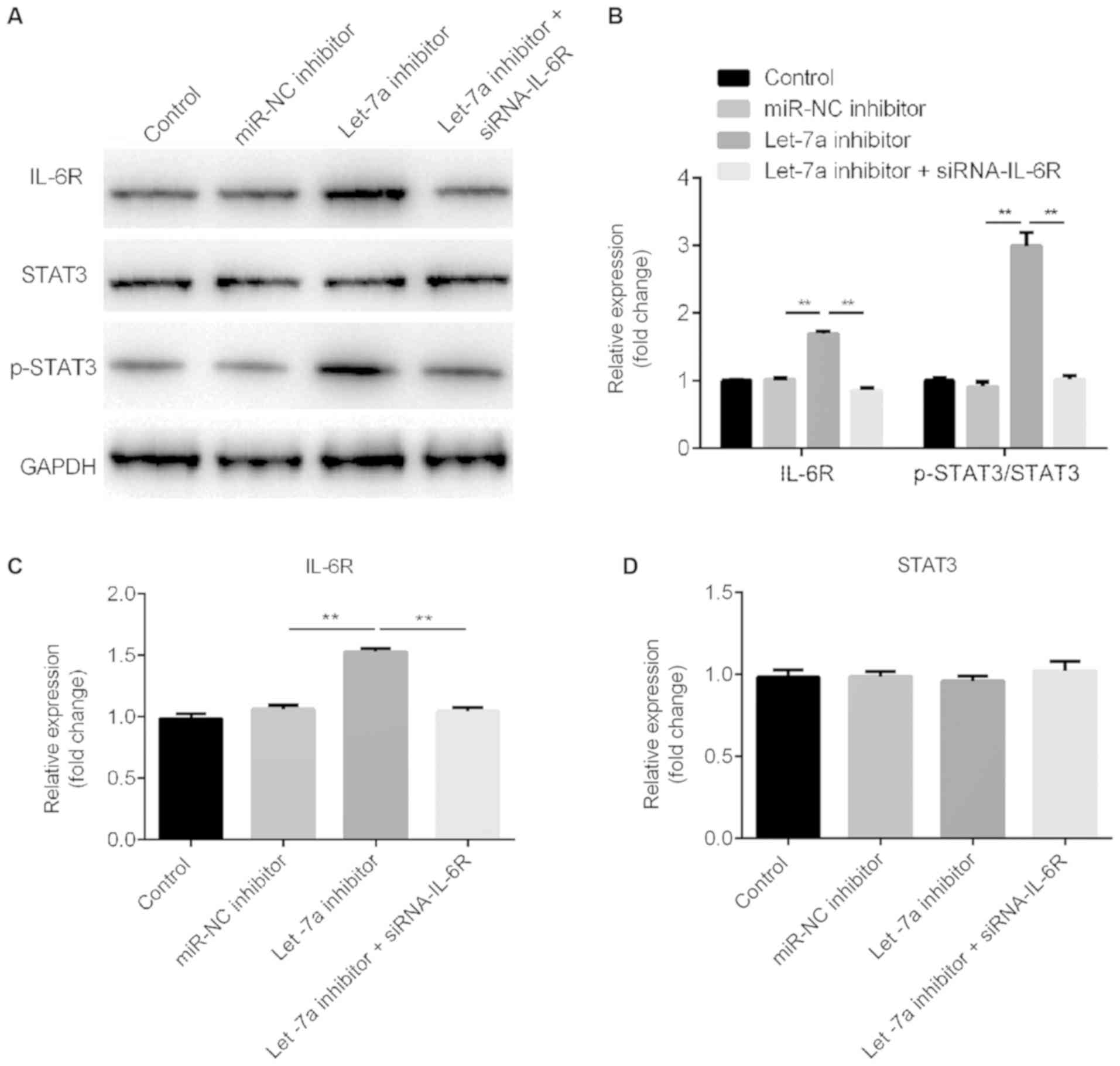
|
1
|
Allen KD and Golightly YM: State of the
evidence. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 27:276–283. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Heijink A, Vanhees M, van den Ende K, van
den Bekerom MP, van Riet RP, Van Dijk CN and Eygendaal D:
Biomechanical considerations in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis
of the elbow. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 24:2313–2318.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cummins JM, He Y, Leary RJ, Pagliarini R,
Diaz LA Jr, Sjoblom T, Barad O, Bentwich Z, Szafranska AE,
Labourier E, et al: The colorectal microRNAome. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 103:3687–3692. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:857–866. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Hydbring P, Wang Y, Fassl A, Li X, Matia
V, Otto T, Choi YJ, Sweeney KE, Suski JM, Yin H, et al:
Cell-cycle-targeting micrornas as therapeutic tools against
refractory cancers. Cancer Cell. 31:576–590.e8. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hammond SM: An overview of microRNAs. Adv
Drug Deliv Rev. 87:3–14. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Drusco A and Croce CM: MicroRNAs and
cancer: A long story for short RNAs. Adv Cancer Res. 135:1–24.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lee H, Han S, Kwon CS and Lee D:
Biogenesis and regulation of the let-7, miRNAs and their functional
implications. Protein Cell. 7:100–113. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hwang HW and Mendell JT: MicroRNAs in cell
proliferation, cell death, and tumorigenesis. Br J Cancer.
