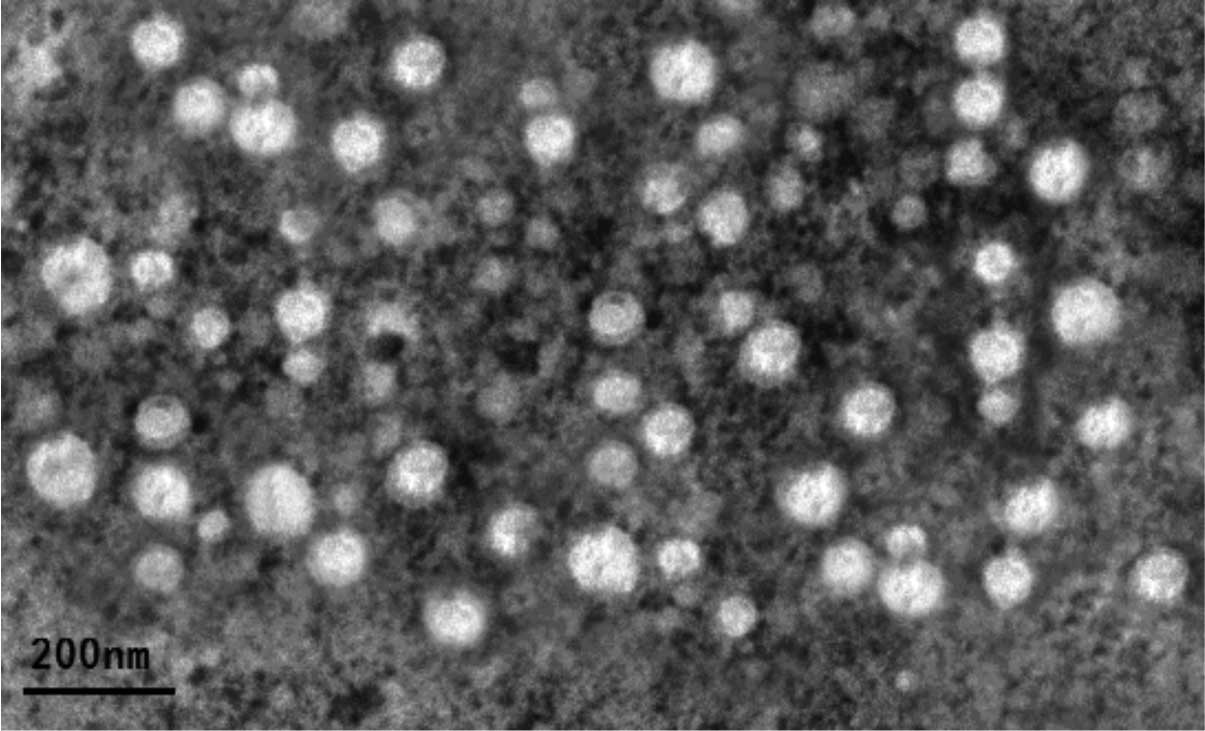
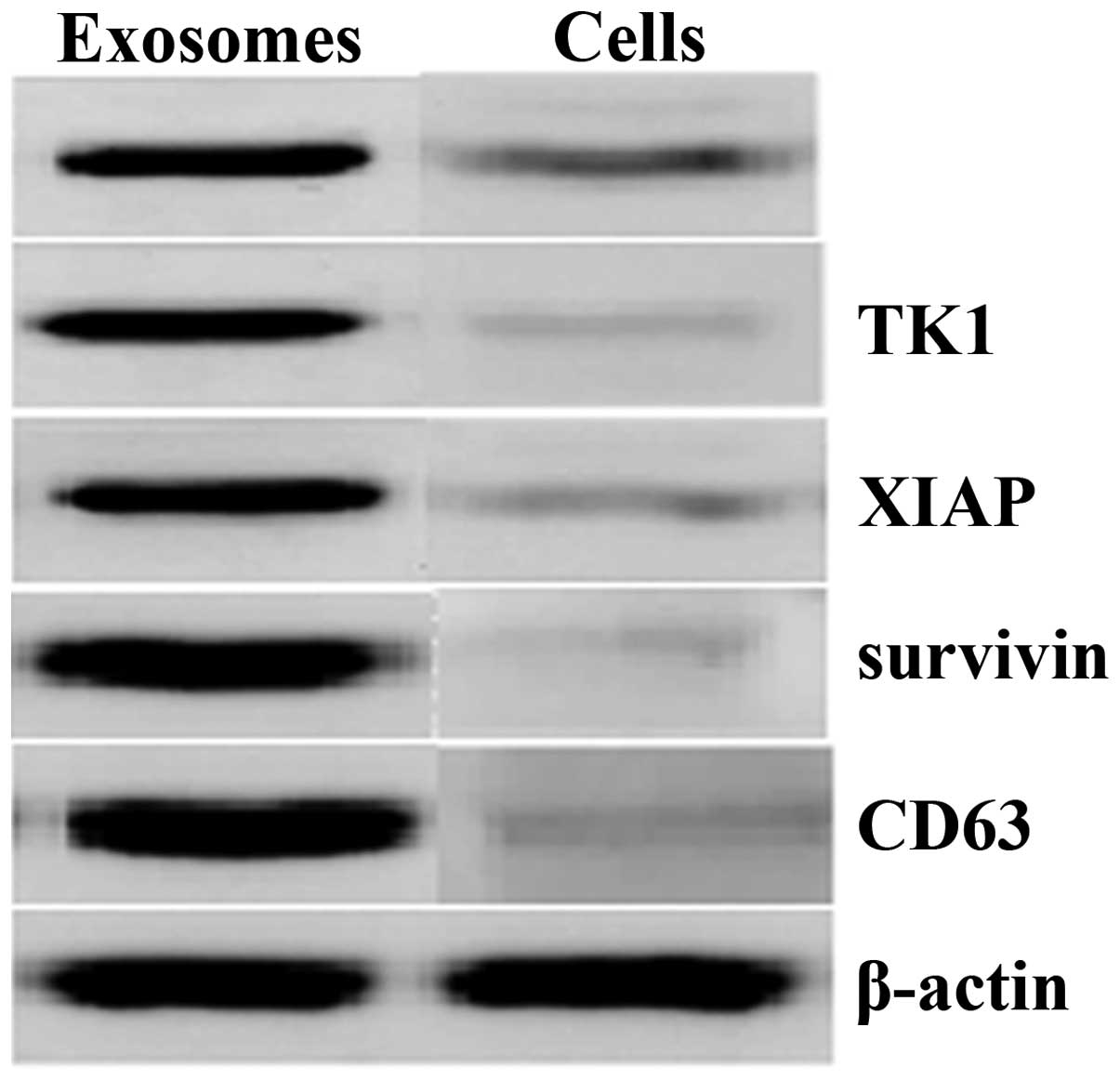
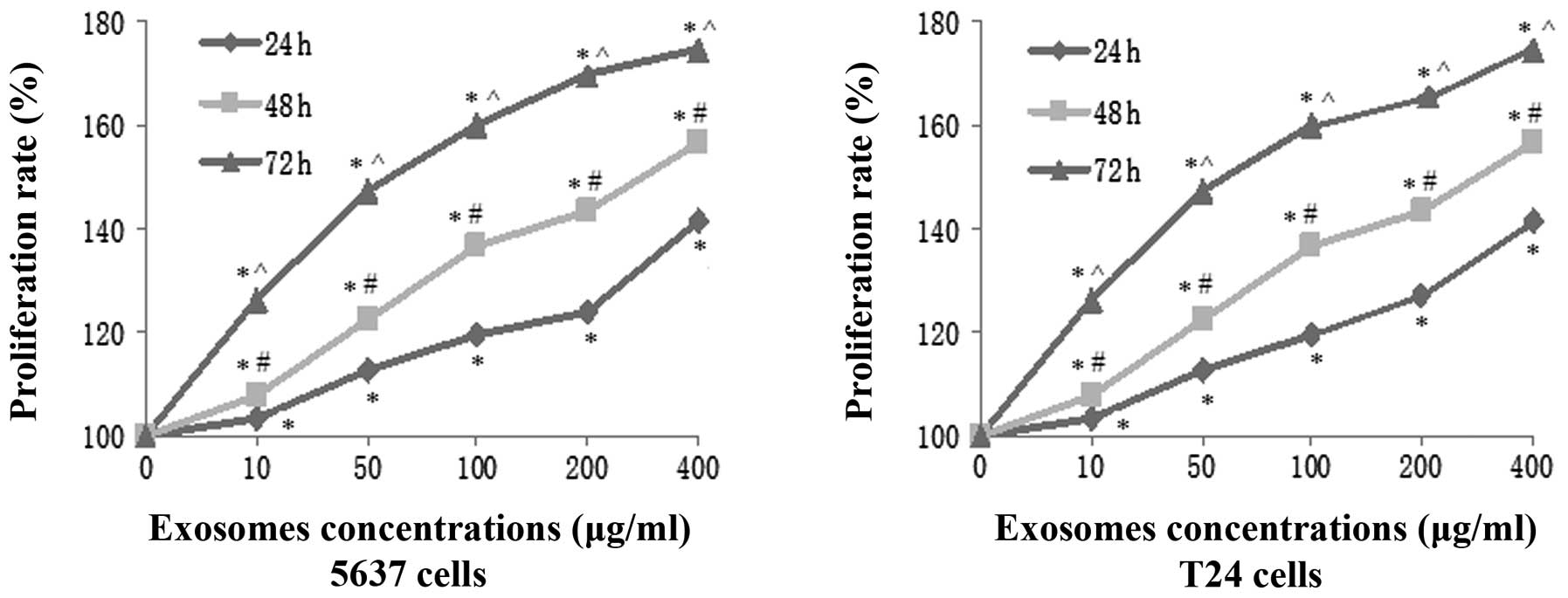
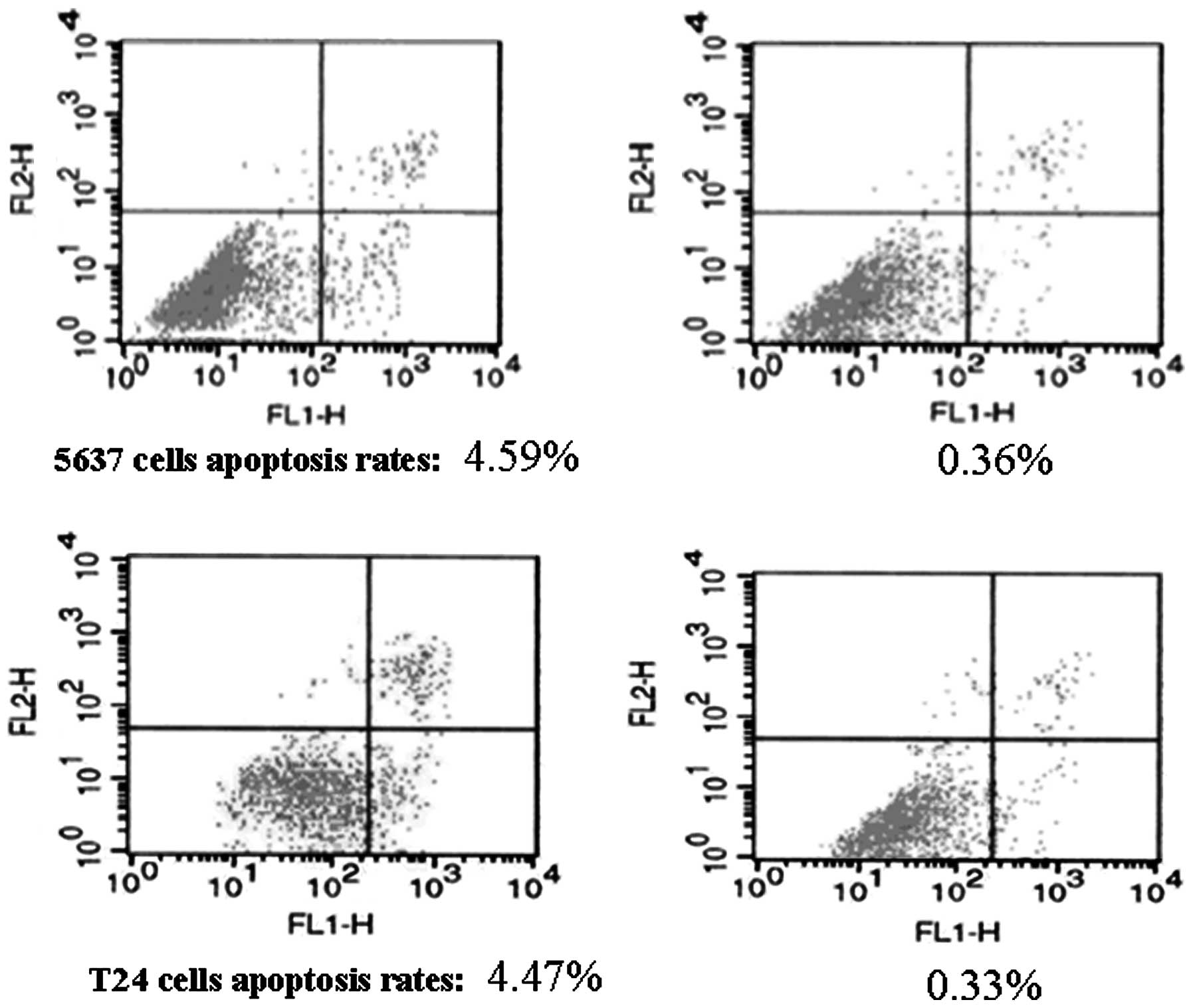
|
1
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J and
Thun MJ: Cancer statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J Clin. 59:225–249.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Hurst R: Does the biomarker search
paradigm need re-booting? BMC Urol. 9:12009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Vlassov AV, Magdaleno S, Setterquist R and
Conrad R: Exosomes: Current knowledge of their composition,
biological functions, and diagnostic and therapeutic potentials.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1820:940–948. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Mathivanan S, Ji H and Simpson RJ:
Exosomes: extracellular organelles important in intercellular
communication. J Proteomics. 73:1907–1920. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Johnstone RM, Adam M, Hammond JR, et al:
Vesicle formation during reticulocyte maturation. Association of
plasma membrane activities with released vesicles (exosomes). J
Biol Chem. 262:9412–9420. 1987.
