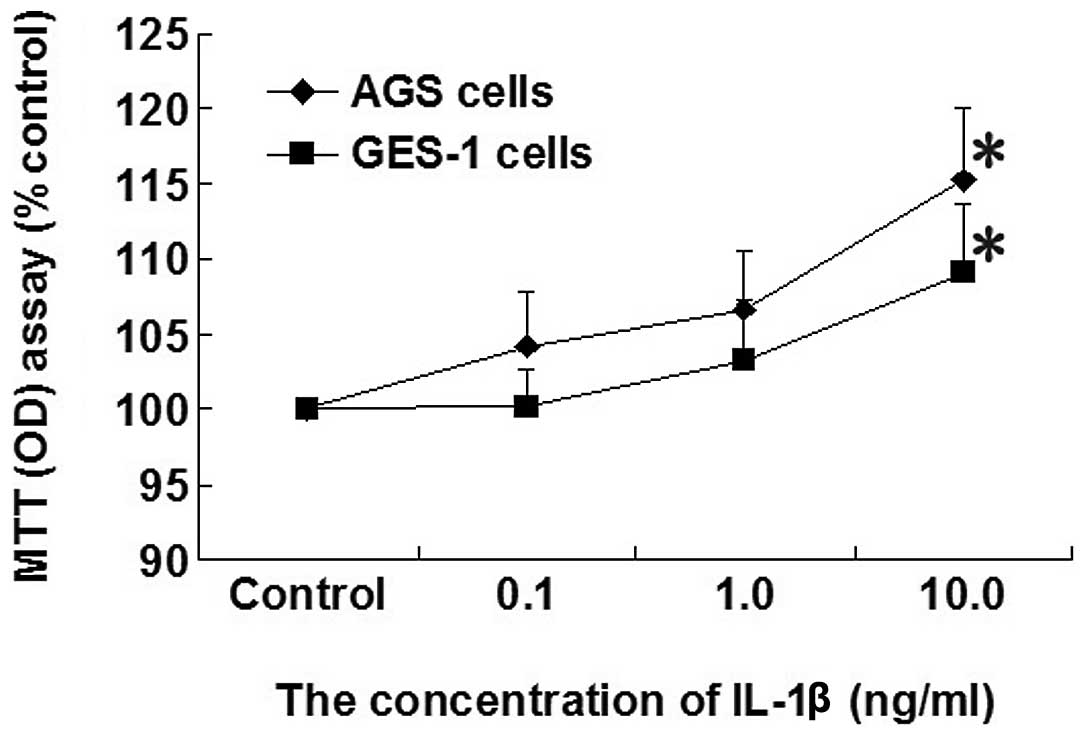
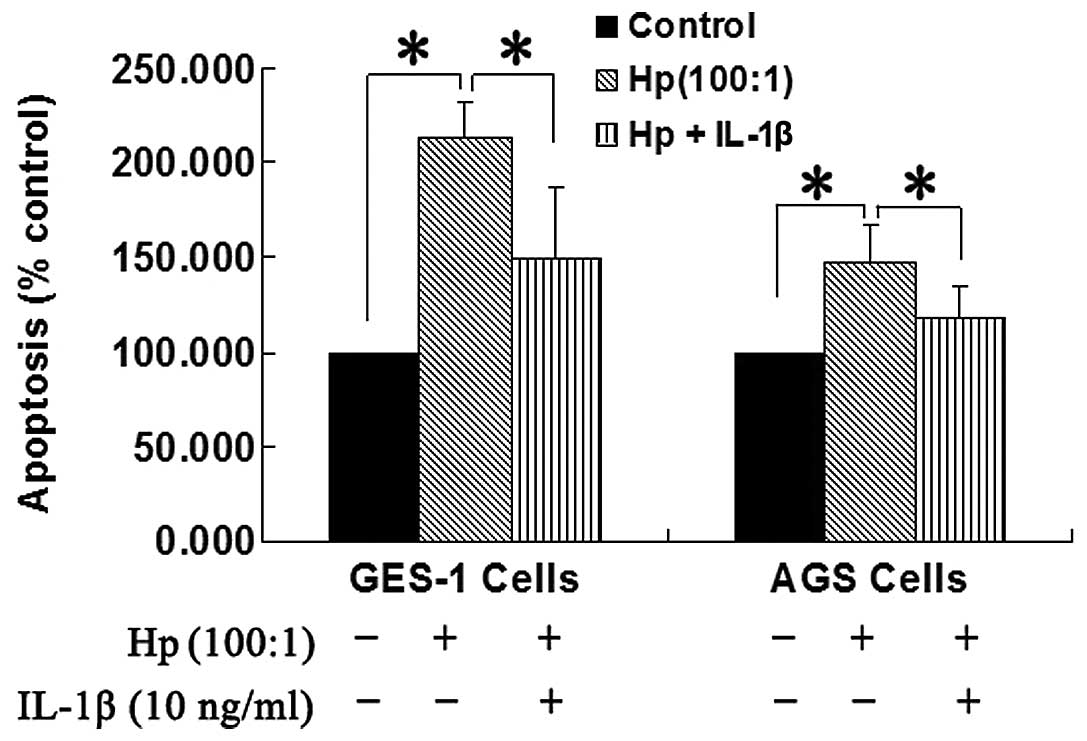
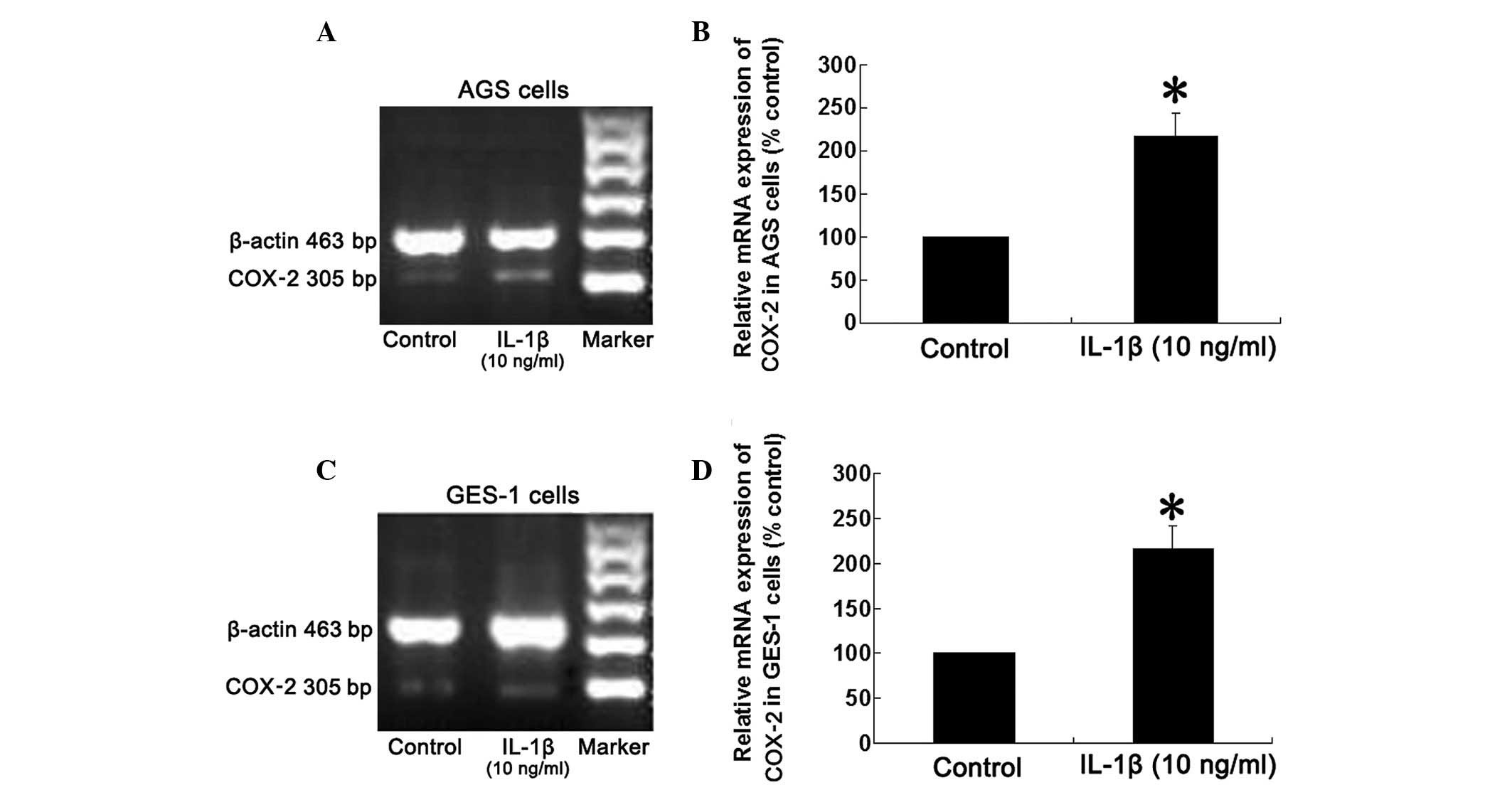
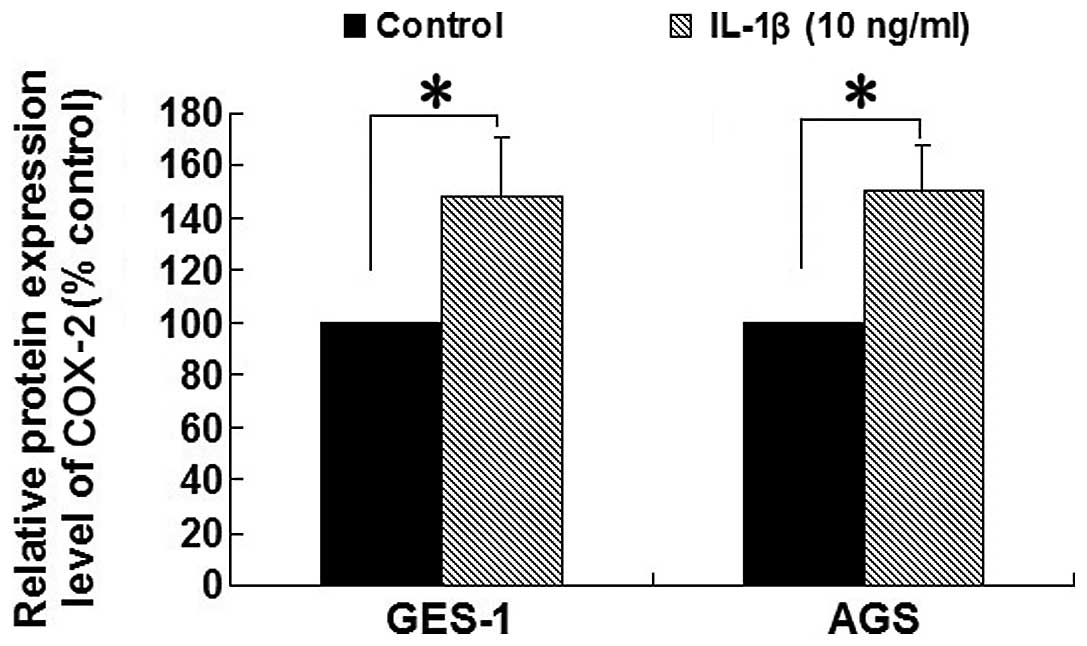
|
1
|
Momtaz H, Souod N, Dabiri H and Sarshar M:
Study of Helicobacter pylori genotype status in saliva,
dental plaques, stool and gastric biopsy samples. World J
Gastroenterol. 18:2105–2111. 2012.
|
|
2
|
Graham DY and Yamaoka Y: Disease-specific
Helicobacter pylori virulence factors: the unfulfilled
promise. Helicobacter. 5:3–9. 2000.
|
|
3
|
Hitzler I, Sayi A, Kohler E, et al:
Caspase-1 has both proinflammatory and regulatory properties in
Helicobacter infections, which are differentially mediated
by its substrates IL-1β and IL-18. J Immunol. 188:3594–3602.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Albaker WI: Helicobacter pylori
infection and its relationship to metabolic syndrome: is it a myth
or fact? Saudi J Gastroenterol. 17:165–169. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
El-Omar EM, Carrington M, Chow WH, et al:
Interleukin-1 polymorphisms associated with increased risk of
gastric cancer. Nature. 404:398–402. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tan IB, Ng I, Tai WM and Tan P:
Understanding the genetic basis of gastric cancer: recent advances.
Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 6:335–341. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cai C and Zhu X: The Wnt/β-catenin pathway
regulates self-renewal of cancer stem-like cells in human gastric
cancer. Mol Med Report. 5:1191–1196. 2012.
|
|
8
|
Wang XC, Li Y, Fan LQ, et al: Integrase
interactor 1 regulates proliferation, apoptosis and invasion in
gastric cancer cells. Chin Med J (Engl). 125:527–532.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tu SP, Quante M, Bhagat G, et al: IFN-γ
inhibits gastric carcinogenesis by inducing epithelial cell
autophagy and T-cell apoptosis. Cancer Res. 71:4247–4259. 2011.
|
|
10
|
Li XB, Qian JM, Chen YJ and Chen YF:
Effect of lansoprazole on histamine-induced acid secretion in
isolated rabbit parietal cells. Chin J Dig Dis. 3:47–50. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Sung JJ, Leung WK, Go MY, et al:
Cyclooxygenase-2 expression in Helicobacter
pylori-associated premalignant and malignant gastric lesions.
Am J Pathol. 157:729–735. 2000.
|
|
12
|
Pero R, Peluso S, Angrisano T, et al:
Chromatin and DNA methylation dynamics of Helicobacter
pylori-induced COX-2 activation. Int J Med Microbiol.
301:140–149. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ohno R, Yoshinaga K, Fujita T, et al:
Depth of invasion parallels increased cyclooxygenase-2 levels in
patients with gastric carcinoma. Cancer. 91:1876–1881. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang Y, Xu X and He P: Tubeimoside-1
inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis by increasing the Bax
to Bcl-2 ratio and decreasing COX-2 expression in lung cancer A549
cells. Mol Med Report. 4:25–29. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gou HF, Chen XC, Zhu J, et al: Expressions
of COX-2 and VEGF-C in gastric cancer: correlations with
lymphangiogenesis and prognostic implications. J Exp Clin Cancer
Res. 30:142011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Huang DS, Shen KZ, Wei JF, et al: Specific
COX-2 inhibitor NS398 induces apoptosis in human liver cancer cell
line HepG2 through BCL-2. World J Gastroenterol. 11:204–207. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Nandi J, Das PK, Zinkievich JM, et al:
Cyclo-oxygenase-1 inhibition increases acid secretion by modulating
H+,K+-ATPase expression and activation in
rabbit parietal cells. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 36:127–134.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Na HK, Inoue H and Surh YJ:
ET-18-O-CH3-induced apoptosis is causally linked to
COX-2 upregulation in H-ras transformed human breast epithelial
cells. FEBS Lett. 579:6279–6287. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Timotheadou E, Skarlos DV, Samantas E, et
al: Evaluation of the prognostic role of a panel of biomarkers in
stage IB-IIIA non-small cell lung cancer patients. Anticancer Res.
27:4481–4489. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Seo JH, Seo JY, Chung HY and Kim H: Effect
of pertussis toxin and herbimycin A on proteinase-activated
receptor 2-mediated cyclooxygenase 2 expression in Helicobacter
pylori-infected gastric epithelial AGS cells. Yonsei Med J.
52:522–526. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tatsuguchi A, Sakamoto C, Wada K, et al:
Localisation of cyclooxygenase 1 and cyclooxygenase 2 in
Helicobacter pylori related gastritis and gastric ulcer
tissues in humans. Gut. 46:782–789. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang X, Zhong R, Zhang Z, et al:
Interaction of cyclooxygenase-2 promoter polymorphisms with
Helicobacter pylori infection and risk of gastric cancer.