94:776–780. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Beyer C, Zampetaki A, Lin NY, Kleyer A,
Perricone C, Iagnocco A, Distler A, Langley SR, Gelse K, Sesselmann
S, et al: Signature of circulating microRNAs in osteoarthritis. Ann
Rheum Dis. 74:e182015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Xue H, Tu Y, Ma T, Wen T, Yang T, Xue L,
Cai M, Wang F and Guan M: miR-93-5p attenuates IL-1β-induced
chondrocyte apoptosis and cartilage degradation in osteoarthritis
partially by targeting TCF4. Bone. 123:129–136. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Malemud CJ: MicroRNAs and osteoarthritis.
Cells. 7:E922018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Reinhart BJ, Slack FJ, Basson M,
Pasquinelli AE, Bettinger JC, Rougvie AE, Horvitz HR and Ruvkun G:
The 21-nucleotide let-7 RNA regulates developmental timing in
caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 403:901–906. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lu L, Katsaros D, Risch HA, Canuto EM,
Biglia N and Yu H: MicroRNA let-7a modifies the effect of
self-renewal gene HIWI on patient survival of epithelial ovarian
cancer. Mol Carcinog. 55:357–365. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu K, Zhang C, Li T, Ding Y, Tu T, Zhou
F, Qi W, Chen H and Sun X: Let-7a inhibits growth and migration of
breast cancer cells by targeting HMGA1. Int J Oncol. 46:2526–2534.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Johnson VL and Hunter DJ: The epidemiology
of osteoarthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 28:5–15. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Loeser RF, Goldring SR, Scanzello CR and
Goldring MB: Osteoarthritis: A disease of the joint as an organ.
Arthritis Rheumatism. 64:1697–1707. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Burr DB and Gallant MA: Bone remodelling
in osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 8:665–673. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kim HA, Lee YJ, Seong SC, Choe KW and Song
YW: Apoptotic chondrocyte death in human osteoarthritis. J
Rheumatol. 27:455–462. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yan S, Wang M, Zhao J, Zhang H, Zhou C,
Jin L, Zhang Y, Qiu X, Ma B and Fan Q: MicroRNA-34a affects
chondrocyte apoptosis and proliferation by targeting the SIRT1/p53
signaling pathway during the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Int J
Mol Med. 38:201–209. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shu Y, Long J, Guo W and Ye W:
MicroRNA-195-5p inhibitor prevents the development of
osteoarthritis by targeting REGγ. Mol Med Rep. 19:4561–4568.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hu Y, Li S and Zou Y: Knockdown of LncRNA
H19 relieves LPS-induced damage by modulating miR-130a in
osteoarthritis. Yonsei Med J. 60:381–388. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ying H, Wang Y, Gao Z and Zhang Q: Long
non-coding RNA activated by transforming growth factor beta
alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory injury via
regulating microRNA-223 in ATDC5 cells. Int Immunopharmacol.