|
|
6
|
Potolicchio I, Carven GJ, Xu X, et al:
Analysis of microglia-derived exosomes: metabolic role of the
aminopeptidase CD13 in neuropeptide catabolism. J Immunol.
175:2237–2243. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Henderson MC and Azorsa DO: The genomic
and proteomic content of cancer cell-derived exosomes. Front Oncol.
2:382012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Taylor DD and Gercel-Taylor C: MicroRNA
signatures of tumor-derived exosomes as diagnostic biomarkers of
ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 110:13–21. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rosell R, Wei J and Taron M: Circulating
microRNA signatures of tumor-derived exosomes for early diagnosis
of non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer. 10:8–9. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Rabinowits G, Gerçel-Taylor C, Day JM,
Taylor DD and Kloecker GH: Exosomal microRNA: a diagnostic marker
for lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer. 10:42–46. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Simpson RJ, Lim JW, Moritz RL and
Mathivanan S: Exosomes: proteomic insights and diagnostic
potential. Expert Rev Proteomics. 6:267–283. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ristorcelli E, Beraud E, Verrando P,
Villard C, Lafitte D, Sbarra V, et al: Human tumor nanoparticles
induce apoptosis of pancreatic cancer cells. FASEB J. 22:3358–3369.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang Y, Luo CL, He BC, Zhang JM, Cheng G
and Wu XH: Exosomes derived from IL-12-anchored renal cancer cells
increase induction of specific antitumor response in vitro: a novel
vaccine for renal cell carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 36:133–140.
2010.
|
|
14
|
Wolfers J, Lozier A, Raposo G, Regnault A,
Théry C, Masurier C, et al: Tumor-derived exosomes are a source of
shared tumor rejection antigens for CTL cross-priming. Nat Med.
7:297–303. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Andre F, Schartz NE, Movassagh M, Flament
C, Pautier P, Morice P, et al: Malignant effusions and immunogenic
tumour-derived exosomes. Lancet. 360:295–305. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yang C and Robbins PD: The roles of
tumor-derived exosomes in cancer pathogenesis. Clin Dev Immunol.
2011:8428492011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Qu JL, Qu XJ, Zhao MF, Teng YE, Zhang Y,
Hou KZ, et al: Gastric cancer exosomes promote tumour cell
proliferation through PI3K/Akt and MAPK/ERK activation. Dig Liver
Dis. 41:875–880. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bradford MM: A rapid and sensitive method
for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing
the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 72:248–254.
1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Camussi G, Deregibus MC, Bruno S, Grange
C, Fonsato V and Tetta C: Exosome/microvesicle-mediated epigenetic
reprogramming of cells. Am J Cancer Res. 1:98–110. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Raposo G, Nijman HW, Stoorvogel W,
Liejendekker R, Harding CV, Melief CJ and Geuze HJ: B lymphocytes
secrete antigen-presenting vesicles. J Exp Med. 183:1161–1172.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Théry C, Regnault A, Garin J, Wolfers J,
Zitvogel L, Ricciardi-Castagnoli P, et al: Molecular
characterization of dendritic cell-derived exosomes. Selective
accumulation of the heat shock protein hsc73. J Cell Biol.
147:599–610. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lamparski HG, Metha-Damani A, Yao JY,
Patel S, Hsu DH, Ruegg C and Le Pecq JB: Production and
characterization of clinical grade exosomes derived from dendritic
cells. J Immunol Methods. 270:211–226. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Koga K, Matsumoto K, Akiyoshi T, Kubo M,
Yamanaka N, Tasaki A, et al: Purification, characterization and
biological significance of tumor-derived exosomes. Anticancer Res.
25:3703–3707. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Khan S, Aspe JR, Asumen MG, Almaguel F,
Odumosu O, Acevedo-Martinez S, et al: Extracellular, cell-permeable
survivin inhibits apoptosis while promoting proliferative and
metastatic potential. Br J Cancer. 100:1073–1086. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|