Mol Carcinog. 50:876–883. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu W, Reinmuth N, Stoeltzing O, et al:
Cyclooxygenase-2 is up-regulated by interleukin-1 beta in human
colorectal cancer cells via multiple signaling pathways. Cancer
Res. 63:3632–3636. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Catley MC, Chivers JE, Cambridge LM, et
al: IL-1beta-dependent activation of NF-kappaB mediates PGE2
release via the expression of cyclooxygenase-2 and microsomal
prostaglandin E synthase. FEBS Lett. 547:75–79. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Etoh T, Shibuta K, Barnard GF, et al:
Angiogenin expression in human colorectal cancer: the role of focal
macrophage infiltration. Clin Cancer Res. 6:3545–3551.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Paduch R, Kandefer-Szerszeń M,
Szuster-Ciesielska A and Plewka K: Transforming growth factor-beta1
modulates metalloproteinase-2 and -9, nitric oxide, RhoA and
alpha-smooth muscle actin expression in colon adenocarcinoma cells.
Cell Biol Int. 34:213–223. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Maihöfner C, Charalambous MP, Bhambra U,
et al: Expression of cyclooxygenase-2 parallels expression of
interleukin-1beta, interleukin-6 and NF-kappaB in human colorectal
cancer. Carcinogenesis. 24:665–671. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sugimoto M, Furuta T, Shirai N, et al:
Evidence that the degree and duration of acid suppression are
related to Helicobacter pylori eradication by triple
therapy. Helicobacter. 12:317–323. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Oridate N, Takeda H, Yamamoto J, et al:
Helicobacter pylori seropositivity predicts outcomes of acid
suppression therapy for laryngopharyngeal reflux symptoms.
Laryngoscope. 116:547–553. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Zhu H, Hart CA, Sales D and Roberts NB:
Bacterial killing in gastric juice - effect of pH and pepsin on
Escherichia coli and Helicobacter pylori. J Med
Microbiol. 55:1265–1270. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Takashima M, Furuta T, Hanai H, et al:
Effects of Helicobacter pylori infection on gastric acid
secretion and serum gastrin levels in Mongolian gerbils. Gut.
48:765–773. 2001.
|
|
32
|
Nguyen NV, Gleeson PA, Courtois-Coutry N,
et al: Gastric parietal cell acid secretion in mice can be
regulated independently of H/K ATPase endocytosis.
Gastroenterology. 127:145–154. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wei XH, Yang T, Wu Q, et al: Peri-sciatic
administration of recombinant rat IL-1β induces mechanical
allodynia by activation of src-family kinases in spinal microglia
in rats. Exp Neurol. 234:389–397. 2012.
|
|
34
|
Shibata Y, Kasai H, Shimada M, et al:
IL-1β stimulates IL-8 production, including prostaglandin E2
receptor EP4-triggered pathways, in synoviocyte MH7A cells. Mol Med
Report. 2:359–363. 2009.
|
|
35
|
Sugimoto M, Furuta T and Yamaoka Y:
Influence of inflammatory cytokine polymorphisms on eradication
rates of Helicobacter pylori. J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
24:1725–1732. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kidd M, Gustafsson BI, Drozdov I and
Modlin IM: IL1beta- and LPS-induced serotonin secretion is
increased in EC cells derived from Crohn’s disease.
Neurogastroenterol Motil. 21:439–450. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Beales IL: Gastrin and interleukin-1beta
stimulate growth factor secretion from cultured rabbit gastric
parietal cells. Life Sci. 75:2983–2995. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Shimamoto C, Nakanishi Y, Katsu K, et al:
Prostaglandin E2 release in gastric antral mucosa of guinea-pigs:
basal PGE2 release by cyclo-oxygenase 2 and ACh-stimulated PGE2
release by cyclo-oxygenase 1. Exp Physiol. 91:1015–1024. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zinkievich JM, George S, Jha S, et al:
Gastric acid is the key modulator in the pathogenesis of
non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced ulceration in rats.
Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 37:654–661. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Sekiguchi F, Ohi A, Maeda Y, et al:
Delayed production of arachidonic acid contributes to the delay of
proteinase-activated receptor-1 (PAR1)-triggered prostaglandin E2
release in rat gastric epithelial RGM1 cells. J Cell Biochem.
112:909–915. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Xiao F, Furuta T, Takashima M, et al:
Effects of cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor on gastric acid secretion in
Helicobacter pylori-infected C57BL/6 mice. Scand J
Gastroenterol. 36:577–583. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Pal J, Sanal MG and Gopal GJ: Vitamin-C as
anti-Helicobacter pylori agent: More prophylactic than
curative - Critical review. Indian J Pharmacol. 43:624–627.
2011.
|