69:313–320. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Goldring MB and Goldring SR: Articular
cartilage and subchondral bone in the pathogenesis of
osteoarthritis. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1192:230–237. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Berenbaum F: Osteoarthritis as an
inflammatory disease (osteoarthritis is not osteoarthrosis).
Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 21:16–21. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Malfait AM: Osteoarthritis year in review
2015: Biology. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 24:21–26. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yuan Q, Zhang D, Liu C, Zhang C and Yuan
D: Chikusetsusaponin V Inhibits LPS-activated inflammatory
responses via SIRT1/NF-κB signaling pathway in RAW264.7 cells.
Inflammation. 41:2149–2159. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Cheng Y, Yang C, Luo D, Li X, Le XC and
Rong J: N-Propargyl caffeamide skews macrophages towards a
resolving M2-Like phenotype against myocardial ischemic injury via
activating Nrf2/HO-1 pathway and inhibiting NF-κB pathway. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 47:2544–2557. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
De Santis R, Liepelt A, Mossanen JC, Dueck
A, Simons N, Mohs A, Trautwein C, Meister G, Marx G,
Ostareck-Lederer A and Ostareck DH: miR-155 targets caspase-3 mRNA
in activated macrophages. RNA Biol. 13:43–58. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Toledano H: The role of the heterochronic
microRNA let-7 in the progression of aging. Exp Gerontol.
48:667–670. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Amin AR: Regulation of tumor necrosis
factor-α and tumor necrosis factor converting enzyme in human
osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 7:392–394. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kapoor M, Martel-Pelletier J, Lajeunesse
D, Pelletier JP and Fahmi H: Role of proinflammatory cytokines in
the pathophysiology of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 7:33–42.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Calzascia T, Pellegrini M, Hall H, Sabbagh
L, Ono N, Elford AR, Mak TW and Ohashi PS: TNF-alpha is critical
for antitumor but not antiviral T cell immunity in mice. J Clin
Invest. 117:3833–3845. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liu M, Gu M, Xu D, Lv Q, Zhang W and Wu Y:
Protective effects of toll-like receptor 4 inhibitor eritoran on
renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Transplant Proc. 42:1540–1544.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Striz I: Cytokines of the IL-1 family:
Recognized targets in chronic inflammation underrated in organ
transplantations. Clin Sci (Lond). 131:2241–2256. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Logan RM, Stringer AM, Bowen JM, Yeoh AS,
Gibson RJ, Sonis ST and Keefe DM: The role of pro-inflammatory
cytokines in cancer treatment-induced alimentary tract mucositis:
Pathobiology, animal models and cytotoxic drugs. Cancer Treat Rev.
33:448–460. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Montaseri A, Busch F, Mobasheri A,
Buhrmann C, Aldinger C, Rad JS and Shakibaei M: IGF-1 and PDGF-bb
suppress IL-1β-induced cartilage degradation through
down-regulation of NF-κB signaling: Involvement of Src/PI-3K/AKT
pathway. PLoS One. 6:e286632011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ying X, Peng L, Chen H, Shen Y, Yu K and
Cheng S: Cordycepin prevented IL-β-induced expression of
inflammatory mediators in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes. Int
Orthop. 38:1519–1526. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Lv SY, Wu Q, Liu JP, Shao J, Wen LL, Xue
J, Zhang XS, Zhang QR and Zhang X: Levels of interleukin-1β,
interleukin-18, and tumor necrosis factor-α in cerebrospinal fluid
of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage patients may be predictors of
early brain injury and clinical prognosis. World Neurosurg.
111:e362–e373. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ataie-Kachoie P, Pourgholami MH,
Richardson DR and Morris DL: Gene of the month: Interleukin 6
(IL-6). J Clin Pathol. 67:932–937. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Bournazou E and Bromberg J: Targeting the
tumor microenvironment: JAK-STAT3 signaling. JAKSTAT.
2:e238282013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Rokavec M, Wu W and Luo JL: IL6-Mediated
suppression of miR-200c directs constitutive activation of
inflammatory signaling circuit driving transformation and
tumorigenesis. Mol Cell. 45:777–789. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Al Zaid Siddiquee K and Turkson J: STAT3
as a target for inducing apoptosis in solid and hematological
tumors. Cell Res. 18:254–267. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|